Pathologies of the digestive tract are most often diagnosed in patients of different age categories. Previously, these complications arose due to functional disorders and genetic predisposition. In modern people, these diseases arise as a result of a passive lifestyle, poor nutrition, and frequent stress.
The biliary system, which consists of the gallbladder and its ducts, is quite complex. Due to disorders of its functionality, the likelihood of various symptoms that worsen the quality of life increases. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend seeking medical help if even the slightest discomfort occurs in this area. Then patients wonder which doctor treats the gallbladder. Only a qualified doctor can detect the disease and establish an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, the patient should know which specialist and in what cases to contact.
Basic information
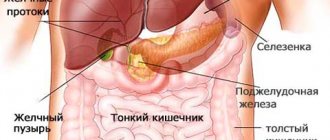
The hepatobiliary system consists of the gallbladder, its ducts, and the liver. These organs are involved in the formation and transportation of bile, which is produced by liver cells. Through the bile ducts, liver secretions enter the gallbladder (GB). After eating food, bile enters the duodenum.
The hepatobiliary system consists of the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts
Liver secretions stimulate the breakdown of fats and vitamins. Bile affects the motor and secretory function of the jejunum. In addition, the secretion neutralizes toxins and medications.
Violation of the functionality of the biliary system occurs as a result of the influence of aggressive compounds (poisons, bacteria, viruses, free radicals). Also, the functioning of the hepatobiliary tract is negatively affected by nutrition, medications, alcohol, stress, etc.
Doctors identify the following types of lesions that provoke disorders of the hepatobiliary tract:
Dyskinesia of the gallbladder in children
- Mitochondrial damage occurs due to blockade of respiratory chain enzymes. As a rule, diseases of this kind are provoked by medications. Then the connective tissue grows in the gallbladder or bile ducts.
- Dysproteinoses are diseases that arise due to disturbances in protein metabolism. Such pathologies appear due to the prolonged action of toxins (ethanol, metabolites of strong drugs, viruses, bacteria, poisons).
- Cholestasis is a decrease or cessation of the flow of liver secretions into the duodenum. This pathology occurs due to the presence of stones in the gallbladder.
- Vascular lesions of the hepatobiliary tract.
- Bile thickening syndrome occurs due to blockage of the bile ducts by mucous or bile plugs.
Specific symptoms of diseases of the hepatobiliary system: nausea, pressure on the right side under the ribs, vomiting after eating, diarrhea. Patients also complain of abdominal pain after eating fatty foods or smoked foods. In addition, pathologies of the biliary system are manifested by the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, jaundice, and hepatic odor from the mouth.
If such symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor for a thorough diagnosis and diagnosis.
Examination by a therapist
Many patients who suffer from disorders of the functionality of the biliary system are interested in who treats such pathologies. The gallbladder and liver are important organs that regulate the activity of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary system. When diseases of these organs occur and there is no proper therapy, the likelihood of dangerous complications that can only be eliminated by surgery increases. In diseases with a chronic course, there is a risk of death of the patient. This is due to the fact that dysfunction of the biliary organs causes irreversible consequences.
If you experience discomfort in the gallbladder area, you should visit a therapist
Treatment of gastrointestinal diseases should be supervised by an experienced specialist. Diagnosis is carried out taking into account many factors: the patient’s age, lifestyle, congenital pathologies.
If pain appears on the right side under the ribs, you should visit a therapist. During the examination, he collects anamnesis and palpates the organs of the biliary tract to identify abnormalities. In addition, the doctor will perform percussion (tapping on individual parts of the body). In this way, the doctor will determine the location of the liver and its size.
If a disease of the hepatobiliary system is suspected, the therapist will prescribe the following studies:
- Clinical blood test. Using the analysis, you can evaluate the functioning of the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts.
- Study of human feces (urine, feces).
- Determination of the concentration of bilirubin (bile pigment) and some enzymes.
Regardless of the results of laboratory tests, instrumental diagnostics are used. Ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract will help study the bile ducts, the density of the gallbladder, the diameter of the blood vessels and tumors. The patient can obtain test results from the doctor.
If the doctor detects diseases of the digestive tract in the patient, he will be referred to a gastroenterologist.
Who to contact for help
Many people who are faced with gallbladder or liver dysfunction are wondering what the specialization of a doctor who deals with such problems is. The gallbladder and liver are the most important organs on which the functioning of the digestive system and the entire biliary tract largely depends. If diseases of these organs occur and there is no timely, competent treatment, there is a high probability that further treatment will not be successful without surgical intervention. If the gallbladder or liver disease progresses to a chronic stage, the possibility of the patient’s death cannot be ruled out, since dysfunction of any of these organs will provoke complications for the entire body, and the consequences may be irreversible. Treatment of gallbladder and liver pathologies should be supervised by an experienced professional who specializes in these problems. When examining a patient and making a diagnosis, the doctor must take into account many factors, including the patient’s age, his lifestyle and the presence of congenital pathologies. If gallstones or cirrhosis are treated by a general specialist, the risk of misdiagnosis will be more than 70%. When a patient is prescribed inappropriate medications that have a choleretic effect, neoplasms and stones in the gall bladder may begin to move and clog the ducts. In case of such complications, surgery will be required to save the patient's life.
