Many people know that the condition of the stool: color, consistency, smell - all these are important indicators of the health of a small child and therefore any changes in this matter, especially the appearance of yellow diarrhea in a child, will certainly alarm parents.
However, is diarrhea always a cause for concern and anxiety? Sometimes this is a completely physiological phenomenon. But how do you know when you can handle cases on your own? When is it time to see a doctor? Observation will help parents here. It is enough to take a closer look at the baby’s mood and behavior.
A child's stool up to one year is normal
First, it’s worth talking about what a baby’s normal feces look like at this age, since they themselves can arouse suspicion. After all, the baby’s digestive system is not yet fully formed, and it feeds mainly on liquid food: mother’s milk or artificial formula.
Of particular concern to many young mothers is the newborn's stool, the so-called black-green meconium. It looks really scary, but at the same time absolutely physiological: these are the remains of epithelial cells, amniotic fluid, hair and the like digested in the prenatal state. After a few days, the intestines will clear out and the stool will become normal.
Over the next few months, the condition of the feces will depend on whether he is bottle-fed or breast-fed. A breastfeeding baby defecates up to 6 times a day, his stool is mushy and yellow in color. White cheesy inclusions are possible - incompletely digested remnants of mother's milk. The yellowness of the stool is also explained by the immaturity of the intestines.
The color of stool in formula-fed babies is darker , sometimes even greenish or bright green. There is no need to be alarmed; the green color appears due to the addition of iron to the mixture to prevent anemia in infants. So there is no need to be afraid of this coloring of feces.
When children are six months old, or even earlier, they begin to introduce complementary foods, that is, regular food: cereal, vegetables, meat. Yes, all this is processed in a special way, but it is no longer milk, not monotonous food.
Changing your diet invariably changes the process of bowel movements . The stool changes color, becomes darker, more dense.
Causes
There are several main reasons why a child develops bright yellow diarrhea:
- Penetration of intestinal infection . The pathological process is accompanied by a deterioration in the patient’s well-being, the appearance of pain in the abdominal area, vomiting, and an increase in body temperature. There may be blood or mucus in the stool.
- Rotavirus . This disease is distinguished by the absence of pain and a stable temperature, which cannot be brought down with conventional antipyretic drugs. Typical for the acute period, yellow stools later become watery, foamy diarrhea with a gray tint. Frequent urge to defecate and copious amounts of stool can lead to severe dehydration.
- Food allergic reaction . In older children, yellow diarrhea occurs after eating foods containing aggressive allergens, for example, chocolate, citrus fruits, soft-boiled eggs, strawberries, and whole cow's milk. The active ingredients in their composition not only weaken the intestines, but also irritate the mucous membranes.
- Whipple's disease is a rare infectious disease that affects various organs and systems. It is manifested by fever, a sharp decrease in body weight, frequent loose stools, impaired absorption of nutrients, and an increase in temperature.
In addition, a child may experience yellow diarrhea due to:
- Taking certain medications.
- Infectious and viral diseases (sore throat, flu, otitis media).
- Severe stress.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Hepatitis A.
- Intestinal diseases.
- Indigestion.
- Fungal infection.
- Appendicitis.
Yellow diarrhea that begins in a newborn is associated with non-compliance with the diet by the nursing mother or improper preparation/storage of formula.
Causes of yellow diarrhea in a child under one year old
Yellow diarrhea in a newborn is not uncommon. This is due to a whole list of reasons.
Among them are the following:
- immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract of a small child;
- binge eating;
- food allergies;
- food poisoning;
- infectious diseases;
- taking medications;
- dysbacteriosis;
- underdevelopment of the digestive organs.
Most often, of course, the causes of diarrhea are found at the top of the list and do not entail any complications. But this does not mean that parents can ignore the yellow diarrhea that occurs in their child. It is very important to closely monitor the baby.
One of the problems of yellow diarrhea in a child was examined by Dr. Komarovsky:
If diarrhea is a one-time occurrence or passes over a period of time and is not accompanied by fever, changes in the baby’s appetite or well-being, then there is nothing to worry about. Most likely, the child simply overate or the immature intestines for some reason could not cope with the food.
