Types of diffusion
In a healthy state, the pancreas has a homogeneous structure; during examination, the contours of the organ, the uncinate process, the standard dimensions of the tail and head, and the correct location are clearly visible. Diffusion can occur in the form of an increase or decrease in density, often combined with an increase/decrease in the size of the gland and its individual parts. There are four main types of such processes:
- a decrease in density level combined with an increase in size;
- a similar process while maintaining the normal size;
- an increase in density when the dimensions remain normal;
- compaction while maintaining the usual dimensional characteristics or increasing them.
On ultrasound, a decrease in density is manifested by a decrease in echogenicity and, on the contrary, compaction leads to an increase in the ability to reflect sound.
Sources of pathogenesis
With the listed transformation options, the pancreas reacts to inflammatory processes; its tissue structure can be evenly compacted in various types of pancreatitis and a number of other diseases. The list may consist of:
To treat gastrointestinal diseases, people successfully use Galina Savinova’s method. Read more >>>
- acute pancreatitis;
- its chronic variety;
- diabetes mellitus;
- fibrosis.
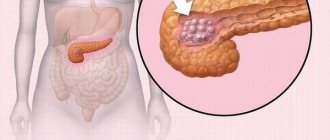
Focal compactions can appear when oncology of the formations of the main body, head or tail of the pancreas occurs.
Acute pancreatitis
Occurs due to stagnation of pancreatic juice inside the organ. The cellular structure is destroyed and scarred, which leads to a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition, with pronounced signs of intoxication. The pathology is accompanied by an increase in the size of the pancreas and a decrease in the density of the walls. The disease is extremely dangerous and can be fatal, in which case immediate hospitalization and surgical intervention are required.
Chronic pancreatitis
More often it is reactive in nature, as a reaction to pathologies of the duodenum, gall bladder, and liver. Accompanied by severe pain after eating fried or excessively fatty foods. Analyzes show an increase in the content of enzymes in the urine and blood, and an abundance of undigested fats in the feces. The gland retains its normal size, but its density decreases.
Diabetes
In diabetes mellitus, a thickened pancreas may result from the replacement of the cellular structure with fatty tissue. This variant of the pathology is called lipomatosis and is typical for people who have reached old age. Usually it does not manifest itself with any symptoms and proceeds unnoticed by the patient. In this case, no special treatment is carried out.
Consolidation due to fibrosis
In this disease, changes in density are caused by the growth of connective tissue in the structure of the organ. Most often it is a consequence of acute pancreatitis or metabolic disorders. Compaction is combined with reduction in size. Treatment is only necessary in situations where dysfunction occurs; in other situations, no special therapy is required.
Other factors
The list of factors affecting the structure of the pancreas is not limited to the listed pathologies. The risk group may include other diseases that provoke degenerative tissue transformations:
- endocrine system problems;
- circulatory disorders;
- gastrointestinal tract.
In rare cases, such transformations occur during the development of the body in childhood or adolescence, mainly under the influence of heredity.
Reasons for changes
The parenchyma of the gland during ultrasound diagnostics has a heterogeneous consistency. In inflammatory diseases, signs of diffuse changes in the parenchyma are clearly visible. The following factors lead to a modified pancreatic structure:
- Pancreatitis and proliferative diseases of the body. The pathology of the pancreas depends on the malfunction of the organ. During an attack of the acute form, the alteration causes swelling of the cells, which initiates the transformation of parenchymal tissue. The chronic process is caused by the constant slow destruction of glandular tissue. It is replaced by fatty or connective components. Defective proliferation of adipose tissue is called pancreatic lipomatosis. Numerous lipomas displace organ cells.
- Diabetes mellitus and any metabolic failure (cystic fibrosis, obesity, nutritional dystrophy and others). Disturbances in the biochemical transformations of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and other elements lead to insufficient nutrition and supply of organ cells, including parenchyma cells.
- Diseases of the liver and bile ducts. The liver is also a parenchymal organ. The tissues are lined with glandular epithelium, the cells of which are called hepatocytes. They are formed from cells that produce bile. The common duct leading to the stomach forms the pancreas and bile ducts. The activities of these bodies are coordinated. And the nature of diffuse disturbances in the structure of the parenchyma occurs simultaneously in the liver and pancreas. Gallbladder diseases and cholecystitis will become a factor in changes in parenchyma cells.
- Tumors of a malignant or benign nature. A growing tumor compresses nearby gland cells. Blood flow is disrupted and necrosis, tissue death, occurs.
- Heredity.
- Surgical interventions performed on abdominal organs.
- Chronic vascular diseases and heart disease.
- Infections.
pancreatitis of the pancreas
The causes of diffuse changes are external influences that correlate with a person’s wrong creed:
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- irrational use of drugs and a large number of toxic agents;
- harmful working conditions associated with poisons and chemicals;
- fried and fatty foods, smoked foods, spicy and salty foods;
- irregular meals with large amounts of food.
And also the presence of diffuse changes occurs in old age and old age due to a decrease in the functions of the pancreas.
