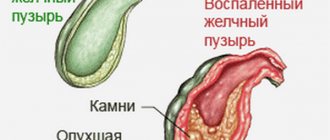
Chronic cholecystitis is an inflammatory process in the gallbladder, accompanied by nagging pain in the hypochondrium after drinking alcohol or fatty foods. With such inflammation, the full functioning of the organ is disrupted; stones are formed in it, preventing the outflow of bile.
The gallbladder is a small hollow sac, 5-9 cm long, with a volume of up to 40 ml, located to the right of the gastrointestinal tract. It is a temporary storage facility for bile produced by the liver. If necessary, a small amount of bile enters the intestines, breaking down fats and speeding up the digestion process.
The gallbladder, despite its size, performs a number of important functions. It promotes the accumulation and concentration of bile, and when food enters the intestines, it releases the necessary amount of bile secretion for digestion.
In addition, bile contains a huge amount of unique active substances that restore intestinal microflora and improve liver function.
What is chronic cholecystitis
Chronic cholecystitis is a long-term inflammatory process in the gallbladder, periodically followed by attacks of exacerbation. Often, the disease is accompanied by enterocolitis and pancreatitis.
When bile stagnates, hard formations (stones) form in the gallbladder. This kind of cholecystitis is called calculous, and if inflammation occurs without the formation of stones, then it is called acalculous.
Acalculous cholecystitis develops as a result of infection in the gallbladder, which leads to inflammation and gradual destruction of the organ. Associated factors are a weak immune system, impaired liver function, degeneration of the mucous membrane and inflammation of the duodenum.
Calculous cholecystitis is much less common, and the formation of stones is facilitated by thickening and changes in the composition of bile against the background of severe inflammation.
At the same time, cholesterol accumulates in sediment and is not excreted from the body, forming small hard stones. The reason for this may be poor nutrition, abuse of fatty foods, excess weight, as well as the presence of infectious diseases and diabetes.
Signs and causes of the disease
Sometimes, chronic cholecystitis appears as a result of the acute course of the disease, but more often, it develops as an independent pathology. The main cause of the chronic form of the disease is considered to be infection.
Possible sources of infection:
| Inflammation of the genitourinary organs | Cystitis, adnexitis or prostatitis, pyelonephritis. |
| Inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract | Dysbacteriosis, enterocolitis, pancreatitis. |
| Parasitic lesions of the bile ducts | Ascariasis or giardiasis |
| Airway inflammation | Pharyngitis, tonsillitis. |
| Oral infections | Periodontal disease. |
| Viral hepatitis | , , , |
The main cause of cholecystitis is prolonged stagnation of bile and its poor excretion. This pathology occurs against the background of a harmful, unhealthy diet, consumption of fatty foods, and overeating.
The main symptom indicating the presence of the disease is aching pain in the hypochondrium, radiating under the shoulder blade, into the shoulder, which intensifies with physical activity, after drinking alcohol. Patients often complain of belching, abnormal bowel movements, bloating, weakness, sweating, nausea and bitterness in the mouth.
You need to see a doctor
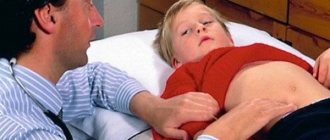
- If there is pain in the right hypochondrium (abdominal pain). In chronic cholecystitis, the pain is dull, aching, lasting from several hours and days to several weeks. A characteristic feature of pain in chronic cholecystitis is its occurrence or intensification after eating fatty or fried foods. In chronic cholecystitis, pain from the right hypochondrium spreads upward to the right shoulder and neck. Often, against the background of a dull aching pain, the patient notes short attacks of acute cutting pain, characteristic of exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis.
- With vomiting, which is a less constant symptom of chronic cholecystitis and, like pain, occurs mainly after the patient violates the dietary regimen. In addition to vomiting, patients with chronic cholecystitis may experience prolonged nausea, a bitter or metallic taste in the mouth, and decreased appetite.
- If you are worried about bloating, constipation and diarrhea, these are quite common symptoms of chronic cholecystitis, indicating a gradual deterioration of its function and a disorder of the digestive process. Bloating, diarrhea, or constipation are rarely caused by chronic cholecystitis alone. As a rule, in patients with more or less long experience of this disease, there is a parallel disorder of the function of the stomach and pancreas (gastritis and pancreatitis), which also affects the quality of digestion.
- Patients with advanced cholecystitis may experience severe weakness, a predisposition to frequent colds, decreased performance, and irritability.
Diagnostics
The occurrence of such symptoms requires urgent consultation with a doctor to clarify the diagnosis. Palpation will help determine the location of the pain and its nature.
Cholecystitis may be a consequence of parasitic infestation, which requires testing for helminths. A general blood test will show nonspecific signs of inflammation, such as increased levels of leukocytes, high ESR. Biochemistry will reveal elevated levels of AST and ALT, phosphatase.
