In our digestive system there is such an important organ as the gallbladder, it is located under the liver and is connected to it by a system of tubes (bile ducts), it is needed to pass through a certain amount of bile coming from the liver. It consists of such sections as the body, fundus and neck. When this organ is healthy, it should have a shape similar to a pear. But deformations still occur, and for various reasons. Even several deformations are possible, but extremely rare.
There is a fairly well-known pathology that has the medical term “shaped gallbladder.” In this case, the gallbladder has a double bend, often at the junction of the body and the fundus.
Basically, this happens either as a result of heredity from parents (congenital), or as a result of the growth of the bladder outstripping the tissues with which it is in close contact.
Inflection of the S-shaped gallbladder is possible in 15 percent of healthy people. They may not realize it. The deformation of the bladder may not affect the digestion process, but over time a number of problems still arise. Perhaps this is the release of sediment at the bottom of the gallbladder, the appearance of stones, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, and the appearance of cholecystitis. Complications depend on the diet, lifestyle and the degree of the pathology itself.
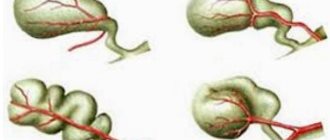
Various forms of gallbladder deformation
Congenital and acquired deformity
Since there are various ways to acquire this pathology, appropriate treatment is prescribed. If the s-shaped gallbladder is a congenital disease, this may not be called a pathology, but simply an unusual shape of this organ. In frequent cases, this goes away with age in the child. Such deformation in a child is possible for several reasons: prolonged stress, obesity, heavy physical activity, chronic cholecystitis.
Cases of the bladder deformation form lead to a number of certain complaints. A kinked bladder is often accompanied by nausea, dull pain under the right hypochondrium, severe loss of appetite, constipation or diarrhea. There is also often a bitterness in the mouth.
The reasons for the acquired s-shaped bladder, which often occurs in adults, are quite different: enlargement of nearby organs, heavy lifting, long periods of sitting, poor nutrition (prolonged fasting or overeating), a number of diseases (acute or chronic cholecystitis), significant prolapse of internal organs, obesity. Quite rarely, deformation of the gallbladder occurs in women during pregnancy (the uterus enlarges and puts pressure on the liver and bladder).
The question often arises as to how dangerous it is to bend the gallbladder. This disrupts the movement of bile through the bile ducts, subsequently causing disruptions in the digestive process, since fats cannot naturally emulsify. Cholelithiasis or calculous cholecystitis may occur.
Treatment methods
Surgical treatment for S-shaped congenital deformity of the gallbladder is almost never performed. And even with the acquired form of the pathology, cholecystectomy is the last thing, since such an operation can lead to more serious health problems. Therefore, special preference is given to conservative treatment methods.
The course of therapy may include:
- diet;
- pharmacotherapy;
- use of folk remedies;
- visiting the gym.
The C-shaped gallbladder in a child creates some difficulties in treatment, since choosing a diet for a small patient is quite problematic. For this reason, parents should not take measures themselves, but leave the issue of drawing up a dietary menu to a competent doctor.
Diet
A diet for a C-shaped bend of the gallbladder normalizes the circulation of bile and improves the digestion process. The patient's diet is saturated with protein products, while products based on animal fats, carbohydrates and natural oils are completely excluded from it.
The following are strictly prohibited:
- alcohol;
- cigarettes;
- sour foods;
- smoked meats;
- pickles;
- fried food;
- carbonated drinks;
- salty dishes;
- honey;
- sugar;
- spices;
- strong tea.
In case of double bending of the gallbladder in a child and an adult, it is necessary to eat low-fat foods. In particular, this applies to “white” meat. So, with such a defect, you can eat chicken, rabbit and other “dietary” varieties of meat.
Don't forget about fruits, vegetables and cereals. It is imperative to maintain a drinking regime and drink at least 1.5 and no more than 2 liters of liquid per day.
Physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises
Physical exercise has a good effect on the functioning of the diseased organ. They are aimed primarily at normalizing the outflow of bile. However, a set of exercises should be developed exclusively by a doctor, since when the gallbladder is bent, sudden and too intense movements are strictly prohibited.
Physiotherapeutic procedures often include electrophoresis and ultrasound treatment. When the gallbladder is bent, such manipulations are useful and highly effective.
Pharmacotherapy
Drug treatment for double bending of the gallbladder involves the use of drugs with choleretic properties. So, among the most effective medications are:
- Allohol;
- Flamin;
- Aristocholus;
- Chophytol;
- Odeston;
- Gepabene;
- Nikodin et al.
Medicines are taken in courses and prescribed exclusively by a gastroenterologist.
