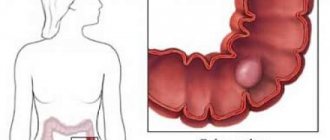
Dyskinesia is a pathology associated with disturbances in the motor activity of the affected organ. For example, dyskinesia of the colon of the hypotonic type suggests the absence of organic damage to this organ, however, the colon is no longer able to function normally. Due to the widespread prevalence of this unpleasant disease, interest in the disease and methods of its treatment has recently increased.
General understanding of colon dyskinesia
This disease has another name - irritable bowel syndrome, spastic colitis. The basis of the pathology is disturbances in the tone and motor activity of the intestinal tract. Colon dyskinesia can lead to disruption of other gastrointestinal organs. For example, dysfunction of the esophagus, stomach and other parts may occur.
Every third inhabitant of our planet has to deal with a similar pathology. Representatives of the fair sex especially often suffer from it.
Classification
According to pathogenesis, primary and secondary dyskinesia of the large intestine are distinguished. In the first case, pathological processes develop as an independent disease. A disease that occurs against the background of other ailments of the gastrointestinal tract is considered secondary.
According to the clinical course, the classification distinguishes three types of the disease:
- The first is characterized by pronounced intestinal signs. Among them, the most common is diarrhea, followed by a prolonged absence of stool.
- The second is accompanied by intense pain.
- The third is characterized by the predominance of symptoms characteristic of nervous disorders.
The possibility of manifestation of symptoms of a mixed type, when there are symptoms of all types of the disease, cannot be excluded.
Etiological classification
In its origin, dyskinesia of the large intestine is quite diverse. There are several varieties, including:
- neurogenic, occurring against the background of pathologies associated with the nervous system;
- psychogenic, developing as a result of prolonged depression, neurotic conditions, asthenic syndrome;
- endocrine-hormonal, which is a consequence of dysfunction of the endocrine system - disruption of the pituitary gland and the activity of the gonads, hypothyroidism;
- toxic, provoked by malicious use of alcohol and poisoning with toxic chemicals;
- medicinal, resulting from the uncontrolled use of medications for constipation or diarrhea;
- nutritional, which occurs with all kinds of diets, insufficient or excessive consumption of food products;
- hypodynamic, developing as a result of surgical intervention in the abdominal organs, hypokinesia and asthenia; the manifestation of this variety also occurs in cases of metabolic disorders, infectious diseases, and allergies.
The treatment method directly depends on the etiological factor. This is why it is so important to undergo a thorough diagnostic examination.
Causes of colon dyskinesia
Among the main reasons that can provoke dyskinesia of the colon are the following:
- Psycho-emotional stress. Psychosomatic disorders are the main reason provoking the development of dyskinesia of this unpleasant disease. The motor activity of this organ is negatively affected by stress, anxiety, neuroses, and internal conflicts.
- Poor nutrition. The disease can develop due to the excessive presence in the diet of high-calorie foods and refined products that do not contain plant fiber.
- Weak physical activity, lifestyle features (sedentary activity);
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Intolerance to certain foods;
- Infectious disorders of various types;
- Disruptions in endocrine processes;
- Gynecological diseases that can provoke intestinal dysfunction in women;
- Excessive enthusiasm for medications that can have a detrimental effect on the motility of the colon;
Despite such an impressive list of reasons, the primary role belongs to hormonal imbalances that affect the state of intestinal motility.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of dyskinesia are very diverse. There are several basic ones by which pathology is recognized.
- The appearance of pain in the abdominal area. Moreover, they can be paroxysmal, constant, cutting or dull in nature. They are usually localized in the navel area. After eating, during stress or emotional turmoil, pain may intensify. The pain usually goes away after the passage of gas or defecation. A characteristic feature of this pathology is that the pain completely disappears at night and returns in the morning.
- Flatulence. The appearance of this symptom is typical in the evening or before defecation. It is possible that pain and rumbling in the abdominal area may occur.