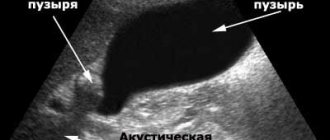
After this, the doctor should prescribe an ultrasound, duodenal intubation, and cholecystography. Using ultrasound, you can determine the thickness of the bladder walls and the presence of stones.
Duodenal intubation allows not only to determine impaired organ motility, but also to take a bile analysis. When examining it, you can find out the cause of the infection and conduct an antibiotic sensitivity test.
Cholecystography will help to see the shape, motility and size of the gallbladder, and arteriography can reveal the thickness of the walls and the proliferation of blood vessels.
Painkillers for cholecystitis
Painkillers for gallbladder inflammation are necessary to reduce the patient's discomfort. They should not be taken uncontrollably, since in acute cholecystitis they can “blur” the clinical picture. This can lead to irreparable consequences - the correct diagnosis will be made late and treatment will not be started in a timely manner, which threatens the health and life of the patient. Any antispasmodic is contraindicated in the so-called “acute abdomen”.
Pain relief for cholecystitis is traditionally taken with the help of drugs that eliminate spasm of smooth muscles. The most popular include Drotaverine and Papaverine. Available in tablet and injection forms.
Objectives of therapeutic measures
The main goal of treatment is not only to relieve symptoms, but also to dissolve stones (if any) and relieve inflammation. When chronic cholecystitis worsens, a person suffers from severe pain, so doctors often prescribe antispasmodics and analgesics.
In addition, it is necessary to take enzymes (Motilium, Mezim) and antacids (Almagel, Gastal), which help normalize digestion and relieve inflammation. Such symptomatic therapy requires a long time and simultaneous adherence to a diet.
Find out advice on chronic cholecystitis from the video:
Dissolving gallstones
Drug dissolution is used only if the patient is not overweight, the stones are small in size and contain a large amount of cholesterol. Cholesterol stones, no more than 2-3 years old, are easily dissolved with the help of medications.
In this case, products based on ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursofalk or Ursosan) are used. You will have to take them for at least 2-3 years in a row, but this only makes sense if the stones are small.
Choleretic medications for cholecystitis
It is impossible to treat cholecystitis without choleretic drugs. They should be taken with caution, only as prescribed by a doctor. A medication from this pharmacological group promotes faster secretion of bile along the ducts and in this way reduces the severity of inflammatory changes. Both adults and children cannot always tolerate choleretic drugs well, especially if there are stones inside the bladder.
Modern gastroenterologists in clinical practice divide choleretic drugs as follows:
| |
| true choleretics, that is, medicines that increase the volume of synthesized bile and its constituent bile acids | a) containing predominantly bile acids (cholenzyme, allochol); b) chemical derivatives (cyclone, nicodine); c) plant components (strawberry, soapberry, rhubarb, rose hips); |
| hydrocholeretics - agents that increase the volume of bile due to the water component | salicylic acid derivatives, valerian, mineral waters |
| |
| cholekinetics - drugs that increase the tone of the bladder and reduce the tone of the bile ducts | magnesium sulfate, cholecystokinin |
| Cholespasmolytics – relaxing only the bile ducts | belladonna extract, common barberry, atropine sulfate |
Regular use of choleretic drugs is most appropriate for chronic cholecystitis to prevent exacerbation periods. The use of such a remedy can be harmful in the acute version of the disease and the formation of a large number of stones - the stone can simply “get stuck” at the point of exit into the bile duct.
Herbal infusions and vegetable oils are deservedly popular among many people. It is advisable to consult a specialist before starting to use them.
Many doctors recommend using a choleretic agent such as blind probing. This medicinal method of exposure involves drinking a hot solution of magnesium sulfate in the morning, after 3 hours the patient is laid on his right side with a warm heating pad. This technique promotes intensive contraction of the bladder and the release of bile.
In case of chronic cholecystitis, another medicinal method of stimulating the secretion of bile such as mineral waters (medicinal), various physical procedures and therapeutic exercises may be recommended.
In some situations, if the stones in the bladder are cholesterol, means can be used to dissolve them, that is, lipolytics. These include medications based on ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursofalk).
Classification of medications
Chronic cholecystitis requires long-term complex treatment, with the use of antibacterial drugs, antispasmodics and painkillers, choleretic agents, hepatoprotectors and sulfonamides, vitamins. Sometimes, it may be necessary to take antifungal and anthelmintic drugs.
Antibiotics
The main drugs against infection and inflammation are antibiotics. Before prescribing a specific drug, the doctor must conduct a bile test for sensitivity to a particular antibacterial drug.
Antibiotics prescribed for cholecystitis:
- Azithromycin;
- Sumalek;
- Zitrolide;
- Azikar.
Azithromycin is prescribed to adults, one tablet per day, for 3 days. It is better to take it an hour before meals with a large volume of liquid.
Sumalek is available in tablets and in powder form for the preparation of a suspension. In any case, the dosage is selected individually, at the rate of 20 mg/kg of weight, and the duration of the course will be only 3 days.
