The incidence of duodenal diseases is high - more than 10% of all inhabitants of the planet suffer from ulcerative lesions alone.
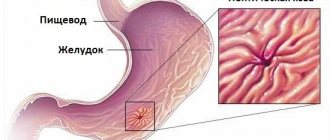
Important digestive processes occur in this section: alkalization of the acidic food bolus coming from the stomach, the entry of bile and pancreatic enzymes into it, and the humoral regulation of the acidity of gastric juice. Anatomists distinguish 7 types of shape and position of this section. The complexity and accuracy of the ongoing processes determines the quality of digestion, and the likelihood of various failures is high.
Symptoms of diseases
Characteristic signs that are of concern during an acute disease or exacerbation of a chronic process:
- night pain in the epigastric region (slightly below the stomach);
- hunger pains - occur after a long break in eating, relieved even by a piece of bread;
- pain that occurs 2-3 hours after eating - from irritation of the intestines with food coming from the stomach;
- permanent white coating on the tongue;
- decreased appetite, partly due to fear of pain;
- frequent nausea;
- constant heartburn;
- frequent constipation;
- admixture of blood in vomit and feces - with ulcerative lesions.
In the case of the chronic form of the disease, persistent digestive disorders are added, leading to loss of body weight, pale and dry skin, weakness, constant fatigue, changes in blood count, and decreased performance.
Diseases of the duodenum affect people of working age, but rarely cause disability. The main provoking factor is considered to be hereditary predisposition, since almost everyone has errors in nutrition, but diseases do not.
Symptomatic manifestation of peptic ulcer
Only people who are truly attentive and scrupulous about their own health can determine the development of a peptic ulcer in the initial stages. As a rule, the development of the disease occurs almost asymptomatically, however, as it gains strength, the disease makes itself felt. The degree of danger a person with a gastrointestinal ulcer is in should not be underestimated; it can turn from a bothersome problem into a fatal pathology.
Note! According to statistics, almost a third of sick patients show no symptoms at all, and the presence of the disease is often determined after death.
However, this is still rare, usually the symptoms are as follows.
1. There is constant pain in the upper part of the peritoneum. They especially bother hungry patients with their severity, and calm down a little after eating. In addition, the following can also increase pain:
- physical exercise;
- stress;
- alcohol consumption.
The nature of the pain can be either dull or acute, in the first case it is more likely paroxysmal, that is, the patient is constantly unpleasant, however, as soon as he gets hungry, for example, it becomes really painful. In the second case, the person constantly feels acute pain.
2. With a stomach or duodenal ulcer, problems associated with stool constantly occur. Thus, the following may equally arise:
- constipation;
- diarrhea.
At the same time, you will not necessarily experience only one specific type of these dyspeptic disorders; it often happens that loose stools are replaced by prolonged constipation, and vice versa.
3. In addition to diarrhea or constipation, attention should also be paid to nausea, which in most cases leads to vomiting. However, in turn, these urges are not always crowned with the release of vomit. The fact is that with a peptic ulcer, reflux occurs - acidic gastric juice enters the esophagus. This is a characteristic symptom that provokes constant heartburn, which torments patients most often after eating.
4. Changes in appetite may occur, which, however, are more associated not with the physical effects of the disease, but with the mental ones. Not wanting to feel nausea again, or suffer from dyspeptic disorders, patients often unnecessarily abstain from food. They are overcome by fear associated with the recurrence of pain.
5. If you allowed yourself to deviate from a strict diet during a peptic ulcer, or, not yet knowing about its presence, ate any undesirable product, you will most likely receive the most unpleasant effects among all possible names:
- burping;
- flatulence.
Unfortunately, the use of antifoaming agents and other drugs characteristic of this situation may bring temporary relief or not give any result at all until the main cause of the disease is eliminated.
6. There is often a feeling of pressure or heaviness in the epigastric area, most often after eating food. At the same time, a person will feel quickly full from a small amount of food.
Diseases of the duodenum
Duodenitis
Main article: Duodenitis: symptoms and treatment
This is a simple inflammation that can develop on its own (primary) and complicate the course of other diseases of the digestive canal (secondary). Duodenitis is often secondary to diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas. In this case, a constant spasm of the sphincter of Oddi develops, which regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice. At the same time, the intestinal walls thicken, and in advanced stages it can lead to mucosal atrophy.
Signs:
- constant dull pain, “whining” in the epigastric region;
- emetic syndrome or nausea interspersed with vomiting;
- heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- weakness due to decreased appetite.
