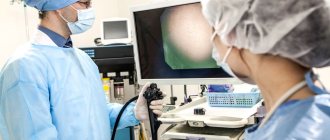
Patients who suffer from frequent diseases of the digestive system (diseases of the stomach, esophagus, intestines) have to deal with gastroscopic examination of the stomach.
Due to the unpleasant sensations, going to the clinic to conduct this type of study causes fear in many patients, and the appearance of signs of fear before performing this procedure.
Currently, a gastroscopic examination of the stomach without swallowing a probe is used. It differs significantly from conventional fibrogastroscopy.
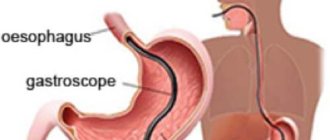
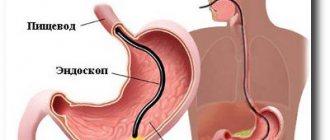
Gastroscopy of the stomach
This is a procedure for which a fibrogastroscope is used. This device is connected to a video monitor and it clearly shows the condition of the internal organs of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
In addition, if necessary, it can be used to collect material for histological examination.
Gastroscopy of the stomach is performed by swallowing a flexible gastroscope hose, at the end of which a small video camera is mounted (among the population, such manipulation is referred to as intestinal swallowing).
Before checking the stomach, a liquid anesthetic is injected to reduce the gag reflex. Most often it is Lidocaine.
Endoscopic capsule
The standard size of a microdevice (capsule) is about 2.5 centimeters. This size passes freely through the larynx and esophagus without causing any unpleasant emotions in the patient. The main components of the capsule are:
- light key operating from 6 to 8 hours;
- digital recorder (camera). Technical parameters of the camera: interval shooting ability is up to 3 frames per second, viewing angle – up to (140°);
- digital microcircuits;
- electromagnet;
- transmitter with its own radio frequency.
Before use, the capsule is stored in a special container. When it enters the human body, it is activated (turned on). The movement of the device through the digestive system is carried out through natural reflex contractions of the walls of the esophagus, stomach and intestines. The foreign object is removed from the body in approximately 12 hours naturally, without causing discomfort.
Who is gastroscopy of the stomach indicated for?
The scope of this procedure is very wide. It is prescribed to check the stomach and identify pathologies of the digestive system.
This research technique is prescribed:
- Gastroscopy of the stomach
When pain occurs, which is localized in the abdominal area, and is accompanied by heartburn, a gag reflex, and a feeling of nausea. - With the development of gastric bleeding.
- If the patient has difficulty swallowing food.
- To exclude the development of an oncological process in the stomach.
- Diseases whose condition affects the gastric mucosa.
- Manifestation of symptoms of anorexia, sudden weight loss, decrease or loss of appetite.
Sometimes gastroscopy is prescribed urgently to clarify the diagnosis.
This may happen in the following cases:
- Development of acute bleeding.
- Complication of the ulcerative process.
- Foreign body in the gastrointestinal tract.
Contraindications for gastroscopy of the stomach
As with any procedure, during gastroscopy there may be cases when its appointment is considered impossible. This manipulation cannot be performed due to absolute and sometimes relative contraindications.
Absolute contraindications for gastroscopy of the stomach are considered to be:
- Severe forms of curvature of the spinal column.
- Acute attack of coronary artery disease, hemorrhagic stroke.
- Acute stage of extensive myocardial infarction.
- Neoplasms that have led to anatomical displacement of the esophagus and stomach.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- Hypertrophy of the thyroid gland.
- Diseases that lead to narrowing of the esophagus.
- Exacerbation phase of bronchial asthma.
Relative contraindications to gastroscopy are most often temporary, and as they are eliminated, gastroscopy is permitted.
They are considered:
- Inflammatory processes of the oropharynx, palate and tonsils.
- Exacerbation of hypertension in severe form.
- Hypertrophy of the cervical lymph nodes.
- Exacerbation of psychoneurological diseases, when the patient behaves uncontrollably and does not give an account of his actions.
It should be remembered that if the patient is in a borderline state between life and death, and his further condition depends on timely diagnosis, then a gastroscopy of the stomach can be performed by a gastroenterologist, even with an absolute contraindication.
In what cases is gastroscopy prescribed?
A gastroscopy requires a doctor's prescription for the following symptoms or if necessary:
- Heartburn, vomiting, or persistent nausea;
- Regular cough and swallowing reflex disorders;
- Frequent or constant bloating, rapid weight loss;
- Anemia and blood in the stool;
- Discomfort and pain in the epigastric region;
- The need to remove polyps, local administration of drugs;
- The need for a biopsy of a certain area;
- Obtaining indicators of gastric juice acidity;
- Obtaining samples to check for the presence of bacteria that may cause gastritis.