Possible consequences
Unfortunately, not in all cases, changes in pancreatic tissue are without consequences. They are often followed by serious functional disorders, which can manifest themselves in disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract and the development of necrosis. The organ becomes susceptible to frequent inflammation, which can cause:
- gastritis;
- oncology;
- calcination;
- atrophy;
- scarring of the inner surface.
Attacks of chronic pancreatitis occur more often. If such complications occur, hospital treatment will be required, and in particularly difficult situations, surgical intervention.
Symptoms of complications
Often, pathological changes are asymptomatic, the patient does not experience serious discomfort, and there are no complaints about the condition of the body. However, when complications arise, the situation changes dramatically. Processes associated with compaction may manifest themselves with symptoms characteristic of concomitant diseases:
- acute pain under the ribs or under the shoulder blade;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- frequent urge to vomit.
The body's reactions may be different, their list depends on the characteristics of physiology. But in any case, they require immediate assistance from a specialist.
Tissue compaction
Thickening of the pancreas is a consequence of a previous illness, which can sometimes indicate the presence of an infection in the body. It is characterized by a change in the thickness of the organ tissue on the inside. When an inflammatory process occurs in the gland, it leaves traces in the form of “depressions” in the wall; later they heal and turn into scars - this is a compaction.
Location of the gastrointestinal tract organs
Diagnostic methods
The main diagnostic procedure in this case remains an ultrasound examination of the patient. The criterion for the condition of an organ is its echogenicity; with an increase in density, ultrasound results will show an increase in the ability to reflect sound; with a decrease, the echogenicity decreases. As a rule, diagnosing only the pancreas is not enough; the doctor conducts an examination of all organs of the digestive system. The following are used as additional diagnostic procedures:
- biochemical blood test, which will reveal the degree of damage to functions;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy or FGS at the site where the ducts exit into the duodenum;
- general analysis for the presence of inflammatory processes;
- endoscopic examination to identify pathologies of the duodenal mucosa.
Interviewing and examining the patient plays an important role in making a diagnosis, therefore, from the moment the first symptoms appear, it is necessary to monitor your own condition and record the slightest deterioration. All this can affect the diagnosis, and therefore the effectiveness of treatment.
Treatment options
In itself, compaction of the pancreas does not require treatment; drug or surgical intervention is necessary to eliminate the causes of pathological changes, especially if there is a threat or presence of complications. In most situations, timely treatment begins with a positive result (90%), diffuse processes stop, and affected functions are restored. The primary therapeutic measure is usually fasting, which reduces the secretion of pancreatic juice. Excessive production of enzymes is reduced by the use of medications (Contrical, Trasylol).
Diagnosis of pancreatic diseases
Symptoms of diffuse changes in the pancreas . When examining the patient, the doctor makes a conclusion which part of the gland is damaged. Gland diseases can also be determined by laboratory test results. Diagnosis of the pancreas is problematic due to its deep location. Its shape and condition can be determined using ultrasound.
An ultrasound examination prescribed by a specialist doctor allows one to determine the parameters of the gland in its different parts, the density of the organ’s tissues, its homogeneity, which allows us to talk about the diffusion of the pancreas, about its malignant lesions, which are called diffuse changes. The pancreas is closely related to the gallbladder and liver; the disease of one of these organs directly affects the work of the other two.
Why does a lump appear in the pancreas?
The main reasons for the formation of seals on the walls of the pancreas are all kinds of degenerative disorders in its tissues. Often, such deviations occur when the usual rate of blood flow is disrupted, and there are also diseases of the endocrine system in a chronic form, which are provoked by the negative influence of the environment. In some cases, seals may appear on the walls of the pancreas during the formation of the body, although this is quite rare and this phenomenon is observed only in patients of childhood and adolescence.
Such diffuse changes in the pancreas are most often detected during an ultrasound examination. The main factors that can provoke this disease are improper functioning of the endocrine system and irregular nutrition of the patient, although there are also manifestations of the disease associated with the continuity or impaired functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. In both situations, only a qualified doctor can accurately determine whether there is a seal on the walls of the organ.
We also recommend viewing: Pancreatic cancer: treatment methods
Causes of diffuse changes
Signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas are its enlargement, thickening, inflammation, and scarring. There are many reasons for this:
- Chronic stress, bad habits, poor lifestyle.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Genetic predisposition. Very often the disease is transmitted to children from parents
- Painful condition of the biliary tract.
- Unbalanced nutrition and metabolic disorders.
- Acute pancreatitis.
- Diabetes.
- Stomach diseases.
- Overdose of medications.
- Age-related changes.
Reasons for deviations
If during ultrasound examination the pancreas is compacted, this indicates a chronic inflammatory process in it. The most common cause of the development of compactions is pancreatitis. In acute cases, they form in the area of the lesion after recovery; in chronic cases, the development of compactions can be observed throughout life.
The more pancreatic tissue is affected and overgrown with connective tissue fibers, the worse the blood flow. Consequently, due to lack of nutrition, healthy cells die, and in their place necrosis and a new inflammatory process occur.
