A hard belly or stiff abdominal muscles may be due to digestive problems or a symptom of abdominal disease. If the reason lies in errors in nutrition, then there is no need to worry, since, in all likelihood, this is a banal gas formation that will go away after some time.
But if the syndrome is accompanied by pain in the epigastric region, nausea, vomiting and fever, then it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, since a hard stomach is often an alarming symptom of pathologies of internal organs.
Flatulence
The cause of hardness in the abdominal muscles is often increased accumulation of gases. Flatulence or gas formation is often a consequence of the fermentation process in the intestines, which can be caused by overeating, eating stale foods, carbonated drinks, baked goods or vegetables containing large amounts of fiber and starch. In some cases, discomfort can be caused by eating food too quickly, resulting in air entering the gastrointestinal tract.
About 500 ml passes through the digestive tract of a healthy person during the day. gases With their increased formation, the intestines become distended, which negatively affects the digestion process. Associated symptoms will be bloating, a feeling of heaviness, nausea, belching, and sometimes heartburn.
If the cause of pain and stiffness in the abdominal area is not an illness or disease
Bloating, severe abdominal cramps and pain are serious reasons to consult a doctor. In most patients, such symptoms are caused by eating disorders or poor quality foods. Snacking on the go can also cause stomach pain because a person is unable to chew food thoroughly and swallows large portions of air along with food.
Eating foods that cause increased gas formation should be strictly controlled. When drinking sweet carbonated drinks, you may experience twisting pain in the abdomen and an increase in its volume. These products also include:
1 sweet pastry (due to the high content of simple carbohydrates, it causes fermentation in the upper intestines);
2 legumes, white cabbage, black bread (due to the high content of fiber and starch, a feeling of fullness appears immediately after eating);
3 baking soda (reduces the secretion of gastric juice, promoting excessive gas formation).
By bloating, severe paroxysmal pain in the abdomen, followed by diarrhea and the release of gas, the body is freed from unsuitable food.
Peritonitis
Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum that occurs as a result of a ruptured appendix, perforation of an ulcer, inflammation of the abdominal organs, internal bleeding and many others. Inflammation of the peritoneum has a toxic effect on the body. Accompanied by pain, nausea, vomiting, fever and muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall. Severe form of peritonitis is fraught with the development of complications and poses a threat to human life. Peritonitis is treated by surgery.
"Women's" reasons
Women's stomach sometimes hurts due to factors not related to the gastrointestinal tract. The cause of discomfort may be illnesses such as ectopic pregnancy or ovarian rupture. Such conditions are characterized by pain in the lower abdomen, which gradually intensifies. Bleeding from the vagina also begins.
An ectopic pregnancy requires urgent surgery, otherwise blood poisoning may begin and the patient cannot be saved. Pain can also be caused by a tumor, cyst and other ailments.
If a woman consulted a general practitioner or gastroenterologist about pain, but the doctors were unable to detect its source, it makes sense to undergo an examination by a gynecologist.
Intestinal obstruction
Intestinal obstruction is a condition in which the movement of intestinal contents is disrupted. The syndrome is caused by mechanical blockage or impaired motility due to the presence of fecal stones, neoplasms, hernias, congenital pathologies, inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs, strokes and poisoning with heavy metal salts. Intestinal obstruction leads to intoxication of the body. The most pronounced symptoms are cramping pain, nausea, foul-smelling vomiting with a putrid odor, headache, weakness, bloating, tachycardia and decreased blood pressure.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on an analysis of all existing complaints, clinical manifestations, medical history, and examinations. The required scope of examinations is determined by the doctor; the following are often prescribed:
- a general blood test to confirm the inflammatory nature of the process and the presence of anemia;
- biochemical blood test to detect pathology in the liver, pancreas, kidneys;
- a general urine test will reveal abnormalities in the functioning of the kidneys;
- Nechiporenko, Zimnitsky tests, biochemical, bacteriological examination of urine if kidney disease is suspected;
- radiography with contrast of the abdominal organs, retroperitoneal space;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys;
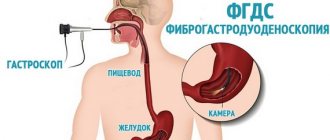
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy;
- stool analysis for worm eggs, coprogram.
Doctors may be involved in the differential diagnosis: gastroenterologist, urologist, nephrologist, gynecologist, oncologist, surgeon.
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, caused by stagnation of intestinal contents due to kinking of the appendix, mechanical blockage or infectious diseases. Symptoms of inflammation are sudden pain in the right lower abdomen, hard muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, nausea, vomiting, defecation disorder, and gas formation. The development of appendicitis can be complicated by an abscess or thrombophlebitis of the abdominal cavity. Treatment of inflammation involves surgery.
Diagnostics and prevention
Most of the ailments described above require urgent surgical intervention; otherwise, you need to contact a gastroenterologist and undergo a comprehensive examination, do an ultrasound, and pass the prescribed tests. After this, appropriate treatment and a special diet can be prescribed.
