A disease such as duodenal diverticulum is expressed by a protrusion that has a sac-like shape and disrupts the organ under the influence of various factors. Inflammatory bowel pathology is similar to a hernia and is called diverticulitis. If the formation is not single, but multiple, then the person develops diverticulosis. However, most often single diverticula are observed in the duodenum.
Description
A diverticulum is a bulging (growth) on the wall of a person’s intestines, somewhat similar to a pocket. It has a widened and narrow neck measuring approximately 2-4 mm. The expansion has a different volume, about the size of an apple. The patient's diverticulum reaches from 5 mm and can reach 10 cm or more.
These growths mainly form in older people. Half of the elderly population has diverticula in the intestines. Many people do not even suspect their presence, since the disease does not manifest itself in any way until the protrusion becomes inflamed. This happens when stool is retained in the diverticulum. Inflamed diverticula are called diverticulitis. Outgrowths are detected during examination of the patient’s digestive tract, in the presence of other pathologies.
In the small intestine, where the duodenum is located, this bulging is observed extremely rarely, in 10% of cases, of which 5% of patients show different signs. And often solitary diverticula occur.
Most of them occur near the enlarged duodenal papilla; they can be localized in the middle of the duodenal bulb. When growths have formed near the nipple of Vater, this indicates parapapillary diverticula.
Reason for appearance
Why does a patient develop diverticula? It is impossible to answer this question yet. But there are so-called risk factors that contribute to the appearance of pathology.
- Age. Age-related changes in the patient that begin in the body also play a role. In some patients, with age, the interstitial fibers become weaker and intestinal motility decreases.
- The patient was not eating properly. He ate a lot of flour and sweets; his diet was low in fiber and water, but high in fat and red meat. To prevent the disease, you need to eat at least 30 g of fiber per day. If you eat less, the patient’s intestinal contents become hard and dry, causing constipation, which then leads to diverticulosis.
- Heredity. In some people, diverticula are congenital in nature, as they have a hereditary connective tissue pathology.
- Constant constipation Severe constipation in a patient, flatulence contributes to the development of diverticulosis.
They also appear in obese people who lead a sedentary lifestyle. A protrusion can only occur where muscle fibers in the intestine have weakened.
Causes
The congenital form of diverticula appears as a result of disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus. Here, muscle weakness of the duodenal mucosa is noted.
An acquired disease arises from the following possible causes:
- poor nutrition;
- constant increase in pressure in the intestine;
- the impact of age-related characteristics;
- existing diaphragmatic hernia;
- adhesions with other organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- inflammation of nearby organs.
It is very important to conduct an examination to exclude duodenal disease, especially if a person has previously suffered from cholecystitis, pancreatitis, or peritonitis.
Laparoscopic resection of duodenal diverticulum
Laparoscopic resection of duodenal diverticulum. Operated by Professor K.V. Puchkov (2015).
The operation is performed for a 6 cm diverticulum located in the descending part of the duodenum on the posterior wall. The film shows the technique of mobilizing the duodenum according to Kocher and isolating the diverticulum from the surrounding tissues with a 5 mm Harmonic Scalpel Ethicon instrument and instruments from the Karl Storz Company. Then, under the control of duodenoscopy, the diverticulum is cut off in the transverse direction using a linear stapler Endo GIA MEDTRONIC COVIDIEN with a cassette length of 60 mm and Tri-Staple technology. This technology provides consistent closure of staples on an expanded range of fabric thicknesses. Next, for the purpose of hemostasis, peritonization from the suture area was performed with interrupted sutures using Polysorb thread. Duration of operation 60 minutes
You can read more about the methodology on the personal website of Professor Konstantin Viktorovich Puchkov
go
Laparoscopic resection of duodenal diverticulum. Operated by Professor K.V. Puchkov (2015).
