Radiation therapy is a proven effective method in practice for cancer patients. It is often prescribed for radiation and post-radiation proctitis (symptoms and treatment are nonspecific) due to damage to the rectum by radiation, the radiation dose of which exceeds 50 gray. The radiation form is the result of previously performed radioisotope treatment for tumors of the intestinal organs.
The harmful effects of ions suppress oncogenic and healthy epithelial cells of the intestinal cavity. Radiation proctitis symptoms and treatment are carried out with medications, diet, and folk recipes. In case of complications, emergency surgery is indispensable.
Causes of the disease
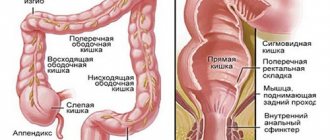
Affected area
Proctitis, provoked by radiation (gamma therapy using isotopes, pure radium) is a pathological condition of the submucosal, mucous part of the anal area with possible involvement of muscles in the degenerative process.
With hemorrhoids and proctitis, due to exposure to radiation, the inflammatory process begins to slowly progress, provoking stagnation of blood in the arterioles of the rectal canal, stenosis of the epithelium with the formation of scars, atrophy and desquamation of cells, perforation, and the formation of a fistula.
Erosion of the rectum is provoked not only by harmful radiation exposure, but also by the entry of infectious agents into the cracks of the intestinal canal:
- Koch's wand;
- cytomegalovirus;
- tuberculous mycobacteria that enter intestinal tissues through microcracks and the bloodstream, forming a fistula and ulcer;
- pale spirochetes (syphilis), causing the formation of chancre;
- gonococci that penetrate through the walls of the vagina in women into the rectal canal, causing gonorrheal vaginitis;
- parasites and protozoa;
- roundworms;
- pinworms.
The chronic form of the disease develops as a result of:
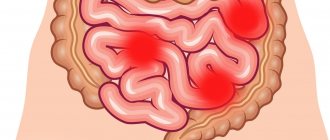
Stomach ache
- formation of benign and malignant tumors;
- genetic predisposition;
- autoimmune, infectious disease;
- hemorrhoids, leading to anal fissures after medical procedures;
- frequent diarrhea, constipation causing scratching, irritation, microtrauma;
- constipation with the passage of dense feces with coarse food elements that damage the mucous membrane;
- medical therapy for anal fissures and hemorrhoids;
- anal rough sex;
- entry of a foreign object into the anus, accidentally injuring the intestinal tissue;
- ruptures during childbirth in women in labor.
Reference! The risk of radiation proctitis increases only when exposed to a total focal dose of radiation exceeding 50-65 Gy. More often, the inflammatory process progresses due to a violation of the integrity of the rectal canal from the use of radiation isotopes and the use of gamma therapy by doctors in women with cancer of the body (cervix) of the uterus. It happens that it is diagnosed after an emergency therapeutic course for oncopathology of coelenterate cells.
Causes of intestinal inflammation after radiation therapy
The following mechanisms underlie radiation damage to the intestine:
- Damage to the intestinal epithelium that develops under the influence of ionizing radiation. This leads to its focal necrosis, desquamation (peeling) and atrophy.
- Development of nonspecific inflammation of the mucous membrane and submucosa. The tissues are infiltrated by neutrophils, hyperemia, swelling, and bleeding are observed.
- Due to trophic disorders (arterioles are damaged), the blood supply to the affected areas of the intestinal mucosa deteriorates, which further aggravates ischemia and necrosis. As a result, atrophic changes progress with the development of fibrosis of the submucosal layer.
- Against this background, pathogenic flora begins to join, which causes infectious complications, including sepsis.
The end result of long-term trophic disorders of the intestinal wall and necrosis is the formation of strictures (narrowing of the lumen), the formation of fistulous tracts, the formation of telangiectasias and the development of bleeding from them.
Forms of inflammation
Radiation proctitis and paraproctitis usually develop slowly. The first unpleasant symptoms appear 2-3 months after exposure to a large dose of radiation to the rectum.
Doctors distinguish:
- early form of the disease if it appears up to 3 months after radiation intervention;
- late when detected after 3-3.5 months.
Taking into account the severity and intensity of symptoms, proctitis is divided into acute and chronic.