The formation of compactions in the pancreas is promoted by:
- eating disorders, fatty fried foods;
- bad habits, especially alcohol;
- hypothermia;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- hazardous industries, environmental pollution;
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic infections, etc.
Signs of diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma
Treatment of diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas . For all diseases accompanied by changes in the pancreas, the initial stage is almost the same. This is a loss of appetite, periodic pain, nausea, heaviness in the stomach, diarrhea or constipation. It has already been said that diffuse changes are not an independent diagnosis, but an accompaniment of any disease, here are some of them:
Acute pancreatitis . In this case, the disease in the ducts increases the pressure, which leads to a violation of the integrity, and food enzymes, leaving through the tissues, decompose and poison the body. The patient experiences sharp pain under the ribs, nausea, and dizziness due to a decrease in pressure. Intensive therapy is urgently needed. In advanced cases, only surgical intervention will help.
Chronic pancreatitis . This disease progresses slowly and the patient gets used to periodic pain. At the initial stage, the gland becomes inflamed and increases in size. Then gradually sclerosis of the organ sets in and it becomes smaller. The pancreas is diffusely heterogeneous. The production of digestive enzymes is disrupted.
Lipomatosis . Only ultrasound can detect this disease. This disease is either genetic or age-related. In this case, the pancreas becomes smaller, and fat cells begin to take up the free space. This process is irreversible. In the first stages, no special symptoms are observed. Over time, when the organ becomes swollen with fat and compresses the parenchyma, painful sensations occur.
Fibrosis . This is a disease when, during the inflammatory process, the gland tissues turn into connective tissue, become scarred and are unable to produce sufficient amounts of hormones and enzymes. Metabolism is disrupted. There is a malfunction throughout the body. The patient experiences rapid weight loss, frequent vomiting and diarrhea. Fibrosis is the first step to diabetes.
If an ultrasound examination reveals diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the pancreas, such as inflammation, thickening, enlargement, to find out the cause, you must begin treatment immediately.
With the uneven nature of the disease, sclerosis of the gland, cysts and tumors are formed. This mainly concerns the parenchyma of the gland. Delaying the treatment of such diseases is unacceptable.
Diffuse reactive changes in the pancreas
These are secondary changes against the background of diseases of other neighboring organs, for example, diseases of the stomach, liver or biliary tract. These organs are not easily located next to each other; they are interconnected, and failure of one organ leads to illness in another.
Diffuse focal changes in the pancreas
These changes indicate that the cause of the change in the structure of the gland is a new formation in the form of stones, cysts or tumors. These problems require immediate diagnosis and surgery.
Diffuse fibrotic changes in the pancreas
This is a compaction in the form of scarring of connective tissue. They appear after suffering from chronic, inflammatory diseases, alcohol, and drug intoxication. Ultrasound clearly shows tissue compactions, increased echogenicity, and a diffusely heterogeneous structure of the pancreas.
Also, with fibrotic changes, the development of a benign fibroma tumor is possible. In the initial stages of development, fibroma does not cause pain or discomfort. It grows slowly and does not metastasize. At later stages, symptoms of jaundice, nausea, and vomiting appear due to compression of other organs, such as the bile duct or duodenum.
Treatment of diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma at the initial stage can be done with medication and diet. Larger fibroids require surgery.
Diffuse dystrophic changes in the pancreas and tail
Lipodystrophy, death of organ cells in a number of diseases. The body cannot restore lost cells and is replaced with fat cells. This is an irreversible process. There are no obvious symptoms for this disease; ultrasound will help establish the diagnosis.
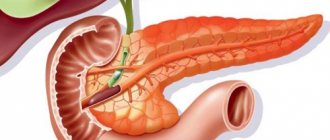
The pancreas consists of a head, body and tail. The tail has a narrowed shape, raised up and closely adjacent to the spleen. The tail contains the excretory duct. When the disease occurs, the tail can expand and its structure becomes denser; this occurs as a result of a violation of the patency of the splenic vein.
Symptoms of the disease
Since the causes of compaction formation can be different, the symptoms of diffuse changes directly depend on the underlying disease.
Acute pancreatitis is characterized by increased pressure in the Wirsung duct of the pancreas; as a result, the duct is damaged and digestive enzymes leak into the nearby integument. This leads to the beginning of digestion and destruction of pancreatic tissue, resulting in intoxication of the body. In this case, symptoms that are characteristic of the formation of pancreatitis appear, such as severe pain in the left hypochondrium, nausea and vomiting, decreased blood pressure, and increased heart rate.
Important. A patient with this disease often has a serious condition throughout the entire attack. Intensive therapy and surgery are required.
With chronic pancreatitis, a protracted course of the disease is visible, and at the beginning of development in the pancreas, only minor hemorrhages and swelling can be noticed. Over time, the organ becomes smaller, becomes sclerotic, and stops producing digestive enzymes in the required volume.
As a result, you can notice the development of symptoms characteristic of disruption of the digestive system:
- appetite worsens;
- there is heaviness in the stomach all the time;
- You may notice constipation and diarrhea appear alternately.