Zitrolide capsules should be taken in the same way as Azithromycin (once a day before meals), for 3 days and only in combination with other drugs.
Azicar is an improved version of Azithromycin, with a minimum of side effects, and is taken according to the same regimen.
It is important to understand that using antibiotics on your own, without a doctor’s prescription, is very dangerous. This may not cure the disease, but will only make the situation worse.
Antispasmodics
To relieve spasms of the gallbladder and relieve pain, antispasmodics must be included in therapy. In addition to relieving acute pain, they help reduce inflammation, improve the flow of bile, and reduce the tone of the organ.
The most popular antispasmodics:
- Took;
- No-Shpa;
- Maxigan;
- Revalgin;
- Spasmalgon.
All these products are available in tablet form and are used strictly on the advice of a doctor. Thus, Bral can increase the symptoms of cholecystitis, so it should be taken with caution.
The daily dose should not exceed 6 tablets, and the drug should not be taken for more than 5 days. It is recommended to drink Maxigan and Revalgin strictly after meals, one tablet at a time. In exceptional cases, it is allowed to take up to 6 tablets per day.
Choleretic agents
Such drugs are used only in the treatment of acalculous cholecystitis, and in the presence of gallstones they are strictly contraindicated.
Frequently prescribed drugs:
- Allohol;
- Artichol;
- Cyclalon;
- Glutargin.
Allochol is taken one tablet 3-4 times a day for a month, after which a three-month break is required. Artichol can be taken 2 tablets three times a day, and the duration of the course should not exceed 3 weeks.
In the acute stage, take 0.3 g per day (in 3 doses) for 3 days. Next, the drug is taken one tablet four times a day, before meals, for a month. The dosage and duration of taking Glutargin is determined by the doctor, based on the severity and form of the disease.
Sulfonamides
Sulfonamides are antimicrobial drugs, derivatives of sulfanilic acid, used for intolerance to antibiotics. Often, experts recommend including Probalance and Fervital in therapy.
The latter, available in powder form, is taken 2 tsp/4 times before meals. Water-soluble powder Probalance is considered a source of valuable dietary fiber, and is taken for about 2-4 weeks.
Antiparasitic and antifungal agents
If studies have shown the presence of parasites in the body, then it is necessary to take anthelmintic drugs. Based on the analysis, the doctor will select the necessary drug to cleanse the intestines of helminths and improve the general condition of the patient. The addition of a fungal infection requires the use of antifungal therapy.
Hepatoprotectors
Drugs that activate the liver (Essentiale, Gepabene, Phosphogliv) will help normalize the flow of bile. These medications will not only normalize the production of bile, but will also restore damaged liver cells and protect it from the effects of toxins.
Vitamins
No less important in the treatment of cholecystitis are vitamin complexes that help strengthen the immune system. You can drink some herbal infusions, echinacea decoction, B vitamins. Separately, to relieve unpleasant symptoms, experts recommend taking medications that eliminate nausea, heartburn, and bloating (Cerucal, Metoclopramide, Motilium).
The drug Papaverine
Currently, the painkiller Papaverine is available in the form of tablets, solutions and rectal suppositories. The instructions for the medicine say that the product can relieve spasms of almost all organs.
As a rule, the drug is taken 3-4 times a day, but the exact dosage is determined only by the attending physician.
It is not recommended to use the medicine for elderly people, children under 6 months, and patients with glaucoma. As for the use of the drug during pregnancy, this issue has not yet been studied. However, it’s not worth taking unnecessary risks, since all medications affect the health of the unborn baby.
As a rule, there are no side effects from using the drug. However, headache, drowsiness, dizziness and weakness may sometimes occur. In individual cases, rash, itching and burning occur. This is because some patients may experience an allergic reaction to the components of the drug.
The main symptoms of the pathology are nausea, bitterness in the mouth and a pulling feeling in the right hypochondrium. Treatment of cholecystitis should be comprehensive and systemic, and the choice of therapeutic methods and medications can only be carried out by a doctor.
Diet
People with chronic cholecystitis will have to adhere to a strict diet for life. They are shown dietary table No. 5, which implies frequent and small meals, and the basis of the diet should be cereals and vegetables.
Everything fatty, salty, spicy and smoked is completely excluded from the menu, and food is boiled or steamed. You will have to completely give up strong tea and coffee, pastries, sweets, and sausages. The main emphasis is on vegetables, fruits, cereals, and low-fat dairy products.
Anti-inflammatory drugs for cholecystitis
The drug from the NSAID group has an analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect. For cholecystitis, you can take traditional (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Piroxicam) or more modern (Rofecoxib, Celecoxib) medications. A medication of this pharmacological group cannot be used as an independent means of therapy, but only in combination with others. When used in combination, the analgesic effect is significantly enhanced. A significant advantage of NSAIDs: safety for short-term use and convenient release form (tablet and solution for injection).