As a preventive measure, there are general recommendations, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and moderate physical activity. For people with sensitive digestion, it is recommended to switch to homemade food prepared with the addition of a minimum of spices.
To avoid infection, it is important to adhere to the rules of hygiene: wash your hands and fruits before eating, do not eat in establishments with a dubious reputation.
Note!
The presence of symptoms such as:
- Stomach ache
- smell from the mouth
- heartburn
- diarrhea
- constipation
- belching
- increased gas formation (flatulence)
If you have at least 2 of these symptoms, then this indicates a developing
gastritis or ulcer.
These diseases are dangerous due to the development of serious complications (penetration, gastric bleeding, etc.), many of which can lead to
LETHAL
outcome. Treatment needs to start now.
Read the article about how a woman got rid of these symptoms by defeating their main cause using a natural method. Read the material…
OPischevarenii.ru
The appearance of a hard and bloated abdomen is a sign of a malfunction in the body. Sometimes the reasons are quite banal, for example, this phenomenon often occurs after overeating, but in some cases the provoking factor becomes a serious illness.
The feeling of an enlarged belly can be subjective. Then there are complaints about a feeling of fullness and heaviness. As a rule, this is a temporary condition that does not require specific measures.
The reasons for the temporary appearance of a hard belly are hidden in the dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. A medical examination will only confirm the real factors of subjective sensations.
The bulge can be caused by excess weight and a defect in the spine (forward-facing curve - lumbar lordosis). A specialist can easily determine these conditions from real swelling after studying the anamnesis and external examination.
If a person does not have any diseases, then this phenomenon is caused by the accumulation of gases or air:
- Swallowing air while eating or drinking too much carbonated drinks leads to temporary bloating. In this case, frequent belching may occur. Partial air exits through the anus and is absorbed by the intestinal walls;
- The stomach hardens when gases form during the digestion of food, as well as after taking soda, which neutralizes gastric secretions;
- Hardness is observed after eating a large amount of sweet foods and baked goods. They are easily digestible carbohydrates, cause a fermentation reaction, accordingly, increasing gas formation;
- A large amount of fiber and starch in the body also causes discomfort (brown bread, legumes, potatoes, cabbage, etc.).
Gases may occur due to the presence of fermentopathy. For example, a deficiency of the enzyme needed to break down complex milk sugar (lactose) into monosaccharides (fructose and glucose) is very common among adults. This enzyme is called lactase, it is synthesized by the small intestines.
If there is a deficiency of this substance, milk passes into the large intestine and only there is it digested with the participation of local microflora. It is this process that, in case of lactase deficiency, causes increased gas formation, a painful feeling of fullness and bloating after eating.
A hard stomach in a small child most often occurs due to dysbiosis. It is worth noting that this disorder is quite common among adults. This disease is characterized by an imbalance of intestinal microflora, that is, the number of opportunistic bacteria increases, and the number of beneficial bacteria decreases.
Both the former and the latter are constantly present in the body, but when an imbalance occurs, the normal absorption of food is disrupted, it is poorly digested, putrefactive processes dominate, and gas formation suddenly increases.
If the abdomen is distended only in a certain place, then one may suspect a mechanical obstruction to the movement of gases, for example, a tumor or intestinal obstruction for other reasons. This phenomenon is observed when intestinal motility is disrupted (often occurs with invasions that provoke intoxication of the intestinal muscles), problems with blood circulation (varicose veins affecting the lower abdomen). Discomfort can be caused by mental pathologies, for example, hysterical disorder.
Usually the first person to discover symptoms is the person himself, who constantly loosens his belt, wears large clothes, and feels constant discomfort. However, in some cases this phenomenon goes unnoticed for a long time, for example, with significant obesity, asymptomatic ascites (abdominal dropsy).
The presence of a disorder may be indicated by a feeling of tension in the groin, on both sides of the lower back, and pain in this area.
Pain syndrome, as a rule, occurs as a result of the body’s reaction to damage by pathology to any internal organ. For example, it could be an enlarged spleen, a congested liver, or a tumor in the large intestine. Local pain, which is uncharacteristic of ascites, occurs against the background of the development of cirrhosis. In addition, it may be inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis) or pancreas (pancreatitis), primary liver cancer (hepatoma).
A distended, painful, and hard abdomen may be a symptom of progressive ascites or growing tumors. This increases intra-abdominal pressure. As a result, food digestion is disrupted, it moves back into the esophagus (reflux), causing heartburn. When the diaphragm rises, shortness of breath is observed in a lying position (orthopnea), shallow rapid breathing (tachypnea).
Diffuse swelling should be a reason for a more thorough examination. The doctor is interested in a tendency to abuse alcohol, a history of hematuria, jaundice, intestinal disorders, and rheumatic heart pathologies. The data obtained make it possible to identify cirrhosis, colon cancer with metastases to the peritoneum, kidney pathologies (nephrosis), and congestive heart failure.
