The pancreas performs an important function in the human body - it participates in the process of digesting food. With the help of the amylase enzyme produced by this organ, carbohydrates are broken down in the duodenum.
When the gland functions well, the level of amylase in the blood is also normal. Changes in its indicators indicate pancreatic diseases. Increased amylase is often observed with pancreatitis - with inflammation.
Normal amylase levels
If a person is healthy and the body is functioning well, the level of amylase in the blood will be low. Indicators are normal:
- in babies from birth to one year – up to 8 units/l;
- in children 1-10 years old – less than 31 units/l;
- in adolescents 11-18 years old – less than 39 units/l;
- in an adult – less than 53 units/l.
In diseases associated with the digestive system, amylase in the blood will either increase or decrease. To determine the presence of the disease and its type, the patient, with complaints of abdominal pain, nausea, problems with stool, vomiting, and increased salivation, is referred for blood biochemistry.
This laboratory test should be taken very seriously, since if certain preparation rules are not followed, a false result can be obtained. Here's how to prepare for the test: avoid taking medications. If this is not possible, during the analysis you need to inform the laboratory assistant about the medications you are taking.
The day before taking samples, you should limit the consumption of fatty, fried and smoked foods, as well as sweets and alcohol. 2-3 days before the study, avoid serious physical activity and stress.
Venous blood is collected in the morning, strictly on an empty stomach. You cannot eat food, even light food, 8-10 hours before.
How to determine the development of pancreatitis using amylase
Amylase or alpha-amylase (diastase) is a digestive enzyme produced by the pancreas. It intensively digests food, breaks down carbohydrates, and helps normal glucose absorption. In addition to diastase, the pancreas is capable of producing another enzyme - lipase, which is responsible for the breakdown of fats.
Amylase levels in human blood
The enzyme amylase is produced to a greater extent in the pancreas, and to a lesser extent by the salivary glands. During normal functioning of the digestive system, amylase converts complex carbohydrates into glucose. Next, glucose enters the intestines, where it is absorbed into the blood, and then excreted by the kidneys.
When testing blood, amylase is the main screening test for pancreatitis; its indicators are used to monitor the activity of the digestive system. Alpha amylase is a pancreatic enzyme and an indicator of the total amount of amylase in the body. One of the components of diastase is pancreatic amylase, which produces pancreatic juice and is completely responsible for the functioning of the pancreas. General amylase and pancreatic amylase have their own normal values. So, the norm in human blood should be:
- from birth to 24 months. norm - 5 - 70 units/liter;
- from 24 months up to 75 years of age, the norm is 15 - 130 units/liter;
- in the senile period the norm is up to 160 units/liter.
The values of pancreatic amylase differ slightly from the values of general amylase. In healthy newborns, pancreatic amylase in the blood should be no more than 8 U/l, and in babies from 12 months and in adults - up to 50 U/l.
Laboratory diagnosis of amylase in pancreatitis
The level of amylase in the blood can be determined by taking a biochemistry test from a vein. It is better to take the test on an empty stomach and in the first half of the day, then the result will be more accurate. Also, the day before the study, it is advisable not to take blood-thinning drugs (aspirin, chimes), eliminate sugar-containing foods, and not eat fatty and spicy foods, as well as alcohol. You should refrain from smoking at least a few hours before the procedure, because nicotine affects changes in blood composition and leads to the formation of blood clots.
The procedure for collecting blood for amylase takes only a few minutes and is carried out by taking biological material (5-10 ml) from a peripheral vein, using disposable sterile medical instruments. A doctor prescribes a blood test based on the necessary parameters in order to diagnose a more precise cause of certain complaints (for example, acute abdominal pain). The procedure for drawing blood is carried out by a nurse in the treatment room of the clinic at the place of residence. The result should not keep you waiting - in an emergency, the indicators can be found out within half an hour.
Deviations from the norm - why is it dangerous?
