Causes of pathology
There are several reasons for the occurrence of intestinal dyskinesia. Here are the most common:
- Malnutrition - the child has very little or no fiber in his diet.
- Primary intestinal dyskinesia appears as a consequence of an infection that affects the intestines; secondary - develops as a result of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Children with diabetes are often susceptible to intestinal dyskinesia.
- With hormonal imbalance, this pathology is sometimes observed.
- There is an opinion that dyskinesia can develop as a consequence of malfunctions of the nervous system. In other words, disruption of nerve impulses leads to spasms and disruptions in the peristalsis of the small intestine.
- The appearance of dyskinesia is caused by enzyme deficiency, which develops due to disruption of the pancreas and chronic stagnation of bile in the bile ducts. This disease is called pancreatin, it is more common in adults, but also occurs in children.
Dyskinesia can be: spastic - this is the pushing of food through the intestines so quickly that the sick child begins to have severe diarrhea, accompanied by abdominal pain; atonic - due to the slow movement of food, the intestine becomes clogged, causing constipation, pain and flatulence.
What do you need to know?
By following one of the diets described above, you need to completely change your approach to your diet. You need to avoid eating fried and fatty foods, especially fried meat. You need to eat small portions 5-6 times a day. The largest portions can be eaten in the morning, and it is better to reduce dinner to a minimum amount, excluding meat and fish from it (lunch is best for these products, since they take a long time to digest in the stomach).
During exacerbations, meat and fish products generally need to be twisted through a meat grinder before consumption to reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract. All natural juices must be diluted with water before consumption, thus eliminating the possibility of their fermentation in the stomach. It is better to avoid coffee and tea, as they cause constipation. The same goes for smoking and drinking alcohol.
To identify products of individual intolerance, it is recommended to keep a diary and write down all the food consumed during the day. You need to start small, with proven products, gradually expanding your daily diet and excluding from it foods that cause discomfort or abdominal pain. Thus, you can create your own individual list of products that contribute to exacerbation of the disease.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptoms of dyskinesia include the following:
- The intestinal muscles are weakened.
- The child loses weight quickly.
- The skin becomes pale and thin.
- A blood test shows a low red blood cell count.
- Dysbacteriosis is noted.
It is impossible to identify any specific symptom, but against the background of these symptoms, the child feels a loss of strength and loss of appetite. Babies constantly cry and scream, their stomachs are swollen, and rumbling can be heard in the intestines, and there is no appetite.
Diagnosis of pathology
Diagnosis of dyskinesia is a complex and multi-stage process. The following types of research may be required:
- Examination of a patient with palpation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Examination of the intestine using an endoscope.
- Stool analysis.
- Irrigoscopy and biopsy are carried out when doctors try to clarify the severity and form of the disease.
- Anamnesis is collected in this case with the child’s parent. The doctor, of course, will not get a picture of the sensations, but at least he will have an idea about the diet and daily routine of the little patient.
During diagnosis, the doctor, based on the symptoms, excludes possible diseases one by one, and in the end one true one remains, which is subsequently treated. This is the diagnostic technique for intestinal dyskinesia.
Diagnostic measures for dyskinesia
Due to its similarity with other gastrointestinal diseases, intestinal dyskinesia is diagnosed by excluding the suspected pathology. A phased examination of a child includes several activities:
- endoscopy;
- coprogram;
- irrigoscopy;
- biopsy - according to indications;
- stool occult blood test;
- exclusion of pathological neoplasms in the intestine.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment for patients of different ages requires different approaches. In infants, the level of enzymes responsible for digestion is first corrected; for this, the baby takes drugs rich in protein elements. For children over 5 years old, infusions of various herbs - tansy, St. John's wort, bittersweet - are added to the diet.
If the baby experiences abdominal pain, then the treatment in this case is taking Nosh-pa or Drotaverine. The dosage should be prescribed by a doctor based on the weight and age of the patient. Giving antispasmodics on your own is very dangerous. If the pain is not very severe, you can try to relieve it with a warm compress applied to the area where the spasm occurs. This treatment can be carried out with a regular rubber heating pad filled with warm water.