In the future, as the disease progresses, you can notice how exacerbations of pancreatitis become more frequent, occurring in a chronic form, which accompany severe painful sensations.
If a patient has pancreatic fibrosis at an early stage, there may be no clinical manifestations of the disease. During the fibrotic inflammatory process, the glandular tissue of the organ is replaced by connective tissue, which leads to a decrease in the production of enzymes and hormones that are necessary for the digestive system to function normally and to maintain the body’s metabolic processes. These include lipase, lactase, amylase and hormones, thanks to which sugar is broken down and absorbed (glucagon and insulin).
The initial symptoms of the disease are similar to those of pancreatitis: there is constant pain in the left hypochondrium, loss of appetite, and the urge to vomit. As enzyme deficiency increases, frequent diarrhea and vomiting appear, and weight loss occurs. Over time, when protein reserves in the body are depleted, an allergic reaction occurs, and when insulin production is disrupted, diabetes mellitus begins to form.
We also recommend viewing: How you can check the pancreas, what tests are needed
If a patient has pancreatic lipomatosis, then healthy cells are irreversibly replaced by adipose tissue. Due to the inability of fat cells to perform digestive functions, the body develops a deficiency of substances that are necessary for the normal functioning of the digestive system.
How severe the symptoms of lipomatosis will be depends on the degree to which healthy tissue is replaced by fat cells. If the pathological focus of the disease spreads slightly, then symptoms may be absent due to compensation of enzymatic deficiency by increased production of the necessary enzymes by other organs. However, when the disease progresses uncontrollably, a significant amount of healthy cells die and are replaced by massive accumulations of fatty tissue. The affected areas begin to compress the pancreatic parenchyma, resulting in pain and impaired organ function.
The degree of diffuse changes in the pancreas
The changes are divided into four degrees according to the form of manifestation and the doctor can prescribe treatment only after an ultrasound examination, supported by test results. Let's take a closer look at these changes.
Minor diffuse changes
These changes in the pancreas occur as a result of past inflammatory diseases, emotional stress and overeating.
You don’t have to worry too much, you just need to improve your psycho-emotional state and stick to your diet. Eliminate fatty, smoked, and alcohol-containing foods from your menu.
Moderate diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma
Moderate diffuse changes in the pancreas. The doctor makes this diagnosis if the organ is enlarged and there are no seals. This can happen with inflammatory diseases, diseases of the gallbladder and duodenum. The digestion of fatty foods is disrupted, pancreatic juices are secreted in insufficient quantities, the parenchyma is replaced by adipose tissue.
Unexpressed and pronounced diffuse changes
Unexpressed changes are typical for diabetics and the elderly, in people with stomach and heart diseases. They do not affect the activity of the pancreas.
Pronounced changes indicate a pathological process in the body , which is accompanied by severe pain, diarrhea and vomiting. The patient must be urgently examined and treated surgically in serious cases.
What is pancreatic tissue compaction?
The parenchyma of the pancreas consists of glandular tissue and ducts that gather into the main one, which opens into the duodenum. The gland is enclosed in a capsule and on ultrasound appears as a relatively homogeneous formation, anterior to the great vessels and the spinal column. In a longitudinal scan, you can see tubular formations - ducts.
Damages to pancreatic tissue caused by the inflammatory process cause changes in the homogeneity of the structure. Here you can find:
- foci of inflammation;
- cystic formations;
- tumors;
- calcifications and stones.
Diet for diffuse changes in the pancreas
With diseases of the pancreas, food intake becomes not only nutrition, but also treatment . In the first three days of exacerbation of the disease, it is better to refuse food altogether and drink only warm boiled water. The diet is selected by the attending physician individually for each patient.
General recommendations are to strictly adhere to the diet; you need to eat meals in small portions, at least five times a day. Food and drink should be warm. Completely exclude fried, fatty, hot, salty, spicy foods from your diet. A variety of pureed soups, porridges, lean fish and meats, boiled or steamed, are welcome. Eliminate tea and coffee from the diet, replace with dried fruit or rosehip compote, milk.
Prevention of pancreatic inflammation
A chronic disease is called chronic because it will haunt a person all his life, but he has the power to learn to live with this disease in peace. With long-term remission, each chronic disease practically does not bother the patient.
The best prevention of chronic inflammation of the pancreas is diet . No medicine in the world can prevent exacerbation of pancreatitis if the diet is not followed. The severity of the diet should depend on the characteristics of the disease, for example, for some it will be enough to exclude the most fatty and spicy foods from the diet, while for others, after eating two or three nuts, another acute attack of inflammation of the pancreas will occur. So the severity of the diet should be selected exclusively individually. However, there are common foods that should not be consumed not only by those suffering from inflammation of the pancreas, but also by absolutely healthy people. So, smoking, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, strong coffee and tea, as well as consumption of fatty, fried, smoked and spicy foods may well provoke attacks of pancreatitis. The pancreas, like all vital organs, does not like foods that provoke the development of obesity .
