A little about lipomatosis
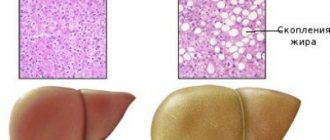
Lipomatosis is a pathology of the pancreas, characterized by changes in its structure and structure, as well as the appearance of fatty formations in the tissues. This disease is often called fatty degeneration.
Lipomatosis can manifest itself in the following three forms:
- Knotted. Fatty nodes form inside the capsule.
- Diffuse. It occurs in the form of many fat cells that form under the lining of the gland.
- Diffuse nodular. Combines the symptoms of two other forms of lipomatosis.
Even after undergoing treatment for lipomatosis, the pancreas does not restore all its functions, which is why it loses its previous performance. However, the sooner treatment is started after diagnosis, the fewer complications can be expected.
What is pancreatic lipofibrosis
Fibrolipomatosis or lipofibrosis of the pancreas is not a separate disease. This medical term refers to a degenerative process in the gland, leading to an uneven distribution of the connective and fatty component of the organ. As a result, there is an excessive replacement of normal tissues with fibro-fatty structures.
According to ICD-10, the disease is designated by code K86.8.
In addition, it is worth noting the following nuances:
- With lipofibrosis, obesity of the gland is observed, as indicated by the increased echogenicity of the organ, which was caused by prolonged inflammation or an incorrect metabolic process.
- Fibrosis is characterized by decreased echogenicity and increased density.
With this pathological process, damage occurs to tissues that try to compensate for their deficiency by actively growing, forming compactions and nodules.
In severe cases of fibrolipomatosis, numerous fibromas appear on the parenchyma of the gland.
Types and forms of painful manifestations
Lipofibrosis, as an inflammation of the pancreas, has several forms of manifestation:
| Forms of the disease | Characteristics |
| Nodal | The presence of nodes, which are characterized by a symmetrical arrangement, surrounded by a capsule. The nodular form appears on the body of the pancreas. |
| Diffuse | Manifests itself in the subcutaneous tissues of the gland. The presence of multiple fat cells actively spreading throughout muscle tissue. There are no restrictions in the form of capsules and other shells. |
| Diffuse nodular | Combines signs of nodular and diffuse forms. |
Medicine distinguishes three stages of development of lipofibrosis:
- The first is that 30% of the gland tissue is affected. The disease is asymptomatic.
- The second is that about 30-60% of the organ is affected by pathology. There are signs of indigestion.
- Third – more than 60% of the affected area of the pancreas is noted. Serious abnormalities throughout the body.
Depending on the stage of the pathology and the provoking cause, specialists select the optimal treatment option.
A little about fibrosis
Fibrosis is a set of changes and complex processes in the pancreas, in which the functional tissue of the organ is replaced by connective tissue. The pathology does not have pronounced symptoms and often occurs in people with diabetes. The course of the disease is slow with periodic exacerbations.
Often the prerequisite for fibrosis is the progression of pancreatitis. It can have two forms: focal (small localized) and diffuse (throughout the entire body of the organ).
Therapeutic measures
There is no cure for pancreatic fibrosis. In modern medicine, there are no drugs yet that can transform the connective epithelium back into functional tissue. All therapeutic measures are aimed at relieving symptoms and alleviating the patient’s condition.
First of all, the patient is prescribed a strict diet. This measure allows you to stop the inflammatory process and relieve the pancreas. Spicy, fatty, smoked, salty, fried and rough foods are excluded from the patient's diet. In addition, it is necessary to avoid products that increase the secretion of gastric juice (seasonings, sauces, marinades). Meals should be small, and the patient should consume large amounts of fluid. Alcohol for fibrosis (even in small quantities) is strictly prohibited.
Important information: Painkillers for pancreatitis in adults
An important factor in treating the disease is controlling enzyme levels. Also, depending on the cause that provoked the inflammation, the gastroenterologist may prescribe the following groups of drugs:
- antispasmodics;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- interferons;
- antibiotics;
- analgesics;
- antiemetics;
- digestive enzymes.
If fibrosis is treated in the right way, the patient’s digestion will normalize and weight loss will stop. But there are a number of cases in which surgical or endoscopic intervention may be required. For example, when:
- constant pain syndrome that cannot be relieved by analgesics;
- compression of the pancreatic flow;
- degeneration of tissue into a tumor;
- development of a postnecrotic cyst in the gland;
- obstructive jaundice.
A favorable prognosis for fibrosis depends on how extensively the gland is affected. If you follow the diet and all medical prescriptions, give up alcohol and smoking, the disease may not develop for a long time.
