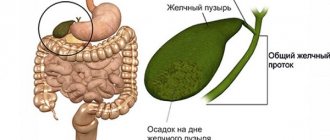
Removal of the gallbladder, or cholecystectomy, is performed for gallstone disease. Despite the development of modern medicine, this procedure is the main method of treating cholecystitis.
Used in case of ineffectiveness of conservative measures. According to statistics, women are several times more likely to suffer from gallstones; the largest number of cases occurs in old age. To perform the operation, the stones must reach a certain size.
Doctors try to eliminate small stones using other methods. This is due to the fact that the absence of an organ implies some restrictions in the patient’s life and diet, which he will have to observe for the rest of his life.
Causes of stone formation
The causes of gallstones have not yet been precisely established. Doctors identify external and internal provoking factors. Internal ones include:
- heredity;
- overweight;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of organs that impede bile outflow;
- cholecystitis;
- chronic hepatitis;
- high cholesterol;
- diabetes;
- tumors or adhesions in the ducts that prevent the flow of bile;
- intestinal operations.
Among external factors, the main one is poor nutrition. It is expressed in long breaks between meals, consumption of too fatty foods, and lack of plant foods. Taking certain medications and drinking alcohol also lead to the formation of stones.
The mechanism of stone formation is as follows:
- Stagnation of bile occurs.
- Cholesterol metabolism is disrupted.
- Cholesterol crystallizes to form sand.
- The grains of sand stick together and stones form.
- Over time, the stones acquire new grains of sand and increase in size.
What are the dangers of cholelithiasis?
Not every person with cholelithiasis immediately learns about his diagnosis. Small stones may not bother you for years; difficulties appear later, when the size of the stones reaches a certain size. In addition to unpleasant sensations, a formed and growing gallstone will cause serious health problems.
Biliary colic
The phenomenon is characterized by extremely severe pain in the right hypochondrium. The situation arises as a result of the development of a stone in the bile duct. The pain can last from several minutes to several hours until the stone passes into the intestines or returns to the gallbladder.
The danger of the situation is that the stone can get stuck in the duct, injure the walls or lead to rupture.
Cholecystitis
The pathology represents inflammation of the gallbladder and is considered a complication of cholelithiasis. The disease occurs as a result of a violation of the outflow of bile and the appearance of microflora in the lumen of the bladder.
Cholecystitis can cause gangrene of the gallbladder, damage to the walls of the organ, and even perforation. If bile stops flowing into the intestines as a result of a blockage of the duct by a stone, intoxication of the body with the components of the secretion may occur.
Acute pancreatitis
This is an inflammatory process of the pancreas that occurs due to the entry of a gallstone into the duct common to the pancreas, blocking it. As a result, pancreatic enzymes do not enter the intestines and, when activated, begin to “attack” the pancreas. As a result, acute pancreatitis develops.
Acute cholangitis
The pathology is an inflammatory process that occurs in the hepatic ducts. The cause of severe illness is gall bladder stones.
Cholelithiasis is considered the cause of a number of dangerous diseases of internal organs and can provoke intestinal obstruction, peritonitis and other deadly situations.
The presence of stones cannot be ignored, even if the stones are small and do not cause concern. Over time, the situation may worsen, and untimely treatment will lead to serious consequences. When you first detect problems in the body, you should undergo an examination and consult a gastroenterologist.
Self-medication is strictly prohibited; the process of “expelling” stones at home can lead to unpredictable consequences.
Types of stones
Concretions in the bladder are divided into:
| Pigment (bilirubin) | They are formed from unprocessed bilirubin deposited on the walls of the organ. The stones are brown in color. |
| Cholesterol | Account for almost 80% of all cases. Formed from crystallized cholesterol. The color of the stones is light yellow. |
| Calcium | They are the least common. The provoking factor is a metabolic disorder in which calcium in the form of limescale deposits on the walls of the gallbladder. |
They come in sizes:
| Small | Up to 10 mm. They do not cause discomfort and exit the body with feces. |
| Average | From 10 to 20 mm. The most dangerous stones, as they can get stuck in the bile duct and cause serious complications. |
| Large | More than 20 mm. They are rare, usually in a stationary state, but they can block the duct and prevent the flow of bile. |
Clinical picture
The severity of symptoms depends on the stage of the disease. There are three stages of pathology:
| Initial | The stones have not yet formed; changes occur in the composition of the bile and are diagnosed using laboratory tests. |
| Second | Stones have formed, but there are no clinical manifestations. Pathology can be detected using ultrasound. |
| Third | At this stage, the first symptoms of calculous cholecystitis appear. |
Symptoms by which a patient may suspect cholelithiasis:
- Sharp or aching pain in the right side, radiating to the shoulder blade, shoulder, and lower back.
- An attack of vomiting with bile. Occurs when the ducts are blocked by stones.
- Bitter taste in the mouth.
- Temperature increase.
- Increased sweating.
- Angina attack.
- Weakness, signs of intoxication.
Important! If the stone has completely blocked the duct, the patient's stool becomes white. Obstructive jaundice may develop.
The above signs indicate an acute attack of cholecystitis. The chronic form is manifested by periodic pain in the right side that occurs after eating.