To prevent exacerbation of pancreatitis, traditional healers recommend eating of cranberries (maybe with honey) before meals 3 times a day. infusions of dried blueberry leaves to prevent exacerbations . You need 1 tbsp. pour 500 ml of leaves. water and bring to a boil. Then let the medicine brew, strain and take ½ cup 30 minutes before meals for 2 weeks. For prolonged illness an infusion of plantain leaves ; it should be brewed like tea - 1 tsp. dry plantain pour a glass of boiling water. This treatment is good not only for the pancreas, but also for the liver and kidneys.
Diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma
The pancreas is a large organ of internal and external secretion. It is located on the posterior abdominal wall in the retroperitoneal zone, consists of a head, body, tail, and is partially covered in front by the stomach. In the thickness of the pancreas there is a duct directed from the tail to the head. The gland produces pancreatic juice, which contains enzymes that help digest proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
The pancreas tissue contains endocrine glands that produce insulin for the absorption of glucose. A healthy pancreas has homogeneous tissue and large contours. The cause of diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the pancreas, according to doctors, is acute and chronic pancreatitis and elevated blood sugar levels.
Often, diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma are diagnosed in elderly people with various problems of the cardiovascular system, diseases of the liver and biliary tract, and digestive tract organs. The cause of changes in the parenchyma of the pancreas can also be infectious and inflammatory diseases of internal organs that contribute to metabolic disorders.
Increased echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma
When performing ultrasound diagnostics, you can find out the density of internal organs. If decreased or increased echogenicity of the pancreas is detected, then this is a serious reason to undergo an extensive examination, providing an accurate diagnosis and determining methods for eliminating problems.
Increased echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma is detected during inflammation with the formation of fibrosis, which develops against the background of metabolic disorders, when healthy parenchyma tissue is replaced by fat, during acute pancreatitis and relapse of chronic inflammation that changes the density of the parenchyma.
The absorption coefficient of ultrasonic radiation depends on the increased echogenicity of the parenchyma. Malignant tumors that form in the parenchyma have a higher absorption coefficient of ultrasonic energy than benign tumors.
Consolidation of the pancreatic parenchyma
Methods for studying the parenchyma of the pancreas include questioning and examination of the patient, laboratory, instrumental and radiological methods. Compaction of the parenchyma can be a consequence of various diseases of the pancreas.
Symptoms include pain in the epigastric region and left hypochondrium, disorders of the digestive system that cause a person to feel discomfort, general weakness, and severe weight loss. The appearance of compaction of the parenchyma of an organ has a certain influence on the diet and nature of nutrition, the presence of cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, and cystic fibrosis.
Folk recipes
I would like to share the folk recipe “Ural chatterbox”. This folk remedy helps cleanse the liver, gall bladder, kidneys, pancreas, spleen and the entire digestive tract.
- 300g natural honey
- 6 raw eggs
- 1.5 liters of raw cow's milk
- Pour honey into a three-liter jar, carefully place washed and towel-dried eggs on top, pour in milk.
- Tie the jar with gauze and place it like dough in a warm place for two weeks. During the process, the honey will dissolve, the shell will too, a thin film will remain, the eggs will float to the surface and increase in size. This means the chatterbox is ready.
- There is no need to skim off the heavy cream from the surface. Drain the entire contents of the jar into a colander with gauze. Pierce the eggs and let the liquid drain out. Wait about twenty minutes until all the liquid drains into the pan. Discard the cottage cheese and hard parts of the egg.
- Strain the product through cheesecloth. You should get 1.5 liters. Pour into a bottle and store in the refrigerator.
Take the product once a day, 50 grams in the morning on an empty stomach. The course of treatment is 1.5 liters. Repeat treatment twice a year, preferably in spring and autumn. Do it and be healthy!
Prescribing an ultrasound for diffuse changes in the pancreas helps to see the heterogeneity of the structure of the affected organ. To clarify the diagnosis, the results of other examinations of the body are necessary. A thorough history taking allows you to get a clear picture of the pathological process and prescribe the correct treatment.
Normally, pancreatic tissue is a homogeneous substance. Changes in density, size and other anomalies of the organ (especially if they are very pronounced) indicate the development of pathology. It is necessary to restore the normal functioning of the affected organ.
The first manifestations of the disease
The signs of reactive pancreatitis in children are practically no different from the symptoms of the disease in adults. The development of the pathological process is accompanied by severe pain in the epigastric region. The clinical picture is complemented by nausea and stool disturbances. Attacks of diarrhea are replaced by constipation. With diarrhea, the stool is liquid, and the feces are covered with a shiny coating. Children often complain of dry mouth and extreme thirst. Appetite worsens, and some babies refuse to eat altogether.
The disease is often accompanied by symptoms of general malaise. The child becomes lethargic and apathetic, loses interest in everything that is happening. He constantly wants to sleep, and the high temperature does not allow him to do his usual activities.