What is fibrolipomatosis?
Pancreatic fibrolipomatosis combines the characteristic features of fibrosis and lipomatosis. It is a fatty degeneration of the gland, in which there is an uneven distribution of fatty and connective tissue throughout the parenchyma. Most often, this term directly refers to a negative change in the structure of the pancreas, the processes of formation of nodules and seals on the organ.
Lipofibrosis goes through three stages of progression:
- Damage to a third of the entire organ.
- Defeat up to 60 percent.
- The spread of fibroids is more than 60 percent.
Prognosis and prevention
The forecast for the condition of the pancreas is made taking into account the current volume of healthy tissue of its parenchyma, which is individual for each patient. It is impossible to eliminate fibrosis, but if a person changes his lifestyle and follows all medical recommendations, then diffuse changes will stop progressing.
Prevention involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding even minimal amounts of fatty and fried foods, and timely treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which can cause exacerbation of pancreatitis with subsequent fibrosis. People diagnosed with fibrosis must undergo a preventive examination once every six months. This will allow timely detection of the progression of the pathology and conduct the necessary corrective therapy.
Causes and diagnosis of lipofibromatosis
What is lipofibromatosis of the body of the pancreas in terms of the causes of its occurrence? Most often, the disease occurs as a complication of chronic pancreatitis, but there are other causes. The death of healthy cells and their replacement by adipose and fibrous tissue can occur due to the following prerequisites:
- mechanical damage to the pancreas;
- toxic injuries (poisoning from alcohol, chemicals, drugs);
- allergies;
- inflammatory processes of various nature, acute and chronic forms;
- diseases characterized by metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, siderophilia);
- age-related atrophy;
- consequences of surgical operations.
Determining the causes is very important for proper treatment. Therefore, diagnosis must be comprehensive. First of all, it includes a survey and study of the patient’s medical history, as well as the following types of research:
- Ultrasound;
- urine tests to detect ketone bodies, diastase and glucose;
- general blood analysis;
- biopsy;
- coprogram;
- MRI, CT.
The main diagnostic method is ultrasound. It is with its help that you can determine the type of lesion, the area affected and the stage of development of the disease. Fatty changes in pancreatic tissue are most easily determined using CT.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
Fibrofatty changes in the pancreas are a morphological manifestation of pancreatitis, are not determined by the doctor during an objective examination of the patient, and in most cases do not cause complaints. This is their danger: it is important to promptly identify the process at the stage when the organ can still be saved.
Laboratory
For any pathology of the pancreas, the patient must undergo mandatory laboratory diagnostics:
- general clinical blood test,
- blood sugar,
- biochemical study (diastase, bilirubin, transaminases, total protein and its fractions),
- coprogram
- urine test for sugar, diastase.
Tests must be taken from patients once every 4-6 months. Patients with cystic fibrosis undergo a stool test for coprogram once every 1.5-2 months.
Functional
The simplest, most accessible and safe functional diagnostic method is ultrasound. During ultrasound, the pancreas is diffusely changed and has increased (if fibrosis predominates) or decreased (with lipomatosis) echogenicity . Basically, the changes are moderate and homogeneous, but in the presence of individual areas of fibrosis or the formation of nodes and cysts, this is visualized on the image.
If an older child with cystic fibrosis is examined, ultrasound reveals a large gland, high density of excess connective tissue, cystically dilated excretory ducts and acini. Sometimes the entire pancreas is filled with cysts with echo-negative content. An accessory pancreas and hepatomegaly may be detected. Such patients are additionally subjected to a sweat test to determine sodium and chloride ions in sweat - in cystic fibrosis they are significantly higher than normal.
To exclude pathology of the stomach and duodenum (peptic ulcer), in which secondary pancreatitis often develops, it is necessary to do an endoscopy - esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy.
In unclear cases, more accurate and expensive functional studies are used:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a modern safe method, without the use of ionizing radiation, that has received good feedback from doctors of all specialties involved in the treatment of pancreatic pathology (general practitioners, gastroenterologists, surgeons). It provides an accurate image of all body tissues in any projection (unlike CT) and detects even minor foci of inflammation. There are some limitations for the study: the presence of metal bodies in the cranial cavity, external pacemaker, pregnancy, claustrophobia.
- CT (computed tomography) is a relatively new method of radiation diagnostics, used in cases where MRI is not possible. Provides a layer-by-layer image of any organ or area with slice thicknesses from 0.5 mm to 10 mm. During a CT scan, the patient is exposed to x-ray radiation, so there are certain contraindications for it: pregnancy, childhood, allergy to contrast.