It is not recommended to self-medicate, especially if this condition occurs frequently or is constantly present. Consult a gastroenterologist for advice. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis, study the medical history, rule out or confirm the presence of diseases.
Often, diagnosis in children and adults involves the following studies:
- Analysis of stool for intestinal microflora;
- Examination of gastric juice;
- Bacterial analysis of stool;
- Bile examination;
- Ultrasound of the digestive system.
Without fail, if the stomach is hard, it is necessary to adjust the patient’s diet. Products that can increase gas formation (cabbage, potatoes, rice, whole milk, etc.) are excluded from the menu. Every day they eat coarse bread, a limited amount of vegetables and fruits, and dairy products.
It is recommended to increase physical activity, and it is not necessary to do exercises in the gym; walking 3 km a day is enough. In the absence of serious diseases characterized by the appearance of a hard belly, changes in diet and lifestyle will certainly relieve discomfort.
Often, doctors prescribe a whole range of drugs to reduce gas formation. It necessarily includes adsorbing agents - polysorb, activated carbon, smecta. Enzymatic drugs are also used - mezim, pancreatin, panzinorm. Sometimes drugs are prescribed that replace bile or stimulate its production - karsil, LIV 80, allohol.
Bloating can be caused by medications that suppress the production of bile, hydrochloric acid and gastric juice.
If the patient is prescribed such drugs, then it is necessary to adhere to a certain diet. In this regard, it is better to consult a doctor if he himself has not given instructions.
Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease, and not just at relieving uncomfortable symptoms. Therefore, it is imperative to find out why this violation appeared.
The action of adsorbents is aimed at collecting gases, but at the same time it is necessary to get rid of the factor that provokes their appearance.
If the cause is dysbacteriosis, you must first eliminate it. Symptomatic treatment, of course, is also suggested, but it will be ineffective if the normal intestinal microflora is not restored.
Did you like the article?
Share with your friends!
mjusli.ru
Photo gallery: Hard belly: causes and treatment
A hard belly can cause discomfort for anyone: men, women, and even children. There are many reasons for this phenomenon. Let's look at the problem of a hard belly in more detail.
Ectopic pregnancy
In women, a hard belly may be due to the presence of an ectopic pregnancy, which in the early stages has symptoms of the usual: drowsiness, nausea, delayed menstruation, breast tenderness. At week 4, cramping pain appears below the navel, painful urination and defecation, and spotting.
If you do not see a doctor in time, then over time the fallopian tube will rupture and internal bleeding will occur.
Excessive blood loss is characterized by a drop in blood pressure, weak pulse, pale skin and hardness of the anterior abdominal wall. An ectopic pregnancy poses a threat to a woman’s life, so at the slightest sign it is necessary to seek medical help.
Causes of a hard belly in healthy people
There are numerous reasons why hardness appears in the abdomen in healthy people:
| Name | Description |
| Acute surgical diseases | Peritonitis, appendicitis, perforation of gastric and intestinal ulcers. The same applies to ectopic pregnancy, strangulated hernia and intestinal obstruction. |
| Damage to the urinary system | The abdomen becomes hard and swollen during exacerbation of cholelithiasis or urolithiasis. When the excretory ducts are blocked, the anterior abdominal wall becomes tense. This also includes the passage of stones. |
| Inflammation and enlargement of parenchymal organs | Liver cirrhosis, pancreatitis, hepatitis, heart failure, the appearance of benign or malignant tumors, the development of malaria, and also hematological pathologies. |
| Worm infestation | Helminths in the intestinal or liver area negatively affect the digestive process. As a result of their development, food moves poorly in the organs of the digestive system, and the risk of intestinal blockage increases. |
| Damage, injuries | Mechanical impact on internal organs can cause the appearance of a hard belly. This happens when they rupture or severe bleeding occurs. |
| Gynecological disorders | The abdomen becomes hard with the development of an inflammatory process in the ovarian area. The same applies to the formation of tumors and hypertonicity of the uterus during pregnancy. |
| Disrupted functioning of the digestive system | With a lack of enzymes, the stomach becomes hard after eating. This happens as a result of lactose intolerance or celiac disease. Against the background of poor nutrition or long-term treatment with antibacterial agents, dysbiosis develops, which also contributes to disruption of the digestive organs. |
There are also numerous provoking factors that trigger the pathological mechanism:
- unhealthy diet (overeating, eating legumes, flour, sweet foods, white cabbage);
- constipation (feces accumulate in the intestines, increasing the volume of the abdomen and its density);
- stressful situations, emotional overstrain (a reflex muscle contraction occurs, so the stomach becomes hard);
- eating (during a meal a person swallows air, as during a conversation);
- varicose veins in the pelvic organs;
- the onset of labor in a pregnant woman (this is a natural process).