Contraindications for gastroscopy:
- Bronchial asthma;
- Neoplasms leading to narrowing of the esophagus and some areas of the stomach;
- Disturbances in the structure of the supporting apparatus (scoliosis, etc.);
- Mental illnesses, nervous disorders;
- Pathology of the cardiovascular system;
- Blood diseases leading to poor clotting.
With extreme caution and only if urgent examination is necessary, gastroscopy can be performed for ENT diseases, in late pregnancy, angina pectoris and arterial hypertension.
Using endoscopic research methods, assumptions about the presence of ulcers, gastritis, and neoplasms are checked and their stage and nature are established. At the moment, capsule endoscopy is an advanced method of examining the gastrointestinal tract, which makes it possible to eliminate discomfort during procedures with virtually no loss in the quality of the examination.
Patients are often frightened by the mere mention of words such as “gastroscopy” or “colonoscopy.” The reasons are clear - these procedures are very unpleasant and even painful for the body. At the same time, painless procedures, such as ultrasound, are not always quite effective. How to check the stomach and intestines without swallowing a probe, is there an alternative to gastroscopy and colonoscopy? Yes, now it exists; it is quite possible to examine the stomach and intestines without gastroscopy. Video capsule endoscopy is the name of this diagnostic method. During this procedure, the gastrointestinal tract is examined without an endoscope. Instead, you just need to swallow a special capsule, with the help of which the research will be carried out.
In addition to non-invasiveness, capsule endoscopy of the stomach and intestines has another important advantage: it allows you to examine not only the upper and distal parts of the intestine, but also the middle sections - the jejunum and ileum, which is much more difficult to achieve with other procedures. First of all, it is precisely when it is necessary to examine the middle sections of the intestine that capsule endoscopy is used.
Both doctors and reviews of patients who have undergone the procedure speak about the effectiveness and painlessness of the technique. We will talk in detail about capsule endoscopy in this article, from which you will learn how to prepare for it and how it goes, about its advantages and disadvantages, contraindications and possible complications.
Fibrogastroscopy
FGDS research can be carried out in two ways:
Transoral method
Carrying out this manipulation, in most cases, takes no more than 5 or 7 minutes. The patient is placed on the couch, lying on the left side. A mouthpiece is inserted into the oral cavity, through the holes of which the flexible hose of the fiber gastroscope is inserted.
The main advantages of this technique can be considered:
- Speed of research.
- Possibility of visual observation.
- If necessary, therapeutic actions can be carried out (taking material for examination, cauterizing bleeding vessels, eliminating papillomas).
- There are practically no complications.
The main disadvantages of gastroscopy of the stomach:
- Long preparation, great restriction of food intake.
- Great discomfort during manipulation.
- High level of contraindications.
Fibrogastroscopy - transoral method
Transnasal method
This technique is considered relatively new. With it, the hose is guided through the nasal passage, and the quality of the manipulation does not differ from the previous method.
The main positive aspects of this procedure:
- The patient does not experience a gag reflex.
- To carry out this procedure, a hose of smaller diameter is used.
- Due to the fact that this type of gastroscopy does not require the use of a local anesthetic to reduce swallowing function, the risk of developing allergies is significantly reduced.
Transnasal gastroscopy has significant disadvantages:
- Due to the small diameter of the tube, the possibility of biopsy and coagulation is excluded.
- After this procedure, nosebleeds may occur.
- It cannot be performed for diseases of the ear, nose and throat.
Fibrogastroscopy - transnasal method
Transnasal fibrogastroscopy method
This method is not widely used and means inserting a flexible tube-probe through the nostril, along the back wall of the larynx into the esophagus. In this case, the gastroscope does not touch the root of the tongue, the uvula of the soft palate, and the patient does not experience anxiety due to the gag reflex. There is no need for anesthesia for this type of examination.
The examination is carried out with a tube with an ultra-thin diameter of up to 0.5 cm, which limits the additional capabilities of gastroscopy: there is no possibility of obtaining a biopsy, it is impossible to coagulate blood vessels during bleeding. On the other hand, with this method, insertion of the tube is facilitated, without leading to a deterioration in the results of the study. It should be taken into account that after gastroscopy using the transnasal method, nosebleeds may occur.
Alternative methods for examining the stomach
Gastroscopy of the stomach using a capsule
To perform gastroscopy without the use of a fiber gastroscope, a capsule is used in which a micro sensor and a video camera are mounted.