If the symptoms indicate that there is a nervous disorder that led to the disease, treatment is carried out with antidepressants or antipsychotics. In this case, the child should be under the constant supervision of the doctor who prescribed the therapy. Treatment with hypnosis or acupuncture is also possible. Additional treatment options include physical therapy.
Principles of disease therapy in children
Treatment of small children for intestinal dyskinesia is based on the organization of the diet and the correct distribution of hours of activity and rest. Patients are recommended to eat frequently and in small portions. In a diet that accelerates the treatment of dyskinesia, the following should prevail:
- juices;
- dried bread;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- slimy water porridges;
- products with vegetable fiber;
- fermented milk products, especially with live lactobacilli.
When treating intestinal dyskinesia in a child under one year of age, it is important to adjust the balance of food enzymes. For this purpose, very young children are prescribed special medications to compensate for the lack of enzymes. For preschoolers and adolescents, treatment is supplemented with herbal preparations with tansy, St. John's wort, and bittersweet.
If a child suffers from severe pain, non-drug assistance can be provided by applying heat to the peritoneal area. If the procedure is unsuccessful, the patient can be given No-shpu or Drotaverine, calculating the dosage according to age and weight.
To relax the nervous system, treatment includes antidepressants or antipsychotics. Additionally, with intestinal dyskinesia, children can be prescribed autogenic training, exercise therapy, hypnosis, and acupuncture.
Traditional therapy
You can also be treated with folk remedies:
- To regulate intestinal motility, you can give your baby a tincture of valerian roots, mint leaves and chamomile flowers. It is prepared as simply as regular tea. Brew 1 spoon of each plant in one 500 g container. Let it brew for at least 30 minutes. Then strain and give the child 100 g to drink 3 times a day before meals.
- Another infusion prepared using the same method (1 tbsp per 500 g of boiling water), but from oak bark, sage, St. John's wort and motherwort, relieves the symptoms of dyskinesia quickly and reliably. The infusion should be taken 4 times a day, 100 g.
Folk remedies for intestinal dyskinesia
Harmless treatment of spastic and atonic colitis is carried out using folk remedies. Mint leaves, chamomile flowers, and valerian roots contribute to the restoration of normal peristalsis of the tract. The components take 1 tsp. each, pour a glass of boiling water over the phyto mixture and leave covered for 20 minutes. The napar is filtered and given to the child 3 times. 100 ml per day half an hour before meals.
Another remedy is obtained from sage and yarrow herbs, oak bark, St. John's wort flowers, and motherwort raw materials. The amount of each ingredient is 2 tbsp. l. The collection is doused with a glass of boiling water and allowed to brew for a couple of hours. Then the drug is filtered and the child is given 4 rubles. per day, measuring 100 ml of drink each time.
- Organize bowel movements in a timely manner if your baby suffers from constipation. Difficulties with the excretion of feces entail not only dyskinesia - their danger lies in general intoxication of the body, loss of appetite and decreased performance. Improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract contributes to stagnation and rotting of food masses, which can subsequently cause the child to develop allergies.
- If dyskinesia causes a frequent urge to defecate, give your baby a decoction of chamomile and calendula flowers, thick jelly or a hard-boiled egg. Specific treatment for intestinal disorder will be prescribed by your pediatrician.
- To relieve spastic colic, use compresses. Apply a bandage soaked in vinegar solution to the intestinal area. The ratio of acidic product and water is ½ cup to 3 liters. If you have the opportunity to give your child a pine bath, be sure to take advantage of it. Treat yourself with paraffin applications.
Prevention of intestinal dyskinesia for children is to create a favorable atmosphere in the family, avoid stress, and eat high-quality foods without dyes, preservatives and flavoring additives. If you have constipation, it is important to limit your intake of rice in your diet.
Intestinal dyskinesia in children is a pathological disorder in the body. The child has dysfunction in the development of motor motility of the gastrointestinal tract. The baby may regularly suffer from colic as a result of irritable stomach syndrome. It is important to promptly diagnose a disease such as intestinal dyskinesia in children. Symptoms and treatment may vary, depending on the form and severity of the pathology.
Diet for dyskinesia
A proper diet is the most basic method of treating not only dyskinesia, but also many other intestinal diseases. Even in ancient times, healers said: “A person is what he eats.” Therefore, this issue must be taken seriously.