Physiological causes cause short-term bloating and hardness in the abdomen. After they are eliminated, the person’s condition stabilizes. If clinical signs worsen or appear, you should go to the hospital and undergo an examination to determine the source of the problem.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. In the chronic form of the disease, bloating occurs after every meal. This is due to insufficient secretion of digestive enzymes. Disruption of the digestive process leads to gas formation, rumbling in the stomach, nausea, frequent vomiting, and fever. Accompanying symptoms with pain localized in the left side of the abdomen and muscle hardness upon palpation suggests an acute attack of pancreatitis.
What else could happen if the stomach has become hard and hurts a lot?
Some diseases are so dangerous that ignoring medical attention can lead to death. Therefore, before treating cramps and severe abdominal pain with improvised means, immediate diagnosis is required. Acute conditions are caused by the following diseases:
1 Inflammation of the appendix. General symptoms can be neutralized by taking painkillers, which is extremely dangerous when making a diagnosis. If surgery to remove the inflamed tonsil is not performed in a timely manner, there is a high risk of rupture and spillage of toxic contents into the abdominal cavity. Peritonitis as a result of purulent appendicitis leads to sepsis and death of the patient.
2 Pancreatitis. Inflammation of the pancreas causes severe pain, spreading from the umbilical region throughout the peritoneum. Acute symptoms are accompanied by attacks of nausea and vomiting, which do not bring relief, the stomach becomes hard as a stone, and pain begins in the iliac region. Such patients are prone to diarrhea.
3 Crohn's disease. Destruction of the mucous membrane, turning into perforation and decomposition of the intestinal walls. The pathology is still little studied, although it is easily diagnosed. Pain haunts the patient constantly, after defecation and at rest.
4 Inflammation of the gallbladder. This disease occurs with high fever and pain in the lumbar region and heart.
5 Pinched diaphragmatic or inguinal hernia. An extremely dangerous disease with severe symptoms. The pain is localized at the location of the hernia. Without the help of a specialist, the condition will rapidly deteriorate.
6 Perforation of the walls of the stomach, duodenal bulb, liver, spleen. The release of blood, enzymes and lymph from organs into the abdominal cavity creates a high level of danger for the peritoneal space. A patient who is not provided with timely medical assistance may lose consciousness and even fall into a coma.
In many cases, ruptures of internal organs occur as a result of mechanical injuries. Pain may not occur immediately after the injury.
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. The disease is most often caused by cholelithiasis. At risk are people who are overweight and lead a sedentary lifestyle; genetically predisposed; those suffering from endocrine diseases and diseases of the cardiovascular system; leading an unhealthy lifestyle. The pathology is accompanied by acute cramping pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, bitter taste in the mouth, gas formation, bloating, yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes.
First aid
Pain accompanied by a hard stomach due to malfunctions of the digestive system can be eliminated by taking sorbents: activated carbon, Smecta, Polysorb, Enterosgel.
For painful sensations associated with PMS, antispasmodics are used: No-shpa, Papaverine, Dicetel.
In addition to medications, folk methods can also help relieve pain, for example, chamomile flower tea or rose hip decoction.
If the pathological process has an unclear etiology, it is better not to take risks with self-medication, but to undergo the necessary range of examinations to establish the cause of the disease.
Tumor
Intestinal tumors of various origins lead to destruction of the intestinal walls. At the initial stages, the pathological process is accompanied by mild episodic pain. Over time, the pain syndrome increases and is not suppressed by analgesics, accompanied by lack of appetite, weight loss, weakness, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, and defecation disorders. There may be blood, mucus and pus in the stool. In this case, the abdomen is hard and painful on palpation.
Treatment of any disease of the digestive system must begin with a review of the diet and diet. So, with increased gas formation, it is necessary to give up foods containing starch and fiber, carbonated drinks, fatty and heavy foods.
If you have a disease, the symptom of which is a hard stomach, you should contact a medical facility. Only a doctor can prescribe the necessary treatment. Self-medication and unsystematic use of medications can worsen the condition and lead to serious consequences.
Other causes of bloating
If a normally healthy patient is faced with the pathology of a tight abdomen, and there is not a single sign listed above, you should look for another reason why men have a hard abdomen. There are several of them:
- Severe stress and anxiety. Nervous breakdowns disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which can cause bloating. It is best to change your diet, lighten it and take a sedative.
- Appendicitis. Often the symptoms are vague and there is normal pain on the right side, no temperature. If the symptom does not go away within an adequate period of time, you should consult a doctor.
- Pancreatitis is another reason why the stomach is like a drum in men. The first symptom is pain in the navel area spreading to the abdominal area. Then vomiting begins, the stomach swells, and sometimes diarrhea appears.
- Acute cholecystitis is manifested by pain in the heart area, increased body temperature, and a man may sweat profusely.