Passing throughout the digestive tract and intestines, the video signal is displayed on a computer monitor.
In addition, it is possible to photograph different parts of the digestive tract. The capsule is disposable and is eliminated naturally.
Gastroscopy of the stomach using a capsule is only diagnostic.
When performing it, unlike fibrogastroscopy, it is impossible to take material for a biopsy or remove a polypous growth.
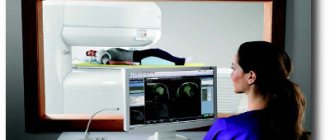
Virtual colonoscopy
This technique is based on the use of x-rays. It takes a few minutes, and the device takes pictures of the internal organs from different angles. It moves around the patient and allows 3D images to be taken.
To carry out this procedure, the patient is placed on a special couch inside the tomograph. A thin hose is inserted into the anus, through which air is supplied. This is necessary to improve image quality.
If necessary, the patient first lies on his stomach, then turns over onto his back. The procedure is completely painless.
When undergoing this type of diagnosis, the following advantages can be noted:
- Do not cause injury to the large intestine.
- In addition to examining parts of the intestine, changes in other organs of the retroperitoneal space can also be observed on the monitor screen.
- Compared to classic colonoscopy, it has a lower cost.
Along with the advantages, this procedure has significant disadvantages:
- Virtual colonoscopy should never be performed on pregnant women.
- Even using modern equipment, the patient receives a dose of radiation.
- It is not always possible to determine which neoplasm is located in the intestine (malignant or benign).
Comparison of computed tomography and gastroscopy of the stomach
If you compare these 2 methods, you cannot give a definite answer which one is better. Each is produced for a specific purpose and has its own advantages and disadvantages.
When using tomography it is impossible to:
- Collect material for biotic research.
- Eliminate polyps or perform vessel coagulation.
- Perform tests to identify pathogenic microflora.
- When examining the mucous walls of the stomach, the diagnostician does not see their color, which significantly complicates the diagnosis.
- X-rays, even in a small dose, can cause health problems to a weakened, sick person.
But unlike gastroscopy, computed tomography allows us to identify some types of malignant neoplasms that cannot be detected using fibrogastroscopy.
Also, using computed tomography, you can examine the structure of nearby organs (liver, bladder, pancreas).
This procedure does not cause psychological or physical discomfort.
Ultimately, only a doctor can determine what type of examination a patient needs to undergo. Gastroscopy is generally preferred, as it is more informative.
X-ray contrast study
Recently, this technique has been rarely used.
This is due to the fact that in its information content and significance it is significantly inferior to gastroscopy of the stomach. To carry it out, barium sulfate is used. This is a thick, white substance. After ingestion, it envelops the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach.
This makes it possible to see the relief and outlines of the organs being studied.
Most often, X-ray contrast examination is prescribed as a complement to gastroscopy of the stomach. Or if the patient for some reason refuses to undergo gastroscopy.
To undergo this type of examination, no special preparation is required; the patient drinks a barium solution and stands in front of the machine.
Sometimes he is asked to turn his body in one direction or another:
- This procedure is absolutely painless.
- Does not cause side effects.
- Ready results (pictures) are taken within 15 minutes.
It should be taken into account that the patient is exposed to radiation, so such diagnostics can be carried out no more than once every six months.
Electrogastrography
This is a relatively “young” research method.
It is prescribed to find out whether the stomach is working correctly and what kind of motor skills it has. Carrying out this procedure resembles the use of an electrocardiogram.
Three sensors are attached to the patient's body, which study signals passing from the stomach. First, the study takes place on an empty stomach.
After which the patient eats food and the examination is repeated. The results obtained are compared and recorded by the doctor.
The procedure can take place over 3 hours in a supine position, is absolutely painless and does not cause any discomfort.
Electrogastroenterography
This technique has two main advantages:
- It is absolutely painless.
- It has no side effects or contraindications.
Diagnosis is made using electronic sensors that are located on the body and transmit signals that can be used to determine the intensity of food movement through the intestinal lumen.
Basically this procedure is prescribed:
- When a pain syndrome occurs, which is associated with the presence of an ulcer.
- Enteritis and enterocolitis.
- Various pathologies of the esophagus that arise due to the backflow of food from the stomach into the esophagus.
This procedure has not yet become widespread in Russia. Although it is completely painless and does not require prior preparation.
Operating principle
After swallowing a tablet with a chamber, it begins its natural journey through the digestive tract. Before the appointment, the patient is put on a special belt. It will subsequently receive all images of organs. Pillcam takes up to 18 high-quality photos in one second. The transparent walls of the capsule allow for maximum quality illumination of the walls of the intestines and stomach.