- If a formation is detected in the tissue, a biopsy is performed. It is used for differential diagnostics. The results obtained play a key role in treatment tactics.
Main symptoms
The initial stages of the disease are often asymptomatic, making it difficult to diagnose. However, if the affected areas reach a maximum and an exacerbation of the pathology is brewing, the following symptoms may occur:
- nausea and vomiting;
- sudden weight loss;
- change in appetite;
- flatulence, heartburn;
- change in stool, diarrhea, indigestion;
- yellowing of the skin and sclera;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- bad breath;
- severe pain in the hypochondrium.
Most often, these signs are observed in older people. In the early stages of progression, lipofibromatosis is usually determined using ultrasound diagnostics. Treating the pathology is quite difficult.
Diet for pathology
Nutritional therapy is the basis for the treatment of any pancreatic disease. It is very important to strictly adhere to dietary recommendations, because any errors in the diet can lead to relapses and complications of the disease. Compliance with table No. 5 according to Pevzner should become part of your lifestyle. It is forbidden to eat fried, smoked, salty, fatty foods. It is recommended to cook food by steaming, boiling or baking in the oven. You need to eat often, in small portions. Daily caloric intake during the period of remission should be approximately 2500-3000 kcal.
Recommended products for diet No. 5
Treatment
Therapy for many diseases of the internal gastrointestinal tract requires a special diet and drug or surgical treatment. To speed up the recovery process, as well as to improve the patient’s general condition, you can also use some folk remedies.
Therapy, diffuse organ changes
Fibrolipomatosis is directly treated in two ways: medication or surgery. In the early stages, as a rule, the following types of drugs are used:
- anti-inflammatory (Ibuprofen);
- containing digestive enzymes (Pancreatin, Festal);
- antiemetics (Metoclopramide);
- painkillers (No-Shpa, Mebeverine).
After such therapy, patients’ digestion improves and is restored, and weight loss stops.
If diffuse changes in the pancreas such as fibrolipomatosis affect more than 60% of the total volume of the organ, surgery is prescribed. In this case, the affected areas, abnormal fat and connective tissue are completely removed. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and requires subsequent rehabilitation, adherence to the regimen and a therapeutic diet.
Patients undergoing treatment for fibrolipomatosis should attend preventive examinations with their doctor twice a year.
Diet
Proper dietary nutrition is one of the most important components of treatment. The list of permitted products includes:
- stale bread, crackers;
- vegetables, unsweetened fruits;
- fermented milk products;
- lean meat and seafood;
- cereals;
- steam omelette.
The following foods should not be consumed if you have fibrolipomatosis:
- fatty meats and fish;
- semi-finished products (especially purchased);
- fresh baked goods and white bread;
- sweets and confectionery;
- liver;
- hard and fatty cheeses;
- fatty and sour sauces;
- spicy seasonings;
- canned food;
- smoked meats
These lists may be changed and supplemented due to the individual characteristics of patients. It is important that gastric and pancreatic juice are released in sufficient quantities for digestion, but do not increase inflammatory processes.
Eating food should be done according to the following rules:
- You need to eat in small portions. The number of meals should be about five to six per day.
- Any food needs to be cooked only with water and steam. You can also bake in the oven.
- It is advisable to add as little salt as possible to dishes.
- Food should not be too hot or very cold.
- Mix ingredients carefully during cooking. They must be combined with each other so as not to cause harm to the digestive system.
By adhering to the correct diet after surgery or drug treatment, you can not fear for your life and lead a normal lifestyle.
Folk remedies
It is important to choose the right recipes for traditional medicine. Potentially dangerous or known harmful drugs should not be included in the course of therapy against pancreatitis or fibrolipomatosis.
The following effective recipes are known:
- Infusion of birch buds. Fill a glass of washed raw material to the top with vodka and leave for one month in a dark, cool place. Take the medicine three times a day, one tablespoon at a time.
- Infusion of lilac buds. Pour a tablespoon of the product into a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Take the filtered product one tablespoon three times a day before meals.
- Plantain infusion. Wash and chop a tablespoon of leaves, pour a glass of boiling water and leave for three hours.
- Take the product three times a day before meals, 70 milliliters.
- Collection of medicinal herbs. Mix valerian, nettle, St. John's wort and calendula in equal quantities. Pour one spoonful of the mixture into a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour. You need to drink this glass of infusion in small sips throughout the day.
You can use recipes for traditional methods of therapy only with the permission of the attending physician and only as an auxiliary treatment. In this case, the gland can restore its functions much faster.
Causes of the disease
The main factor that can cause lipomatosis or pancreatic fibrosis is pancreatitis. The replacement of natural tissues with connective or fatty tissue occurs precisely during this disease.
