What is catarrhal gastroduodenitis?
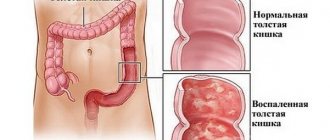
Diffuse catarrhal gastroduodenitis is manifested by an extensive, uniform inflammatory process throughout the entire mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum.
This disease mainly affects the upper level of the intestinal epithelium.
With catarrhal gastroduodenitis, moderate symptoms of gastritis are present. Gastritis has the same causes of occurrence as catarrhal gastroduodenitis:
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- irregular meals;
- poor quality food (stale food contaminated with pathogenic bacteria);
- drug poisoning.
With diffuse gastroduodenitis, the entry of any food into the stomach provokes irritation of the mucous membrane. Food is poorly digested and the natural digestion process is disrupted. The patient feels unwell and severe discomfort.
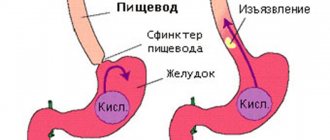
Inflammation of the mucous membranes can be caused by infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Gastroduodenitis can provoke more complex conditions, such as ulcers.
To avoid the disease developing into a complex form, do not select treatment yourself. Visit a gastroenterologist and undergo a thorough diagnosis for correct and effective treatment. Properly selected treatment and timely consultation with a doctor predicts a favorable recovery.
Incipient catarrhal gastroduodenitis can be quickly cured and return to normal life, because the mucous membranes are restored quickly, provided the cause of the disease is eliminated.
What it is
Catarrhal gastroduodenitis occupies a significant place among many diseases developing in the digestive tract. In gastroenterology, this disease is often designated by other terms, in the form of simple, alimentary or food gastroduodenitis. As a rule, the pathological process affects only the upper layer of the epithelium, however, in the absence of timely measures taken, the disease can quickly progress, worsening the general condition of the patient. Conversely, timely therapy aimed at eliminating the disease can significantly alleviate the nature of the disease in a few days.
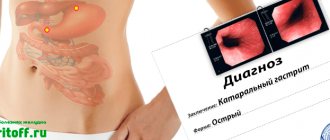
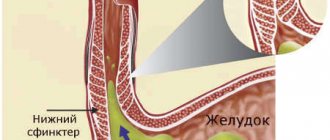
The catarrhal form of gastroduodenitis is an acute inflammatory process that affects the mucous membranes of the stomach and part of the intestine. The disease is one of the stages of gastroduodenitis, which allows you to see in the photo a pronounced redness of the mucous membrane called erythema. The degree of damage largely depends on the time during which the pathological process developed. Thus, in the initial stage of the disease, the modified area is small in size, however, due to the ability to progress rapidly, after some time the affected area will look much larger.
Causes
We have already slightly touched on the reasons for the development of acute catarrhal gastroduodenitis, but still, I would like to sort everything out.
There are a lot of reasons and they all depend on the quality of life that a person provides for himself.
- The modern rhythm of life often becomes a provocateur of various diseases. Catarrhal gastroduodenitis can be triggered subsequently by severe stress, anxiety, and worries. After all, the stomach and intestines have their own nervous system, which is called enteric and partially covers the autonomic system. When there is severe stress, a disruption occurs in the interaction between the brain and the stomach (the brain sends incorrect signals to the stomach, and it, in turn, gives incorrect information about its work).
- No matter how trivial it may sound, it is a fact - drinking large amounts of alcoholic beverages can cause not only catarrhal gastroduodenitis, but also many other dangerous ailments.
- The problem of our time has become the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which provokes many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Catarrhal gastroduodenitis becomes the result of the proliferation and activity of bacteria on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Medicines that affect the gastrointestinal tract. Taking potent medications can cause dysbiosis, inflammation of the mucous membrane and, as a result, catarrhal gastroduodenitis. This disease may be a consequence of drug poisoning. To avoid unpleasant consequences, always read the instructions and follow the daily dosage of the medications you take.
- Food poisoning.
- Prolonged fasting, diets.