The resulting images are sent to the doctor’s computer, who analyzes them. A tablet with a camera has proven to be especially effective in detecting Crohn's disease.
The Pillcam is about 25mm long and only 10mm high. The drug weighs about 4 grams. The device is as easy to swallow as a regular capsule. In practice, the use of such advanced devices has shown excellent effectiveness compared to the well-known endoscopy.
Indications for capsule endoscopy of the stomach
This type of diagnostic can be used:
- If other diagnostic methods have not led to identifying the causes of the pain syndrome.
- If the patient has blood in the stool during bowel movements.
- With the development of Crohn's disease, which excludes the possibility of a colonoscopy.
- In the event that the patient refuses to undergo conventional gastroscopy, or vomiting occurs during the procedure.
Also, this type of gastroscopy can be used to clarify the diagnosis if the patient has the following symptoms:
- Increased gas formation.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Nausea and heartburn.
- Difficulty passing food through the esophagus.
Description of the procedure
This type of examination is performed using a capsule containing a color camera and LEDs. It is swallowed by the patient, after which the inner walls of the gastrointestinal tract are photographed.
Movement through the intestines is carried out due to its peristalsis , while the capsule moves independently, without external effort.
Before the procedure, the patient is put on a special vest with a fixing device, which collects all the information and transmits it to the doctor’s monitor. Also, the video capsule is capable of taking photographs, the number of which can reach 80,000 during the procedure.
The procedure lasts no more than 10 hours , after which the capsule is released along with the feces.
It takes the diagnostician approximately one and a half to two hours to process the data.
Preparing the patient for the study
The type of camera is selected for each patient individually, taking into account which part of the gastrointestinal tract needs to be examined. For diagnostic results to be as effective as possible, it is necessary to adhere to some dietary recommendations.
Two days before the start of the examination, exclude foods that cause gas formation in the intestines: cabbage, legumes, milk, fresh baked goods. Avoid carbonated drinks and alcohol. Stop eating 12 hours before the event. A week before diagnosis, you should stop taking iron supplements. 24 hours before the study, the patient is prescribed medications that reduce flatulence.
A person carries out direct preparation of the body at home. He is prescribed Fortrans, a drug to completely cleanse the intestines. The drug is diluted in water at the rate of 1 sachet per 1 liter. The evening before the test, you need to drink 4 liters of solution (one liter per hour, from 16-00 to 20-00).
Going through the procedure
The patient is given a disposable capsule, which he drinks with a sufficient amount of water.
The period of its passage through all parts of the gastrointestinal tract can occur within 10 hours.
The patient returns home and can go about his daily activities.
The following are not allowed:
- Heavy physical activity.
- Sports activities.
- Sudden movements.
After the specified time has expired, the patient returns to the hospital or clinic where the information is processed and deciphered. To do this, a special sensor is attached to the abdominal area. If there is a need for additional examination of the intestines, the patient is placed in a hospital.
To remove the capsule, you do not need to use any action; it comes out on its own, naturally, during bowel movements.
Contraindications
But in some cases, capsule examination is contraindicated. Let's list them:
- intestinal obstruction;
- narrowing of the gastrointestinal tract;
- the likelihood of perforation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysphagia (impaired swallowing);
- intestinal diverticulosis;
- problems with the evacuation function of the stomach.
It is also not recommended to perform capsule endoscopy during pregnancy or if the patient requires a pacemaker. Before undergoing capsule endoscopy, you must undergo a complete allergen screening.
Preparation for the procedure
The preparatory process involves compliance with certain rules that will help to efficiently carry out this type of examination.
The patient needs:
- For two days, eat only boiled food. It should be low-fat and not contain grains or fruits.
- Be sure to drink Fortrans or similar medicines (Lavacol, Moviprep) in the evening before the procedure. It has a mild laxative effect and will prepare the intestines for the correct implementation of this procedure.
- Before the procedure , do not drink alcohol one day and stop smoking.
- You must not eat during the procedure. This may affect the image quality of the camcorder.
- Be sure to drink plenty of water. The interval of drinking liquid should not exceed 1 hour.
- A small meal is possible only after 4 hours after consuming the capsule.
- A full meal is possible only after the procedure is completed.
- Immediately before starting the procedure, it is recommended to take an Espumisan tablet. This will relieve unwanted symptoms of increased gas formation.
- Some patients, before undergoing gastroscopy of the stomach using a capsule , need to undergo a preliminary X-ray examination of the intestine to establish its patency.