Classification
There are several types of diverticula:
| By number of entities | Multiple | Single |
| By location | Diverticula in the lower intestine | Diverticula in the upper intestine |
| According to the structure of the bulge | Absentee | Face-to-face |
| By time of appearance | Acquired growths | Congenital growths |
| According to the development mechanism | False | True |
| According to the nature of the disease | Uncomplicated | Complicated |
Full-time formations are observed quite rarely; they arise as a result of the pathological development of the fetus in the womb. The location area becomes the lumen zone where food particles are digested.
Absentee outgrowths are acquired papillary formations that develop in the area of the papilla of Vater; here the bile and pancreatic canals are included in the duodenum. The protrusion ranges in size from 2 mm to 4 cm. It appears in the area of weak muscle fibers.
Regardless of the form of the disease and location, it is important to identify the disease in time and take all measures to eliminate and prevent it.
Complications
- inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis);
- bacterial infection;
- cholelithiasis;
- obstruction of pancreatic and bile ducts;
- inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis);
- perforation of the walls of the duodenal organ;
- intestinal obstruction;
- development of internal bleeding;
- hiatus hernia.
People with diverticula in the duodenal process experience sagging skin, weakness of the muscle fibers of the anterior peritoneum, umbilical and inguinal hernias.
Symptoms and complications
The disease has no clinical manifestations for a long time. A person feels dangerous signs at an advanced stage of development. Constipation, nagging pain in the lower abdomen (can be constant or appear periodically), and flatulence are also noted.
With inflammatory changes in the duodenum, the following symptoms are observed:
- increase in body temperature;
- false urge to have a bowel movement;
- subsidence of pain after defecation;
- loss of appetite;
- metabolic disorder;
- nervousness, irritability;
- intense bleeding or the formation of a blood clot in the stool;
- alternating diarrhea and constipation;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement;
- feces with mucus.
Upon palpation, the specialist identifies pain in the epigastric zone of the abdomen and increased gas formation. If the diverticulum is located near the nipple of Vater, there is a possibility of gallstones. Often it becomes inflamed and cholecystitis occurs. Pathogenic microorganisms located along the channels lead to an intense inflammatory process. Complications of diverticulitis in a patient may include pancreatitis and biliary colic.
Intact diverticula are associated with blockage (duodenal obstruction), which has the following symptoms:
- diarrhea or constipation;
- decreased appetite;
- one-time or multiple vomiting;
- fever;
- constant feeling of pain.
If you have such signs, you need to consult a doctor for medical help; self-medication is unacceptable here.
Symptoms
Diverticulum is often asymptomatic. Sometimes after eating there is mild pain, heaviness, and discomfort in the right side. Possible nausea . Obstructive jaundice occurs less frequently if the diverticulum affects the gallbladder. This is possible due to the proximity of the duodenal and bile-producing organs.
Severe pain occurs when the protrusion becomes inflamed. Along with pain, the inflammatory process in the diverticulum contributes to the appearance of other symptoms:
- severe bleeding;
- the appearance of blood clots in the stool;
- severe flatulence, bloating;
- heat - up to 38-39°C;
- nausea;
- stool variability.
Diagnostics
Since diverticulosis is asymptomatic, it is very difficult to identify this disease. It is usually detected unexpectedly, during examination of the duodenum for suspicion of other diseases. When a patient has an intestinal diverticulum, a thorough examination will be required, because the pathology is often confused with colitis, polyposis, or cancer.
To diagnose duodenal diverticulum, the doctor prescribes the following measures:
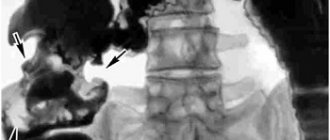
- X-ray – examines the intestines, often used with contrast. With its help, you can clearly examine the parts of the stomach and duodenum and recognize diverticula.
- Ultrasound - allows you to see all the loops of the intestine and exclude the presence of foreign bodies and anomalies in it.
- Irrigoscopy - barium sulfate is injected into the intestines through an enema, then a couple of pictures are taken for study.