Pathology with an acute course can occur as:
Mucus discharge
- catarrhal mucous with active leakage of mucus from the anus, swelling and swelling of the rectal mucosa;
- hemorrhagic with the appearance of swelling, redness, multiple hemorrhages inside the intestinal cavity;
- purulent with cooling of pus from the anus;
- purulent-fibrous with the formation of a fibrous purulent film on the inner surface of the intestine;
- ulcerative with the formation of necrotizing ulcers in places of intestinal damage;
- polyposis with the formation of polyps, growths on the intestinal mucosa.
Chronic proctitis with rectal erosions is divided into forms:
- atrophic, causing thinning of the mucosa, transillumination of blood vessels located in the submucosal layer;
- normotrophic, accompanied by severe pain during the inflammatory course, although no changes in the thickness or relief of the anus are observed;
- hypertrophic, leading to thickening of the inner lining of the intestinal mucosa, the formation of focal growths, false polyposis.
If proctitis is not treated for a long time (ICD code - K 62.7), it will become chronic. Mucosal ulcers and intestinal bleeding can become obsessive and constant. One of the dangerous consequences of radiotherapy is a sharp narrowing of the intestinal canal, constipation, and stone obstruction. Such symptoms cannot be ignored and you need to contact proctologists for examination and therapeutic therapy.
Development mechanism
Radiation proctitis occurs after radiation therapy if the total dose of radiation absorbed by tissues exceeds the tolerable value of 50 grams/rad. The higher this indicator, the greater the likelihood of developing pathology.
Under the influence of radiation, cell reproduction (proliferation) in the intestinal tissues is disrupted, exfoliation (desquamation) and atrophy of the epithelial layers occur. The mucous membrane becomes inflamed, and muscle fibers are often involved in negative processes. The blood supply deteriorates, which may result in areas of necrosis and ulceration and cicatricial narrowing of the rectal lumen. Sometimes ulcers lead to the formation of fistulas and intestinal bleeding.
According to the clinical course, the following types of rectitis are distinguished:
- Mild (catarrhal) . This is the initial stage of the disease, characterized by redness and swelling of the mucous membrane.
- Medium (erosive-desquamative) . At this stage, epithelial cells are exfoliated and tissue integrity is disrupted.
- Severe (ulcerative) . The most dangerous stage of the disease, in which ulcers and intestinal obstruction form.
Ulcerative rectitis often becomes chronic and is difficult to treat. Obstruction (blockage) of the rectum requires surgery and a colostomy.
Signs of acute proctitis
From the effects of radiation on the colon, there is a disruption of the normal division and maturation of cells, their peeling, atrophy, and covering with scales.
In acute proctitis, symptoms begin to appear at an early stage:
- periodic painful urge to empty the intestines;
- paroxysmal pain that gets worse after going to the toilet
- effusion of blood, pus and anus;
- burning, itching, presence of a foreign object in the anal canal.
Additional symptoms of inflammation of the rectal mucosa:
Manifestations of the disease
- physical weakness;
- high temperature up to 38 degrees;
- chills with purulent-ulcerative proctitis.
Usually after 3-4 days, acute symptoms begin to subside. Especially if patients are undergoing treatment taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. But after a certain time, symptoms can flare up again, as if delayed, 3-4 months after exposure to radiation. Frequent urination, passing feces in small portions, pain in the anus, dull pain in the left iliac region (in the rectal area) begins to bother me.
Reference! An obvious sign of radiation proctitis is the passage of stool with mucus. The manifestation of early symptoms cannot be ignored: false urges during bowel movements, paroxysmal intense pain after emptying the intestines and the release of feces, constant secretion of mucus, burning, itching in the anus with intensification after bowel movement, a pulling urge to defecate with pain radiating to the abdominal muscles, rectal bleeding, unusual mucus discharge, weight loss.
Diagnostics
If signs of radiation proctitis appear during radiotherapy, the patient is immediately referred to a proctologist. To diagnose this disease, clinical, laboratory and instrumental methods are used. The examination begins with an objective examination and clarification of complaints. With radiation proctitis, there is always a connection with radiation therapy. Laboratory methods include a general blood test, which usually reveals inflammatory changes, such as leukocytosis, accelerated ESR and a band shift to the left. Laboratory diagnostic techniques can determine the severity of inflammation, but they cannot be used directly to diagnose radiation proctitis.