- Problems with stool. As a rule, constipation alternates with short bouts of diarrhea. It happens that mucus comes out along with the feces.
- There is a feeling that the stomach is swollen, bursting, and heaviness appears. Nausea and belching of air may occur.
- Psychoneurotic disorders. You can learn about them by manifestations of depression, anxiety, and nervousness.
Often, people experiencing colonic dyskinesia complain of constipation, alternating with short-term diarrhea. Emptying the bowel occurs with difficulty, and after defecation there remains a feeling that the intestines are not completely cleared of feces.
Important! A condition in which feces accumulate in the body is dangerous due to the development of intoxication. And this is fraught with dizziness, loss of appetite, weakness, and decreased performance.
Symptoms
The disease is characterized by the manifestation of a characteristic clinical picture. To make it easier to identify the disease, the patient must navigate all its manifestations and quickly distinguish abnormal signs. Symptoms of chronic colitis are characterized by the following indicators:
- pain in the abdomen - manifests itself in a spastic nature in the left iliac zone;
- bowel dysfunction - constipation is characterized by the release of mucus with stones, attacks of defecation occur 15 times a day;
- increased release of gases;
- bloating;
- rumbling in the intestines;
- belching;
- nausea and malaise;
- fast fatiguability;
- weakness;
- stench in the mouth;
- disturbed sleep;
- pale skin tone.
Pain is the leading symptom of chronic colitis
Since the chronic form of the disease develops in different types, it is important to understand how nonspecific ulcerative and spastic colitis can manifest itself.
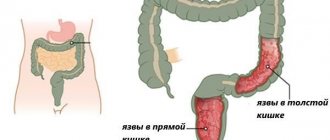
A disease characterized by ulcerative formations, in moments of exacerbation, is characterized by the appearance of swelling of the intestinal walls, they begin to bleed, which leads to the release of stones mixed with blood or a dark shade, as well as the formation of neoplasms.
Signs of chronic colitis of nonspecific ulcerative form:
- pus and blood in the stones;
- diarrhea turns into prolonged constipation;
- lower abdominal pain;
- increase in the volume of the lower abdomen;
- heat;
- loss of appetite;
- eye inflammation;
- muscle weakness;
- attacks of joint pain.
Symptoms of chronic spastic colitis:
- painful spasms form - at night or when refusing to eat;
- abdominal enlargement;
- strong release of gases;
- replacement of diarrhea with constipation, and vice versa;
- insomnia;
- bowel movements occur every few days;
- rumbling in the stomach.
To reduce the exacerbation of symptoms, the patient should always adhere to the correct therapy and diet.
Types of dyskinesia
There are two types of dyskinesia, each of which has its own characteristics.
- Hypertensive dyskinesia of the colon involves the presence of increased hypertonicity and spastic contractions of the intestine. The result is the appearance of colic and constipation, which progresses. Cramping pain appears, localized mainly in the inferolateral and lower abdomen. Typically, this type of disease develops in those who suffer from foodborne illnesses or eat foods that are incompatible.
During the examination, abdominal bloating may be noted, the patient’s mouth smells unpleasant, and a white coating appears on the tongue.
If we are talking about the hypertensive type of pathology, the development of fecal incontinence is possible.
- Hypotonic dyskinesia is characterized by the fact that the patient suffers from weakened peristalsis and intestinal tone. The result is not long in coming and is manifested by constipation, pain, bloating, and heaviness.
Most often, the patient has problems determining the exact location of the pain.
As a result of a reduced level of peristalsis, metabolic processes in the body slow down, resulting in excess weight gain. In this case, defecation occurs rarely, the volume of feces is small, but a lot of gases are released. During bowel movements, the intestines are not completely emptied. Stagnant feces can lead to intoxication of the body.
Intestinal motility may weaken if a strict diet has been followed, as well as due to low physical activity or excessively sparing nutrition.