It is also possible that feeding rules were not followed: for example, the bottle was not sterilized before preparing the formula. If he was given some new product that day, then perhaps he should refuse it for now.
Why else can a breastfed newborn have yellow diarrhea? Of course, because mom ate something wrong. If a woman has somehow changed her diet, then she should give up new products, spices or some cooking methods.
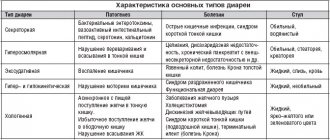
Types of baby diarrhea
Physiological – in the first days during the “tuning” of the digestive tract.
Associated with complementary feeding and the appearance of new foods in the diet.
Infectious: bacterial (for salmonellosis, dysentery) and viral (for infection with rotavirus, adenovirus and viral hepatitis). In the latter case, there is a rather long incubation period (up to 3 weeks). Infectious diarrhea occurs with fever, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
Toxic. Appears when the body is poisoned with salts of heavy metals or with kidney or liver failure.
Nutritional. Occurs when there is a malnutrition or monotony.
Allergic – with intolerance to certain foods.
Medication - after taking certain medications, diarrhea occurs especially often after antibiotics: they lead to an imbalance of microflora in the intestines and dysbiosis.
Neurogenic – as a result of stress or fear.
Infestation by worms, protozoa or fungi.
Disruption of microflora growth in the intestines after acute diarrhea.
Change of climate and living conditions - food and water. It may go away on its own after adaptation.
Hereditary pathology - cystic fibrosis, lactase deficiency and deficiency of other enzymes, celiac disease, congenital intestinal abnormalities.
Symptoms and causes of yellow diarrhea in a child after one year
After a year, the child’s feces already have a more familiar appearance to humans: formed, light brown in color. Thanks to this, if the baby begins to diarrhea at this age, it is much easier to recognize it.
There is no need to compare or guess whether the baby’s stool has become more watery than usual. This makes it easier to recognize the problem as such, but does not help to understand why the situation has arisen.
The intestines of a one-year-old child are already more or less developed and accustomed to cope with many “adult” foods. However, like a baby, a baby over the age of one year can overeat, eat something stale, and experience food allergies or infections.
At the same time, it is easier for the baby’s body to cope with the consequences of overeating or mild allergies. But help is still needed to overcome poisonings and infections. How to understand that this time there is nothing to worry about?
The signs are approximately the same as in the case of a very young child:
- diarrhea quickly goes away on its own;
- the baby is cheerful and does not complain of pain;
- does not refuse food;
- he has no fever;
- there is no blood or mucus in the stool.
If there is no reason for concern, then all that remains is to remember what has changed in the child’s life recently. Now this question concerns not only nutrition, but also the psychological state of the baby, as well as his environment. The cause of diarrhea at this age can be a sudden change of environment, for example, moving, or some other stress.
Types of diarrhea
Foamy diarrhea in an infant, which has a strong odor and is accompanied by an increase in temperature, as well as symptoms of intoxication, indicates the presence of an intestinal infection. Classification of acute intestinal infections by type of diarrhea:
- Invasive type. Acute intestinal infections of bacterial etiology. They are caused by Salmonella, Shigella, some types of Escherichia, Yersinia and other pathogens. Pathogens can invade the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract and cause foamy stool. Watery diarrhea with yellow-green mucus mixed with blood in a child often indicates salmonellosis. Green stool and small amounts (“rectal spitting”) indicate the occurrence of shigellosis.
- Secretory type. Such diarrhea in an infant can be of bacterial etiology (Vibrio cholerae, enterotoxigenic Escherichia, Klebsiella, Campylobacter, etc.) or viral (rotaviruses, coronaviruses). These pathogens multiply only on the surface of the intestinal epithelium. This type of diarrhea causes very loose stool in a newborn, looking like “water.” Yellow diarrhea in infants and older is a clear sign of rotavirus infection.