Folk remedies
When using folk remedies for double inflection of the gallbladder, the emphasis, as in previous cases, is on the choleretic properties of herbs. These include peppermint, marigold (calendula), and chamomile. To achieve maximum effect from therapy, these plants must be mixed and brewed.
A special herbal tea - collection No. 3 - has a good effect on a diseased gallbladder. It can be purchased at a pharmacy without a prescription and taken according to the instructions. However, remember that herbal treatment is a long process, and not always effective. Therefore, before starting therapy, it is better to ask your doctor for advice.
If you seek help from a doctor in a timely manner, if there is an acquired deformity of the gallbladder, the prognosis for a complete recovery is very favorable. Consequently, the risk of dangerous complications is significantly reduced. But it is better to take care of your health in advance, because if the situation reaches a critical point and the patient needs surgical intervention, this will negatively affect his quality of life in the future.
Diagnosis of the disease
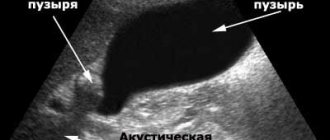
The bending of the gallbladder is diagnosed by ultrasound examination (ultrasound), this helps to see the pathology, as well as the state of its functional state and the state of the body, neck and walls of the organ. The gallbladder must be examined from all sides; sometimes the deformation is clear even when the patient is standing or has stretched his stomach. However, identifying the cause of this organ shape (congenital or acquired) using ultrasound is not easy. To do this, an ultrasound is first done on an empty stomach and after eating egg yolks, or after any other choleretic breakfast or choleretic drugs. If the bend of the organ is congenital, the deformity does not change. Ultrasound is also effective. Its advantage is that it is harmless and it is possible to see several adjacent organs at once. Attention is paid to the shape, structure, and size of the organ. The normal length of the gallbladder is 70 -100 mm, and the width is 30 - 40 mm.
What does this study show?
The lumen of the bladder should normally be completely anechoic (black), especially in a child. The presence of a putty-like suspension against this background indicates stagnation of bile, which becomes thick and absorbs ultrasonic waves.
The presence of a heterogeneous suspension occurs with inflammation of the gallbladder - cholecystitis.
The presence of bright structures, with a dark path of the so-called shadow, in the lumen is a characteristic picture of cholelithiasis.
Thickening of the wall often indicates inflammation; it is observed in chronic and acute cholecystitis, and in the latter case it also acquires a layered structure. Also, thickening, unevenness of the wall or the inability to visualize it is observed in tumor processes.
Treatment of s-shaped gallbladder
It is quite possible that a person may not find out about a congenital pathology until an ultrasound examination is performed. In this case, proper nutrition and taking special herbs that help keep the organ in good shape can eliminate the problem of deformation. If the bend is due to some disease, special, long-term treatment is necessary. This includes medications, diet and physical therapy. The course of treatment usually lasts about two weeks (10-14 days); for greater effectiveness of treatment, three such courses are prescribed. Patients are often advised to undergo “blind probing.”
Clinical symptoms of gallbladder bending.
Congenital pathology can be asymptomatic or with certain clinical symptoms, depending on the degree and location of the inflection of the bladder. In pediatrics, such an anomaly is often detected by chance during an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
With pronounced anomalies - double kinks, symptoms of gallbladder dysfunction appear from birth. If there are no significant deviations in the structure and location, then this does not affect the secretion of bile and the general well-being of the baby. If congenital bends of the gallbladder are asymptomatic, no treatment is required, although with age, symptoms of the disease may gradually appear as bile secretion is impaired. Children after 2-3 years of age, like adults, may have complaints of discomfort or abdominal pain or nausea after eating, or may have vomiting or diarrhea. The gallbladder may become enlarged.
Diet for gallbladder deformation
Following a diet promotes the proper flow of bile and does not allow it to stagnate. The diet includes protein products and excludes those containing animal fats, natural oils, and easily digestible carbohydrates. Thus, one should exclude fatty, spicy, smoked, sour foods, and give up honey, sugar and other sweets. It is also important to reduce the consumption of coffee, salt, and chocolate. You need to stop drinking carbonated drinks and alcohol. Diet is also important; you need to eat often (5-6 times a day), but little by little (servings of 200-300 grams). Include porridge, baked vegetables, fish, and meat in your diet. Everything should be non-greasy. Eat more fruits and drink enough water (1.5-2 liters per day) between meals. The food consumed should not be very hot or cold. Overeating is highly undesirable. Any load on the digestive tract is not desirable.
Treatment
Treatment of a bent gallbladder depends on the nature and causes of the development of the pathological process. A congenital condition that has no clinical manifestations does not need to be treated. This means that the changes are such that they do not disrupt the functional state of the biliary system. If congenital inflection is accompanied by a number of symptoms, specialists prescribe a treatment regimen that eliminates the manifestations, and not the cause. Acquired problems are treated with medications and diet.