Be sure to read:
Causes of seething and rumbling along the intestines, methods of elimination
Erosion
Main article: Duodenal erosion
This is a defect in the internal mucous membrane that does not reach the muscle layer. Erosion differs from an ulcer in that it heals without forming a scar.
The danger of erosion is the possibility of bleeding if a vessel passing into the mucous membrane is affected. The cause may be not only prolonged and deep inflammation, but also active hepatitis or cirrhosis, chronic heart rhythm disturbances, in which all circulatory parameters change, as well as kidney diseases that disrupt all types of metabolism. Erosion is a common consequence of stress and uncontrolled use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Symptoms of erosion that occurs without bleeding are practically no different from those with duodenitis.
Bulbit
Bulbit is a lesion of the duodenal bulb, which can be catarrhal (superficial, simple) or erosive.
The symptoms of bulbitis are complex, ranging from acute manifestations to subtle and erased ones. A person may be concerned about:
- acute pain in the epigastric region with severe nausea and repeated vomiting of bile;
- slight nagging discomfort in the same area;
- subsiding and increasing bitterness in the mouth.
Manifestations of bulbitis often develop following the use of medications or mild food poisoning. In the erosive form, accompanied by bleeding, anemia or anemia may occur.
Duodenostasis
This is a violation of the motor-evacuation function of the duodenum, which has another name - dyskinesia. For an unknown reason, normal peristalsis or pushing through of the bolus of food is disrupted. Young women are more likely to get sick. Food stagnates in the intestine, causing it to expand, and neighboring organs - the stomach, small intestine, liver and pancreas - suffer. Symptoms:
- dyspepsia or a combination of spastic pain with nausea, belching, vomiting, often bile;
- intoxication in the form of irritability, fatigue, headache, weakness.
Diagnosis presents certain difficulties; a thorough examination is required.
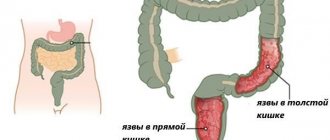
Peptic ulcer
Main article: Duodenal ulcer
Ulcerative lesions are one of the most commonly diagnosed. Ulcers develop either after inflammation or immediately. The process continues continuously, and if it is not stopped, the entire muscle layer is damaged. As the ulcer deepens, it can lead to perforation or breakthrough of the intestine with the release of its contents into the abdominal cavity.
Peptic ulcer disease has a predominantly chronic course with seasonal exacerbations occurring in spring and autumn.
Manifestations:
- rhythmic severe pain that occurs 2-3 hours after eating, which then spontaneously subsides;
- hunger pains that go away immediately after eating;
- severe and frequent heartburn;
- belching sour taste;
- periodic nausea and vomiting;
- constipation;
- intoxication due to the inability to have bowel movements;
- weight loss due to decreased appetite.
Be sure to read:
Ileum: location, structure and functions
Other diseases
Other diseases of the duodenum are rare, among them:
- developmental anomalies - stenosis (narrowing) and diverticulum (open muscle pocket, protrusion);
- obstruction caused by the movement of gallstones into the intestinal lumen;
- cancer found more often in older people;
- parasitic infestation by nematodes entering the body with dirty hands or poorly prepared food.
Treatment regimens
To understand which drugs are appropriate in each specific case, it is necessary to determine the set of goals that doctors want to achieve through the use of each specific name.
1. When treating peptic ulcers, it is imperative to reduce the level of stomach acid in order to prevent further growth of ulcers.
2. To stop the patient from experiencing acute pain, it is necessary to use painkillers.
3. Another goal is to relieve and eliminate inflammation that develops inside the stomach or duodenum.
4. If the Helicobacter pylori bacterium is present, it is also necessary to take care of its removal from the gastrointestinal tract, otherwise all other treatment will be in vain, since this harmful microorganism will continue to resolve the mucous membrane.
Therapy in adults with Helicobacter pylori
1. First of all, antibiotics are prescribed:
- penicillin series - for example, Amoxicillin, used for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori;
- tetracycline series - “Tetracycline” tablets;
- macrolides - for example, Clarithromycin.
2. In addition to therapy aimed at destroying bacteria, the patient must also take medications that reduce the activity of the production of gastric juice, which corrodes the mucous membranes. They belong to the so-called antisecretory group.
These include:
- proton pump blockers;
- substances that inhibit histamine receptors;
- anticholinergics.