- A strangulated hernia also leads to tightening of the abdominal muscles. Symptoms: sharp pain in the hernia area, spreading in breadth. If the hernia cannot be repaired, immediate assistance from a surgeon is required.
- A very tight abdomen is a symptom of a peptic ulcer of the stomach and/or duodenum. When perforation occurs, vomiting of blood begins, and the stool turns black. The patient may lose consciousness. Failure to treat will result in death.
- Due to injury to internal organs, a bloated abdomen may also appear.
Important! The pre-infarction state is accompanied by pain in the stomach and swelling of the abdominal muscles. You should remember this if you have heart problems. Self-medication is ineffective; emergency medical attention is needed.
A hard stomach in men occurs due to abscesses, abdominal ascites (dropsy), and disruption of the blood vessel located on the abdominal wall. There are many reasons, and in order to prevent the development of the disease, you should be attentive to the symptoms that appear.
Mechanical blockage of the intestine
This condition is characterized by pain (sometimes hardening is felt in some part of the intestine), stool retention, and the patient may not pass gas.
The pain can vary in intensity, the nature of the sensations and their localization can be clear, but not always. The cause of mechanical blockage is constipation (it is caused by various factors, from poor nutrition to pathologies in the development of the digestive organs), tumors, etc.
For an accurate diagnosis, you must consult a doctor. If the problem is caused by ordinary constipation, then performing a cleansing enema and further proper nutrition will help solve the problem.
If the matter is something else, then a medical examination will be needed.
Hard belly during pregnancy
It’s another matter if a woman’s lower abdomen becomes hard and swollen in the first weeks of pregnancy. This can be a signal of a dangerous pathology - uterine hypertonicity, which can lead to termination of pregnancy and loss of the child.
At later stages - around 25-27 weeks - a tense and hard abdomen often indicates the beginning of “training contractions” - this is how the body prepares to give birth. And in the last trimester - at 38-39 weeks, this part of the body may become tight and hard (and even hurt a little) due to the proximity of childbirth.
Pain on palpation
Palpation of the digestive organs is of great diagnostic value. The formation of a symptom is influenced by a number of factors and nuances (infection, structure of the reproductive system).
Features of pain on palpation
The process of palpation of the stomach and intestines is important in terms of diagnostic examination of the human body.
Monitoring of the digestive organs is carried out as follows: at the first stage, a qualified specialist carefully palpates the sigmoid colon - this is the most common landmark and the most accessible organ for palpation.
Next, the doctor proceeds to study the condition of the cecum and transverse colon. The ascending and descending sections of the suction organ are quite problematic to palpate.
In practice, during palpation, fingers must be carefully immersed on the surface of the body area and gently pressed onto the organ being examined (toward the posterior abdominal wall). Using sliding movements, you can clearly determine the contours, density, and the presence of various neoplasms and abnormalities.
When you touch (feel) the sigmoid colon, you get the impression that there is a smooth, dense and mobile cylinder in the human body. The size of such a “geometric figure” does not exceed the thickness of a person’s thumb.
The formation parameters are directly related to the condition of the walls, which are densely filled with gases and decay products (feces/feces).
During the inflammatory process of the infiltrating walls, a significant thickening of the membrane occurs. Ulcerative manifestations form a lumpy and uneven surface of the suction organ.
Acute inflammation of the sigmoid colon is accompanied by the formation of a dense consistency of painful manifestation. Due to the dense overflow of gases and liquid contents, motor inhibition occurs. The spasm is felt in the form of a cord and cord.
The patient experiences systematic rumbling + false urge to defecate (false diarrhea).
In normal condition, the cecum is easily palpable. A specialist can detect a cylinder up to 3 cm that is moderately active in movements. Its mobility in a pathological disorder is significantly increased.
The internal consistency becomes significantly thicker during coprostasis and chronic inflammation. The volume and shape of the cecum directly correlates with the contents. In a normal functional state, the intestines do not growl.
The patient should remember that the presence of pain upon palpation in the area of the cecum indicates the development of a pathological process. The digestive organ requires systematic and comprehensive treatment.
In practice, after examining the cecum (+ appendix), it is possible to examine the less accessible parts of the large intestine. Palpation is carried out from the ascending to the transverse colon and descending colon.
The transverse colon part of the suction organ can be qualitatively palpated only in the case of chronic inflammation. Tone, consistency, volume, shape depend on the tone and degree of muscle tension.
For example, an inflammatory process of the ulcerative type forms serious preconditions for the transformation of the transverse colon. At the same time, the muscles of the organ thicken significantly, and its configuration changes.
Today, chronic colitis and percolitis are quite common. With these ailments, the wall of the suction organ begins to painfully contract. Due to the lumpy surface, palpation is accompanied by sharp pain. For example, with pericolitis, respiratory and active mobility is lost.
Palpation of the abdomen allows you to feel an intestinal tumor, which is often confused with the pathology of various organs. Oncology of the cecum and transverse colon is distinguished by already known mobility. The pain is activated during the act of breathing (tumors below the navel are motionless). Palpation of the abdomen during enterocolitis is accompanied by rumbling in the navel area.