Endoscopy plays a key role in diagnosing the disease. The simplest, most accessible and informative method is sigmoidoscopy. When conducting this study, the doctor detects redness, swelling of the mucous membrane and hyperproduction of mucus in the rectum. In addition, the technique allows us to identify changes characteristic of complications such as bleeding, abscess formation, and ulceration. Ulcers are usually localized on the anterior wall of the rectum; in some cases they can lead to the formation of fistulas. During rectoscopy, a biopsy of the rectal mucosa is necessarily performed. It makes it possible to clarify the severity of inflammatory and atrophic changes in the mucosa. In order to determine the presence of an infectious agent, a bacteriological examination of a smear from the rectum is carried out.
Due to the fact that the symptoms of radiation proctitis have much in common with ulcerative colitis, the main differential diagnosis should be between these two diseases. Proctitis is supported by a history of radiation therapy. In addition, radiation proctitis is distinguished by the presence of ulcers on the anterior wall and in the middle third of the rectum. At the same time, this disease rarely affects the posterior wall and lower part of the rectum. In nonspecific ulcerative colitis, inflammatory changes are diffuse and affect the entire rectal intestine. A biopsy is used to definitively differentiate between these two diseases.
The diagnosis of radiation enteritis and colitis is based on identifying a history of radiation exposure. Careful clinical examination and exclusion of other causes usually allows this diagnosis to be made.
Diagnosis of radiation enteritis, in addition to anamnesis, involves complete and consistent visualization of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Using fluoroscopy of the stomach with examination of the small intestine or enterography, the extent of the lesion is assessed and the presence of strictures or fistulas is determined. CT scan of the abdomen is useful in excluding metastases, abscess, and fluid collection in the abdominal cavity.
H2 breath tests using lactose and lactulose as substrates are used to diagnose lactose intolerance and bacterial overgrowth. 14C or 13C glycocholate test - to determine bacterial overgrowth, bile and fat malabsorption. 14C xylose breath test - to verify bacterial overgrowth. Serum folate levels may be high due to its synthesis by bacteria.
The main method of diagnosis, assessment of the severity and extent of radiation colitis is colonoscopy. The endoscopic picture is usually characterized by various combinations of ulceration, inflammatory changes, mucosal atrophy, narrowing of the intestinal lumen and telangiectasia. Morphological examination of biopsy samples of the colon mucosa has no diagnostic value, since surface changes are nonspecific.
Irrigoscopy verifies the extent and location of the stricture and fistula. In this case, the following changes may be detected: a decrease or absence of haustrations, smoothing of the surface of the mucous membrane, ulceration and formation of fistulas in the affected segments of the intestine, narrowing of its lumen.
Radiation enteritis should be differentiated from diseases of the small intestine that occur with impaired absorption. Differential diagnosis is not difficult if there is information about previous radiation sickness and exposure. In contrast to diseases with primary malabsorption (celiac disease, primary lactase deficiency), with radiation enteritis hyporegenerative atrophy of the mucous membrane of the small intestine is observed. For radiation injuries of the colon, differential diagnosis is made with IBD, ischemic colitis and tumors.
Symptoms of chronic inflammation
Coloproctologist
A latent form of chronic proctitis due to inflammation of the rectum (symptoms and treatment) with progression 3.5 months after radiotherapy is diagnosed in 10-15% of patients. Symptoms are minor or absent even at a late stage of the disease. Only periodically feces with mucus admixtures leave the rectum, and dull pain occurs in the intestines. If left untreated, the mucous membrane of the rectal epithelium will gradually become strictured and may become covered with scars.
Worth knowing! With chronic proctitis, pain in the anus is dull, aching, and mild. The inflammation progresses, but symptoms may be virtually absent for a long time. In the absence of treatment for radiation proctitis, the disease flares up unexpectedly, in waves, causing a sharp deterioration in well-being.
Basic measures of drug therapy
Treatment of radiation proctitis should be carried out only after confirmation of the diagnosis. When primary symptoms of the disease appear, the patient undergoing radiotherapy is referred for consultation to a proctologist. Diagnosis is carried out using clinical, instrumental and laboratory measures. First of all, a medical history is collected and an objective examination of the patient is carried out. Among the laboratory techniques, OAC should be distinguished. Endoscopy and sigmoidoscopy are mandatory. To determine malignancy, a diagnostic method is used, such as taking a small amount of material for further study - a biopsy.
To treat radiation proctitis, the negative effects of ionizing radiation on the body are reduced. For these purposes, patients are prescribed ascorbic acid and B vitamins.
Among the main measures of drug therapy to combat radiation proctitis are:
- Compliance with the treatment regimen.
- Carrying out hygiene measures.
- Taking medications.
At the initial stage of development, treatment can be carried out on an outpatient basis. In severe cases of the disease, there is a need for inpatient monitoring.