Causes of food gastroduodenitis
To avoid such stomach problems, you need to find out what factors lead to the development of the disease. The causes of food gastroduodenitis are:
- A systematic violation of the diet, which can provoke serious problems of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often, the reason can be long feasts during the holidays, overeating and lack of exercise.
- Eating spoiled and low-quality foods. It is necessary to carefully approach the process of choosing food products and pay attention to the expiration date of the product.
- Drug poisoning. This may be caused by a long course of treatment or incorrect proportions.
- Constant stress can have a detrimental effect on the functioning of the stomach.
- Diet. Often, fanaticism in the struggle for an ideal figure leads to various kinds of intestinal disorders, when the body does not receive the required amount of nutrients, which causes its depletion.
- Incorrect way out of the diet. Following a diet is only half the battle. The main task is to properly return to your usual lifestyle without overloading your stomach.
- Congenital problems with the digestive system.
- Bacteria Helicobacter pylori.
- Heredity.
Symptoms
To accurately determine the problems of the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to understand the symptoms that characterize inflammation of the mucous membrane. Catarrhal gastroduodenitis has characteristic signs and symptoms, on the basis of which diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
- severe, acute pain with a tendency to intensify;
- flatulence, bloating, colic, spasms, which are accompanied by rumbling;
- dry mouth that is not relieved by drinking water;
- malaise, nausea and vomiting;
- headaches and dizziness, weakness throughout the body;
- disorder (diarrhea).
All symptoms may resemble an exacerbation of gastritis, but in any case, the patient should immediately seek help from a medical facility.
Many modern citizens believe that gastritis is not a very serious disease. Such a strong misconception provokes additional inflammation, which gradually leads to severe disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diseases of the intestines and stomach provide great discomfort to patients. Some symptoms make it difficult to lead a full, active life.
Classification of the disease
Experts distinguish several types of gastroduodenitis depending on the chronology of the disease:
- Spicy. The disease can last up to three months.
- Chronic. This form of the disease can drag on for six months or more. Symptoms and treatment may be similar to those in the acute form.
If we take morphological changes in the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum as the basis for the classification, we can distinguish the following types of gastroduodenitis:
- Catarrhal is a process of redness of the gastric mucosa without violating its integrity.
- Erythematous. The next stage of development of the catarrhal form. In this case, severe redness of the mucous membrane is observed, the so-called erythema.
- Erosive. In this case, many small wounds form on the mucous membrane. A characteristic feature of this form of the disease is the appearance in the stomach of cells that are not inherent to it. During normal functioning of the body, the presence of such cells in the stomach is excluded.
Classification of pathology
Doctors in the field of gastroenterology have developed a classification of the disease, based on the indicators and symptoms of the disease.
- Acute form (up to three months).
- Chronic form (may last six months or longer). Symptoms may be identical to those in the acute form.
Based on changes in the epithelium of the stomach and intestines, the following types of gastroduodenitis are distinguished:
- catarrhal - the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, severe redness is visible, but the integrity of the epithelium is not impaired;
- erythematous - this is the second stage of the disease, when erythema of the mucous membrane is visible (severe inflammation and redness);
- erosive - a severe form of the disease. Wounds are visible in large numbers, changes are observed in the stomach at the cellular level.
Dietary recommendations
Treatment of gastroduodenitis involves mandatory adherence to a diet. A properly selected diet will avoid harmful thermal and mechanical effects on the affected gastric mucosa, and will also speed up the patient’s recovery process.
The main dietary recommendations are:
- All dishes must be served ground. To do this, it is advisable to grind them in a blender to a puree consistency. This will make them easier to digest. When it comes to soups, it is preferable that they have a creamy, delicate structure.
- Food temperature. It should be within 36-38 degrees. Eating excessively hot or cold food can negatively affect the course of the disease and cause pain.
- Fractional power system. Patients are advised to eat 5-6 times a day in small portions. This way the body will receive the amount of nutrients it needs, but at the same time the person will protect himself from overeating and a feeling of fullness in the stomach.
- Allowed dishes. These include porridge, boiled ground meat and fish, as well as low-fat fermented milk products. In addition to this, the consumption of heat-treated vegetables is allowed.