All of these groups of drugs help not only reduce the amount of hydrochloric acid secreted by the stomach, but also reduce the degree of its aggressiveness.
Specific representatives of the drugs sought may be as follows:
- "Nexium", sold in the form of ampoules, tablets, and powder in bags;
- "Ranitidine" - sold in the form of tablets;
- "Gastrotsepin" - also sold in pharmacies in the form of tablets.
Note! The dosage of each drug should be calculated exclusively by physicians; they are not intended for independent use. In addition, the sought-after names may be accompanied by various side effects that are impossible to foresee without medical education, and attempts to treat them with other medications may end in failure.
3. The third group of drugs necessary to combat ulcers is bismuth-containing. This substance, bismuth, is famous for its drying properties. Reaching the ulcer, it creates a protective sheath on its surface, promoting tissue healing. Typical representatives of these drugs:
- "De-Nol";
- "Pilocid";
- other drugs with similar properties.
4. Since we are talking about a disease of the system that digests food, it is necessary during treatment to stimulate its work, improving peristalsis, as well as preventing various dyspeptic disorders, nausea and vomiting. For this they take:
- "Motilium";
- "Neobutin" and similar medications.
5. Gastric acid neutralizers also need to be taken while fighting peptic ulcers. These include medications such as:
- "Phosphalugel";
- "Gastratsid" and similar drugs.
The required drugs are indicated to combat heartburn, also eliminate dyspeptic symptoms, and, among other things, adsorb toxins and remove them from the body.
The treatment period for an ulcer is a minimum of two weeks, but the maximum amount of time spent on eliminating the consequences and suppressing the disease is two months. This line, however, may vary depending on the correctness of the chosen course of treatment, as well as on the individual tolerance of certain drugs.
Therapy for adults with peptic ulcers that appear against the background of increased acidity
If the disease did not develop due to the colonization of harmful bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract, but the increased acidity of the internal environment contributed to the appearance of ulcers, a course of treatment consisting of three components is prescribed:
- antibacterial drugs of the penicillin or tetracycline series;
- antiprotozoal antibacterial agents;
- proton pump blockers or drugs containing bismuth.
To normalize the patient’s emotional background, doctors can also supplement the required list with sedative drugs that eliminate problems with mood, sleep and other consequences of stress. In especially severe cases, antidepressants are prescribed.
Also, to eliminate spasms, various antispasmodics are prescribed; in the presence of constipation, probiotics are prescribed.
If the course of the disease is accompanied by constipation, the doctor may also prescribe to the patient:
- laxative suppositories for rectal use;
- enema;
- additional oral laxatives.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
In addition to taking pills and various medications in other forms, physical therapy is also necessary for a complete recovery. This is necessary during an exacerbation, since medications alone may not be enough.
1. Most often, the attending physician prescribes warming compresses based on alcohol. These “poultices” are prepared directly by medical personnel. Applying bandages moistened with alcohol increases blood circulation in the place where they were applied, which helps not only to improve many processes occurring in the body, but also helps relieve pain that is tiring for the patient.
2. Another effective physiotherapeutic method is treatment with current impulses. Their use has the following purposes:
- anesthetize;
- relieve the inflammatory process.
Among other things, current treatment helps improve cellular nutrition, and therefore provoke more efficient functioning of the body’s tissues. As a result, the patient begins to feel better, in particular, the problems associated with one of the dyspeptic manifestations - constipation - are eliminated.
3. Another procedure performed using current pulses is electrophoresis. With its help, a drug is introduced into the body through the patient’s skin, as well as his mucous membranes; in the case of a peptic ulcer, it is an anesthetic. At the same time, local stimulation of blood circulation and cell life support occurs.
4. To reduce the secretory function of the stomach, ultrasound treatment is also often used.
Diet
As we mentioned above, the occurrence of gastric or duodenal ulcers can be caused by poor diet. Of course, when you are already sick, and even if an unbalanced diet was not the reason for this, consuming food in unreasonable quantities and of dubious quality is contraindicated.
The specific diet will be prescribed by the attending physician or nutritionist working in the hospital, however, the following requirements will apply to each product that is part of the diet:
- gentle effect on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract;
- saturation with necessary (and in addition) microelements and vitamins.
In addition, going on a diet usually means eliminating:
- drinks containing alcohol;
- sweet sodas;
- flour foods, especially yeast foods;
- fried food;
- smoked meats;
- canned food and preserves;
- coffee;
- strong tea.
