Why is pathology prevention needed?
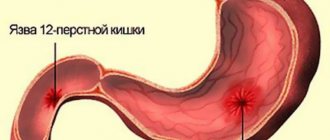
When a lesion develops not only on the gastric mucosa, but also in its deeper layers, the patient is diagnosed with a peptic ulcer. Gastric ulcers are considered a chronic disease, with periods of exacerbations alternating with remissions. This disease manifests itself with such serious symptoms as an acute and painful feeling of hunger, pain in the upper abdomen, upset stool, weakness, bloating, vomiting at night, and loss of appetite. The sets of preventive measures to prevent the development of gastritis and stomach ulcers are very similar, because the causes of these diseases are also common.
Diagnostics
Correct diagnosis plays an important role in the fight against any disease. To determine diseases of the stomach and duodenum, a number of measures are carried out:
- First of all, during a conversation with the patient, the doctor finds out general information about the disease.
- After this, the patient is examined.
- X-ray examination helps to identify pathologies that have arisen in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Tests to determine the presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria help determine the presence of peptic ulcer disease.
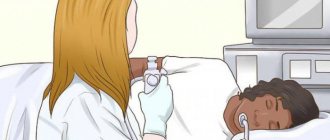
- Endoscopy. Using an endoscope (a long thin tube inserted into the patient's gastrointestinal tract), the condition of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum can be assessed.
- Blood analysis.
Types of prevention
Prevention of gastric ulcer development is usually divided into primary, secondary and tertiary:
- Primary. In this case, the patient has a predisposition to developing the disease, but it has not yet been diagnosed.
- Secondary. The disease was detected in a mild form. The goal of prevention is to prevent its further progression. To do this, the patient needs to consult a specialist.
- Tertiary. The patient suffers from an ulcer in acute or chronic form. Preventive measures are limited to preventing the development of complications and exacerbations.
Primary
Primary prevention measures for gastric ulcers are carried out if the patient has functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, a predisposition to the development of the disease is often revealed. The following recommendations will help you avoid illness:
- Minimizing stress. This is especially true for impressionable and vulnerable people. They should, if possible, eliminate stressors from their daily lives.
- Full sleep. The body must receive daily rest, lasting at least 6 hours. The optimal sleep duration is 7-8 hours. Chronic lack of sleep can cause ulcers.
- Rejection of bad habits. Smoking, alcohol abuse and strong coffee - all this should be excluded from your life.
- Timely treatment of diseased teeth and gums. In the absence of high-quality chewing of food, the stomach has an increased load.
- Timely treatment of inflammatory processes in the stomach, gastritis. These diseases lead to the development of ulcers.
- Proper and timely nutrition. A person's daily diet should include liquid and hot food. It is advisable to eat according to a schedule, with short intervals between meals. Spicy, smoked, fatty foods should be avoided. The same applies to carbonated drinks.
- Exercise regularly. Such loads help increase immunity, preventing the development of various gastrointestinal diseases.
- Avoid self-medication. The effect of most medications negatively affects the stomach and intestines. Therefore, you should take medications only after consulting a specialist.
The best way to prevent stomach ulcers is to undergo periodic medical examinations. This measure will help to identify disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and respond to them in a timely manner.
Prevention of exacerbations
If the disease has already been identified, then the main task of preventing gastric and duodenal ulcers is to prevent its exacerbations. In this case, attention should be paid to the following preventive measures:
- Treatment in dispensaries and sanatoriums.
- Drinking mineral waters with a certain composition.
- Taking courses of drug therapy in the spring and autumn, since it is at this time that the disease worsens.
- Maintaining proper diet.
- Regular examinations of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Timely fight against infectious diseases that can become one of the causes of ulcer formation.
- Many doctors recommend their patients systematically perform special therapeutic exercises. Such exercises are aimed at reducing the pain syndrome that accompanies peptic ulcer disease.
Prevention of complications
If the patient already has an ulcer, then he should do everything possible to avoid complications of the disease. If the ulcer is not treated, then in addition to increased pain, internal bleeding may occur and perforation may develop, when a through hole is formed on the gastric wall.
The consequence of this condition is peritonitis. To prevent the development of complications, a patient with an ulcer must take the following precautions:
- Completely stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Follow the diet strictly.
- Be examined at least twice a year.
- Eat food according to the schedule, in small portions.
- Take medications, including those to normalize acidity.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Normalize wakefulness and sleep patterns.