The disease has specific signs and symptoms: painful diarrhea (mushy, mucous stools, abdominal pain, hard colon). Palpation of the abdomen is carried out in combination with a digital examination of the rectum (sigmoidoscopy + radiography). These actions make it possible to predict the formation of rectal cancer and the formation of various syphilitic structures.
It will also be possible to clearly determine the presence of inflammatory processes, cracks, fistulas, hemorrhoids and all kinds of tumors. The specialist can get a clear vision of the sphincter tone and the level of filling of the colon ampulla. In some cases, it is rational to palpate adjacent organs (bottom of the bladder, prostate gland, uterus with appendages).
This will reveal an ovarian cyst, a tumor of the genital organs, the degree of constipation, etc.
Mechanism of the procedure
Palpation is the last stage of a full and objective examination of the abdominal area. The patient will need to cough vigorously before the procedure. In practice, a person with developed peritonitis manages to do this only superficially (holding his stomach with his hands).
It is allowed to make a small impact on the couch on which the patient is located in a supine position. The vibration impulse will provoke the manifestation of pain in the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, it is quite easy to establish the diagnosis of peritonitis without touching the hand.
To identify symptoms of peritoneal irritation, it is allowed to gently shake the patient after grasping the crests of the ileum (or jumping on one leg).
The palpation procedure begins with the patient being asked to clearly indicate the area where the first pain formed (the primary localization of the disease).
The specialist needs to closely monitor the actions of the patient himself. This is how you can identify the causes of peritoneal irritation.
Diffuse visceral pain in the abdomen is easily determined using circular movements of the palm. Your hands should be warm.
The procedure begins as far as possible from the main source of pain. This helps to avoid unplanned pain at the very beginning of the study. Children, and sometimes adult patients, sometimes prevent a quality examination due to pain.
First of all, the doctor must perform gentle and careful palpation (superficial). An experienced specialist moves gently, methodically and consistently. The fingers make a minimum number of movements.
It is strictly forbidden to palpate the abdomen randomly! The pressure on the body surface should not be high. Otherwise, protective tension in the abdominal muscles will occur.
Touching the sore spot must be done until the patient says that it really hurts.
A qualified specialist can always determine the degree of tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. The physician must distinguish between voluntary and involuntary muscle tension. To clearly determine this factor, during palpation a person takes a deep breath and exhales. If muscle activity persists, this indicates the development of peritonitis.
It is rational to carry out deeper palpation if peritonitis was not detected during a superficial examination. This makes it possible to detect various tumor formations, hepatosplenomegaly, and aortic aneurysm. It is very important for a physician to remember the optimal sizes for normal structures so as not to confuse them with malignant ones. Pain on palpation of the abdomen and intestines has two types:
- immediate local pain – the patient experiences sharp pain at the test site;
- indirect (referred pain) – pain sensations are formed in a different place when palpated. For example, during acute appendicitis, pain accumulates at McBurney's point on the left side of the iliac fossa. This symptom is called “Roving” and is a reliable sign of peritoneal irritation.
It is easy to carry out comparative palpation of a patient with tense abdominal muscles. For this, the patient, who is in a supine position, is asked to gently lift his head above the pillow.
The classic symptom of parietal peritoneal irritation is not difficult to identify.
To do this, at the time of the examination, the doctor must sharply remove his hand from the surface of the body and observe the patient’s reaction. In most cases, patients experience a significant increase in pain.
This classic examination technique is quite crude; some scientists classify it as a barbaric method of study.
With the development of various pathologies in the digestive organs (for example, acute appendicitis), hyperesthesia of the skin in the abdominal area is observed.
It is for this reason that if you pinch or lightly prick a patient, a painful reaction of the body will immediately occur.
This is a fairly common clinical symptom, but its establishment is not enough to firmly diagnose acute appendicitis and other diseases of the abdominal organs.
An integral part of the palpation examination is gentle tapping on the lumbar region (+ sides of the abdomen) to determine the degree of pain in these areas. Quite often, pyelonephritis and urolithiasis correlate with severe pain in the abdomen (costovertebral region).
In doubtful clinical situations, examination alone is not enough. An accurate assessment of the dynamics of the disease is established by repeated palpation of the abdomen by the same doctor.
Causes of pain in women
Today, medicine identifies two types of fundamental causes that affect pain when palpated. Organic factors include:
- inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system (cyst, endometritis, fibroids);
- using the IUD as a contraceptive;
- formation of various pathological formations;
- the presence of inflammation in the gall bladder (including appendicitis, pyelonephritis);
- sharp pain during pregnancy (placental abruption, miscarriage).
The functional reasons are as follows:
- systematic disruptions in cycles during menstruation;
- discharge of uterine bleeding;
- ovulation + uterine inflection.