Not always, but in most cases, pancreatic amylase can be increased during inflammatory events in the pancreas, when pancreatitis may develop. This is a pathology that most often occurs from excessive alcohol consumption and poor diet, when the gallbladder becomes blocked with the formation of stones.
In the case when the analysis for pancreatic amylase in the urine is more than one thousand units/l, and the patient has a history of burning pain in the epigastrium on the left side, then one can suspect that he has acute pancreatitis.
Amylase can be increased in case of impaired kidney function, acute cholecystitis, acute peritonitis and various other aggravated processes in the digestive system. In the stage of chronic pancreatitis, the indicators may not be increased to a significant extent, since the disease is sluggish and permanent in nature with periodic remissions. Do not panic if the amylase level is zero - this is normal, which means that the pancreas is able to keep this enzyme normal.
If, as a result of the analysis, pancreatic amylase is increased by 7-10 times, this indicates an exacerbation of the pancreas and the development of acute pancreatitis. A couple of hours after the onset of an exacerbation of the pancreas, alpha-amylase in the blood jumps one step higher, but after 2-3 days the analysis will return to normal levels. If the indicator is exceeded by at least 5 times, it means that you need to undergo additional pancreas screenings (computed tomography, MRI, ultrasound).
Treatment for elevated blood amylase
Since alpha-amylase is an indicator of the condition of the pancreas in the body, it means that if the enzyme level is elevated, special attention should be paid to the work of this organ, especially with pancreatitis.
If alpha-amylase in the blood increases, treatment is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. Self-medication for such diagnoses is prohibited, because each body reacts to medications in its own way.
In case of acute pancreatitis, therapeutic fasting is carried out for medicinal purposes for several days. You should also reconsider your diet. Heavy smokers need to give up their addiction, as cigarettes increase the level of amylase in the blood. It is recommended to avoid unhealthy foods - spicy, fried, fast food, sweets, alcohol, and switch to a low-carbohydrate and salt-free diet. Include in your diet foods that are gentle on the pancreas - slimy porridges, pureed soups and soft foods. You need to eat small meals and at least six times a day.
With elevated pancreatic alpha-amylase, treatment will not bring the desired result without drug intervention. Since there is an inflammatory process in the pancreas, antibiotics from a number of penicillins (Augentin, amoxicillin) and cephalosporins (cefixime, cefuroxime) are prescribed for antimicrobial action. Also important in reducing exacerbations and treating pancreatitis are antifibrinolytic agents, which reduce blood circulation, suppress the production of enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract and are specific antidotes for alpha-amylase. Such drugs include gordox, trasylol, aprotinin.
To suppress immune inflammation, hormonal therapy is prescribed. One of the effective drugs in this category is octreotide. Its action is to relieve inflammation, reduce enzymatic activity, as well as reduced secretion of the stomach and pancreas.
To avoid the development of oncological processes in the pancreas, when amylase increases, it is advisable to prescribe antimetabolites and antitumor drugs. An example here is 5-fluorouracil (5-FU).
To relieve pain during pancreatitis, antispasmodics (no-spa, papaverine, platifillin) are prescribed. Antihistamines (tavegil, suprastin) will help relieve inflammation and have a sedative effect, and diuretics (furosemide) will help remove severe swelling from the pancreas.
For adherents of traditional medicine, teas infused with nettle, mint, chamomile, and St. John's wort will help lower the level of alpha-amylase and reduce the inflammatory process.
Correct and timely treatment can quickly relieve an attack of acute pain and bring amylase levels back to normal.
From the video you can learn how to prevent the development of pancreatitis:
Sources used: peptic.ru
Reasons for the low level
A decrease in the level of an enzyme in the blood does not always indicate any disease, but is not the norm. A decrease indicates that the pancreas has begun to work more slowly. Possible reasons:
- With hepatitis, metabolic disorders occur. The load on the pancreas increases, which cannot cope fully with the work. As a result, amylase begins to be produced in smaller quantities.
- Pancreatic necrosis, in which pancreatic cells die.