Diet
The patient should eat small, frequent meals. This will reduce the load on the hepatobiliary system. It is especially important to teach your baby to eat every 3 hours and limit overeating at night. Food should be warm and mechanically gentle. Experts recommend stewing, baking and boiling foods. It is forbidden to eat fatty foods, smoked meats, canned food, sauces, and margarine. It is necessary to limit mushrooms, radishes, garlic, hot spices, carbonated drinks and alcohol.
Physiotherapy and folk remedies
Exercising helps improve gallbladder function. Therapeutic gymnastics strengthens the diaphragm and abdominal walls. Ultrasound or electrophoresis are also often prescribed. Physiotherapy is considered quite effective in treating the kinked bladder shape.
A good addition to all treatment is traditional medicine. Corn, peppermint, yarrow and other herbs help normalize gallbladder function. There are many choleretic preparations that can be bought at any pharmacy. They are easy to brew and drink well. For example, there is a popular choleretic collection No. 3. The combination of mint, chamomile, calendula and other choleretic herbs helps relieve inflammation and feel better. Treatment with traditional herbs is a good remedy against such diseases.
Choledochus and its pathology
Dilation of the ducts, and the common bile duct in particular, is always associated with a violation of the outflow of bile. The causes may be internal (stones (with obstructive jaundice), polyps, papillomas, helminthic infestation (tangles of roundworms, the refuge of which is the common bile duct), protozoa, narrowing of the lumen due to inflammation - cholangitis, due to decreased tone with dyskinesia, wall tumors) or external duct (compression by an enlarged organ (head of the pancreas), tumor, dilated vessel (varicose vein or aneurysmal enlarged artery), lymph node, with helminthic infestation, for example, with echinococcosis of the liver).
The common bile duct has four sections: the first passes over the duodenum, the second behind it, the third between it and the head of the pancreas, and the fourth in the thickness of the intestinal wall in contact with the head of the pancreas. This explains the need for a comprehensive additional examination of the condition of the pancreas and its excretory duct (Wirsung duct), which is connected to the common bile duct and can also be a source of stones that can disrupt the excretion of bile into the intestinal lumen.
Drug treatment
By prescribing medications for the treatment of pathology, gastroenterologists mean taking choleretic drugs. Such as: Flamin (a drug used for diseases of the digestive system, a choleretic agent for inflammation of the bladder or bile ducts), Odeston (increases the outflow of bile, prevents the formation of stones in the gall bladder), Aristochol (normalizes the secretion of bile, restores liver function and relieves spasms) , Hofitol (also a choleretic drug, often prescribed as a drug for complex therapy), Csqualon (choleretic and anti-inflammatory drug, enhances the outflow of bile, it is often prescribed before probing), Gepabene (choleretic drug of plant origin, also improves the outflow of bile), Ursofalk (hepatoprotective agent, dissolves cholesterol in gallstones), Nicodin (choleretic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory agent). These medications must be taken in periodic courses prescribed by your doctor.
Important anatomical and physiological information
Knowledge of anatomy is extremely necessary when performing an ultrasound of the gallbladder and biliary tract. In the process of phylogenesis (historical development of organisms) of the intestinal tube, the formation of its specialized sections, at a certain stage the need arose for the formation of endocrine glands to participate in the complex process of digestion. The liver developed simultaneously as a filter organ and as a gland that produces bile - a universal emulsifier (breaker) of fats. The gallbladder formed in parallel, having a storage function. The pancreas, located in close proximity, works in tandem when breaking down proteins, which is why its excretory duct is usually connected to the bile duct.
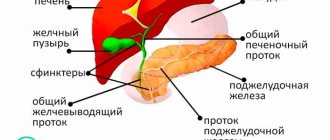
The close relationship of their functions and the increase in specialization with the increasing complexity of the structure of organisms have led to their close proximity, which often dictates the need, when looking at one organ, to at least briefly examine the other. Based on the fact that in this article we are directly considering the process of bile secretion, the liver itself will be affected only indirectly. So, the gallbladder is a hollow muscular organ that performs storage and contractile functions. It has an elongated shape with narrow ends at the mouth and wider ends at the neck and bottom. Above the gallbladder is the liver .
Diagram of the structure and location of the liver and gall bladder
The fundus may protrude from under the liver and touch the anterior abdominal wall. On the left, the bladder borders the stomach, duodenum, and on the right, with intestinal loops and the flexure of the colon. Therefore, in some situations, for example, with a tumor affecting the wall of the bladder in the bottom area, it is necessary to exclude shielding of the echo picture by gas from the adjacent large intestine, especially in conditions of excessively developed subcutaneous fat. The cystic duct connects to the common hepatic duct. These 2 ducts form the common bile duct - the common bile duct. The common bile duct, in turn, connects with the pancreatic duct and removes bile directly into the cavity of the duodenum.