To treat proctitis after radiation therapy, the patient needs to normalize the diet. This measure involves avoiding spicy, salty, fatty and sour foods. It is imperative to exclude alcohol-containing drinks, fruit juices and sweets. It is important to adhere to the correct drinking regime. Main courses should include low-fat soups with pureed meat and foods containing lactobacilli.
Antibiotics are used to relieve the inflammatory process. Drugs are prescribed after receiving the results of a culture test, which is carried out to determine the sensitivity of pathogenic microflora. Experts prescribe drugs that have sulfonamide and glucocorticoid activity. Antihistamines are mandatory, which are necessary to relieve unpleasant symptoms. Most often, for radiation proctitis, drugs such as Loratadine, Clemastine, Hifenadine, etc. are prescribed.
An important stage of drug treatment is local therapy. This measure involves complete cleansing of the intestines, which helps eliminate inflammation. For these purposes, medications such as solutions of collargol and potassium permanganate are used. Local therapy can be carried out using suppositories containing anesthetics, mesalazine and glucocorticosteroids.
Hygienic methods are enemas, which are carried out on the basis of special antiseptic solutions. After the intensity of the inflammatory process has decreased, cleansing procedures are replaced by sitz baths, which are prepared using a solution of potassium permanganate.
Erosive proctitis
Acute stage of the disease
With erosive proctitis, symptoms appear as superficial erosions (defects, flaws) on the tissues and mucous membrane of the rectum. Gradually they heal and do not leave scars, becoming covered with a crust and subsequently falling off. This form of the disease can be provoked by nonspecific infectious agents (simple streptococci, staphylococci) that provoke various types of inflammatory purulent processes.
In form, depending on the provoking factors, erosive proctitis occurs as: radiation, immune, somatic, stagnant, traumatic, alimentary.
In patients, feces begin to stagnate in the rectal passage, compress the venous vessels, and impair the outflow of venous blood in the walls of the large intestine.
The chronic form of erosive ulcerative sphincteritis develops after:
- carrying out diagnostic procedures;
- masturbation, anal sex;
- effects of radiation therapy;
- chemical trauma to the rectal mucosa;
- introducing aggressive substances by mistake or purposefully (with a criminal connotation), for example, to punish a person during interrogation.
A thermal cause of the development of erosive ulcerative proctitis is possible in the case of accidental (intentional) introduction of a hot or cold solution into the rectum, location of the perineum on a hot surface, contact of patients with radiation sources or radioactive substances with unauthorized access to them, for example, during combat operations.
Symptoms of erosive proctitis are acute, sudden:
- fever, chills;
- burning, itching, pain in the anus;
- violation of the act of defecation;
- feeling of heaviness, a foreign object in the anus;
- general deterioration of health;
- discharge of liquid feces with impurities of mucus, blood, pus;
- characteristic pain, frequent tenesmus.
Note! A feature of erosive proctitis is the formation of multiple defects on the surface of the rectal mucosa. Most often, pathology develops after contact gamma therapy or other radiography methods.
When can you use candles?
It is important to recognize the disease immediately, while proctitis is in its early stages. When it becomes chronic, the disease is dangerous due to its complications - the formation of polyps, inflammation of the colon and sigmoid colon, the formation of fistulas and tumors.
Suppositories are used when the disease is at the first stage of development and does not occur in a very acute form. In case of erosive proctitis, a severe chronic form, treatment with suppositories is prohibited, since in contact with damaged areas the suppositories will act as an irritant and can further damage the tissue and cause bleeding.
Types of suppositories for proctitis
Pimafucin cream will help cope with the fungal cause of the pathology.
Depending on the nature of proctitis, suppositories should contain substances that relieve inflammation, painkillers, and corticosteroids that will accelerate tissue regeneration. If the cause of proctitis is fungal infections, it is necessary to use additional Pimafucin cream. In severe cases of the disease, suppositories with antibiotics and antiviral components are used. Candle therapy is carried out for a short period of time and under the supervision of a doctor.
Sea buckthorn
Accelerate healing, relieve inflammation and normalize metabolic processes in mucosal cells. Prevents injury during constipation. Used for the development of proctitis against the background of hemorrhoids. The natural product is approved for breastfeeding women; additional consultation is required during pregnancy. If you are allergic to sea buckthorn, use is prohibited.