For any diet prescribed to a baby, there are certain rules:
- Products that a child consumes should not contain preservatives, colors and artificial flavors.
- The diet should include cereals such as wheat, buckwheat, and oatmeal. They should be prepared in the form of sticky porridge; only in this consistency will they be most beneficial for the baby.
- In order not to distort the picture of the course of the disease, you should not give your baby rice porridge. They fix feces too well.
- A child can get the missing fiber from apples, cabbage, carrots and beets. Fruits should be given fresh, pureed.
- If the disease is accompanied by constipation, then you need to give the child a lot of fresh juices from carrots and apples. Beetroot juice is very useful. An unsweetened decoction of rose hips is suitable for the same purposes; in addition, it is very rich in vitamin C.
- All food is either steamed or boiled. You can add salt, but in very limited quantities.
- Be sure to give your child dairy products, especially kefir, cottage cheese and sour cream. They contain not only lactobacilli, but also calcium, which is beneficial for baby’s bones.
- Under no circumstances should a child eat fried fatty meat or fish. You should not give him spicy or smoked food, flour, or sweet foods (cakes, cakes).
Portions should be small, the baby should not pass it on. But feedings should be at least 6 times a day. It is very important that a small child follows a sleep schedule; he should sleep not only at night, but also during the day.
Nutrition for intestinal dyskinesia
People suffering from intestinal dyskinesia are advised to take boiled and steamed food. To stimulate intestinal motility, it is necessary to consume vegetables and fruits in moderate quantities, which enhance the evacuation function of the intestines, but do not cause irritation of the mucous membrane and fermentation of food.
The diet for hypomotor dyskinesia of the colon consists mainly of foods rich in fiber (cabbage, lettuce, tomatoes, carrots, pumpkin, beets, zucchini, and so on). Only those foods that contain essential oils (garlic, mushrooms, onions, turnips, radishes, etc.) are excluded from the daily diet. Regular bread should be abandoned in favor of wholemeal wheat or rye bread (it is recommended to eat bread with bran). The main emphasis is on various porridges cooked in water (buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley, wheat).
For hot dishes, it is best to eat soups (broth can be made from vegetables, as well as lean fish and meat). In general, with intestinal dyskinesia, you should give preference to baked and boiled vegetables.
It is allowed to eat steamed omelettes and soft-boiled eggs if the protein is well tolerated by the body (no more than two pieces per week). Up to four times a week you can eat small quantities of boiled or baked fish and meat (if you have a double boiler, you can cook meat and fish in it).
It is best to drink freshly squeezed vegetable and fruit juices. You are allowed to eat dried fruits (prunes, dates, dried apricots, figs), bananas and apples. These products contain sugar and organic acids that stimulate intestinal motility, but you should not abuse them either. It is best to follow a simple rule - eat little, but often.
It is strongly recommended to regularly consume lactic acid products (fresh natural kefir, acidophilus, yogurt). You can prepare your own drinks with bifidobacteria by purchasing the ingredients at the pharmacy.
To avoid problems with regular bowel movements, you should drink a glass of cool water on an empty stomach in the morning immediately after waking up. You can also take bran to empty the intestines; they can be consumed both in pure form and cooked (pour boiling water). For six weeks, take the treatment, so you need to take it three times a day, one dessert spoon at a time.
Also, quite often doctors prescribe their patients with hypomotor intestinal dyskinesia to consume animal or vegetable oil (olive, sunflower, butter or corn). As a rule, the daily dose does not exceed one tablespoon once a day.
It is not recommended to consume fatty meats, chocolate, smoked meats, coffee, canned food, tea and spicy foods. Also, if possible, it is necessary to avoid or reduce the consumption of potatoes, pasta, rice and foods that cause increased gas formation (concentrated grape or apple juice, cabbage, spinach, legumes, sorrel, and so on).
Patients with hypermotor intestinal dyskinesia are prescribed a similar diet, from which foods containing toxins are excluded. All food on this diet is prepared using vegetable fats. As the patient’s condition improves, his daily diet is expanded, first with boiled vegetables and fruits, and then with fresh ones. It is allowed to take bran in small quantities (with hypermotor dyskinesia, they can provoke flatulence and subsequent abdominal cramps, so not every person can use them).