Treatment of any pathology caused by gallbladder dysfunction should take place in several stages. The patient will need to consult with several specialists at once: a therapist, a gastroenterologist and a hepatologist.
Consultation with a gastroenterologist
This specialist deals with the treatment of diseases of the digestive tract and their relationship with other organs. In addition to combined pathologies, the doctor examines patients with diseases of unknown origin. Sometimes a person does not understand which organ of the abdominal cavity provokes pain. This can be detected using instrumental and laboratory studies. The gastroenterologist will prescribe the necessary tests and make an accurate diagnosis.
A gastroenterologist treats gastrointestinal diseases
Most often, this specialist identifies the following diseases of the biliary system: inflammation of the stomach, pancreas, cholecystitis, ulcers, cholelithiasis (stones in the gallbladder).
In addition, such pathologies can occur against the background of disruption of the natural bacterial flora. Sometimes during diagnosis, a doctor also discovers liver diseases. Since this gland is associated not only with digestion, but also with cleansing the body of toxic substances, and is involved in the synthesis of proteins and hormones, another specialist deals with its pathologies.
Which doctor should I contact?
A gastroenterologist treats diseases of the gallbladder, but not all government centers offer easy access to him for a consultation. Often the problem is a lack of specialists, so a referral to one is given by a general practitioner or family doctor, to whom the patient must tell about his problem. The doctor is authorized to conduct an examination, refer the patient for tests and evaluate their results. If the problem is confirmed, the patient goes to a gastroenterologist.
Gastroenterologist
A doctor specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. At the initial appointment, the patient is interviewed and the painful area is palpated. Family history must be checked. It is better to visit a doctor with the results of basic laboratory tests: biochemical and general blood tests, urinalysis and coprogram. This will save time, and the doctor will make a presumptive diagnosis, after which he will issue a referral for an ultrasound scan of the liver and gallbladder.
In mild cases, therapy is provided on an outpatient basis. If there are gallstones or other serious damage to the organ, hospitalization is required. The patient must understand that restoring the functionality of an organ is not always possible, so surgery may be required. Damage to the gastrointestinal tract always determines the need for lifestyle changes and nutritional correction.
Visit to a hepatologist
This doctor will examine the gallbladder. To establish a diagnosis, instrumental and laboratory techniques are used. If violations are detected, the hepatologist will select the most optimal treatment method.
A hepatologist treats cirrhosis, hepatitis, cholelithiasis, etc.
This specialist treats cirrhosis, viral hepatitis, cholelithiasis, helminthiasis (infection with worms), etc. If such diseases are identified, urgent and competent therapy must be carried out. Otherwise, the disease becomes chronic, and this can lead to dangerous complications. Particularly dangerous consequences occur in the presence of stones in the gallbladder or its ducts. This is due to the fact that the stones are getting larger every day. If the diameter of the formation reaches 3 mm, then modern medications and herbal decoctions are used to destroy it. With a further increase in the size of the stones, surgical treatment cannot be avoided.
Nutrition for cholelithiasis
After stone removal, a diet is usually needed, since after surgery stones can appear in the bile ducts, and special nutrition is designed to prevent recurrence of the disease. Apply diet (table) No. 5. The essence of the diet is to limit fat in food and eat frequent, but small portions, which promotes uniform separation of bile, better absorption of nutrients, and good intestinal function. It is especially good to train yourself to eat at a strictly defined time. To reduce the load on the gallbladder, it is better to chop food. It is recommended to boil, bake (but without crust) or steam the products. To prevent bile from thickening, you need to drink enough fluid - at least two liters a day - and limit your salt intake. But you need to give up alcohol completely, as it causes spasms of the bile ducts.
Despite some general principles, therapeutic diets for gallbladder disease are prescribed individually, based on the characteristics of the body, nervous system, and metabolic processes. Sometimes such diets include recommendations for losing excess weight.
In any case, more effective than any diet, taking care of yourself will help you avoid illness. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, preventive examinations with doctors and fighting stress - such simple actions significantly increase the chances of preventing gallstone disease and living in peace.
Treatment of viral hepatitis
Depending on the pathogen, doctors distinguish the following types of hepatitis: diseases of types A and E, as a rule, end favorably, and hepatitis B, C, D, G become chronic and threaten dangerous complications (cirrhosis, cancer).
The clinical picture for all types of hepatitis is similar: pain on the right under the ribs, yellow discoloration of the skin and sclera, rash, discoloration of feces, darkening of urine. If such symptoms appear, you should visit an infectious disease specialist.
As a rule, hepatitis is treated in an inpatient department. The doctor prescribes antiviral drugs that affect the cause of the disease. In this case, the infectious disease specialist must engage in systematic monitoring of the condition of the liver. Indeed, in many cases, active inflammation provokes liver failure.