You can and should use:
- porridge from crushed cereals;
- dairy products;
- honey;
- soups;
- jelly;
- compotes.
The meal regimen should be as follows:
- food is consumed frequently;
- Portions are small.
Compliance with the above requirements allows you not only to get rid of the pain of a peptic ulcer, but also to stop the process of its development.
Surgical intervention
Surgery for peptic ulcer disease is performed in cases where a complication occurs. This approach is considered radical, therefore, it is used even when there is no hope that conservative treatment, which involves the use of medications and physical therapy, will bear fruit.
The complication develops, as a rule, in particularly advanced cases, for example, when the patient suffered for a long time and as a result the disease progressed rapidly.
Symptoms of complications are as follows:
- vomiting with blood;
- with constipation, bleeding from the anus;
- During the act of defecation, there is an admixture of blood in the stool.
Why does blood accompany the complication? Because the term complication itself in this case means the occurrence of bleeding from ulcers.
This process is also accompanied by the formation of scars, that is, connective tissue, the pylorus narrows, and food absorbed by a sick person has difficulty moving through the intestines. Ultimately, this can lead to a fatal consequence, the so-called penetration - intestinal rupture. The rupture is accompanied by serious pain that the person cannot withstand and requires immediate medical assistance.
Unfortunately, in this case it is impossible to do without surgical intervention. The operation involves removing the affected part of the intestine. After its completion, during the rehabilitation process, the previously mentioned drugs continue to be taken, however, now their dosages are adjusted taking into account post-operative complications that have arisen.
Of course, it is better not to proceed to the removal of part of the intestine, despite the fact that modern medicine allows patients who have undergone such an operation to live a full life, the likelihood of repeated complications increases several times.
Treatment of peptic ulcer in children
Unfortunately, not only adults, but also children can acquire this difficult disease; it is diagnosed even in children aged 4-5 years. The causes of the pathological process are the same as in adults, the treatment is correspondingly similar, however, the emphasis is on the most gentle drugs, in addition, if possible, drugs whose side effect is deformation of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract are completely excluded.
In the case of illness in children and adolescents, serious emphasis is placed on psychotherapy. Adults can continue to control themselves through fear and nervousness; in addition, their more stable psyche recovers more easily, especially in cases where they are prescribed sedatives or antidepressants. For the child and adolescent nervous system, taking the required medications is undesirable, as it can have a negative effect.
That is why, in order to stabilize the psyche of children, it is necessary to conduct individual psychotherapy, otherwise the patient’s condition may seriously worsen.
Diet therapy for children usually consists of the following:
- food is cooked using steam or water, without adding any spices;
- a minimum of salt is consumed;
- For especially young children, food is ground, each of its components is served in this form, however, sometimes it is given in its original form.
Diagnostics
A gastroenterologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the duodenum . In rural areas, primary (rather approximate) diagnosis can be carried out by a general practitioner or family doctor, but with a mandatory, at least one-time, consultation with a gastroenterologist.
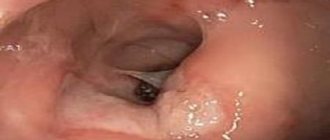
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy
FGDS or gastroscopy is the most informative method in which the internal surface is examined using an endoscope inserted through the mouth. The fibrogastroscope is equipped with a video camera that allows you to take pictures, a biopsy instrument and a probe through which you can inject medicine directly into the lesion. The device also allows you to apply hemostatic clips.
The procedure is unpleasant, but harmless, and in many cases allows one to avoid surgery.
Biopsy
Main article: Intestinal biopsy
Excision of a tiny piece of living tissue for further histological examination. The cellular composition, tissue fluid, and pathological formations are examined. Allows you to reliably distinguish between acute inflammation and chronic inflammation, a benign tumor from a malignant one, and a developmental anomaly from a scar.
Analysis for Helicobacter
Main article: Methods for diagnosing Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter is considered the main etiological factor of peptic ulcers and gastric cancer. This is the only bacterium that can live in the hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach. The test is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or ELISA for antibodies to Helicobacter; venous blood sampling is required.
Some laboratories examine stool or exhaled breath.
General blood analysis
The severity of inflammation, the presence of anemia and other general clinical indicators reflecting the general level of health are determined.
Occult blood test
Main article: Fecal occult blood test: preparation and implementation
The stool is examined, in which altered red blood cells can be detected. Allows you to detect hidden bleeding from the digestive canal. The pharmacy has express tests for detecting occult blood in the stool on your own.