With propolis
Suppositories have an antibacterial, anti-inflammatory effect and prevent the formation of tumors. Suppositories containing cocoa butter have the greatest effect. Fat helps the necessary components be absorbed into the blood and act faster on the source of inflammation. Suppositories are absolutely safe during pregnancy and are allowed during breastfeeding.
Candles "Relief"
Shark liver oil in the drug promotes rapid recovery and relief of symptoms.
Shark liver oil relieves pain, reduces swelling, relieves pain and itching, and heals tissue. Due to the vasoconstrictor effect of phenylephrine, they help stop bleeding and reduce purulent discharge. Allowed to be used for erosions. The course of treatment provides a long-term therapeutic effect. It is not advisable to use during pregnancy and lactation.
"Salofalk"
The drug relieves inflammation, has antibacterial properties, and is effective for proctitis caused by infection, as it destroys E. coli bacteria and some types of cocci. It acts locally; harm from suppositories during pregnancy or breastfeeding has not been proven. Restrictions on use: age under 18 years, kidney and liver disease. Regular use helps avoid exacerbation of the disease.
"Ultraproct"
The drug is used for proctitis, hemorrhoids or anal fissures. The composition includes the anesthetic cinchocaine and the glucocorticosteroid fluocortonol. Removes pain, itching and burning, regenerates tissue. Acts quickly and provides a long-lasting effect. Cannot be used for proctitis caused by tuberculosis or STDs, pregnant or lactating women.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
The examination of patients begins with a visual examination, examination of existing signs, and identification of the connection of the disease with radiation exposure.
The proctologist prescribes laboratory tests:
Diagnostic tests
- blood for the ratio of the total leukocytes (in%) to assess the severity of the disease;
- general blood test to determine increased ESR, leukocytes in the blood;
- sigmoidoscopy is an effective informative examination method;
- histological examination to determine the degree of pathological changes in tissues;
- bacteriological smear from the anus to detect infection (a nutrient medium is inoculated to grow colonies of the pathogen);
- stool analysis for occult blood and worm eggs in cases of suspected worm infestation or infestation;
- biopsy of the mucous membrane for complications of proctitis, fistula formation.
In case of erosive sphincteritis of the rectum, the doctor will examine the perineum, note defects: spastic contraction or relaxation of the sphincter, and determine whether blood is bleeding from the anus. Next, he will conduct a rectal examination for swelling and mucous discharge from the rectum.
Other instrumental research methods:
- sigmoidoscopy with the introduction of a sigmoidoscope into the intestinal lumen to view changes in the mucosa;
- rectoscopy with the introduction of a special mirror into the anus to identify redness of the walls, the presence (absence) of fibrinous-purulent plaque;
- biopsy with tissue sampling from different parts of the intestinal epithelium mucosa, followed by histology and cytology examination.
Reference!
Diagnosis of erosive proctitis is differential. It is important to find differences from similar conditions: anal fissures, oncology (with the disintegration of neoplasms in the walls of the rectum), internal hemorrhoids, non-erosive proctitis. Therapy for radiation proctitis is complex. The initial goal is to reduce the harmful effects of radiation on the body.
Patients are prescribed:
- vitamins B, A, C to remove and neutralize free radicals;
- antihistamines to relieve itching and swelling;
- antiviral, antibacterial drugs based on test results;
- painkillers for severe pain due to exposure to radiation etiology;
- hormonal agents for restoration of the intestinal mucosa, healing of lesions caused by radiation.
If proctitis progresses, the intestinal canal has clearly narrowed, scars, fistulas and neoplasms have formed, then doctors resort to surgical intervention.
Diagnosis of radiation proctitis
At the first signs of radiation proctitis, the patient is prescribed an examination by a proctologist. The study of the disease is carried out using laboratory, clinical and instrumental methods. The doctor begins the examination with a survey, finds out what specific signs are observed in the patient, when they began to bother.
A general blood test is prescribed. As a rule, with radiation proctitis, analysis shows a band shift to the left, accelerated ESR, and leukocytosis. Such indicators indicate the presence of an inflammatory process.
To more fully identify the disease, endoscopy is prescribed, which makes it possible to visually examine the mucous membrane of the rectal wall for the presence of ulcers or erosions, purulent infiltrate, and evaluate the color and moisture content of the tissue.
A sigmoidoscopy is performed. The procedure allows you to detect swelling of the mucous membrane, redness, and increased mucus production. The method makes it possible to determine the presence of bleeding in a patient, as well as the presence of ulcers and necrotic lesions. Mostly, ulcers form on the anterior wall of the intestine; in some cases, fistulas are formed from them. During rectoscopy, a biopsy of the mucous membrane is performed, which helps to determine the degree of inflammation and atrophy.