Inflammatory processes are the main cause of pain during palpation of the stomach and intestines. The disease begins with classic acute manifestations and is supplemented by various signs of intoxication of the body, namely:
- Endometritis is accompanied by aching pain in the abdominal area. Their manifestation can be determined by light palpation. The patient experiences heaviness in the area of the appendages + hardening of the uterus;
- Endometriosis is a pathological disorder that affects the uterus and appendages. Severe pain is observed when palpating the middle of the abdomen;
- Ovarian apoplexy correlates with ovulation. In this case, some of the blood penetrates into the abdominal cavity due to strong physical exertion;
- Uterine fibroids. The pain syndrome is localized in the lower abdomen (compression of neighboring organs);
- Appendicitis requires surgical medical intervention. Pain on palpation in the area where the appendix is located;
- Cholecystitis is an inflammatory process of the gallbladder. The pain radiates clearly to the lumbar region and back;
- Cystitis is a lesion of the bladder. Pain is observed both during palpation and during urination.
Intestinal dyskinesia
Intestinal dyskinesia is a complex of intestinal disorders that arise due to impaired motor function of the intestine (mainly the colon).
That is, despite the fact that there are no organic changes in it, it cannot work normally.
According to the World Health Organization, intestinal dyskinesia affects almost a third of the world's population, most of them women.
The manifestations of this disease are extremely unpleasant. First of all, these are abdominal pains of a very different nature: from aching to cutting, lasting from several minutes to many hours. At the same time, it is very difficult to determine exactly where it hurts.
Various pains “in the whole abdomen” (pulling, sharp, boring, cutting, aching) most often disappear when falling asleep, gradually increasing upon awakening. For many, the pain intensifies when eating or after eating.
The pain may subside after bowel movements or the passage of gas, but may intensify with stress and emotional tension.
With intestinal dyskinesia, in addition to pain, bloating, rumbling, and stool disorders appear. And this is all against the backdrop of dislike for life, because being in such a state in public places is extremely unpleasant.
Sometimes bloating or loud rumbling may be the only symptom, regardless of what you ate. All sufferers of intestinal dyskinesia experience bowel dysfunction, most often constipation. Sometimes constipation is replaced by short-term diarrhea.
(Constipation can be considered the absence of stool for 2 days. Diarrhea is very loose stool 3 or more times a day). Often, mucus is released with the stool, which is either mixed with feces or located on its surface in the form of films.
However, stool disorder is not necessary, just like pain during diarrhea (“nervous diarrhea”), there are also painless dyskinetic constipation. But even with frequent diarrhea, those suffering from intestinal dyskinesia do not lose weight; rather, they even gain weight. Very often they have mental disorders.
They are distinguished by increased anxiety, nervousness, or, on the contrary, depression. Complaints of pain in the heart, joints, and back are possible, although these organs turn out to be healthy when examined.
With spastic (hypermotor) intestinal dyskinesia, its tone and spastic contractions increase, which leads to constipation and paroxysmal colic-like abdominal pain.
With atonic (hypomotor) dyskinesia, its tone and peristalsis are sharply weakened, which leads to constipation, dull bursting pain in the abdomen, and sometimes intestinal obstruction. With constipation, a buildup of dense stool forms in the rectum.
If products are not removed from the colon in a timely manner, dizziness, nausea, weakness appear, mood deteriorates and performance decreases. Due to the long stay in the intestines, food undergoes putrefactive decomposition, which can lead to allergies.
Chronic constipation can cause hemorrhoids, anal fissures or rectal polyps.
Description
Intestinal dyskinesias are primary, when intestinal motor disorders are an independent disease, and secondary - symptomatic, occurring in other diseases, primarily the gastrointestinal tract. True, it can be very difficult even for a specialist to distinguish them.
It is believed that the most common causes of primary dyskinesia are psychogenic factors, but its occurrence often depends on the excessive consumption of foods low in dietary fiber. There are many causes of secondary dyskinesia, especially if they manifest themselves as constipation.
These can be diseases of the digestive system (liver diseases, chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, chronic pancreatitis and cholecystitis), as well as diseases of the endocrine system - pituitary disorders, myxedema, diabetes mellitus, hyperparathyroidism.
The development of constipation may well be facilitated by uncontrolled use of drugs that affect colon motility: anesthetics, antibiotics, sulfonamides, muscle relaxants, anticonvulsants, anticholinergics, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, opiates, diuretics, psychotropic drugs.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made only by excluding other diseases with similar symptoms by examining stool for occult blood, dysbacteriosis, scatological examination, irrigoscopy and endoscopy are prescribed. A colon biopsy is required.
Diagnosis of the causes of secondary dyskinesia is based, first of all, on the study of the medical history and general clinical examination of the patient.
Treatment
Treatment for dyskinesia depends on its type. For hypermotor dyskinesia, antispasmodics of various groups, metoclopramide, are prescribed; the use of laxatives is completely contraindicated.