Forms of the disease
Intestinal dyskinesia can be hypermotor and hypomotor . In medical practice, there are several stages - primary and secondary. With the development of hypermotor dyskinesia, symptoms of mild intestinal irritation occur. The activity of the colon begins to gradually fade away.
At the primary stage of the disease, clinical manifestations occur after suffering stress. It is necessary to monitor the diet and not give children heavy foods. The secondary stage of the disease progresses against the background of other diseases of the digestive system.
Hypomotor dyskinesia of the stomach is characterized by regular spasms in the intestines and increased tone. Food lingers in the body and does not have time to be digested. Because of this, constipation occurs along with pain. If diagnosis is delayed, there is a risk of developing intestinal obstruction. Intoxication of the body occurs as a result of excessive accumulation of feces. This condition provokes intestinal hypertonicity. The patient may feel nausea and dizziness, and vomiting often occurs .
Causes of intestinal dyskinesia
If parents do not care about the baby’s health and do not monitor his diet, dyskinesia may develop. Unhealthy diet affects body weight, often leading to obesity at a young age. Diabetes mellitus is considered a provoking factor.
Scientists have not identified the exact reasons, because the disease manifests itself in combination with other pathologies or independently. It is almost impossible to detect the disease in a timely manner and begin treatment. Gastroenterologists recommend not overloading the stomach, eating right and leading a healthy lifestyle.
Reasons for the development of gastrointestinal dyskinesia in children:
- nervous overstrain, stress, fear;
- maintaining an unhealthy lifestyle;
- the sleep and rest schedule is not observed;
- penetration of infection into the digestive system;
- genetic predisposition;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- obesity and overweight.
Enzyme deficiency often leads to the development of dyskinesia. The pathology occurs as a result of impaired functioning of the pancreas, chronic stagnation of bile in the ducts. These are the main factors that contribute to the development of dyskinesia. Depending on the reasons that led to the onset of the disease, spastic and atonic forms of the pathology are distinguished. As the spastic form progresses, food quickly passes through the intestines in the child’s body. The little patient begins to suffer from profuse diarrhea and severe pain in the abdomen.
Atonic dyskinesia is characterized by slow movement of food, so the intestine begins to become clogged with feces. The baby experiences pain, bloating, flatulence, and frequent constipation .
Prevention of dyskinesia
- The main preventative method is following a healthy lifestyle.
- You should include in your daily diet foods that can provide your body with vitamins, minerals and fiber. You should not limit protein foods. Bad habits contribute to intestinal dysfunction.
- If a person has a mental disorder, they should see their therapist regularly.
- And in general, you need to monitor your psychological health - try to avoid severe stressful situations if possible, give yourself time to rest, and maintain a sleep-wake schedule.
- You should also include more activity in your lifestyle. We are not necessarily talking about the port, but if a person leads a sedentary lifestyle, then just regular half-hour walks every day will play into his hands.
Video on the topic: Colon cleansing with castor oil and lemon
Clinical manifestations
The main symptoms of gastrointestinal dyskinesia:
- gradual weakening of the intestinal muscles;
- the child is rapidly losing weight;
- the skin becomes pale and too thin;
- when taking a blood test, the level of red blood cells is quite low;
- clinical manifestations of dysbacteriosis appear.
It is impossible to single out one symptom because several of them can occur at the same time. The child’s general health sharply deteriorates, there is a loss of strength, and there is no appetite. Babies are constantly capricious and restless, crying and screaming. The abdomen becomes hard and bloated. Rumbling is heard in the intestines, children refuse food .
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of dyskinesia is a complex and multi-stage process. The child undergoes the following tests:
- examination and palpation of the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- internal examination of the intestine using an endoscope;
- taking stool for analysis;
- irrigoscopy and biopsy (to clarify the form and severity of the disease);
- collection and analysis of medical history (questioning parents to determine the child’s diet and daily routine).
During diagnosis, the doctor carefully examines the symptoms. It is important for him to consistently exclude the development of concomitant diseases in order to accurately determine the cause and make a diagnosis.