- Prohibited products. These include all alcoholic drinks, fatty fish and meat, sausages, and fast food. Also, patients should not eat sweet confectionery, chips, fresh baked goods, or hot sauces.
Nutrition for gastroduodenitis is gentle. The most strict diet is provided in the acute phase of the disease. When the disease becomes chronic, the diet can be supplemented with permitted foods.
Treatment of the disease
After a thorough diagnosis, the gastroenterologist draws up a plan that provides for step-by-step treatment of catarrhal gastroduodenitis.
The first step on the path to recovery should be dietary nutrition in the right mode. At the same time, you can brew herbal tea to stabilize motor skills and relieve the inflammatory process.
The doctor will personally develop a nutrition plan to relieve painful symptoms. The main stage will be drug therapy, which is selected only by the doctor, taking into account the general condition of the patient’s body.
After complete recovery, you should follow a diet for some time and avoid eating spicy, fatty, hot and heavy foods.
Treatment
Through vomiting and diarrhea, the body tries to get rid of undigested food. The attacks pass within 2-3 days. At this time, table 1a with processed food is used. If there is increased secretion, drink milk. Salt is excluded. If catarrhal gastroduodenitis is suspected, treatment is carried out by a doctor, since the symptoms of the disease are similar to ulcers and dangerous diseases that require surgical intervention.
Choleretic, antispasmodic and laxatives are used to remove stomach contents. For the same purpose, a heating pad is applied to the abdominal area to force stool to pass through the large intestine faster.
In severe cases, gastric lavage and siphon or oil enemas are prescribed. The weight loss will be replenished afterwards. Sometimes up to 10 kg of feces are retained in the body. The patient takes medications:
- For low acidity - enzymes, hydrochloric acid solution (stomach juice).
- For high acidity – belladonna, alkalis.
Mineral water, vitamins and microelements are prescribed according to the condition to prevent anemia and negative consequences.
Prevention
Preventive measures are as follows:
- eat right, follow a routine, eat only high-quality and healthy food;
- do not overeat or starve, eat often, but in small portions;
- stop drinking alcohol;
- treat gastrointestinal diseases in a timely manner and prevent exacerbations of chronic diseases;
- take medications only after consulting a doctor.
If a patient is diagnosed with catarrhal gastroduodenitis, then he must follow the above preventive measures in order to prevent the development of complications.
The following preventive measures will have a positive impact on the quality of the gastrointestinal tract:
- consumption of fruits and vegetables;
- moderate physical activity;
- regular walks.
Diagnostics
Based on the symptoms, the doctor will prescribe additional examination. It will help to make a more accurate diagnosis and determine the extent of damage to the mucous layer of the digestive tract. It will include a blood test and instrumental diagnostic methods:
- General blood test - an increase in ESR and leukocytosis indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- A study to determine the level of acidity of gastric juice - low or high acidity requires a different approach to treatment;
- Ultrasound of the stomach and abdominal organs - the need to clarify the presence of an ulcer and examine the functioning of other organs involved in the functions of digestion. The development of gastroduodenitis may be accompanied by additional disruptions in the body (diseases of the liver, biliary tract, pancreas and gall bladder);
- FGDS (fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy) - this method is the most informative and allows you to determine the source of inflammation and see the condition of the mucous layer of the stomach and duodenum. During the procedure, the tissue will be analyzed for a biopsy and for the presence of bacteria.
All these procedures will help the specialist decide on further treatment. After all, adequate and timely treatment is the key to a quick recovery and preventing the disease from becoming chronic.
Chronic form
Chronic catarrhal gastroduodenitis is characterized by a long course of the disease with exacerbations and periods of remission. In this case, pronounced symptoms are inherent in the exacerbation stage. Most often, exacerbation can occur during the off-season.
The period of complications can be determined by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of pallor on the skin.
- Sudden onset of severe pain.
- Bad breath.
- Weakness and dizziness.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Intestinal disorders.
- Fainting may often occur.
To prevent the transition to a chronic form, you need to consult a specialist in time and take the course of treatment seriously.