- Oncological diseases in the last stages.
- Surgery on the pancreas, when part of the organ is removed.
- Hereditary predisposition.
Amylase in the blood is increased
Amylase is one of the essential enzymes in the human body. It acts in the digestive system and ensures the processing of carbohydrates. Amylase breaks down starch into polysaccharides.
The enzyme is mainly produced in the pancreas. Therefore, an increase in amylase in the blood can signal disease processes originating in this organ. Prompt identification of pathology will help to carry out timely therapy and successfully cope with the disease.
Amylase is elevated: possible causes
Exceeding the norm by several units of amylase may be temporary and not affect your well-being in any way.
But when the level of the enzyme doubles or more, then painful processes undoubtedly occur in the body. They signal themselves with the following symptoms:
- pain in the right side of the abdomen, especially after eating;
- stool disorder: mainly diarrhea appears;
- general malaise and lethargy.
An increase in the amount of amylase occurs due to increased work of the pancreas. It secretes an enzyme in excess, which immediately enters the bloodstream. This becomes possible because:
- There is an excess production of pancreatic juice - a digestive fluid that is secreted by the pancreas directly into the duodenum.
- There are obstacles to its movement along the ducts.
- There are inflammatory processes in the pancreas or in neighboring organs. Their result can be tissue destruction, necrotic and traumatic.
Such conditions of the body are caused by the following pathologies:
- Acute pancreatitis is a rapidly developing inflammatory process in the tissues of the pancreas. The organ is damaged by its own enzymes. They enter the bloodstream in significant quantities and create a real danger to life. The disease can develop into pancreatic necrosis - a severe condition that is accompanied by the death of part of the pancreas or the organ as a whole, the development of infections and peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum).
Adults suffer from the disease, especially those who abuse strong drinks. Amylase levels increase eightfold. The mortality rate, despite modern treatment methods, is high - from seven to fifteen percent.
- Chronic pancreatitis is a gradual disruption of the pancreas. Its dysfunction leads to an increase in amylase - from three to five times.
- Neoplasms anywhere in the pancreas . Cancer may primarily involve the head of the organ. The concentration of amylase in the blood increases fourfold.
- Gallstone disease is the formation of stones (calculi) in the gallbladder and ducts.
- Diabetes mellitus is a disease that leads to systemic metabolic disorders. Carbohydrate metabolism is no exception. There are disruptions in the consumption of amylase. It is used irrationally, which increases its content in the blood.
- Peritonitis is an inflammation of the layers of the peritoneum, plunging the body into a severe condition. The pancreas is irritated, which increases the activity of its cells and the production of amylase.
- Mumps is a childhood disease known as mumps. The disease is acute and is caused by a paramyxovirus. Mumps is characterized by inflammation of the salivary glands, which are involved in the secretion of amylase. The enzyme production process is activated and returns to normal only after recovery.
- Kidney failure is a painful condition of the kidneys. They cannot form and excrete urine in a timely manner. Kidney dysfunction leads to amylase retention in the body, namely in the blood.
- ectopic pregnancy;
- macroamylasemia;
- injuries in the abdominal area;
- intestinal obstruction;
- herpes virus type four;
- complications after abdominal surgery.
Exceeding the enzyme norm can also occur in the presence of:
Disorderly eating and alcohol poisoning can also significantly increase amylase levels. The enzyme content is affected by taking certain medications, in particular diuretics and oral contraceptives.
Sometimes certain genetic factors may manifest themselves that prevent amylase from entering the urine and contribute to its accumulation in the blood.
Even moderate-level stress can interfere with all metabolic processes in the body and cause enzyme growth.
Causes of elevated pancreatic amylase levels
When the pancreas becomes inflamed, alpha-amylase produced in large quantities enters the blood instead of the duodenum, which is detected as a result of biochemical analysis.
Elevated amylase levels can be observed in the following diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- The most common reason is the development of acute inflammation, i.e. pancreatitis.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Cancer.
- Kidney diseases.