- Mixed type. Caused by a mixed infection, clinical signs include symptoms of both invasive and secretory types.
To isolate the suspected pathogen, feces, vomit, and gastric lavage are used, where it is identified using bacteriological examination. Its main disadvantage is the long time it takes (5-7 days); sometimes diarrhea in a newborn can be cured even before results are obtained. Serological tests are also used to detect the titer of antibodies to a specific pathogen.
Treatment of acute intestinal infections is prescribed by a doctor, since loose stools in an infant can quickly lead to dehydration with serious consequences. Rehydration and detoxification therapy are prescribed, and antibacterial drugs are prescribed for bacterial infections.
Treatment of diarrhea in infants
Even if the baby’s condition does not cause concern to parents, yellow diarrhea should not be ignored. After all, diarrhea leads to dehydration, and this is already a rather dangerous condition. Its consequence can be hospitalization and even death of the child.
It is very important to remember dehydration syndromes well, so that if something happens you don’t waste time:
- strong thirst;
- dry skin;
- dry mucous membranes;
- sinking fontanelles;
- sunken eyes;
- lethargy, drowsiness of the child;
- weight loss.
Therefore, the first answer to the question of what to do if a newborn has yellow diarrhea is to put it to the breast more often, and, if necessary, give it more water. This can be water or decoctions. However, if the child is not yet a year old, it is better to be careful with herbal decoctions, since some of them are quite potent.
Carefully read the instructions for herbs for decoction and purchase them only in pharmacies.
You can resort to traditional methods of treating diarrhea. For example, rice water helps very well. To prepare it, you need to take one part rice and three parts water and bring to a boil. The product is given to the child one tablespoon every two hours.
A remedy such as chamomile and mint tea helps with diarrhea. Herbs are mixed in equal proportions. Place a teaspoon of the mixture in a glass, pour boiling water over it and cool to an acceptable temperature. This tea is drunk in small sips in 4-5 doses per day.
To fix the stool, you can give the child smecta to drink. Children under one year old are given 1-2 sachets of the product per day. You can dilute it with milk or formula if he is less than 3 months old, or with boiled water if the baby is older. Before use, the mixture must be shaken, as the smecta settles to the bottom. The mixture is divided into equal portions, a teaspoon each, and given to the child regularly. The course lasts 3 days.
Activated carbon can also be a good remedy for diarrhea, which, like smecta, draws out all toxins and cleanses the intestines. However, it is not absorbed into the blood, but passes through the intestines through. Babies up to one year old are given 1 tablet per day divided into several doses.
Eliminating diarrhea in a child
If a child has loose stools once, then there is no need to start drug therapy. It is necessary to remember what foods were in the baby’s diet over the last 24 hours and, if the symptom repeats, analyze whether there is a pattern. Thus, it will be possible to identify foods to which the child has an individual intolerance, and in order to reduce the load on the digestive system, they simply need to be excluded from the diet.
If pathological inclusions are visible in the stool, such as fat, food particles, a large amount of mucus, or blood, then you need to take blood and stool tests, and undergo an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs. Only after an examination will it be possible to make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy that eliminates not the symptom, but the cause of the disease.
If diarrhea is frequent and profuse (regardless of the color of the stool), then you should seek medical help. To prevent the development of dehydration, children under one year of age are recommended to be hospitalized for infusion therapy.
Diet therapy
If yellowish diarrhea occurs, regardless of the cause of the symptom, a therapeutic diet No. 4 is prescribed, which helps reduce the load on the digestive tract and reduces the severity of putrefaction and fermentation processes in the intestines. It is recommended to feed the child in reduced portions, but more often, so that food is absorbed in the intestines and does not pass through in transit.
Any foods that stimulate the secretion of gastric juice and intestinal motility should be removed from the menu. Cold drinks and dishes have a laxative effect, so they should not be given during diarrhea. To reduce the severity of the fermentation and putrefactive process, you need to remove legumes, cabbage, fatty meat, milk, fresh vegetables and fruits from the diet.