UZ "Mogilev City Emergency Hospital"
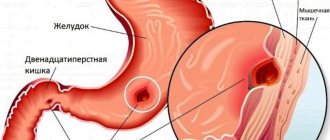
Peptic ulcer is a chronic disease, the main symptom of which is the formation of ulcerative defects in the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum. It usually has a cyclical nature and occurs with periods of exacerbation (autumn and spring). Peptic ulcer disease occurs in people of any age, but more often at the age of 30-40 years; men get sick 6-7 times more often than women. As a rule, an ulcer occurs against the background of gastritis (inflammation of the gastric mucosa) or duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenal mucosa) associated with Helicobacter pylori infection.
Currently, the leading causes of peptic ulcer disease are:
1. Exposure to the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
2. The predominance of aggressive factors (hydrochloric acid, pepsin, bile acids) over the protective factors of the mucous membrane.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease include:
- prolonged neuro-emotional stress;
- genetic predisposition;
- the presence of chronic gastritis or duodenitis;
- violation of the diet (irregular, spicy, hot or cold food, fizzy drinks, excess carbohydrates);
- drinking strong alcoholic drinks and smoking;
- use of certain medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: acetylsalicylic acid, indomethacin, etc., cytostatics, hormonal drugs).
The most characteristic manifestation of a peptic ulcer is pain in the upper abdomen, which often occurs on an empty stomach, i.e. Between meals, night pain is also typical. Less specific symptoms are nausea, heaviness after eating, a feeling of fullness in the stomach, vomiting, loss of appetite, weight loss, and heartburn.
Peptic ulcer disease is dangerous due to its complications. The most common is bleeding. The most severe and life-threatening complication of peptic ulcer disease is perforation or perforation of the ulcer, which is the formation of a hole in the wall of the stomach or duodenum. Malignization is the transformation of an ulcer into a malignant tumor. That is why you should never delay treatment of an ulcer or interrupt therapy.
Prevention of peptic ulcer disease allows you to prevent this common and dangerous disease with its complications, as well as to avoid relapses if a person is already sick.
Types of prevention of peptic ulcer:
- Primary prevention of peptic ulcer. Aimed at preventing the development of the disease and eliminating risk factors.
- Secondary prevention of peptic ulcer. Aimed at reducing the risk of exacerbations and relapses of an existing disease.
- Tertiary prevention of peptic ulcer. Aimed at reducing the likelihood of developing complications of the disease.
Methods of primary prevention of peptic ulcer
- Maintain oral hygiene, timely treatment of teeth and gums. Diseased teeth are an entry point for infection, and in addition, diseased teeth make it impossible to chew food properly, which leads to increased stress on the stomach.
- Organizing a proper diet and regimen. You should develop the habit of eating at the same time every day. In addition, it is recommended to exclude from the diet or limit the consumption of smoked meats, excessively hot, spicy and salty foods. Culinary processing of dishes should be gentle - without over-frying the dishes. Carbonated drinks, very hot or, conversely, very cold foods should also be excluded.
- Prevention of vitamin deficiency.
- Quitting bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
- Prevention and treatment of hormonal disorders.
- Dosed physical activity, rational organization of the daily routine.
- Refusal to take medications frequently (if possible), especially unsystematic use and self-prescription of medications.
- Prevention of Helicobacter pylori infection - use of individual dishes and towels.
Secondary prevention of peptic ulcer:
- Spa treatment.
- Regular courses of anti-relapse therapy in the autumn and spring.
- Strict adherence to an anti-ulcer diet.
- Sanitation of diseases and chronic foci of infection that can provoke a relapse.
- Regular monitoring of the ulcer in a medical facility.
In addition, psychological comfort is very important to prevent peptic ulcers: sometimes stress and nervous disorders can also cause the development of the disease.
Medicines for the prevention of stomach ulcers
The best preventive measure for any prevention is vitamin complexes. They have no side effects and will strengthen the body.
Preparations based on pancreatin to facilitate digestion:
Mezim forte 10000 . A multienzyme drug that compensates for the lack of enzymes secreted by the pancreas. Improves food digestion. Use 1-2 tons per day during meals. Suitable for one-time, periodic and long-term consumption. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to components, acute pancreatitis or exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis.
Enzistal . Improves digestion, promoting a more complete breakdown of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Improves food absorption. Use 1-2 t during meals 3 times a day. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to components, jaundice, bile duct obstruction.