- Diabetes.
- Stones in the gall bladder and ducts.
- Gastritis and stomach ulcers.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
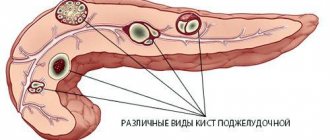
- Pancreatic cyst.
- Peritonitis.
- Intestinal obstruction.
Description and significance of the enzyme pancreatic amylase
Pancreatic amylase is a digestive enzyme of the pancreas
Amylase is one of the digestive enzymes produced in the largest quantities by the pancreas and salivary glands. This enzyme is designed to break down carbohydrates, that is, it is involved in the digestion of foods such as potatoes, rice and many others that contain starch.
Pancreatic amylase is a component of pancreatic juice, which is released into the duodenum, where it participates in the process of food digestion.
In case of disease of the pancreas or blockage of the duct between it and the duodenum, pancreatic amylase begins to be released into the blood, indicating a significant problem in the condition of this important digestive organ.
Normally, more than half of all amylase is produced by the salivary glands; it is of a different type from the enzyme produced by the pancreas.
If a blood test reveals that pancreatic amylase is elevated, this may indicate the presence of acute pancreatitis and many other dangerous diseases of the pancreas.
However, there are cases of dangerous diseases of this organ when the amylase level was either within normal limits or was slightly increased. This suggests that pancreatic amylase testing alone is not sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis; other additional tests are needed. A small amount of amylase is also produced in other organs, for example, in the ovaries, large skeletal muscles and intestines, so these data must be taken into account when interpreting the test readings.
For acute pancreatitis
The level of amylase in the blood during pancreatitis is not a diagnosis, therefore, if it is elevated, it is not the indicator itself that needs to be treated, but those diseases that are associated with pancreatic pathologies.
After decoding the results and in the presence of other symptoms, the doctor assumes that the patient has acute or chronic pancreatitis, gallstone disease, diabetes or cancer. Such diagnoses require immediate treatment or death may occur.
Symptoms of acute damage include the following:
- acute pain in the left side, sometimes in the entire abdomen;
- increased heart rate;
- pale skin;
- bloating;
- flatulence;
- vomiting and stool disorders.
The first principle of treating the pancreas is to follow a strict diet, as a result of which pancreatic amylase is normalized in the body. The diet is designed to relieve the affected organ. It is aimed at frequent split meals with limited consumption of fiber, fats and carbohydrates, as well as alcoholic beverages of any strength.
The patient needs to avoid fatty, fried, smoked and sweet foods. You need to eat protein - lean meat and fish, cottage cheese, kefir, and cereals. Of the food processing methods, steaming, when many vitamins and minerals are preserved in the dish, and boiling are preferable.
With pancreatitis, the level of alpha-amylase is 6-7 times higher. The first days after an attack, the patient not only follows a diet, he fasts. The surgeon prescribes treatment that relieves symptoms, relieves pain and restores pancreatic function.
The main painkillers used for pancreatitis include No-shpa, Papaverine, Baralgin, etc. To suppress the secretory function of the gland, enzymes are prescribed intravenously through droppers - Contrikal, Tsalol, Trasylol.
In acute pancreatitis, it is necessary to stop the process of fat necrosis. To do this, use a 5% glucose solution with insulin. To neutralize the acid, an Almagel solution is injected through the probe, and every three hours 3 tbsp. still Borjomi.
Typically, treatment of acute pancreatitis continues for 7-10 days, after which the patient must follow a strict diet, take enzyme preparations and, if necessary, painkillers. Otherwise, untreated pancreatitis goes into the chronic phase of the disease.
What is pancreatic amylase.
The pancreas is the site of production of pancreatic amylase.
The digestion process is a multi-level system, one of the elements of which is the breakdown of all components of food. In the body, this work is performed by various enzyme compounds. Amylase is an enzyme that is one of the first to start the digestive chain, as it is present in saliva and pancreatic juice. The intestines, liver, muscles and ovaries contain small amounts of this biologically active substance. The generalized amount of the enzyme in the body is called alpha-amylase.