When yellow diarrhea appears, a child's menu may include mucous soups, cereals, dietary meat and fish, crackers, fermented milk products, jelly, and jelly. All dishes must be steamed or boiled. Diet is an important component of therapy, so compliance with it is mandatory for several more days after the yellow diarrhea disappears.
Drug treatment
Enterosorbents are used to eliminate diarrhea. These drugs are not absorbed in the digestive tract, but pass through it, absorbing toxic substances. The product helps compact stool and slow down its passage. Enterosorbents are divided into absorbents (convert liquid toxins into a solid substance, so that they are not absorbed into the bloodstream), adsorbents (absorb poisons like a sponge) and chemical absorbers (react with poison).
Taking sorbents is contraindicated for chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, intestinal atony, bleeding from the digestive tract. Taking this product accelerates the elimination of toxic compounds, but it has no effect on bacteria and viruses that secrete these substances, therefore, for intestinal infections, the sorbent only reduces the severity of the symptom.
Sorbents are prescribed for children in case of poisoning, an allergic reaction, or indigestion. Most often, young patients are recommended:
- Smecta. The drug additionally coats the intestinal walls, protecting them from irritation. Children under one year of age are given two sachets of the product per day for three days. For older children, first give a dose of 4 sachets, and then reduce it by half. The drug has almost no side effects (constipation or dermatological reactions may occur).
- Polysorb. Has a high degree of adsorption. The dosage of the medicine is calculated based on the child’s weight (per 10 kg daily dose 2 grams).
- Enterosgel. Available in the form of a sweet paste. Children from one to 5 years old are given a teaspoon three times a day. In case of acute poisoning, the first dose is doubled. Children under 14 years of age are given medication by dessert spoon, also three times a day.
- Polyphepan. Available in powder, which must be diluted with water. Children under one year old are given a teaspoon of the product, children under seven years old the dose is increased to a dessert spoon.
- Activated carbon is given to children over seven years of age.
Intestinal antiseptics can also be used to treat diarrhea, for example:
- Enterofuril. Available in the form of yellow capsules or suspensions. Refers to broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents. In case of acute bacterial diarrhea, it restores the intestinal microflora; in case of infection with enterotropic viruses, it does not allow the development of superinfection. Indications for use are bacterial diarrhea without fever, intoxication or deterioration of general condition. Capsules are given to children over three years of age; the yellow suspension is suitable for treating children from one month of age.
- Baktisubtil. Refers to eubiotics. Contains bacteria that produce broad-spectrum antibiotics that inhibit the growth of pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria. The product has an antidiarrheal effect and restores intestinal microflora. Prescribed for children over 7 years of age.
- Nifuroxazide. An antimicrobial agent that reduces the production of toxic substances by bacteria. Does not cause dysbacteriosis. Prescribed for children over 6 years of age.
If yellow diarrhea in a child occurs as a result of long-term antibacterial therapy, then drugs are prescribed that normalize the microflora of the large intestine. These can be probiotics or prebiotics containing the necessary lacto- and bifidobacteria or a substrate for their accelerated development. They may prescribe Bifidumbacterin, Lactiale, Lacidofil.
If yellow diarrhea is caused by a disease of the digestive system (liver, pancreas, stomach, intestines), then several groups of medications are required. For example, to restore liver function, vitamins, hepatoprotectors, and choleretic drugs can be prescribed, and to reduce the inflammatory process in the stomach, antacids and antihistamine receptor blockers cannot be used.
With increased intestinal motility, antidiarrheal drugs, for example, Imodium, are prescribed. To combat intestinal infections, antibacterial or antiviral drugs are prescribed that destroy the pathogen. If no specific treatment has been developed, then symptomatic therapy is carried out (droppers are placed to normalize the water-salt balance, antipyretics and enterosorbents are given).