How to treat correctly
Treatment of gastric dyskinesia in an infant begins with adjusting the level of enzymes that contribute to the functioning of the digestive system. For this purpose, medications are prescribed that contain protein elements. For children over five years old, it is important to add infusions based on medicinal herbs to their diet. The most effective plants are St. John's wort, bittersweet, and tansy.
To normalize intestinal motility, the child is prescribed Metoclopromide . If acute abdominal pain causes discomfort to your baby, you need to take No-shpu or Drotaverine. These are two drugs that have the same effect. Drotaverine is an analogue of No-shpa. Medicines belong to the group of myotropic antispasmodics.
Action of No-shpa
The active component is drotaverine hydrochloride, which is included in the drug in an amount of 40 mg. The product is produced in the form of yellow tablets or solution for injection. The action of the drug is aimed at instantly eliminating spasms in the body. No-spa helps to dilate blood vessels and reduce muscle tone in internal organs.
The components contained in the composition do not affect the child’s central nervous system. Young children are not given No-shpa in tablet form, but are administered intramuscularly. The dosage is set individually, depending on age. The drug is not prescribed to children under six years of age.
Drotaverine for children
Drotaverine contains drotaverine hydrochloride in an amount of 40 mg. The drug helps children eliminate spasms in the smooth muscles of the intestines and internal organs. This occurs by reducing muscle tone and reducing the supply of calcium ions.
Drotaverine is an effective and efficient drug that has virtually no contraindications for use. The drug, like No-shpa, is not prescribed to children under six years of age. Dosage and method of application are prescribed individually.
It is strictly forbidden to buy antispasmodics for children on your own. If intestinal colic does not manifest itself intensely, you can try applying a warm compress to the stomach. Treatment is recommended using a rubber heating pad filled with hot water.
Traditional medicine
Treatment of children with traditional medicine is recommended only after consultation with a pediatrician. This therapy is most effective when combined with medications. Traditional medicine recipes:
- To improve the functioning of intestinal motility, the child is given a tincture based on valerian roots, chamomile flowers and mint leaves. The medicine is easy to prepare at home. You can buy plants at the pharmacy. To make an infusion, you need to take valerian root, chamomile flowers and mint leaves one tablespoon each. The dry mixture is poured with two glasses of boiling water. Infusion time is 20-25 minutes. You need to strain the broth and give the child 100 ml 3 times a day before meals.
- Recipe for the second decoction: take a tablespoon of oak bark, sage, St. John's wort and motherwort. Pour everything over with two glasses of boiling water. You need to drink 100 ml 4 times a day. This medicine will help quickly eliminate the negative symptoms of dyskinesia.
All traditional medicine can be used if the child does not have an allergic reaction to medicinal herbs. You need to take the decoction at regular intervals.
Proper nutrition
It is important to additionally follow a few basic nutritional rules:
- products should not contain preservatives, dyes, flavors and other additives of artificial origin;
- the diet should consist of cereals (porridges are prepared not too dry, so that their consistency is more liquid);
- It is recommended to stop eating rice cereals;
- the daily menu should contain fiber (apples, cabbage, carrots, beets);
- carrot and apple juice, rosehip decoction;
- food is boiled by steam or in water;
- salt restriction;
- Be sure to include dairy products (kefir, cottage cheese, sour cream) in your daily diet;
- refusal of fatty and fried foods, meat, fish.
How is the treatment carried out?
The treatment of intestinal dyskinesia is approached in a comprehensive manner:
- Drug treatment.
- Help from a psychologist or psychotherapist.
- Physiotherapy.
In addition, the patient is often advised to make changes to his daily diet.
Medicines
- Antispasmodics are prescribed: nifedipine and its analogues.
- Preparations with polytropic action (no-spa, papaverine, gastrocepin, halidor).
- Indomethacin and other drugs that have absorbent, astringent and enveloping effects are prescribed against diarrhea. Imodium is often prescribed.
Folk remedies
Any “folk recipe” should be agreed upon with the attending physician who prescribed the course of medications. Not all drugs and the ingredients in them can be “friends” with each other.
Herbal infusion. Ingredients:
- peppermint;
- sage;
- motherwort;
- yarrow;
- St. John's wort;
- Oak bark.