Preparatory stage and capsule gastroscopy
The rules for preparing for a study with a capsule differ slightly from the preparatory stage for FGDS. First of all, it is recommended to adjust your diet. Changing eating habits is necessary in order to relieve the digestive system. This will allow you to get the most complete picture of the state of the gastrointestinal tract.
Capsule diagnostics are not performed spontaneously; the patient is given 3–5 days to prepare for the procedure. At this time, you should follow a diet, the main provisions of which are:
- Refusal of heavy and spicy foods. Fatty meats, mayonnaise, baked goods, smoked foods, nuts, spicy seasonings, peas and beans are excluded from the diet. The consumption of alcoholic beverages and soda is strictly prohibited.
- Limiting roughage. Fruits and raw vegetables, baked goods are allowed in minimal quantities.
The specialist will tell you what diet is needed when preparing for diagnosis.
During the day before the actual study, it is necessary to exclude solid foods. Meals should consist of liquid and creamy soups, vegetables stewed in water (excluding cabbage). Eating any food stops 12 hours before capsule gastroscopy. To cleanse the body, a laxative drug is usually prescribed (at the discretion of the gastroenterologist), which is taken on the eve of the examination.
The procedure is performed on an empty stomach. The patient swallows the capsule with 0.25 liters of plain water. Once in the digestive tract, the capsule begins to transmit a signal to the recorder, which is pre-attached to the patient’s waist. For eight hours a person can live as usual. Only food intake is subject to correction. You can eat no earlier than 4 hours after introducing the capsule into the body, drink water - after two hours.
It is mandatory to follow a preparatory light diet and drink plenty of fluids. On the day of the examination, sports and excessive physical activity are not recommended. In the evening of the same day, the registrar is removed from the patient. The endoscopic device leaves the body painlessly within two days.
Advantages and disadvantages of capsule gastroscopy of the stomach
In addition to its advantages, any type of diagnostics has a number of disadvantages. Gastroscopy of the stomach using a capsule is no exception.
Positive aspects of this type of research:
- The procedure does not cause fear and is absolutely painless.
- Has a high degree of diagnostics of the pathological process.
- Advancement of the capsule does not produce any clinical manifestations, pain or discomfort.
- Unlike conventional gastroscopy of the stomach, the tablet penetrates those segments of the intestine where the probe does not have access.
- Early detection of pathological processes.
- Slow processing of the examination results allows the doctor to carefully study the information received.
- When performing this form of gastroscopy, injury to the intestinal walls is completely eliminated.
The main disadvantages of this procedure include:
- Impossibility of collecting material for biopsy.
- It is impossible to carry out minor treatment to remove papilloma.
- The high cost of the procedure does not allow it to be made publicly available.
Where can I get tested? Price
To undergo this type of diagnosis, you need to consult a gastroenterologist. This is a rather expensive procedure, and it is currently possible to carry it out in private clinics or regional hospitals.
The gastroenterologist will also recommend additional types of tests that this procedure involves.
This diagnostic method has a high price, but it varies in different cities and regions of Russia:
- In Moscow, such a procedure will cost from 15,000 to 70,000 rubles . It all depends on the clinic you visit.
- In St. Petersburg, its average price will be from 25,000 to 30,000 rubles.
- In Krasnodar, such a procedure will not exceed 22,000 rubles.
- An economical option can be considered the city of Minsk. This type of diagnosis will cost no more than 20,000 rubles.
Misconceptions about tubeless gastroscopy of the stomach
Can gastric capsule endoscopy completely replace FGS?
Many patients believe that after examination by this method, if they do not have any pathology, they can consider themselves healthy people. This is a fairly common misconception, because to establish an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination using tomography and fibrogastroscopy.
There is also an opinion that capsule gastroscopy of the stomach will help avoid fibrogastroscopy.
This is an incorrect judgment, because the capsule moves spontaneously; it is impossible to direct it to a suspicious area; in addition, there is no possibility of taking material for a biopsy, and it is impossible to carry out minor surgical actions to eliminate polyps.
Many patients believe that FGS is a painful procedure, but, in fact, it does not bring pain, but only delivers unpleasant sensations of discomfort, which are easily removed by spraying an anesthetic onto the root of the tongue.
What to choose, a painful procedure or a pain-free method?
There are many methods that are alternatives to fibrogastroscopy. But at the present stage of development, with all the achievements of science and medicine, it is impossible to replace this type of examination.
Any other technique can be used as an additional or alternative method. Because fibrogastroscopy allows not only to examine organs, but also to perform minor surgical interventions and take material for histological examination
The pain of gastroscopy is a rather controversial issue; many people, after undergoing this procedure, note that it does not cause pain, and the gag reflex that occurs is easily eliminated with deep breathing.