Examination by a dermatologist
If diseases of the hepatobiliary system are accompanied by a rash, itching, redness of the skin, then you can visit a dermatologist. The doctor will engage in diagnostic procedures and special studies to identify functional liver failure and refer the patient to a more specialized specialist. In this case, you should take the tests responsibly. It is important to identify pathology at an early stage so that the outcome of treatment is favorable.
A dermatologist is visited if skin manifestations occur in diseases of the biliary tract
Surgeon's help
The liver is capable of recovering on its own, but with regular poisoning and lack of treatment, liver failure occurs. In this case, drug treatment will not give a positive result. The patient should consult a surgeon who deals with severe disorders of liver function.
The surgeon deals with severe disorders of liver function
Treatment by an oncologist
In recent years, the number of cancer diseases has increased. According to statistics, liver cancer ranks 5th in terms of prevalence. In this case, the pathological process rarely begins in the liver cells. Most often, cancer metastases spread through the biliary system from the intestines, pancreas, and lungs.
The likelihood of developing neoplasms increases with cirrhosis, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, and a toxic form of hepatitis. In addition, there is a risk of tumors with the following diseases: toxic hepatitis, cholelithiasis, infectious diseases of the genital organs. To receive specialized care, you should contact an oncologist. The doctor will conduct a highly accurate diagnosis (blood test for tumor markers, targeted biopsy). In addition, the specialist will carry out therapeutic measures: chemotherapy, surgery to remove the tumor, radiofrequency ablation, etc.
Contact an oncologist if a neoplasm is suspected
Gallbladder removal
The operation to remove the diseased organ is called cholecystectomy. With this intervention, the organ is completely removed. There are several types of surgical intervention; the laparoscopic method is considered effective and safe.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy involves making small punctures in the peritoneum. Through them, the doctor inserts instruments and pumps the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide to create space for manipulation.
The progress of the operation is monitored using a video camera, the image from which is displayed on the monitor. During the operation, the doctor, using clamps and electrodes, identifies the cystic artery and duct, places clips on them and crosses them.
High-quality video images allow for manipulations, controlling the situation better than with classic open surgery. The surgeon separates the bladder from the liver and removes it through the previously made puncture.
The advantages of laparoscopy are minimal trauma to the abdominal wall, reduction of pain, acceleration of the rehabilitation period. The patient can leave the hospital after 2 days; after such an operation, strength is quickly restored, and you can return to normal activities. On the second day the patient is already walking.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy has contraindications. In 1-5% of all identified pathologies, the affected organ cannot be removed in this way. The reason is the abnormal anatomical structure of the ducts, the presence of adhesions or a strong inflammatory process, etc. If laparoscopy is not possible, open surgery is performed. Usually this is a minimally invasive conversion, sometimes it is a classic abdominal operation.
Joints: which doctor treats
to contents ^
Comprehensive examination for gallbladder diseases
If you experience pain in the gallbladder area, it is recommended to visit a doctor who will prescribe a comprehensive diagnosis:
- Liver tests are a biochemical blood test to determine indicators that reveal damage to hepatocytes, disorders of bile excretion and disruption of its protein-synthetic function.
- A coprogram is a study of stool. The analysis reveals the amount of undigested fats, which also indicates an insufficient supply of liver secretions.
- Ultrasound examination is the most informative method for identifying stones in the gallbladder and kidneys. During the examination, the doctor will determine the severity of the inflammatory process.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is a diagnostic method that examines the esophagus, stomach and intestines.
After carrying out the above tests, the patient will be referred to a specialist with a narrower profile for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases.
Thus, it is impossible to accurately answer the question of which doctor should be consulted for diseases of the hepatobiliary system. The choice depends on the diagnosis and causes of the pathology. It is strictly forbidden to carry out independent treatment, as this increases the likelihood of worsening the patient’s condition. The attending physician will establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the most appropriate medications, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Symptoms of gallbladder disease
Pathologies of the gallbladder are quite difficult to determine in the early stages. Symptoms of gallbladder pain usually begin to manifest themselves already in the advanced stage, when the disease becomes acute. But even in this case, the clinical picture of the pathological process may not differ from the symptoms of ailment that a person mistakes for a common disorder.
The main symptoms that may indicate problems with the gallbladder are:
- Painful sensations in the right side, in the area of the liver or under the ribs.
- The appearance of a bitter taste in the mouth in the morning.
- Belching sour.
- Increased body temperature.
- Defecation disorder.
- The occurrence of unpleasant sensations after eating.
- Change in skin color.
- Nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief usually occurs with cholecystitis, gallbladder and liver disease of an inflammatory or infectious nature.
In addition, pathologies such as cholelithiasis can manifest themselves as acute, sharp pain in the right hypochondrium, especially during the period when the stone begins to move along the ducts or blocks the outflow of bile. If problems occur in the functioning of organs, you must urgently go to the hospital , where a decision will be made to prescribe additional methods of examination and therapy.