Fibrous changes in the pancreas can occupy most of the organ, it all depends on the duration of the pathological changes. Most often they occur against the background of impaired metabolism (metabolism), the cause of which is:
- Nutritional errors - excessive consumption of fatty, fried, spicy foods.
- Bad habits - alcohol and nicotine have a detrimental effect on the functions of the gland and prevent the release of digestive enzymes into the intestines.
- Injury to the gland can occur during surgery of a neighboring organ, causing the affected cells to be replaced by growing fatty cells.
- Cholelithiasis - calcifications prevent the exit of pancreatic fluid from the main excretory duct of the pancreas, which leads to self-digestion of the organ and replacement of its connective tissue.
- Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease characterized by the accumulation of mucus in the excretory ducts of the gland, which leads to stretching or rupture of their walls and can cause diffuse lipofibrosis (changes evenly distributed throughout all tissues of the organ).
- Intoxication of the body is the result of the presence of a purulent focus on the body, from which pathogenic bacteria penetrate the blood and spread throughout the body. Intoxication can also be caused by alcohol, food or chemical poisoning, and smoking.
- Obesity - poor nutrition and an inactive lifestyle lead to the formation of fat deposits in the body. If fat cells grow near the ducts of the gland, they compress them, which causes stagnation of pancreatic juice.
Lipomatosis, fibrosis and fibrolipomatosis of the gland are dangerous conditions that need to be prevented. Their progression can cause diffuse changes not only in tissues, but also in the excretory ducts of the organ, which can provoke the appearance of tumors, calcifications and cysts.
Traditional methods
It is recommended to use folk remedies only after consulting a doctor.
Here are some useful recipes for fibrolipomatosis:
- Herbal collection. You will need calendula, nettle, St. John's wort, and valerian in equal proportions. 1 tablespoon of the collection is poured with boiling water (200 ml) and infused. Next, the infusion is filtered and drunk in small sips throughout the day. You need to drink it every day for 3 weeks, then take a break for 7-10 days, after which the procedure can be repeated.
- Hemlock tincture. Take 1 drop on the first day, 2 on the next. This continues up to 40 drops. Then the process follows the reverse pattern, that is, 40 drops, then 39 and so on until 1.
- Herbal mixture of fennel, mint, yarrow, immortelle, corn silk, rose hips, valerian root. All herbs in the amount of 2 tablespoons are mixed. Then one spoon of the mixture is poured with boiling water (200 ml) and left for half a day, then drunk in equal parts 3 times a day. Repeat daily for 25-30 days.
Medicines
Medicines cannot cure pancreatic lipomatosis. However, they are able to alleviate the manifestation of symptoms and stop its development.
The following drugs are usually prescribed:
- Daedalon, Cerucal, Metoclopramide. Helps fight vomiting and nausea.
- Ibuprofen, Baralgin, No-spa. Helps reduce pain.
- Loperamide. It is taken when symptoms such as diarrhea occur.
- Mebeverine. Reduces intestinal spasms.
- Mezim and Festal. Normalize the activity of the digestive system.
- Omez, Almagel. Suppresses the aggressive acidic environment of the stomach.
- Pancreatin. Eliminates enzyme deficiency in the body.
These drugs are often recommended to be taken during stage 2 of the disease. All drugs have side effects. If they do not help cope with the disease, then surgery will most likely be required.
Options for diagnosing the disease
If any deviations in general health and signs indicating pancreatic dysfunction occur, you should contact a gastroenterologist. If this is required, you should additionally obtain advice from:
- Surgeon.
- Endocrinologist.
- Oncologist.
After a visual examination, the doctor will prescribe an examination, which includes laboratory and instrumental procedures.
Lab tests
Laboratory tests recommended:
- General blood analysis.
- Blood sugar test.
- Urine analysis for diastasis.
- Studying urine for sugar.
- Coprogram.
What is pathology
To maintain the integrity of the pancreas and maintain its shape, the body includes a so-called “protective reaction.” The dead cells are replaced by adipocytes, or fat cells. This is where lipomatosis, or pancreatic obesity, develops.
The structure of the pancreas
Unfortunately, the regrown tissue cannot properly do the job of the “old” one. Gradually, the organ loses more and more of its native cells and becomes overgrown with fat. This causes disruption of normal processes in the body:
- material metabolism and the process of food digestion are disrupted;
- the general health of the sick person worsens;
- the synthesis of enzymes decreases, which takes an active part in carbohydrate, fat and protein breakdown, etc.