Important! Hypomotor dyskinesia of the colon can provoke such a dangerous complication as intestinal obstruction, requiring immediate surgical intervention.
In very rare cases, a mixed type of dyskinesia occurs.
Causes of pathology
Dyskinetic colitis manifests itself as a result of the following factors:
- Bad heredity.
- Infections. In this situation, microorganisms can provoke such disorders
- Autoimmune disorders, during the development of which the body independently destroys formed elements in tissues.
- Oncological processes.
Let's consider other causes of chronic colitis:
- Medicines that undermine the functioning of intestinal microflora, laxatives or antibiotics.
- Intoxication.
- Lack of enzymes for gastritis, pancreatitis, and other gastrointestinal diseases.
- Intestinal atony.
- Genetic predisposition to the manifestation of the disorder.
The risk group includes patients whose parents suffered from chronic colitis. Pathology appears in people, regardless of racial characteristics, and is most often diagnosed in representatives of Caucasian nationality. Such patients are more likely to develop proctological disorders. Separate studies have identified a possible interaction between isotretinoin use and intestinal ulcers.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosing dyskinesia is not an easy process. Based solely on the patient’s stories, it is very difficult to draw conclusions regarding the nature of the disease, because many deviations in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract have similar symptoms. Diagnostic measures involve more than one stage in order to exclude the possibility of other types of pathologies. In this case, one cannot do without laboratory and instrumental research methods.
From the laboratory, a blood test is required, and stool is examined for hidden blood and dysbacteriosis. A scatological analysis will also have to be done.
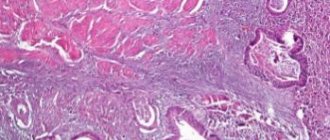
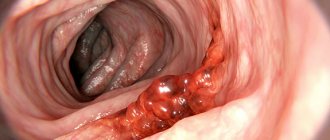
Instrumental diagnostic methods are widely used. Irrigoscopy, fibrocolonoscopy, and endoscopic tests are performed, during which the doctor takes a tissue biopsy. This is necessary to exclude tumor formations of malignant etiology, which X-ray signs will help to draw a conclusion about.
Typically, in patients experiencing dyskinesia, tumors are not detected, but weakened peristalsis or intestinal hypertonicity and dysbiosis are detected.
Treatment tips
As additional therapeutic measures, it is recommended to carry out:
- Physiotherapy. It includes:
- performing massage;
- enemas;
- intestinal lavage with mineral waters;
- acupuncture;
- carrying out paraffin applications.
- Taking carbon dioxide baths.
- Carrying out electrophoresis with novocaine and calcium.
In addition, it is very important to maintain proper nutrition when treating hypomotor dyskinesia. This diet includes:
- Quitting drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Avoidance of use:
- fatty foods;
- fried;
- acute;
- meat broths;
- spices and sauces;
- flour products;
- sweets;
- lard;
- canned food;
- vegetables that contain coarse fiber;
- coffee;
- garlic
- Minimize consumption of beans, mushrooms, hard cheese and potatoes.
- Replace eating white bread with rye bread.
- Eat porridge cooked in water every day.
- Drink at least two liters of water daily, not counting liquids from soups and juices.
- Drink rosehip decoction.
- Eat small portions.
- Switch to fractional meals.
- Consume vegetable oil regularly.
Important! Overeating should be avoided to prevent intestinal overload. The last meal should be no later than three hours before bedtime.
- Food should be steamed, baked or boiled.
- The menu should include fresh vegetables and herbs every day.
- Every day it is advisable to eat stewed zucchini, lean meat, fish and fruits.
Treatment of intestinal dyskinesia with medications
When giving preference to one or another method of treating pathology, it is necessary to take into account a number of important factors. Namely:
- type of dyskinesia;
- main symptoms;
- reasons that provoked the development of the disease.