When performing sigmoidoscopy, a sigmoidoscope is used to examine 30 cm of the rectum. The equipment has the form of a flexible plastic tube, equipped with a light source and a camera. It is inserted through the anus for the purpose of detailed examination of the walls and determination of pathology.
Before conducting the study, it is required to exclude foods rich in fiber from the diet 3 days before the procedure. The patient is given enemas every hour until the result becomes clear. The procedure is done on an empty stomach; before the examination, an enema is performed again until a clear result appears. Before the study, a digital examination of the organ is performed.
A finger examination allows you to establish inflammation and detect its cause. Sometimes proctitis occurs as a result of mechanical damage, a hidden tumor or a foreign object.
The patient takes a knee-elbow position. If there are difficulties with this position, the patient is asked to lie on his side and press his knees to his stomach.
Anoscopy is also performed using a rectal speculum coated with petroleum jelly. It is inserted into the anus and expanded slightly, allowing for a full view.
To determine the presence of infection in the patient’s body, a bacteriological smear of the rectum is taken.
Because radiation proctitis has similar symptoms to ulcerative colitis, studies should rule out or confirm this diagnosis. With radiation proctitis, ulcers are distributed along the anterior and middle part of the intestine. Nonspecific ulcerative colitis is detected by diffuse changes in the entire rectal area. A final diagnosis can be made by a biopsy, which excludes or confirms the development and growth of tumors against the background of a chronic process.
Diet for proctitis
With proctitis, diet plays an important role. It is worth refusing to take irritating foods. Include steamed or boiled food in your diet, taking a little at a time in a warm, semi-liquid form.
The diet for inflammation of the rectum is a special one with limited use of sweet products and plant foods. It is important to completely eliminate alcohol, spicy, salty, and sour foods. Fermented milk products, broth-based soups, and lean meat are shown. It is possible to expand the diet only during the period of regression of radiation proctitis.
Drug treatment
For proctitis, it is necessary to suppress the negative effects of ionizing rays on healthy tissue. If radiation therapy is carried out, it is canceled by doctors or the administered doses are reduced.
To treat inflammation of the rectum, anti-inflammatory and antihistamines are prescribed:
Popular drugs
- Loratadine with antipruritic, antiallergic properties;
- Clemastine with exudative, antihistamine, antipruritic effects;
- Hifenadine is a cholinergic protector with a local anesthetic, antiserotonin effect;
- potassium permanganate, cholibacterin for severe inflammatory process;
- antibiotics (Levomycetin, Metronidazole) to suppress the negative effects of antibiotic drugs;
- antispasmodics (Spazmaton, Drotaverine) for disturbing severe rectal pain.
If an infectious agent is detected, antibacterial therapy is carried out.
Causes of proctitis
Proctitis develops for many reasons:
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease;
- haemorrhoids;
- helminthiases;
- STIs: gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, etc.;
- tuberculosis;
- long-term antibacterial therapy;
- allergic reactions;
- rectal injuries.
The risk of developing proctitis increases after radiation therapy for certain types of malignant diseases, as well as with poor diet and chronic constipation. Stagnation of blood in the pelvis and rectal veins may be a predisposing factor. This is observed with weakness of the pelvic floor muscles, hemorrhoids, a sedentary lifestyle or prolonged bed rest.
Only a doctor can identify the causes of proctitis.
Suppositories for inflammation of the rectum
Suppositories for proctitis help well in the treatment of proctitis caused by radiation:
Rectal suppositories
- Salofalk (for the treatment of proctitis, suppositories) based on mesalazine with anti-inflammatory properties;
- Proctosedyl is a local antibiotic (suppositories for paraproctitis in adults) placed in the anus after emptying the intestines;
- Pentasa (suppositories for inflammation of the rectum) to neutralize free radicals, inhibit chemotaxis and leukocytes, reduce the formation of cytokinins and leukotrienes;
- Asacol with a local anti-inflammatory effect.
Rectal sea buckthorn suppositories are very helpful for the treatment of proctitis. In severe cases, suppositories are prescribed for paraproctitis: Sulfasalazine, Prednisolone, Proctosan, Ultraproct.