Attention! If the changes in the gland are minor, that is, a small number of cells are replaced, then the person is unlikely to experience any discomfort. He can live with such changes all his life and not even know about the presence of a problem. However, the process of replacing normal cells with fat cells often gets out of control. New tissue begins to gradually grow, forming large fatty areas.
Pancreatic lipomatosis
Preventive measures
The prognosis for treatment of lipofibrosis largely depends on the initial data about the disease. If you follow all the recommendations and diet suggested by your doctor, it is possible to lead a full life with a low risk of relapse and lifelong use of medications.
We also recommend viewing: Treatment methods for pancreatic diseases
In order to minimize the likelihood of pancreatitis and fibrosis, the following basic recommendations should be used:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- create a diet based on the principles of a healthy diet;
- give up fast food and heavy meals;
- avoid stressful situations and depression;
- Take enough vitamins and minerals daily with food or in tablet form;
- Take feasible physical activity every day.
Important: If pancreatitis occurs, it is necessary to undergo systematic examinations by a gastroenterologist in order to prevent possible complications of the pathology.
Symptoms
The symptoms of fibrosis are quite varied and largely depend on the cause of its occurrence. It is very important to notice their occurrence in time, since the sooner treatment for this disease begins, the lower the risk of complications arising from it.
In cases where fibrotic changes in the pancreatic parenchyma occurred against the background of acute pathological processes in the gland, the clinical picture most often includes:
- vomiting that occurs after eating food;
- pain in the epigastric region of a girdling nature;
- changes in the characteristics of feces (it takes on a grayish tint, contains lumps of undigested food and fat, which gives it an unnatural shine);
- diarrhea.
The main signs of the development of pancreatic fibrosis are intestinal disorders. Carefully inspect the stool after defecation. A change in its character is the first symptom of the onset of pathology
If the development of this disease occurs as a result of long-term chronic pathological processes in the gland (for example, with pancreatitis), then in this case the symptoms may be erased. The symptoms are mild and occur at regular intervals. The most frequently noted among them are:
- bloating;
- decreased appetite (an aversion to certain foods may appear);
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- weight loss;
- dull and aching pain in the left hypochondrium.
Diffuse fibrosis has no specific symptoms. Most often, the symptoms that arise during its development are confused with pancreatitis. But to make an accurate diagnosis, you will need to undergo a full examination.
Nutrition for lipomatosis
Many products, by their structure and type, help the pancreas to function fully, preventing the development of diffuse changes.
The most useful products for lipomatosis are:
- Sea kale – cleanses the gastrointestinal tract and improves digestion. It is saturated with many useful microelements: iodine, calcium, iron, potassium.
- Apple – helps remove toxins from the body.
- Kiwi contains vitamin C, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium and substances involved in insulin metabolism.
- Orange, lemon, lime, pomegranate are sources of potassium, calcium, as well as vitamins A, B, C.
- Walnuts improve digestion.
- From cereals - millet, buckwheat and oatmeal. Contains vitamin B and essential microelements.
- Pasta is made only from durum wheat.
- Meat products (chicken, beef, veal), fish (pike perch, perch), seafood (squid).
- Fermented milk products: fermented baked milk, kefir, yogurt.
But there are not only foods that promote the functioning of the pancreas, but also those that adversely affect it. In case of lymphatosis, their use should be limited as much as possible.
These products include:
- Sugar (including carbonated drinks and juices saturated with it) and baked goods. These foods, when consumed in excess, contribute to the development of diabetes.
- Alcohol, in particular beer, provokes a narrowing of blood vessels.
- Table salt leads to fluid stagnation in the body, increasing blood pressure.
- Smoked sausages and sausages worsen the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Mayonnaise, vinegar, marinade and various sauces negatively affect the digestive system.
When drawing up a diet, you must be guided by the specified list of products, including them in your diet and wisely distributing calories. There are many variations of diets that you can follow.
Menu example:
- Breakfast. Any porridge to which you can add fruit.
- Snack. It should be light, such as crackers or carrot salad.
- Dinner. The first is soup without frying; second – stewed vegetables; dessert – walnuts.
- Dinner. Durum wheat pasta with chicken or fish. An alternative is an egg omelet.
- Drinks: fruit drink, tea without sugar, regular filtered water at room temperature.
The third stage of lipomatosis - features
At stage 3, the weight of adipose tissue is 60% of the total mass of the organ. The patient's condition deteriorates significantly, and disturbances occur throughout the body. The distribution of adipose tissue plays an important role - they are concentrated in one place or distributed throughout the organ.
After the examination, it is likely that the specialist will diagnose the presence of a tumor.