Ultrasound
Sonography of the duodenum reveals thickening of the intestinal walls or an ulcerative defect found in the form of a crater. The boundaries of inflammation and the place of transition into healthy tissue, as well as tumors, if any, are clearly visible.
MRI and CT
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography detect lipomas (tumors from adipose tissue) and leiomyomas (from muscle tissue). These tumors are benign. Duodenal cancer or adenocarcinoma is a rare case, but they are also visible in these studies.
Be sure to read:
Function of absorption of substances in the intestines
Drug treatment of duodenal ulcers
Peptic ulcer of the duodenum is currently treated with the following groups of drugs.
Medicines that reduce the production of gastric juice
The leading positions in this group are held by proton pump blockers, which slow down the secretion of hydrochloric acid:
- Products based on omeprazole - omez, gastrozole, bioprazole, demeprazole, lomac, zerocid, krismel, zolser, omegast, losek, omezol, omitox, omepar, zhelkizol, pepticum, omipix, promez, pepticum, ricek, orthanol, romsec, sopral, ultop , chelicide, cisagast, chelol.
- Medicines based on pantoprazole - controloc, sanpraz, nolpaza, peptazole.
- Lansoprazole preparations - helicol, lanzap, lansofed, lanzotope, epicure, lancid.
- Based on rabeprazole - zulbex, zolispan, pariet, ontime, hairabezol, rabeloc.
- Esomeprazole - Nexium.
H2-histamine receptor blockers have practically ceased to be used to treat peptic ulcers, as they cause withdrawal syndrome (with abrupt cessation of use, the symptoms of the disease return).
- These are ranitidine (Gistac, Rannisan), famotidine (quamatel, ulfamid, gastrsidine), cimetidine (Belomet).
Selective blockers of M-cholinergic receptors (gastrocepin, pirencipin) reduce the production of pepsin and hydrochloric acid. Used as auxiliary medications for severe pain. May cause palpitations and dry mouth.
Agents that increase the protective properties of the mucous membrane
- Sucralfate (Venter) forms a protective coating at the bottom of the ulcer.
- Sodium carbenoxolone (Ventroxol, Biogastron, Kaved-s) accelerates the restoration of the epithelium of the mucous membrane.
- Colloidal bismuth subcitrate (de-nol) forms a film on the ulcer.
- Synthetic prostaglandins (enprostil) stimulate mucus production and cell restoration.
- Vinilin - or Shostakovsky's balm. An excellent tool. It has regenerating and wound healing properties. anti-inflammatory, antibacterial properties. Take orally, at night, 5 hours after dinner, a teaspoon (hereinafter a dessert spoon) for 10-16 days. Contraindicated for kidney and gallbladder diseases.
Other drugs
- Medicines that calm the central nervous system. Tranquilizers (seduxen, elenium, tazepam), antidepressants (amitriptyline), sedatives (tenoten, valerian preparations, see sedatives).
- Blockers of central dopamine receptors (metoclopramide, raglan, cerucal) normalize intestinal motor activity.
The course of treatment for ulcers can take from two to six weeks, depending on the size of the defect and the general condition of the body.
It should be noted that a competent doctor who can monitor the treatment process and evaluate its results should prescribe treatment for duodenal ulcers, select medications and dosage regimens.
Treatment
Depends on the type of disease, severity, presence of complications, concomitant diseases and age of the patient.
Surgery
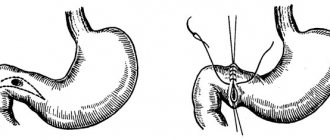
Immediate surgery is required in case of ulcer rupture and bleeding that cannot be stopped by other means. The scope of surgical intervention includes excision of the ulcer followed by suturing the wound, maintaining intestinal patency.
Surgery is also necessary for cicatricial stenosis (narrowing), if food cannot pass on its own. The site of stenosis is excised, and the intestine is sutured end to end.
Drug treatment
Prescribed individually using the following groups of drugs:
- antacids (acid reducers);
- antibiotics;
- agents that inhibit Helicobacter;
- painkillers;
- antiemetics;
- Digestive aids.
Diet food
An integral part of treatment, without which recovery is impossible. Therapeutic nutrition consists of pureed boiled dishes containing a lot of mucus - rice water, jelly, steamed meat. The diet creates conditions for the healing of erosions and ulcers and the cessation of inflammation.