For food allergies, medications that reduce the effect of histamine are prescribed. This could be Alerzin, Zodak, Tsetrin. Diarrhea and vomiting are the body’s protective reaction to the presence of pathogenic bacteria and viruses in the digestive tract, as well as toxins that affect the mucous membrane. It is not advisable to relieve these symptoms; it is necessary to treat the disease that caused the symptoms, so medication should be prescribed by the attending physician.
If a child has diarrhea, then it is necessary to adjust his diet and increase the amount of fluid consumed in order to normalize the water-salt balance. If additional symptoms appear (nausea, fever, flatulence, headache and abdominal pain, foreign impurities in the stool), you should call a doctor. The doctor will tell you what to do if bright yellow or yellow-green diarrhea occurs after a physical examination of the child and assessment of his condition.
The child's body has its own characteristics of functioning. The gastrointestinal tract is no exception. In children, it is still immature, and the secretory function of the digestive glands is low. The color of stool depends on many factors, including the food you eat. Since the main food of infants is milk, it is not surprising that the color of stool and the frequency of bowel movements differs from adults. What to do if a child has yellow diarrhea? What kind of feces is normal for infants?
Treatment of diarrhea for children after one year
Treatment of diarrhea in children over one year of age is in many ways similar to those measures that are used for infants. Yellow diarrhea in a 1-year-old child can also cause dehydration, although a one-year-old baby is already able to remind his parents of his needs.
It is necessary to increase the amount of fluid consumed to avoid unpleasant consequences.
In the same way, enterosorbents, such as smecta and activated carbon, are used to remove toxins. Naturally, with increasing age, the dose also increases. Children over one year old are given 4 sachets per day for the first 3 days, then for a few more days - a reduced dose, 2 sachets per day. Children over one year old are given activated carbon 4 tablets per day.
Diarrhea may be a reaction to antibiotics. The fact is that antibiotics kill not only pathogenic microflora, but also those microorganisms that help a person in the process of digestion. To restore damaged microflora, the child needs to be given a drug with beneficial microflora.
These drugs themselves can cause diarrhea, so they should be taken only after consulting a pediatrician.
Yellow diarrhea in a year-old child without fever can be treated with folk remedies. In addition to those indicated in the previous section, a decoction of hawthorn fruits helps well . In addition to the fact that it will help cope with dehydration and strengthen the stool, it will also saturate the body with microelements and vitamins.
After all, diarrhea provokes the loss of all these substances. In addition, it also helps remove toxins from the baby’s body. 5 g of hawthorn fruits are poured with boiling water and then boiled for about 10 minutes. After this, the finished broth is cooled. The child is given a tablespoon of decoction 3 times a day.
Causes of white diarrhea in children
Experts cannot always accurately determine the reasons for the appearance of such bowel movements and give an answer as to what kind of stool in a child can be considered normal. Its character is influenced by a fairly large number of factors: age, nutrition, medication use and much more.
The feces of a newborn baby can be of any color and consistency - yellow, white, brown, liquid and mushy. Pediatricians say that light-colored stool is often observed in babies during the period when they are teething. This is physiological diarrhea, which is not dangerous and goes away on its own.
It is much worse if white diarrhea is caused by intoxication (a condition equivalent to poisoning, which develops under the influence of various poisons and toxins that enter the body from the external environment) or any serious diseases.
Bile duct diseases
Biliary dyskinesia in a child is a failure of the process of bile formation and bile secretion. Stagnation of bile is formed, which leads to poor functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, the motor activity of the gallbladder and biliary tract is disrupted without their organic changes.
Blockage of the bile ducts is often accompanied by loose stools and white feces. The normal color of feces is ensured by the presence of bile acid impurities in them. When this substance is not released into the duodenum in the required volume, the color of the stool gradually changes and becomes lighter, even white.
With biliary dyskinesia, the absorption of nutrients, especially fats, deteriorates. After all, in order for fats to be better digested, they must be broken down into smaller “droplets”, and this function is performed by bile. Biliary dyskinesia is usually accompanied by reactive pancreatitis - an inflammatory process in the pancreas.
Cholangitis is an inflammation of the bile ducts that occurs against the background of obstruction of the biliary tract or bacterial infection of the bile itself. It can also cause white diarrhea in a child.