For hypomotor dyskinesia, drugs that enhance intestinal motility are indicated, as well as metoclopramide, choleretic drugs and enzyme agents, potassium chloride in combination with vitamin B1...
If there is no effect from therapy with the above remedies, laxatives of plant origin are prescribed: senna leaf, buckthorn bark, zoster, rhubarb.
Moreover, they should be used no more than twice a week, alternating.
But still, many experts believe that drug treatment of intestinal dyskinesias should be used as a last resort.
For example, you can get rid of intestinal atony with the help of decoctions of dry herbs (Alexandrian leaf, buckthorn, rhubarb, lingonberries), products that have a laxative effect (yogurt, kefir, melon, cucumbers (and fresh, salted), lingonberries (soaked, fresh and canned ), rhubarb in any form, prunes (dried and decoction), plums, apricots, peaches, raw or boiled water (1 glass on an empty stomach). Recommended vinaigrettes, salads, meat boiled and stewed in its own juice, fish, millet porridge, pumpkin, zucchini, squash. You cannot eat foods and berries that have a strengthening effect: bird cherry, sloe, barberry, blueberries (raw and dried), pears, smoked sausages, hard-boiled eggs. Mineral waters are taken on the recommendation of a doctor.
Lifestyle
You can get rid of intestinal dyskinesia with proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle, including getting rid of stress, playing sports, and timely treatment of various diseases. It is important to learn to empty your bowels at the same time.
In all cases, a physiologically complete diet should be prescribed, providing the body with essential vitamins, microelements and minerals, and including mechanical and chemical stimulants of intestinal motor function. It is necessary to exclude foods that cause increased fermentation and rotting processes in the intestines (apples and cabbage, including sauerkraut).
Food should be boiled or steamed, not chopped. As motility stimulants, those varieties of berries, fruits and vegetables are used that enhance the evacuation function of the intestines without causing fermentation processes and irritation of the intestinal mucosa (beets, carrots).
At the same time, the diet depends on the type of dyskinesia, since it must correspond to certain intestinal motility. For example, with hypomotor dyskinesia of the colon, the main principle is to add foods rich in plant fiber to the diet.
Among them: beets, carrots, zucchini, pumpkin, cauliflower in raw, boiled, baked form, as well as tomatoes and lettuce. White cabbage, mushrooms and vegetables such as turnips, radishes, onions, garlic, and radishes are excluded, since they contain a lot of essential oils.
Bread made from coarse rye and wheat flour with the addition of bran, porridge with water from wheat, buckwheat, pearl barley, and oatmeal are healthy.
We recommend soups with low-fat meat and fish broth, vegetable broth, boiled, steamed, and baked lean meat and fish. If protein foods are well tolerated, you can eat soft-boiled eggs (with liquid yolk) or in the form of steam omelets, but no more than 2 pieces per day.
Figs, dates, prunes, dried apricots, bananas, apples are shown - the organic acids and sugars they contain stimulate intestinal motility.
During diet therapy, lactic acid products are needed: fresh (2-3-day) kefir, yogurt, acidophilus, as well as drinks with the addition of a live culture of bifidobacteria. For any disease of the gastrointestinal tract, the body must receive a sufficient amount of vitamins, microelements and mineral salts.
Therefore, it is recommended to drink half a glass of natural vegetable, berry and fruit juices several times a day, as well as warm rose hip decoction without sugar.
Nutrition for constipation
Cold food is necessary for bowel movements. It is recommended to add wheat bran to food, which should be doused with boiling water (in the first two weeks, 1 tsp 3 times a day, then 1-2 tbsp 3 times a day, followed by reducing the dose to 1.5 tsp.
l. 3 times a day). They should be taken for at least 6 weeks. For hypomotor dyskinesias, it is useful to take vegetable and animal oils (sunflower, corn, olive, butter, etc.) - add to food or take 1 tsp on an empty stomach.
Not recommended: bread made from premium flour, butter dough, fatty meats, smoked meats, canned food, spicy foods, chocolate, strong coffee, tea, rice and semolina porridge, noodles, potatoes, foods that cause increased gas formation (legumes, cabbage, sorrel , spinach, apple and grape juices).
For hypermotor dyskinesia of the colon, as well as for proctogenic coprostasis (accumulation and retention of solid feces in the intestine), the fundamental difference is the prescription of a slag-free diet.
This is an easily digestible, refined food containing a minimum of indigestible substances: soups with low-fat meat broth, vegetable broths, various dishes from lean beef, veal, boiled chicken, in the form of cutlets, meatballs, soufflé; dishes from cod, pike perch, perch, pike; foods rich in calcium (low-fat cottage cheese, cheeses), compotes, jelly and juices containing tannins (blueberries, bird cherry, pomegranate, black currant, dogwood and pear).
This diet must include vegetable fats.
© Dr. Peter
Source: https://doctorpiter.ru/diseases/49/