The severity of the symptoms of the disease depends on the age of the patient. The older the child, the stronger the signs of the disease appear. In newborns, abdominal pain is expressed by moodiness and increased motor activity. Reactive pancreatitis in young children is also accompanied by severe discomfort in the navel area. However, they cannot show the exact location of the pain. Older children usually complain of severe nausea and vomiting. All of the above symptoms may warrant immediate consultation with a doctor.
Understanding the mechanisms of pathology
Diffusion is translated from Latin as “interaction.” Diffuse change is characterized by the process of replacing some cells of an organ or structure with others. This means that sick cells begin to be located next to healthy cells, provoking the development of a pathological phenomenon.
Diffuse changes in the pancreas are as follows:
- Pronounced echogenicity. In this case, there is no change in the size of the organ. In this case, diffuse changes in the pancreas develop according to the type of lipomatosis, i.e., the growth of normal tissue into lipid tissue. Neglect of the process leads to complete blocking of the parenchyma with fat.
- The echo density is reduced, the pancreas is diffusely heterogeneous, the size is moderately increased. Acute inflammation develops due to impaired excretion of digestive enzymes. As a result, self-digestion occurs, swelling of the organ occurs, and its parenchyma changes. Can be detected in children with malnutrition.
- Reducing echo density, echogenicity, maintaining size. Similar phenomena occur in chronic pancreatitis. Typically, the reasons for its development are due to degenerative metabolic processes in relation to lipids. Sometimes, twisting of the pancreatic juice excretory duct is detected.
- Echoscopic defects. They manifest themselves in a disorder of the density of the echostructure (for example, compaction of the pancreas can be detected), replacement of cells with fat cells. Characteristic in the presence of diabetes mellitus.
- Echographic pathologies. They manifest themselves in increased echogenicity, increased echo density, no changes in size (or a slight decrease). These deviations may be symptoms of fibrosis, in which organ tissue is replaced by connective tissue. The defect is caused by inflammation or digestive disorders.
- Irreversible diffuse dystrophic changes. There are no characteristic signs of the disease. The development of the pathological process is moderate.
- Increased echogenicity of the organ. Occurs with the development of a pseudocyst or abscess.
- Heterogeneous diffuse changes that characterize the echostructure. They are a sign of mixing areas.
All of the indicated echo signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas, in addition to ultrasound, require analysis of biological materials (blood, urine) and additional diagnostic procedures. Only a complete history will help cope with a disease that has changed the normal functioning of an organ.
Ultrasound of the pancreas in acute pancreatitis
The pancreas of a healthy person has a homogeneous structure, equal echogenicity, clearly visible contours, an uncinate process, correct position and normal dimensions of the head and tail. Deviation from the norm is determined by an increase in the size of individual parts of the pancreas and the heterogeneity of the structure of its tissues.
Diffuse heterogeneous changes can be caused by edema, inflammation and the formation of pseudocysts. Reactive changes in the parenchyma are a consequence of inflammation of the pancreas due to the aggressive effect of the liver and gallbladder on it.
The parenchyma of the thyroid gland is the epithelial functional tissue of the organ, containing actively dividing cells. Similar transformations in tissue can occur due to age, with diseases of both the pancreas and other organs.
Uniform transformations of pancreatic parenchyma tissue can be caused by a number of diseases. The structure of the gland during such transformations is homogeneous. The development of such transformations signals diseases of organs directly connected to the pancreas. Diffuse changes in the pancreas are reactive, that is, secondary in nature, and occur as a reaction of the gland to a disease of neighboring organs.
The main reasons for compaction of the pancreas are various dystrophic changes in the structure of its tissues. In this case, the ultrasound data are described as moderate changes in the pancreas. The presence of such changes indicates a decrease in the size of the pancreas or a thickening of the structure of its tissues.
This diagnosis can be made by a medical specialist after the patient undergoes an ultrasound and a number of other examinations. Such changes may indicate the presence of any disorders in the body.
In the presence of an inflammatory process or a previous disease, the pancreas may undergo various functional changes. They are expressed as follows:
Chronic pancreatitis is an ongoing inflammation that can be characterized by fairly slow damage to the entire tissue. Over time, atrophy may occur and the tissue may calcify or even die. Hardening of the pancreas is associated with scarring of the organ from the inside. The more often relapses occur, the denser the walls of the pancreas become. Acute pancreatitis can provoke necrosis of areas of pancreatic tissue. When the disease is detected on time and treatment is carried out correctly, the inflammatory process is eliminated, and at the site of inflammation, compactions of various locations may appear, which are caused by scarring of the tissue.
Causes of pathology
Diffuse changes in the structure of the pancreas can be caused by various factors. The most common reasons:
- drug and alcohol addiction;
- nutritional disorder: the prevalence of fatty, floury, salty, sweet and spicy dishes in the menu (often changes in the pancreas in a child are caused by the consumption of chips, kirieshki, foods with dyes);
- hereditary burden;
- frequent stressful situations;
- chronic pathologies of the digestive system;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- age-related changes.
Therapeutic methods
Treatment of compaction in the pancreas is determined by the severity and severity of the disease. Typically, the doctor prescribes two types of therapy.