Cholecystocholangitis in children is usually of an infectious nature: bacterial, viral, fungal. May be of toxic origin. The connection of this inflammation of the biliary tract with appendicitis, scarlet fever, dysentery, sepsis, sore throat, chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, dental caries, infectious hepatitis (Botkin), helminthiasis, tuberculosis intoxication has been proven.
Cholecystocholangitis in children occurs more often as a primary chronic disease. It requires long-term treatment with mandatory medical examination of patients for 3-4 years.
Taking medications
The intestinal microflora is disrupted for various reasons. Most often, dysbiosis develops after prolonged use of antibiotics; in rare cases, this causes white diarrhea.
Drugs that interfere with liver function can cause white diarrhea in a child:
- Tetracycline;
- Aspirin;
- Ibuprofen;
- Paracetamol;
- Methotrexate.
Diarrhea after antibiotics in a child is caused by the same circumstance - the death of beneficial microflora. Antibacterial drugs in many cases become indispensable in the treatment of diseases of the upper respiratory tract, but at the same time they can affect both pathogenic microorganisms and beneficial ones with equal force.
Microflora disturbance
Modern pediatricians believe that dysbiosis is not a disease, but a condition of the mucous membranes in which the balance of the microflora is disturbed. Dysbacteriosis in children under one year of age is a very common phenomenon. The work of the gastrointestinal tract of a newborn is still just getting better, and there may not be enough beneficial bacteria for stable intestinal function.
If a child has taken antibiotics, the natural microflora of his intestines is disrupted, because antibiotics kill any bacteria, without distinguishing whether they are pathogenic or beneficial. It can also be caused by poor diet, stress and other factors. Symptoms in a child, including white diarrhea, with dysbacteriosis appear quite clearly and cause discomfort, especially for infants.
Colitis
This disease is inflammatory and is characterized by dystrophic changes in the large intestine. Among its symptoms are periodic abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea or frequent urge to defecate, chills, dehydration, and blood clots in the stool.
When to see a specialist
However, it is not always possible to treat diarrhea at home, without contacting a specialist. It is important to watch for other symptoms.
Severe dehydration, fever, refusal to eat, vomiting, diarrhea that does not stop for more than a day, blood and mucus in the stool - all this is a reason to immediately consult a pediatrician for advice.
The same should be done if a child has yellow diarrhea with foam or water diarrhea.
Don't put off going to see a specialist. It may even be worth calling a doctor at home or calling an ambulance. In some cases, delay can cost the child his health, and sometimes his life.
Now you know what to do if your newborn has yellow diarrhea. In any case, it is very important not to panic, but to adequately assess the situation and your strengths. If there is even the slightest doubt that everything is fine with the child, it is better to call a doctor and listen to his recommendations.
Pathological diarrhea
The most common cause of bowel dysfunction among children is an intestinal infection. It develops when the pathogen enters the oral cavity. The source of infection is:
- dirty hands;
- unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- spoiled food;
- dishes contaminated with microorganisms;
- pets, etc.
In most cases, Giardia, streptococci, and rotavirus are detected in the intestines of children. A little less often - Pseudomonas aeruginosa and salmonella.
Sometimes the causative agent is Candida, Proteus or Klebsiella fungi. These representatives are inhabitants of the natural human microflora and begin to actively reproduce when immunity decreases. If these microorganisms are frequently cultured in a child, you should consider testing. The causes of such diarrhea are acute or chronic diseases:
- stomach;
- intestines;
- liver;
- gallbladder and other organs.
The appearance of loose stools is observed with appendicitis and other surgical pathologies of the abdominal cavity. It happens that regular light diarrhea in a child occurs due to congenital lactase intolerance. Other factors that provoke yellow diarrhea in a child include:
- pancreatitis;
- malabsorption syndrome;
- hepatitis;
- helminthiases;
- allergic reactions;
- poisoning with chemicals and medications.
Seeing a doctor and conducting an examination will help determine the cause of the disease.