2 tablespoons of the mixture are poured with boiling water and left for 2 hours. After you have strained the infusion, drink half a glass before eating 4 times a day
Recommendations during treatment:
What to avoid:
- exclude alcoholic drinks;
- drink less coffee and strong tea;
- exclude whole milk.
what you should start taking:
- more berry and fruit juices;
- you can take spike decoction;
- eat more rye bread.
Description of intestinal dyskinesia
Intestinal dyskinesia is a decrease in the tone of the intestinal wall and a violation of its motor function. The disease is accompanied by pain, as well as changes in stool in the form of diarrhea or constipation. This pathology can affect almost the entire intestine. Most often, dyskinesia affects the following parts of the colon:
- blind;
- colon (ascending, transverse, descending);
- sigmoid.
With dyskinesia, only intestinal function is disrupted, there are no organic changes.
Dyskinesia affects almost all parts of the large intestine
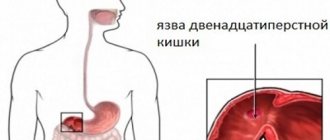
Somewhat less frequently, damage to the small intestine, in particular the duodenum, occurs.
Sometimes dyskinesia also affects the duodenum.
- stomach;
- spleen;
- gallbladder;
- liver.
Proper functioning of the colon - video
Classification of the disease
According to the nature of the disorders, intestinal dyskinesia in adults and children is divided into the following types:
- Spastic or hypermotor (hypertonic/hyperkinetic). This type is characterized by increased tone of the intestinal walls and their spastic contraction. This leads to painful colic and frequent constipation.
- Atonic, or hypomotor (hypotonic/hypokinetic). It manifests itself as a significant weakening of tone and slowing of intestinal motility. The patient is concerned about constipation, dull aching pain in the umbilical region, and a feeling of fullness, which over time leads to disruption of intestinal patency.
Considering the mechanism of development, dyskinesia occurs:
- primary. It develops independently, without the presence of predisposing factors.
- secondary. Occurs as a secondary disease. Depending on the initial cause, the following types are distinguished:
- medicinal;
- allergic;
- hepatogenic;
- pancreatogenic;
- gastrogenic.
Drug-induced dyskinesia develops as a result of prolonged and improper use of laxatives or fixative drugs. Food allergies also disrupt intestinal motility as a result of pathological reactions to humoral and nervous stimuli. Other types of secondary dyskinesia occur due to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract or liver.
There are often cases when it is extremely difficult to determine the type of dyskinesia.
Causes and provoking factors
The causes of intestinal dyskinesia, including the secondary type, are extremely diverse. These include:
- low physical activity;
- hereditary predisposition;
- poor nutrition;
- chronic stress, increased nervous excitability, dissatisfaction;
- endocrine disorders;
- infectious diseases;
- gynecological diseases;
- individual intolerance to certain products;
- improper use of certain medications;
- hypovitaminosis (especially in children).
The cause of the disease can only be determined by the attending physician. Most often, hormonal disorders such as obesity, hypothyroidism and diabetes mellitus lead to the development of dyskinesia.
Causes and risk factors
The main cause of intestinal dyskinesia is considered to be acute or chronic stress. Persons with a neurotic character, a tendency to somatization, increased anxiety, and emotionally unstable individuals are more susceptible to pathology.
Risk factors include:
- genetic predisposition;
- acute infectious intestinal diseases (in particular, those caused by Campylobacter and Shigella);
- endocrine disorders;
- pathologies of the central and peripheral nervous system (neoplasms and spinal cord injuries, syringomyelia, parkinsonism);
- diseases of the urogenital tract;
- poor nutrition (including eating too quickly, irregular meals, eating excessively spicy, fatty, hot foods);
- excessive mental stress;
- overweight;
- individual intolerance to certain foods;
- irrational use of medications (especially antibacterial, diuretic, psychotropic drugs);
- bad habits.
Main manifestations
Common symptoms for all types of intestinal dyskinesia are:
- Pain syndrome. The pain can be sharp, aching, stabbing, or dull. They intensify when eating and are localized mainly in the umbilical region. Unpleasant sensations disappear after defecation, passing gas and at night.
- Nausea, bloating, feeling of fullness in the intestines, belching.
- Flatulence. It occurs in the evening and is accompanied by rumbling.
- Weight gain.