Treatment with drugs
Therapeutic measures are prescribed depending on what disease provoked the formation of seals. The goal is to eliminate the symptoms of the disease. For example, when disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas appear due to pancreatitis, the doctor prescribes an appointment:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain;
- antispasmodics to relax muscles in the ducts of the organ and eliminate spasms;
- enzymatic medications to eliminate the urge to vomit and diarrhea;
- vitamin preparations.
We also recommend viewing: Reactive pancreatitis in children: symptoms and treatment
When lumps appear in the pancreas due to diabetes, additional medications are prescribed to help lower glucose levels in the bloodstream. It should be noted that self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Manifestations of diffuse disorders
Vivid or unexpressed diffuse changes always manifest themselves as symptoms of the underlying disease. Frequent complaints with which a person turns to their doctor for acute pancreatitis include:
- feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region;
- changes in stool;
- painful sensations on the left behind the sternum;
- nausea, sometimes ending in vomiting;
- increased heart rate;
- decrease in blood pressure.
If these symptoms occur, the patient should be hospitalized for further treatment.
Chronic pancreatitis is initially characterized by the appearance of swelling of the organ and hemorrhages in its tissue. In the absence of medical intervention, dystrophy turns into atrophy, which is manifested by a decrease in the size of the gland.
At the same time, the parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue, and the production of digestive enzymes ceases.
With fibrosis, connective tissue grows and there is a lack of production of hormonal and enzymatic substances. The initial period of development of the pathology is manifested by minor symptoms that are similar to the onset of the inflammatory process. Ultrasound can reveal moderate diffuse changes in the pancreas.
Clinical manifestations
The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of pain, which can vary in intensity and location. This depends on the nature and topography of the pathological process.
Thus, damage to the body leads to pain in the epigastrium, damage to the head is manifested by pain in the right hypochondrium, and pathology of the tail usually leads to pain in the left hypochondrium.
In addition to pain, other clinical signs appear:
- nausea and vomiting;
- weakness;
- drop in blood pressure;
- bowel dysfunction - constipation or diarrhea;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- belching, etc.
Necessary diagnostic procedures
The primary detection of structural abnormalities of the pancreas occurs during ultrasound examination. Thanks to it, changes in the density, structure of organ tissue, and areas of the inflammatory process are revealed.
Ultrasound allows you to assess the size of the organ, the condition of the ducts, and the presence of tumors.
Additional methods of examining the patient include:
- detailed medical history;
- inspection and palpation;
- use of instrumental methods.
The latter includes a general analysis, blood biochemistry, endoscopic examination of the organ, and urine. Computed tomography and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) may also be prescribed.
Consequences and complications after detection of pancreatic lumps
All deviations from the norm (with the exception of neoplasms, cysts, pseudocysts, calcifications) detected by ultrasound of the pancreas are morphological. Based on them, it is impossible to make a diagnosis, prescribe treatment and make a prediction about further consequences or complications. Detection of compactions is an initial stage that can be continued to identify other changes through additional research methods, or should be a reason to give up bad habits and change your lifestyle with the right diet and diet. Usually, further dynamic observation and ultrasound control are necessary, as well as timely consultation with a doctor at the first symptoms of deterioration in health.
Bibliography
- Drobakha I.V., Yakusheva L.V., Malysheva T.F., Chavgun L.B. Ultrasound examinations in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. Congress of the Association of Ultrasound Diagnostics in Medicine, abstracts. M., 1995, p. 82.
- Lemeshko, Z. A. Ultrasound diagnosis of gastric diseases. M. GEOTAR-Media, 2009
- Maev, I.V. Ultrasound diagnosis of diseases of the digestive system. Tutorial. Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation. M. Federal State Educational Institution VUNMC Roszdrav, 2005
- Fedoruk, A.M. Ultrasonography in the diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis. Minsk, 2005
- Mitkov V.V. Doppler ultrasonography of celiac blood flow is normal. Ultrasound and functional diagnostics 2001 No. 1 pp. 53–61.
Source
If symptoms of disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract are detected, you should remember that only a highly qualified doctor can diagnose the disease. Although he will not be able to detect a lump in the pancreas with the help of visual inspection and palpation alone. To ensure an accurate diagnosis, certain tests and examinations are carried out to help determine what is actually happening in the patient's body.
When palpating the peritoneum, it is felt that a small area of the pancreas is denser than the rest, but to some extent this is the norm, since the layers are uneven, and a slight deviation is considered quite acceptable.
A more detailed diagnosis shows how serious the diffuse compaction on the walls of the organ is. In addition, a thorough examination makes it possible to find out why disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas occurred.
Therapeutic measures
Diffuse changes in the pancreas without treatment can develop into various neoplasms. With the development of diabetes mellitus, a set of measures is necessary. It includes not only the use of drugs that stabilize sugar levels. A special diet is required that eliminates the load of food consumed on the gland.
Detection of pancreatitis requires appointment:
- painkillers;
- antienzyme agents;
- antispasmodics;
- detoxification treatment.