Amylase, which is part of the digestive juice, is called pancreatic. Pancreatic amylase (P-amylase) promotes the breakdown of high molecular weight carbohydrates, converting them into glucose. The main field of its activity is the small intestine, where a favorable environment is provided for the digestion of carbohydrates. A small amount of the enzyme circulates in the blood plasma, is neutralized by the liver, and is excreted from the body in the urine.
The level of absorption of carbohydrates and the degree of absorption of complex elements by the intestine depend on the action of amylase. Without this important enzyme, the body would not be able to obtain the nutrients it needs, since it would not be able to accept complex compounds in the form in which they come from food.
Pancreatic amylase in pancreatitis
Published: February 6, 2015 at 11:40 am
Pancreatic amylase belongs to the group of digestive enzymes that are actively involved in carbohydrate metabolism. Pancreatic amylase secreted into the blood plasma is P-type; there is also an S-type enzyme synthesized by the salivary glands. The main function of the substance is to break down starch molecules into oligosaccharides, which are simpler forms of carbohydrates.
The process of digestion and assimilation of carbohydrate foods largely depends on the level of amylase. Changes in tests may be characteristic of a number of diseases of an inflammatory or metabolic nature. The most common indication for testing for this enzyme is suspicion of pathological processes in the pancreas, and much less often in other organs.
Blood amylase in pancreatitis
Damage to the cellular structure, which is a consequence of pancreatitis, leads to a massive release of pancreatic secretion, which also contains amylase. An increase in its level in the blood serum occurs within a few hours after the exacerbation of the process and persists for up to 3-5 days. If the enzyme activity exceeds the norm by more than 5 times, there is every reason to suspect an acute form of the disease.
There are cases when blood amylase during pancreatitis increases slightly or even remains within normal limits, but such test results cannot completely refute the diagnosis. The enzyme level does not indicate the severity of the process, but if the indicators do not return to normal for a long time, complications can be expected to develop.
Amylase level in pancreatitis
The total enzyme content normally differs in different age groups and is as follows:
- 5-65 U/l in children under 2 years of age;
- 25-125 U/l - from 2 years to 70 years;
- 20-160 U/l in persons over 70 years of age.
The level of amylase during pancreatitis can increase several times, especially during an acute process or exacerbation of chronic inflammation. Also a characteristic sign of the disease is an increased concentration of the enzyme in the urine. Clinical observations show that the excess of normal content can be up to 30 times. The information content of biochemical analysis for this enzyme is quite high and amounts to almost 90%.
Amylase in chronic pancreatitis
With a long course of the disease, biochemical blood parameters may differ little from the normative level. Thus, amylase in chronic pancreatitis is slightly elevated in the early stages of the process, with further approaching the norm, and in some cases even lower than it. A sharp increase in the enzyme is typical only for periods of exacerbation, accompanied by severe symptoms.
Since a chronic process may be accompanied by varying degrees of enzyme activity in different patients, this analysis is not informative and decisive in making a diagnosis. To increase the sensitivity of the results, it is recommended to take samples on the first day of hospital treatment, twice after instrumental examinations and when pain increases.
Alpha amylase for pancreatitis
This digestive enzyme is a summary indicator reflecting the secretory activity of both the pancreas and salivary glands. Alpha-amylase in pancreatitis increases due to its pancreatic fraction, normal values of which range from 0 to 50 U/l. Another specific sign is an increase in the enzyme in the urine.
Fractional testing of the level of this enzyme is very important for diagnosis. So, in a chronic course, there are often cases when the overall enzyme level is normal, but the pancreatic enzyme level is elevated, reaching 75-80%. Such indicators may indicate an exacerbation of the process. A decrease in the fraction of pancreatic secretion in the composition of total alpha-amylase is characteristic of atrophy and fibrosis of organ tissue during long-term pancreatitis.
zhkt.guru