Forecasts
The appearance of an s-shaped gallbladder does not mean that it needs to be removed, since removal also brings with it a number of new problems and difficulties. The gallbladder must often be removed in cases where it has double bends that cannot be treated. It is extremely important to detect the pathology in time and take measures to get rid of the serious consequences. Since for a person with a removed gallbladder, following a diet and proper regimen is a new way of life. However, lifelong dieting, although beneficial, can still become boring. It is especially difficult to change a child’s diet. Therefore, doctors recommend not to rush into removal. After all, the main thing in cases with an s-shaped gallbladder is not to let the bile stagnate (sit less, if you sit, then under no circumstances should you slouch), completely isolate yourself from all kinds of sweets and accustom yourself to the rule of three “Fs”, this is complete avoidance of fried, fatty foods and egg yolks. If new pain in the abdominal area nevertheless appears, then seeing a doctor is a must.
Types of deformation
Normally, the bubble is pear-shaped, but there are pathological varieties.
Kink
The bend most often occurs at the junction of the bottom and body. There is a violation of the bile duct, it is characterized by severe symptoms, pain and discomfort. The bend is dangerous due to severe stretching of the organ and its rupture.
S – shaped deformation
The S-shaped deformity is characterized by a double bending of the organ. Basically, this is a congenital form of pathology; in children it disappears on its own. Rarely occurs the acquired form, which occurs due to the rapid growth of the organ.
In adults, it forms due to stress, overexertion or cholecystitis. The problem arises if it touches the body or bottom of the gallbladder. Often symptoms are not detected until other organs are affected.
Padding
Constriction is a dangerous form of anomaly, most often congenital. It is characterized by a complete change in the shape of the gallbladder, which leads to dangerous disorders within the body. An anomaly detected in childhood can be completely treated, but in adults it will remain chronic.
Contour deformation
This deformation is characterized by a violation of the contours of the bubble, its curvature. The anomaly can be either congenital or acquired. It can appear after prolonged inflammation, heavy exertion or stress.
Painful attacks worsen after eating or exercising. Signs of bile stagnation appear, its consequences can cause rupture of the biliary organs.
Labile bend
The labile form of deformation occurs against the background of excessive loads and goes away on its own. Signs of impaired digestion after physical activity decrease at rest.
Twisted gallbladder
When ties inside an organ are diagnosed, this means that deformation has formed. It can be complete or partial. Complete torsion of the gallbladder requires urgent surgical intervention. Violation of the body and bottom of the organ is especially dangerous; it can lead to rupture of the walls.
Diagnostics
To prescribe adequate treatment, it is important to establish the correct diagnosis. You cannot independently determine the disease and prescribe a course of therapy, as this is a waste of time and there is a high probability that the problem will worsen.
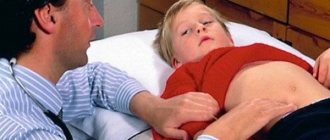
If you notice one or more of the above symptoms, you should consult a therapist. After listening to complaints, conducting a thorough examination, reading the medical history and prescribing a number of mandatory laboratory tests, the doctor gives a referral to be examined by a gastroenterologist.
Taking an anamnesis is important information. The patient must remember the medical history in detail, and also indicate diseases that are inherited in the family, if any. It is also worth mentioning concurrent illnesses and possible allergic reactions to medications. Physical examination - palpation of the peritoneum and organs located on the right side. The mucous membranes, skin color, and sclera are examined. Thermometry and auscultation are performed.
Laboratory research:
- general analysis;
- biochemical;
- liver tests;
- for helminths.
Instrumental methods are primarily important in diagnosis:
- Ultrasound is performed in two stages, on an empty stomach and half an hour after taking choleretic food. Ultrasound is one of the most informative methods. This way you can see pathological changes, deformation of the gallbladder, compaction, stones, and fluid accumulations. Pain in the right hypochondrium is the basis for prescribing this diagnostic method.
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography are prescribed if the doctor has any doubts. The methods allow us to study the disease in several projections, at the cellular level.
Only after reviewing the results of all studies can the doctor make a diagnosis and begin developing a treatment regimen.
Diagnostic methods
A gastroenterologist diagnoses pathology. He prescribes an ultrasound examination to the patient - the most informative method of determining the problem. Ultrasound diagnostics is allowed for the examination of pregnant women and newborns.
Using ultrasound, it is easy to detect changes in the shape and density of the wall of the internal organ from different angles. In addition, the specialist may notice stones or tumors in the cavity. Ultrasound diagnoses problems in other organs.
Additional examination methods are visual examination, palpation, blood and urine tests.