Panolez . It has proteolytic, anabolic, lipotropic effects. Actively used for chronic gastritis, during the recovery period after operations on the intestines, gall bladder, etc. Used 2-3 times a day during or after meals, 1 tablet. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to components, hyperbilirubinemia, obstruction of the bile ducts.
The following remedies will help relieve the feeling of heaviness and nausea in the stomach.
Motilium . Antiemetic drug in the form of suspensions and tablets. Accelerates digestion and speeds up the movement of food in the gastrointestinal tract. Use half an hour before meals, 1 tablet (10 mg) 3 times a day. Exceeding the dose is unacceptable. Contraindications: old age, heart disease, liver disease.
Motilak . Eliminates nausea and vomiting, speeding up digestion and improving stomach function. Use 10 mg (1 t.) 3 times a day before meals. Used to relieve nausea and vomiting without identified stomach and duodenal ulcers. Contraindications: liver failure, stomach damage, intolerance to the drug itself and its components.
Rennie . An antacid that affects the acidity of the stomach, protecting the walls from damage due to excessive secretion of gastric juice. Used for feelings of heaviness in the stomach and pain, heartburn, flatulence. Take 1-2 t every 2 hours until symptoms disappear, but no more than 16 tablets per day. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to components, hypercalcemia, acute renal failure.
Gastal . Designed to combat heartburn, normalize acidity in ulcers, gastritis and erosions of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as pancreatitis. Use 1-2 t. 4 times a day, an hour after meals. The course of admission is no more than two weeks. Contraindications: hypophosphatemia, Alzheimer's disease, sensitivity to components, renal failure.
Gastracid . Adsorbent and enveloping antacid to regulate acidity and protect the walls of the stomach. Apply 1 t 3-4 times a day an hour after meals, keeping it in your mouth until completely dissolved. Contraindications: intolerance to components, hypophosphatemia, any kidney disorders, Alzheimer's disease.
The described tablets for the prevention of stomach ulcers and gastritis are designed to prevent diseases, and significantly weaken the symptoms in cases where pathologies already exist.
Main stomach diseases, symptoms
The classification of stomach diseases is as follows:
Acute gastritis
The basis of this disease is the inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the gastric walls. As a result, food digestion is disrupted, general well-being worsens, and performance decreases.
Patients complain of pressure and bloating felt after snacks in the stomach area; some feel nausea, vomiting, and heartburn. It is possible that there will be an acute, burning pain in the upper abdomen, and belching that smells of acid may occur.
Chronic gastritis
The disease is characterized by clinical and functional disorders of gastric digestion. As a result of morphological changes in the mucosa, a nonspecific inflammatory process develops. Atrophy gradually develops.
The chronic form may be accompanied by stool problems and flatulence.
Such diseases cannot be ignored, as complications can arise in the form of gastric bleeding, peptic ulcers and degeneration into oncology.
Read this article on how to identify and cure gastritis in time.
Peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease develops due to disruptions in the nervous and humoral mechanisms that are responsible for regulating secretory-trophic processes. As a result, ulcers appear on the walls of the stomach and duodenum. Often this pathology does not have pronounced symptoms and can only be detected through accidental diagnosis.
Symptoms of peptic ulcer disease manifest themselves as follows:
- pain arises, and it can manifest itself in different ways: it can be cutting or piercing, sometimes cramping, and sometimes dull and weak. The deeper and larger the ulcer, the more pronounced the pain.
- The localization of pain is noted in the epigastric zone, and can radiate under the scapula or right hypochondrium.
Peptic ulcer disease is characterized by pain, which manifests itself mainly after the patient eats. When it comes to duodenal ulcers, pain occurs 2-4 hours after eating, at night or on an empty stomach. In this case, when the patient eats, the pain goes away.
Duodenitis
In the case when the inflammatory process is localized in the area of the duodenum, we are talking about a disease such as duodenitis. Patients faced with a similar pathology complain of being hungry. night pain of cramping and aching in the epigastric region. The disease is often accompanied by sour or rotten belching and constipation. The patient suffers from nausea, and in rare cases, vomiting occurs.
In cases of chronic duodenitis, the general health of the patient worsens, complaining of weakness, headaches, and loss of appetite.
Stomach cancer
This is a malignant neoplasm that forms from epithelial tissue. The danger of stomach cancer is that in the early stages it can only be detected as a result of a random examination, since the disease is asymptomatic. Signs that appear in the form of deterioration in health, weakness, loss of appetite, and causeless weight loss indicate that the process is far advanced.
Important! If you suspect the development of one of the listed diseases, you should seek advice from a specialist. Any delay can result in undesirable consequences in the form of complications.