Characteristics of rectal suppositories
When inflammation develops in the intestinal mucosa, it is recommended to use the following inexpensive rectal suppositories:
- Anti-inflammatory (“Natalsid”, “Proctosan”). Their effectiveness is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process and quickly relieving the symptoms of the disease. Suppositories have minimal side effects. The only contraindication is individual intolerance to the substances included in the composition.
- Restorative (“Methirulacil”). Designed to restore metabolism and accelerate the regeneration of the mucous membrane. This helps to cope with the inflammatory process and eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
- Antiviral and antibacterial (“Prednisolone”, “Metronidazole”). Prescribed for advanced and severe forms of proctitis. The course of therapy does not last long. The introduction is carried out by an experienced specialist.
This form of medicine, such as suppositories, for the treatment of proctitis is dangerous because it can cause mechanical damage to the thinned walls of the rectum. Despite this, many experts still recommend resorting to this method of combating the disease. Such a decision is made when the expected benefit outweighs the possible harm.
- Review of the hemostatic agent "Natalsid".
Suppositories "Natalsid" are developed on the basis of sodium alginate. It is recommended to use suppositories for grade 1-2 hemorrhoids and proctitis. The price of the medicine is 312-430 rubles. It is administered rectally to eliminate the inflammatory process in the rectal area. It is recommended to carry out the laying procedure 2 times a day after spontaneous cleansing of the intestines. The duration of therapy varies from 7 to 14 days depending on the complexity of the inflammation. If the recommended dosage is exceeded, an allergic reaction may develop.
- Review of rectal suppositories "Methirulacil".
The medicine is developed to normalize metabolic processes in the body and improve trophism. The active substance – dioxomethyltetrahydropyrimidine – stimulates recovery processes and leukopoiesis. "Methirulacil" is intended for the treatment of intestinal ulcers and radiation sickness. With its help, the symptoms of proctitis are effectively eliminated.
The price of the medicine is 80-85 rubles. The drug is not recommended for use in the presence of hypersensitivity, leukemia and malignant neoplasms. The course of application is 7-10 days, 1 pc. in a day. Before use, you should consult a specialist.
- Review of the drug "Prednisolone".
Effective rectal suppositories, which are widely used for colitis and proctitis. It is recommended to use the drug only after consulting a doctor. Used to treat infectious and inflammatory diseases in the intestinal area.
The cost of suppositories ranges from 67 to 90 rubles. The drug is based on prednisolone. It is not recommended for use in case of systemic fungal infections and hypersensitivity to the constituent substances.
Rectal suppositories should be placed once a day before bedtime. The course of treatment ranges from 7 to 15 days, depending on the severity of the disease.
Treatment of chronic proctitis
Doctor for delicate problems
The chronic form is characterized by a sluggish course, so treatment is a course. For radiation proctitis, patients are prescribed supportive treatment with long-term medication to relieve inflammation and strengthen the immune system.
When treating radiation proctitis, it is recommended to use candles, sign up for a massage and radon baths. Physiotherapy methods have proven themselves well: exercise therapy, mud therapy, balneotherapy, stay in a sanatorium. Also enemas for proctitis with the introduction of decoctions, herbal infusions (oregano, lemon balm, chamomile, calendula).
Reference! If you treat ulcerative proctitis in a timely manner, reduce the frequency of exacerbations, adhere to a healthy lifestyle and a special diet, you can achieve stable remission even after treatment of chronic proctitis or diagnosis of oncology.
List of effective suppositories for the treatment of proctitis and rules for their use
In candle therapy, you need to know the rules of administration. The best effect is expected after cleansing the intestines, sitz baths with antiseptic solutions, herbal decoctions, and washing. Since the rectal mucosa is extremely vulnerable, you need to insert the candle with washed hands and gradually push it into the depth by 2/3 of a finger.
After the procedure, it is recommended to lie down for 20-30 minutes at rest so that the drug is absorbed into the tissue. The most convenient time is before bed. The doctor will select the best option and frequency. Only in extremely severe cases are strong drugs immediately prescribed.
Candles with sea buckthorn oil
Suppositories for proctitis with sea buckthorn oil contain active biological elements to fight inflammation and stimulate local immunity. Their antitumor properties have been proven, which is important in chronic diseases to prevent complications. Includes:
- vitamin complex of K, E, D, F, C, A;
- unsaturated fatty acids;
- tannins;
- tocopherols;
- magnesium;
- glycerides.
Suppositories with sea buckthorn oil eliminate the main symptoms of the pathology - itching, burning. They are an excellent wound healing agent.