Folk remedies
Herbal medicine for diseases of the stomach and duodenum should support the directions of basic drug treatment. Healers recommend:
- decoction of oats, flaxseed;
- Drink warm chamomile tea daily;
- infuse a collection of marshmallow and licorice roots;
- alcohol or water tincture of propolis;
- oak bark decoction.
Sanatorium-resort treatment consolidates the results of therapy and restores the functions of the duodenum. The health resorts of Essentuki and Kislovodsk are suitable for this purpose. Natural mineral water and mud in the form of applications contain a natural complex of healing substances.
Diseases of the upper intestine rarely occur in isolation and are more often accompanied by other lesions of the digestive organs. Timely detection allows you to prevent serious consequences.
Prevention
It can be primary and secondary. Primary – measures aimed at not getting sick, secondary – preventing exacerbations in those who are already sick.
If there is a hereditary predisposition, you need to pay special attention to nutrition. Food needs to be fresh, boiled, baked or steamed. No fast food or other food of suspicious quality, snacks or other foods full of flavor enhancers and preservatives. If possible, it is advisable to avoid stress.
Secondary prevention is timely and high-quality treatment of seasonal exacerbations, preferably in a hospital. It is advisable to use a temporary disability certificate to give the body the opportunity to cope with an exacerbation. During calm times, sanatorium treatment, especially alkaline mineral waters, is useful.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Rectal fissure: causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
- Rectal cancer: symptoms, stages, treatment and prognosis for life
- Duodenal ulcer: how is the pathology manifested and treated?
- Causes of bloating and increased gas formation, treatment methods
- More about hemorrhoids: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
- Causes of abdominal pain: pathological and non-pathological cases
- Details about bowel cancer: stages, symptoms, treatment and prognosis
- Duodenal erosion: symptoms, treatment and prognosis for life
- Duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum): symptoms and treatment methods
- Intestinal diseases: symptoms of pathologies, diagnosis and treatment
Location of duodenal pain
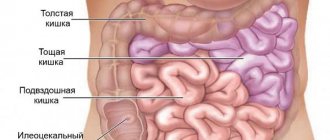
Duodenal pain refers to any pain coming from the duodenum. This is the first part of the small intestine, which begins where the stomach ends and continues approximately 25 to 38 centimeters (about 10 to 15 inches) to the jejunum, which is the second part of the small intestine. The C-shaped duodenum is located approximately in the epigastrium (upper middle part of the abdomen). However, there are many other organs that are in or near this area, and other symptoms are needed to identify duodenal pain. Refer to the location of the duodenum for more details.
The duodenum is the gateway to the intestines that communicates with several parts of the digestive system
The duodenum is the gateway to the intestines and communicates with several parts of the digestive system. It is clear that he is predisposed to diseases that may be associated with the surrounding areas and neighboring organs such as the stomach, pancreas, gallbladder and common bile duct. But the duodenum is not just a point of communication. It also plays an important role in digestion and nutrient absorption. Therefore, diseases of the duodenum can not only cause pain, but also manifest themselves in a number of digestive symptoms.
Alternative treatment for duodenal ulcers
Complete or partial distrust of traditional medicine most likely does not bode well for an ulcer sufferer. There are drugs for the treatment of ulcers, the effect of which has been proven in serious random studies in humans. Also, the effect of drugs is checked by everyday medical practice. Schemes are being refined and side effects of drugs are being identified. At the same time, no one canceled the alternative possibility of being treated with folk remedies.
Freshly squeezed potato juice is considered one of the most effective traditional medicine for stomach and duodenal ulcers. It tastes rather unpleasant, but you can get used to it quite easily. It is better to use the Morning Rose or American varieties, but any unspoiled potato tuber will do. Preparing juice is quite labor-intensive, given that you only need to drink it fresh and 3 times a day, but you can get the hang of it if you want. The raw potato tuber is peeled, grated and squeezed through several layers of gauze. The juice should be drunk immediately, otherwise it turns black and loses its medicinal properties. The first 3 days only take a tablespoon before meals 30 minutes, preferably 3 times a day, then 3 days 2 tablespoons, gradually increasing to half a glass per dose and so on for 21-28 days. This requires adherence to a diet. After 2-3 weeks the course can be repeated. This really helps!
You can resort to traditional medicine, use treatment with sea buckthorn or olive oil (1 dessert spoon on an empty stomach for 3 months), honey, propolis, herbs (calendula, plantain, St. John's wort), after going on a duodenum-friendly diet and taking twice a day 20 mg omeprazole daily.
Author:
Postnova Maria Borisovna general practitioner