In addition to basic therapy, a specialist can recommend traditional medicine recipes. In case of advanced pathology, surgical intervention is required. One of the important areas of treatment is a strict diet.
For inflammation of the duodenum, it is necessary to use:
- antibiotics;
- drugs that reduce acidity levels;
- traditional medicine methods.
Cholecystitis is treated by prescribing the following medications:
- antispasmodics;
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory;
- choleretic;
- folk
If moderate changes occur in the structure of the pancreas due to age-related characteristics, nutrition is adjusted and treatment is carried out with folk remedies.
These methods are relevant for minor diffuse changes and the absence of other manifestations.
In some cases, pathology can be cured simply by changing your diet.
Features of diet therapy
With diffuse changes in the pancreas, diet is of great importance. Its basic principles are as follows:
- exclusion of alcoholic beverages from the menu;
- introduction of fermented milk products, various cereals and vegetables;
- Dishes prohibited: smoked, high fat, with a lot of seasonings, salt;
- fractional meals, i.e. in small portions, but often (to exclude strong enzyme production);
- compliance with the calorie content of dishes, so it is better to boil or steam them;
- exclusion from the diet of tomatoes, citrus fruits, some berries (strawberries, raspberries, strawberries), garlic, acetic acid.
In some cases, it is enough to follow the recommendations of nutritionists in order to alleviate the condition and restore the functioning of the gland. A diet for diffuse changes in the pancreas is prescribed by a doctor.
Symptoms of seals
Despite the fact that diffuse changes in the pancreas are only a sign of the presence of any pathologies, they may have their own symptoms:
- sudden causeless loss of body weight;
- gastrointestinal tract disorder, stool disorder;
- nausea, discomfort in the abdominal area, vomiting.
Diffuse changes in themselves are not dangerous, however, if they are signs of serious diseases of the internal organs, you should not hesitate to start treatment. To do this, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis in a timely manner.
Help from traditional medicine
Often, in the presence of moderate changes in the structure of the pancreas, a specialist recommends the use of traditional medicine. They promote a milder, more smoky effect on the affected organ compared to drug methods. The following recipes are effective:
- Oat jelly. First, make the base for the drink. To do this, pour 1/3 of ripe oats into a 3-liter container and fill it with water. For fermentation, add a piece of rye bread (it can be replaced with 0.5 liters of kefir). Leave the container for 3 days. After this, the mass is filtered through cheesecloth and left for 12 hours. After time, separate the grounds and put them in the refrigerator. For jelly, simmer 0.5 liters of water with 8 tbsp. l. prepared porridge for 5 minutes. The resulting mass is consumed in the morning before breakfast. You can add milk and low-fat cream.
- Sage infusion. To prepare the product, pour a glass of boiling water into a mixture of herbs: calendula, sage, iron ore in a ratio of 3:2:1 (in teaspoons). The medicine is insisted. Drink filtered liquid 1/2 cup 2 times a day.
- Decoction of iris and wormwood. The herbs are mixed in equal quantities, poured with hot water, and infused for 60 minutes. The product is consumed 15 minutes before meals.
- Decoction of blueberry leaves. Take the solution for 2 weeks, after which they take a break and repeat the treatment.
- Use of bee products. As prescribed by a doctor, propolis can be used in the acute phase. It is enough to chew it for 5-10 minutes several times a day. Solutions are prepared based on bee products. To do this, mix 15 ml of tincture and 1/2 cup of water.
Diffuse disorders in the pancreas in children and adults can be caused by various factors. A change in structure entails dysfunction of this organ. A specialist can tell you how to treat the pathology after a thorough examination. In some cases, it is permissible to use traditional medicine in consultation with a doctor. The diet prescribed for diffuse changes in the pancreas plays an important role. Sometimes, to restore the functioning of an organ, it is enough to carefully analyze and change your diet.
Symptoms and manifestations of pathology
If an ultrasound scan reveals a thickening of the pancreas, the patient does not always have any complaints, because the underlying disease that led to this has usually already passed. That is, if earlier there were pains in the epigastrium, girdles, nausea, vomiting, stool disorders, then at the time of the appearance of the seal they are either less pronounced or absent.
The change in organ function due to gradual degeneration and cell atrophy comes to the fore. This is expressed by indigestion and stool problems. Vomiting and nausea are possible due to poor digestion and stagnation of food in the stomach and intestines. Sharp, sudden pain in the abdomen may also occur. The patient begins to lose weight, as the process of breaking down nutrients is disrupted.
If the cells that produce insulin are affected, the patient will experience symptoms of diabetes. The patient unnoticed begins to drink more fluid. He complains of thirst and dry mouth. In primary diabetes, found in children and adolescents, diffuse compactions are also often found in the pancreas; the cause may be a genetic pathology or hereditary predisposition.
At the same time, it is not enough to find out the cause; in order to begin pathogenetic treatment, it is necessary to create gentle conditions for the functioning of the organ, preventing further decline in pancreatic function. This is achieved by eliminating harmful factors. First of all, you should prevent exposure to harmful substances and establish a nutritional regimen (diet).