The patient has indigestion, sometimes constipation, sometimes diarrhea. Also in the morning the patient is bothered by heartburn and a bitter taste in the mouth. Nausea begins periodically, followed by vomiting and relief.
What stones are removed
An operation to remove an organ is prescribed if the stones have reached a size of 1-2 cm and fill the bladder by more than 30%. This increases the risk of stone movement and blocked ducts.
If the size of the stones is small, then drug therapy or crushing of stones with ultrasound is prescribed. This procedure is called percutaneous lipotripsy. The fragmented formations come out naturally after the procedure. For accelerated removal, agents that dissolve stones are prescribed.
The operation is indicated for large stones. They are less susceptible to movement, but form bedsores in the walls of the organ, causing necrotic processes.
Indications for surgery:
- The size of the stones is from 10mm and more.
- The bladder is more than one-third full of stones.
- Constant attacks of exacerbation of cholecystitis.
- Blockage of the bile ducts.
- Complications of calculous cholecystitis: pancreatitis, cholangitis, gangrene, phlegmon.
Diagnostics
- To determine a biliary stone, the patient is prescribed laboratory tests and an ultrasound examination, which will show changes inside the gallbladder, stones and thickenings in the walls, the lumen of the duct, its narrowing or expansion;
- on an x-ray with a contrast agent, carbonate stones can be detected, which have x-ray positive properties;
- when the duct is blocked by stones or is localized in the common bile duct, endoscopic examination methods are used;
- when it is impossible to conduct other examinations or there are inaccuracies, magnetic resonance cholangiography is performed. It allows assessment of the biliary tract;
- When examining the patient’s stool and urine under a microscope, specialists pay attention to the value of bilirubin and cholesterol, triglycerides. If these values greatly exceed the norm, urgent drug therapy is necessary.
Read also: How to treat gallbladder atony?
Operation
It is impossible to remove formations from the bladder without removing the organ itself. The operation to remove the gallbladder is called cholecystectomy. There are two types:
- Laparoscopy.
- Abdominal (laparotomy).
In case of planned surgery, laparoscopy is performed. Access is carried out through three small punctures under ultrasound guidance.
If the patient's condition is severe and complications are suspected, abdominal surgery is performed. An incision up to 15 cm long is made on the abdominal wall. The incisions are vertical, angular and oblique. Sometimes the operation is started using a laparoscope, and if necessary, it is transferred to laparotomy.
This happens if pathologies are discovered that were previously impossible to diagnose. For example, tumors, foci of necrosis, peritonitis, damage to neighboring organs, etc. Both types of interventions are performed under general anesthesia.
There are two ways to remove a bubble: from the neck and from the bottom. The first access is easier and less likely to cause complications and bleeding. The second method is used when it is impossible to reach the bile duct. With this approach there is a high risk of bleeding.
Contraindications to surgical intervention using laparoscopy are:
- Serious heart disease.
- Pulmonary, liver, kidney failure.
- Intolerance to anesthesia.
- Peritonitis.
- Obstructive jaundice.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Poor blood clotting.
Important! With these contraindications, it is only possible to perform emergency abdominal surgery if the patient’s condition is critical.
Life without gall
After organ amputation, the digestive system begins to work differently. Bile from the liver enters directly into the intestines, irritating its mucous membrane. Due to the low concentration of bile, food breakdown processes occur more slowly. These deficiencies can be corrected with proper nutrition.
Watch a video about eating without a gallbladder:
The early rehabilitation period involves following a strict diet. The optimal table is No. 5. Its principles:
- Fractional meals in small portions. There should be at least 5-6 meals. Long breaks in eating should not be allowed.
- Eating only warm foods, not hot and cold foods.
- Cooking by baking, boiling or steaming.
- Complete abstinence from alcohol and tobacco.
- Limiting physical activity.
| The following foods are excluded from the patient's diet |
|
| The menu includes such products |
|
Over time, a person will diversify his table, but some restrictions will remain for life. To improve digestion, enzymes are prescribed (Pancreatin, Mezim, Creon).
The patient is prescribed annual sanatorium-resort treatment and moderate physical activity. If the doctor's recommendations are followed, the patient will be able to recover very quickly after surgery and return to an active lifestyle.
Dietary recommendations for pain in the gallbladder
During and after treatment, you should adhere to a dietary diet for diseases of the biliary system:
- Spicy, spicy and fatty foods should be avoided. Under no circumstances should you eat fried foods.
- Eating such food is fraught with an increase in the amount of bile, some of which will remain in the liver.
- Refuse sweets, flour, and rich foods. Also exclude chocolate. This promotes weight loss and overall health of the body.
- Porridges made from various cereals are useful. Buckwheat and oatmeal are especially recommended. Meat, poultry and low-fat fish are best steamed or boiled.
- Fresh fruits and vegetables must be included in your diet. Pumpkin, zucchini and apples are very useful. Garlic, onions and hot peppers are not recommended.
- Low-fat cottage cheese, cheese and milk.
- Strictly exclude alcohol, coffee and cocoa.
Food must be taken in small portions. Bile will not stagnate if you eat at the same time. You should not overeat, as this can provoke a spasm of the gallbladder and cause an exacerbation of the disease.