- Incomplete emptying of the colon after defecation.
- Abnormal stool. Most often it manifests itself as constipation, which can be followed by diarrhea. At the same time, mucus is abundantly released along with feces.
- Neurological disorders (mental). Expressed in drowsiness, loss of appetite, anxiety, decreased performance.
With duodenal dyskinesia, vomiting occurs with an admixture of bile and mucus; painful sensations are localized in the right hypochondrium and are most pronounced in the evening.
Symptoms of spastic and atonic dyskinesia - table
| Spastic dyskinesia | Hypotonic dyskinesia |
|
|
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia
All symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia are divided into those related directly to the intestines, to other organs of the gastrointestinal tract and non-gastroenterological manifestations. A feature of this disease is the lack of a tendency to progress.
One of the main signs of intestinal dyskinesia is abdominal pain of moderate intensity, without clear localization, occurring from time to time or regularly. It can be stabbing, cutting, dull or aching. Most often, pain is noted in the left iliac region. The pain appears some time after eating, weakens or disappears after passing gas or bowel movements, and never occurs at night.
Another symptom is flatulence, which appears a certain time after eating or in the evening. Loose stools are usually observed in the morning after breakfast and are absent at night. After defecation, there is sometimes a feeling of incomplete bowel movement. With constipation, stool resembles sheep feces; dense feces often lead to semi-liquid stool. The feces may contain an admixture of mucus, but no blood or pus is found in it.
Diagnostic methods
Due to the fact that the symptoms of the disease are not unique, several studies are necessary to clarify the diagnosis. The main diagnostic methods include:
- Complete blood count and general urine test.
- Coprogram - a study is necessary to identify hidden blood, which is a sign of inflammation.
- Sigmoidoscopy is one of the main methods for detecting dyskinesia. If you have this disease, contractions of the intestinal walls will be observed in response to the introduction of a proctoscope.
- Irrigoscopy helps determine the area with hyper- or hypotonicity. In the first case, there will be a spasmodic part of the colon with difficult movement of feces, in the second - an expanded area with reduced tone.
- Colonoscopy allows you to take a biopsy to rule out cancer. In addition, with the hypotonic form of dyskinesia, pale and dry mucous membranes with a complete absence of peristalsis will be observed.
There are also additional studies that help make the diagnosis as accurately as possible. These include:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- scraping for enterobiasis;
- FGDS;
- plain radiography;
- sigmoidoscopy (examines the mucous membrane of the sigmoid and rectum);
- MRI.
Thanks to these studies, the doctor can not only make a correct diagnosis, but also prescribe effective treatment.
How to treat pathology
The following methods of treating intestinal dyskinesia are distinguished:
- diet;
- drug treatment;
- gymnastics and yoga;
- physiotherapy methods;
- ethnoscience.
Any therapy will not have a positive effect without following a diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Proper nutrition
Therapy for intestinal dyskinesia begins with diet. It includes not only proper nutrition, but also regular eating.
- It is advisable that the dishes are thoroughly cooked.
- It is not recommended to heat them before eating.
- The frequency of meals should be at least 5 times a day, and the portions should be small.
- For both atonic and spastic dyskinesia, it is necessary to avoid fatty, spicy and fried foods.
Basic principles of therapeutic nutrition for children
The diet of a child with ADHD is based on compliance with the following nutritional principles:
- You cannot completely abandon the use of vegetable oil and butter: parents, having read about the need to reduce fat in the diet, mercilessly remove even olive oil from simple dishes. This is mistake. After all, cooking food by frying is prohibited. But adding healthy vegetable oils to dishes is necessary.
- It is forbidden to completely remove meat from a child’s diet. Under no circumstances should you get carried away with the currently fashionable veganism, raw food diet and vegetarianism. A diet for biliary dyskinesia in a child implies a regular intake of protein into the body. It is almost impossible to achieve this without eating meat products.
- Refractory fats (lamb, pork, beef, goose, duck) should be completely excluded from the diet. They not only make the dish heavy on the stomach, but are also difficult to digest. If consumed regularly, such fats can provoke the development of fatty liver hepatosis.