Treatment of dyskinesia should be comprehensive and include not only conservative drug therapy, but also adjustments to diet and lifestyle, physiotherapeutic procedures, psychotherapy, and therapeutic exercises.
Treatment with medications consists of taking medications prescribed by the doctor, designed to normalize stools and regulate intestinal activity. In addition, patients should simultaneously take psychotropic and sedatives.
If we consider a physiotherapeutic technique, we can highlight acupuncture, paraffin baths, and enjoy oxygen and pine baths. In addition to these procedures, patients receive massage.
Patients facing this unpleasant disease are recommended to drink mineral water. Moreover, if the patient is confirmed to have a hypotonic type of pathology, then he should take highly mineralized water. The hypertonic type involves medicinal water with a low degree of mineralization. Water should be consumed an hour before meals, always warm and without gases.
In addition, patients are recommended to engage in therapeutic exercises containing relaxation exercises. You can improve your well-being through hydrotherapy procedures, warm radon and carbon dioxide baths.
Drugs prescribed for hypotonic dyskinesia should be aimed at having an enhancing effect on peristalsis and motor functions of the intestinal tract. Your doctor may prescribe laxative medications to increase the volume of your stool and make it easier for you to empty your bowels.
Forecast and prevention of intestinal disorders
In general, the prognosis for symptomatic intestinal disorder is favorable, provided clinical recommendations are followed. The course of the disease will not develop complications in the form of intestinal obstruction, formation of fistulas, perforations or strictures if all the prescriptions of the attending physician are carried out by the patient in good faith. Among the preventative measures, the following must be observed:
- Monitor your own weight and nutrition.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Avoid nervous and mental stress.
- Comply with the sanitary and hygienic rules of the hostel.
- See a doctor promptly.
When performing intestinal prophylaxis, do not forget to teach children to do this.
Treatment of dyskinesia with traditional methods
To eliminate an unpleasant pathology, you can also use folk remedies, but only after the approval of the treating doctor has been obtained.
- Irritable bowel syndrome can be eliminated by drinking a glass of cabbage or potato juice every morning.
- A medicinal decoction will help normalize intestinal activity and eliminate constipation. To prepare it, you need to prepare a decoction based on lingonberry berries, rhubarb, buckthorn, hay leaves and Alexandria leaves.
- A decoction based on raisins, dried apricots, and boiled beetroot salad are excellent laxatives.
- Compresses made with vinegar are designed to relieve pain in the abdominal area. 100 ml of this product is diluted in 3 liters of water. A piece of gauze is soaked in the prepared composition, which is then applied to the problem area for 1.5 hours.
- With the help of a sedative infusion of herbs, you can get rid of intestinal hypertonicity. To prepare it, you need to take equal quantities of sage, mint, motherwort and yarrow leaves, St. John's wort flowers and oak bark. 2 tablespoons of this herbal mixture are poured with 200 grams of boiled water. The decoction should steep for 2 hours. Strain the finished drug. Drink a third of a glass in the morning, lunch and evening for 7 days.
Non-drug treatments
For chronic colitis, sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated. The best resorts for treating the digestive system are rightfully considered the sanatoriums of Pyatigorsk, Essentuki, and Kislovodsk. In addition to drinking mineral waters, they use baths, intestinal lavages, and treatment with microenemas enriched with active biological substances.
Gastroenterologists recommend courses of physiotherapeutic procedures (magnetic therapy, mud applications, acupuncture). Surgical intervention is resorted to for urgent indications in the complicated course of chronic colitis.
From folk recipes shown:
- For inflammation - decoctions of sage, mint, St. John's wort, caraway.
- Nettle, motherwort and mint help with increased gas formation.
- To relieve spasms in the intestines, microenemas with a decoction of chamomile and calendula are recommended.
- For ulcerative colitis, sea buckthorn oil is indicated in a microenema at night.
All auxiliary methods require a long time and are carried out in courses with breaks. It is better to first consult with your doctor. [adsense3]