Diet adherence
The diet is aimed at accelerating the process of regeneration of the mucous membranes of the stomach. It should be followed for at least 1 year after the diagnosis was made.
To prevent gastric ulcer (GUD), it is recommended to follow the following preventive recommendations:
- Divide the daily diet into 5-6 parts.
- Chew food thoroughly.
- Do not eat hastily, on the go, dry.
- Don't overeat.
- Do not eat cold or too hot food.
- Avoid fatty, fried, salted, smoked and pickled foods.
What foods can be consumed and what is not advisable are shown in the table:
| Recommended | Forbidden |
| Wheat bread | Hot spices - mustard, horseradish, red and black pepper |
| Soups with secondary broth (the first broth is drained) | Fatty, rich meat or fish broths |
| Bread crackers without preservatives and flavorings | Sweet sparkling water |
| Milk and cereal soups | Coffee |
| Lean meat and fish | Strong black tea |
| Steamed meatballs, meatballs, cutlets | Mushrooms |
| Soft-boiled egg or steam omelet | Wild rice |
| Low fat dairy products | Cakes, sweet buns |
| Pasta | Corn |
| Baked or grated sweet varieties of pears and apples | Legumes |
| Honey | Tomatoes and products made from them - juice, paste, sauce |
| Jam or jelly | Sour varieties of fruits and berries - currants, gooseberries, citrus fruits |
| Vegetable or olive oil | Onions and garlic (limited) |
Lifestyle correction
Rejection of bad habits. Smoking and drinking alcohol, especially on an empty stomach, negatively affects the condition of the gastric mucosa. In an empty organ, during smoking, the secretion of hydrochloric acid increases, which “corrodes” the gastric walls. In addition, the poisons of alcohol and nicotine destroy the structures of the oral cavity - mucous membranes, gums, teeth. Pathogenic bacteria multiply in the resulting microwounds, which subsequently enter the stomach. The resulting ulcer heals poorly due to oxygen starvation of the tissues.
Avoiding stress. A constant feeling of anxiety provokes the activity of the hypothalamus, a part of the brain that is responsible for many processes in the body. In stressful situations, corticosteroid hormones are released, which inhibit the production of gastric mucus, which protects the lining of the organ. Because of this, epithelial tissue is destroyed and is difficult to restore. Therefore, the prevention of gastritis and stomach ulcers consists of measures such as:
- avoiding conflict situations;
- performing relaxing breathing exercises;
- yoga classes;
- use of tonic herbal infusions;
- taking baths with herbal decoctions, essential oils or sea salt.
Maintaining hygiene. PUD often occurs when the bacteria Helicobacter pylori is ingested. Infection occurs through airborne droplets from a sick person, when using non-disinfected household items and utensils. The secretion of the stomach and duodenum is negatively affected by parasites - worms and protozoa. Therefore, for prevention, it is recommended to follow the following recommendations:
- wash your hands thoroughly when coming from outside, after visiting the toilet, before eating;
- do not use clothes and objects of strangers;
- do not eat fish and meat prepared in violation of culinary technology;
- wash vegetables and fruits before eating;
- Avoid random kisses with strangers.
Strengthening the immune system. To avoid the appearance of stomach ulcers, it is recommended to increase the body's protective properties. To do this, you should take strengthening vitamin-mineral complexes, such as:
- "Complivit";
- «;
- "Immunal-forte";
- "Supradin";
- "Multi-tabs";
- "Undevit";
- "Cycloferon".
Before using medications, it is recommended to consult a doctor. The following actions will help strengthen your immune system:
- swimming;
- long walks in the fresh air;
- practicing feasible sports;
- daily exercise;
- weight control;
- adherence to daily routine;
- full sleep.
Timely examination. At the first suspicion of a stomach ulcer, you should immediately contact a medical facility for examination. If the patient has a history of a chronic disease of the gastrointestinal tract, this is a reason to visit a gastroenterologist at least 2 times a year, even if nothing bothers the person. Especially if a secondary ulcer is suspected. Timely diagnosis will help to avoid pathological and dangerous complications of the disease, such as cancer.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
Which doctors should I contact?
If symptoms of gastric and duodenal ulcers appear, you should contact or. The doctor will draw up an individual examination and treatment plan, taking into account the clinical form of the disease, and, if necessary, prescribe consultations with specialists. Observation is often required to select rational diet therapy, drug treatment and prevention of exacerbations. In case of development of surgical complications of peptic ulcer, consultation is necessary. In the presence of concomitant diseases, such as diabetes mellitus and heart failure, participation in the selection of therapy will be required. If a peptic ulcer has developed against the background of severe psycho-emotional stress, consultation with a medical psychologist or psychiatrist is necessary.
Treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers
Treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers is complex and includes diet therapy, medical conservative and surgical treatment. With conservative drug therapy for peptic ulcer associated with H. pylori, two eradication treatment regimens (aimed at destroying the pathogenic microorganism) are possible: three-component and four-component therapy.
Triple standard therapy includes proton pump inhibitors and antibacterial drugs of two groups in different dosages. In addition to the proton pump inhibitor and antibacterial drugs of two groups, the four-component therapy for peptic ulcer includes bismuth preparations.
Choosing a treatment regimen and calculating dosages of antibacterial drugs is the responsibility of the doctor, who will tell you in detail about the duration of therapy, the frequency of drug administration, and how to check the effectiveness of the chosen treatment.
If these treatment regimens are ineffective, individual options are used, selected taking into account sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
In the case of peptic ulcer not associated with H. pylori, proton pump inhibitors and h2-blockers are used to reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid and reduce the impact of aggressive factors on the mucous membrane of the wall of the stomach and duodenum. Also, to relieve symptoms for a short time, the doctor may prescribe antacids; in case of gastrointestinal motility disorders, antispasmodics and prokinetics.
Surgical treatment of peptic ulcer is used when complications develop that cannot be suppressed by conservative treatment methods.
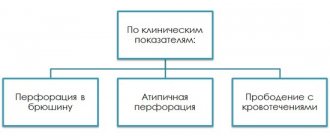
Complications of gastric and duodenal ulcers
Complications of gastric and duodenal ulcers are life-threatening conditions.
If symptoms of a complicated ulcer appear, you should urgently seek medical help. Bleeding
is one of the most dangerous and rapidly developing complications of peptic ulcer disease. Its sign is the presence of blood in the vomit (black or dark brown vomit, “coffee grounds”) and/or black tarry stool. The development of bleeding is accompanied by pain, which stops abruptly, but sudden weakness and dizziness occur, blood pressure decreases, the pulse quickens, and loss of consciousness is possible. With minor bleeding, blood is found in the stool.
Perforation of the organ wall
accompanied by “dagger” pain in the abdomen, severe weakness, dizziness, weak pulse, low blood pressure, nausea, and vomiting.
Ulcer penetration
into neighboring organs (penetration) is characterized by abdominal pain, which can radiate to the back, vomiting, which does not bring relief.
Stenosis of the pyloroduodenal zone
, or narrowing of the ulcer site. As a result of a decrease in the diameter of the outlet of the stomach and duodenum, food stagnation occurs in the stomach, bad breath appears, vomiting of “yesterday’s” food, pain and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum is a precancerous condition and increases the risk of developing stomach cancer
several times.
Prevention of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Specific prevention of gastric and duodenal ulcers has not been developed.
The main measures to prevent ulcer formation include: normalizing the work and rest regime, giving up bad habits, eradicating H. pylori in infected individuals, limiting the use of painkillers (if long-term use of non-steroidal and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is necessary, they must be combined with antisecretory drugs).
An important component of the prevention of peptic ulcer disease and its relapse is adherence to the principles of proper nutrition.
Limit very hot and spicy dishes and alcohol. Long breaks between meals are unacceptable.
To prevent relapses of the disease, sanatorium-resort treatment is actively used. It is important for the patient to provide psycho-emotional peace and avoid stressful situations.
Sources:
- Peptic ulcer disease. Clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2021.
- Clinical guidelines of the Russian Gastroenterological Association for the diagnosis and treatment of peptic ulcers, 2016
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Physiotherapy
The essence of physiotherapy is the use of natural and artificially generated physical factors: magnetic field, electric current, ultrasound, laser - for therapeutic and preventive measures. To prevent relapses of peptic ulcer disease, the following procedures are used:
- electrophoresis on the epigastric region with zinc, Novocaine, Dalargin, Solcoseryl, Platiphylline;
- low-frequency pulse currents using the electrosleep technique;
- UHF on the collar zone;
- transcranial electroanalgesia;
- magnetic therapy; amplipulse therapy.