- Meals should be fractional - five to six times a day. A child should not experience hunger and then eat huge portions of food for a stomach ache. The optimal amount of food consumed at one time is about 200 grams. If the child has not reached the age of six, 120-130 g will be enough. When weighing portions, it is advisable to use special kitchen scales to avoid overeating.
Manifestations of dyskinesia in children
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia in a child are similar to those in an adult. In children, the disease is indicated by alternating constipation with diarrhea. In addition, in the spastic form, the pain syndrome is so severe that it is practically not relieved by taking antispasmodics. Children also experience bloating and severe gas formation.
Characteristic symptoms are:
- pale skin;
- frequent regurgitation;
- decreased appetite;
- decreased physical activity.
With a long course of the disease, the child may develop symptoms such as:
- muscular dystrophy;
- weight loss;
- anemia;
- dysbiosis.
To somewhat alleviate the baby’s condition, you can apply a warm heating pad to the stomach for a while, and in case of severe constipation, give a laxative prescribed by your doctor. If you are worried about diarrhea, it is recommended to drink chamomile infusion or thick cranberry jelly. It is important to organize your child proper nutrition, daily routine and limit physical activity.
Features of the course of intestinal dyskinesia in children
Intestinal dyskinesia in children of the first years of life is manifested by an imperative urge to defecate, spasmodic pain in the abdomen or rectal area, pain often appears after physical exertion. Body weight may decrease or gain too slowly, muscular dystrophy, anemia, and dysbacteriosis may appear. Children with intestinal dyskinesia are characterized by pale skin, weakness, fatigue, and irritability. Sometimes a slight increase in body temperature is possible.
Features of dyskinesia during pregnancy
Intestinal dyskinesia occurs in almost every pregnant woman. This is due to both psychological factors and the effects of progesterone, which weakens the tone of the intestinal wall. In addition, the body and its enzyme systems have to adapt to new conditions and increased stress.
Pathology in pregnant women is most often manifested by constipation, heaviness in the stomach and pain. With a severe course of this disease, there may be a risk of miscarriage, since the spastically contracting intestines will irritate the uterus, and the urge to defecate and straining will increase pressure on the fetus. Therefore, at the first symptoms of the disease, you should consult a doctor.
The difficulty of therapy in pregnant women is that many drugs are contraindicated during this period. Among the methods that can improve well-being are:
- drinking at least 1.5 liters of fluid per day;
- a glass of water in the morning on an empty stomach;
- moderate physical activity;
- proper and regular nutrition;
- wearing a bandage.
A pregnant woman should strive to regulate her bowel movements and, if possible, have bowel movements at the same time.
Forms of intestinal dyskinesia
Intestinal dyskinesia can be primary (occurs as an independent pathology, usually due to prolonged stress or poor nutrition) and secondary (develops against the background of another disease). The primary form of intestinal dyskinesia is more often diagnosed in children.
Depending on the consistency of stool, intestinal dyskinesia is divided into the following forms:
- with diarrhea (more than 1/4 of all acts of defecation occur with stool of liquid consistency, less than 1/4 with constipation);
- with constipation (more than 1/4 of all acts of defecation occur with dense and fragmented feces, less than 1/4 with diarrhea);
- mixed (constipation and diarrhea are observed in more than 1/4 of cases);
- unclassifiable (changes in the consistency of stool are expressed implicitly, not enough to determine the form of pathology).
Depending on the characteristics of the clinical picture, intestinal dyskinesia is distinguished with a predominance of pain, intestinal symptoms and flatulence.
It is necessary to maintain a water regime - drink 1–1.5 liters of water daily, this serves to prevent constipation, and in case of diarrhea, it prevents the development of dehydration.
Depending on the etiological factor, intestinal dyskinesia can be stressful, nutritional (associated with dietary errors) or post-infectious.
Prevention methods
To prevent the development of intestinal dyskinesia, you must adhere to several rules:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Healthy food;
- exercise;
- avoid stressful situations:
- try to spend more time outdoors;
- carry out hardening procedures;
- to refuse from bad habits.
The sooner intestinal dyskinesia is detected in an adult or child and the sooner measures are taken to eliminate it, the greater the likelihood of avoiding serious complications and the higher the possibility of a quick recovery. You should not ignore the manifestations of the disease and self-medicate, as this can cause significant harm to your health.