Inflammation is eliminated by the destruction of mediators (cytokine, histamine, prostaglandin). Vitamin K restores blood clotting, Vitamin C strengthens capillary walls.
Sea buckthorn oil is used to treat hemorrhoids and minor erosions.
Important! The components of sea buckthorn suppress the DNA synthesis of pathogenic microorganisms, therefore stopping the proliferation of infection in the outbreak.
For ulcerative and radiation proctitis, they are prescribed for 15 days twice a day. In the case of catarrhal form, relief of symptoms occurs after a week.
Relief
For proctitis, suppositories for treatment from the Relief series are correctly prescribed only by a doctor. Relief, Relief Advance and Ultra have the same base - shark liver oil, but different additional components, therefore they differ in indications.
Unique healing substances have been discovered in shark fat:
- amino acids - restore destroyed proteins of tissues and blood vessels;
- Omega-3 polyunsaturated acid - regulates lipid metabolism in cells;
- a combination of fat-soluble vitamins and microelements ensures the process of energy formation;
- squalene is a complex biochemical compound that provides fish with the opportunity to obtain oxygen under water; when applied topically, it stimulates healing, delays cell aging (atrophy), produces a good antioxidant effect, and kills bacteria.
Relief is one of the most popular and effective remedies for hemorrhoids and other rectal diseases today.
The composition of Relief is supplemented with phenylephrine hydrochloride. It is an α-adrenergic agonist that contracts small vessels. Therefore, the effects of shark oil include a hemostatic effect, pain relief, and improved outflow from the veins of the rectum. The property is useful for erosive and ulcerative proctitis with a tendency to bleeding.
Important! Rapid absorption helps to achieve results within 5 minutes after administration and lasts about two hours. Spasm of coronary vessels is excluded. Candles are prescribed 1-2 times a day. The course of treatment is chosen by the doctor. Exceeding the dose contributes to dangerous manifestations: increased pressure (arterial and intraocular), decreased pulse.
First of all, patients with proctitis and concomitant diseases may suffer:
- thyrotoxicosis and tumors of the endocrine glands;
- hypertension;
- severe atherosclerosis;
- glaucoma.
Traditional medicine recipes
When treating the rectum with folk remedies, sitz baths with the addition of sea buckthorn oil and medicinal herbs (chain, tansy, chamomile, horsetail) successfully help to relieve pain and inflammation in the intestine. Solutions are introduced into the intestine through the anus in a warm form (t + 37 degrees).
Effective recipes for the treatment of proctitis with folk remedies:
ethnoscience
- Herbal mixture (oak bark, toadflax, water pepper) to relieve pain and inflammation in the intestines. Take 2 tbsp. l. dry powder, pour in pork fat, leave overnight. In the morning, heat, strain, insert moistened tampons into the anus, leave for 5-6 hours.
- Sweet clover tincture for anemia, to reduce tissue swelling. 1 tbsp. l. pour boiling water (0.5 l), leave for 30 minutes. Take 1/3 cup three times a day.
- Pour boiling water (1 liter) over horsetail (50 g of dead wood), leave for 15-20 minutes, strain. Add to baths when treating proctitis at home, sitting down and holding for up to 30 minutes.
Prevention
In general, the prognosis is positive for 80% of patients if they undergo timely treatment with suppositories and ointments for proctosigmoiditis, paraproctitis, and proctitis. Although today it is quite possible to avoid harmful gamma radiation effects on internal organs. Modern protocols and techniques in the treatment of oncological diseases of the abdominal and intestinal cavity are not capable of harming intact tissues or epithelium. In case of a cancerous tumor, only the affected cells are suppressed, without affecting healthy ones.
For prevention purposes, it is recommended:
Doctor's recommendations
- treat gastrointestinal diseases, inflammation of the anorectal area in a timely manner (for proctitis - treatment with medications, suppositories);
- eat right, do not abuse fatty, fried, spicy foods;
- stop smoking, alcohol;
- monitor genital hygiene;
- do not neglect contraceptives during casual sexual intercourse
The danger of radiation proctitis is complications, a sharp narrowing of the rectal canal, constant constipation, anal fissures, severe pain in the left iliac region and the passage of hard feces with mucus. The main thing is to prevent serious complications from radiation (erosive) proctitis by neglecting treatment. When 1-3 sections of the intestine are affected, fistulas form and severe bleeding occurs. Then emergency surgery is performed, and treatment with gels, suppositories, and ointments for proctitis becomes ineffective.