Spa therapy
A course of spa treatment is especially recommended in autumn and spring, when the risk of exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease is high. Spa therapy is treatment using natural remedies. It includes the following resorts: Balneological: Svetlogorsk, Kislovodsk, Pyatigorsk. Baths, showers, bathing in mineral waters, ingestion, and inhalation are used here. Mud: Saki (Crimea), Sadgorod (Vladivostok), Kashin (Tver region).
It is suggested to use mud from salt lakes, peat and sapropel mud. Climatic: Petrozavodsk, Sestroretsk, Sochi. Such resorts use the healing features of a certain area, its topography, vegetation, and altitude. Treatment is carried out with air, sunbathing, and swimming.
Prevention of stomach ulcers with folk remedies
Herbal decoctions are suitable for the prevention of gastric ulcers. Before use, consult your doctor.
The following plants are used to prepare decoctions and tinctures:
- aloe;
- plantain;
- calendula;
- St. John's wort.
Decoction options:
- Mix 250 g of aloe and honey and heat to 60 degrees. Pour 500 g of red wine and leave for 7 days. Use 1 tsp. 3 times a day, and after a week you can move on to a tablespoon. Course – 3 weeks.
- 1 tsp. Pour boiling water (200-300 g) over plantain and cool to 30 degrees. Way to glass 3 times a day.
- Take plantain juice 3 times a day, starting with 1/2 tsp. Gradually increase the dosage to 1 tbsp. l.
- Mix 30 g of calendula flowers with 100 g of olive oil, place in a steam bath and heat to 70 degrees, holding for 2 hours. Leave for 24 hours, strain and take 5 g before meals. Course – 14 days. Contraindications: period of exacerbation, allergy to calendula. Taken only with the approval of a doctor.
- Pour 15 g of dried St. John's wort into a glass of water and place in a thermos for 6-8 hours. Strain and take 50 grams of broth half an hour before meals. The course is 2-3 weeks, can be repeated after a week. Contraindications: allergies. During the course, do not drink alcohol, coffee, or chocolate.
The following also have a positive effect:
- honey;
- mumiyo;
- propolis;
- potato and potato-carrot juice.
Please note that choosing traditional medicine recipes without the participation of a specialist can lead to serious complications.
Prevention of exacerbations of the disease
If the patient already has a confirmed diagnosis of stomach ulcer, care should be taken to prevent exacerbations. For this purpose, hospitalization and passing the necessary tests in a hospital at the first episodes of pain attacks are indicated. Bed rest and a strict diet are prescribed. In the first couple of days after an exacerbation, the patient eats practically nothing, but subsequently slimy porridges and jelly, boiled and ground meat are allowed on the menu.
The next stage of corrective therapy is the prescription of medications that reduce the acidity of gastric juice. It should be noted that they cannot be taken for a long time. The doctor prescribes a course, usually up to one month. To maintain a normal acid balance, it is recommended to turn to herbal medicine and folk remedies, which you should also not overdo. Sports and feasible exercises will help strengthen the body and reduce pain after relief of acute conditions.
Sources: profilaktika-zabolevanij.ru/sistemy/pishhevaritelnaya/profilaktika-yazvennoj-bolezni-zheludka-i-dvenadcatiperstnoj-kishki/ https://vnorg.ru/zheludok/yazva/255-profilaktika-yazvy-zheludka.html https:/ /www.kp.ru/guide/profilaktika-gastrita-i-jazvy-zheludka.html https://etozheludok.ru/rany/innoe/profilaktika-yazvy-zheludka.html https://tvoyzheludok.ru/yazva/drugoe /profilaktika-yazvy-zheludka.html https://vrachmedik.ru/2732-profilaktika-yazvennoj-bolezni-zheludka.html This material is exclusively subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/20/2020
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed by a gastroenterologist individually for each patient!
Today's techniques make it possible to treat diseases of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum conservatively. Drug treatment and diet therapy in most cases give good results.
Treatment with medications is aimed at suppressing the activity of Helicobacter pylori infection (taking antibiotics), normalizing motor function and gastric acidity.
With the development of complications that occur in 25-30% of cases, surgical treatment is possible. It involves excision of ulcers, tumors, and resection of part of the stomach.
Diet therapy is an obligatory component in complex therapy; it is necessary for rest and stabilization of the gastrointestinal tract. Physiotherapy and spa treatment are also indicated for the treatment and prevention of relapses.
Attention!
The selection of drug therapy should be made individually, taking into account the severity of the disease, the presence of concomitant diseases, the patient’s age and the risk of possible side effects.
We ask you not to self-medicate based on Internet data!
Branch phone:
+7 (495) 695-56-95