- Colonoscopy - a probe with a camera is inserted into the anus. The procedure allows us to exclude polyposis, cancer and diverticulosis of the colon.
The doctor may prescribe other diagnostic procedures.
Types of diverticula
Diverticula are divided into internal or congenital, and absent or acquired. Full-time ones appear due to developmental disorders in the embryo. This type of disease is quite rare. Acquired or absentee diverticula are also distinguished. They are associated with intestinal dysfunction. Most often, they do not occur immediately, but when the patient reaches an advanced age. If we talk about the duodenal diverticulum, it often appears in Vater’s nipple.
Diverticula can be true, that is, in this case the protrusion consists of all layers of the intestine, and false, when only the submucosal and mucous layer of the intestine protrudes.
Treatment
Conservative treatment methods are most often used. When the diverticulum regularly recurs, becomes complicated, the growths noticeably increase, and surgical intervention is performed. Pathology is determined by air insufflation using a duodenal probe.
Drug treatment
For effective therapy, you will need to follow a dietary menu, take medications to normalize intestinal microflora and eliminate constipation.
In case of inflammation and aggravation of the disease, the following are used:
- laxatives (Regulax, Duphalac) and anti-diarrhea medications (Fthalazol, Smecta) - improve bowel movements;
- sorbents (Polysorb, activated carbon);
- enzyme preparations (Creon, Mezim);
- antibiotics (Cefotaxime, Tetracycline);
- painkillers (No-Shpa, Spasmol);
- medications that increase peristalsis (Domperidone).
An important aspect of treatment is the improvement of stool and daily bowel movements.
Diet
A diet is prescribed for intestinal diverticulosis, which, along with medications, will help cope with the disease.
Recommended products are:
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- low-fat varieties of fish and meat;
- bread, pasta made from wholemeal flour;
- eggs in small quantities;
- dried fruits;
- compotes, juices, green tea;
- various cereals;
- dairy products;
- purified water.
The following products should be excluded:
- rice, semolina porridge;
- coffee, carbonated drinks, alcohol;
- chocolate;
- seasonings, spices;
- wheat bread;
- cabbage, beans, mushrooms;
- raspberries, kiwi;
- fatty dairy products.
You need to eat in small doses, but often, at least 6 times a day, and do not overeat. Food must be chewed thoroughly. Eat boiled, baked or steamed food. Drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day.
Surgery
The operation is performed for complications of the disease that threaten a person’s life. Manipulation is carried out in case of bleeding, intestinal obstruction, as well as in the presence of peritonitis. An emergency operation is being carried out.
Planned interventions are performed for fistulas, failure of conservative treatment with subsequent deterioration of the patient’s well-being, and chronic exacerbations. After the operation, you will also need to adhere to a certain diet.
What methods does pathology therapy include?
An important element of therapy is the prevention of complications and adherence to dietary nutrition. The use of traditional medicine under the supervision of a physician is allowed.
Use of medications
In the absence of complications, it is necessary to follow a diet, take medications that help restore gastric microflora, and prevent constipation. For inflammation of diverticula and other complications use:
- medications that normalize stool. These are laxatives (Guttalax, Regulax, Dulcolax) and anti-diarrhea drugs (Smecta, Phtalazol, Levomycetin);
- antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Tetracycline);
- enzymes (Mezim, Creon, Pancreatin);
- sorbents (Activated carbon, Enterosgel);
- medications that increase gastric motility (Motilak, Dromperidone);
- painkillers (Spazmol, No-shpa, Ketanov).
An important element of therapy is normalization of stool and regular bowel movements. The desired result can be achieved by following a diet, taking medications and special massage.
To avoid clogging of diverticula, a special technique is used, in which a position is selected for the patient for better emptying of the formations. It is recommended that the patient spend a few minutes in this position every day before going to bed.
Carrying out the operation
The operation is performed when complications develop that pose a risk to the patient’s life. Intervention is indicated for peritonitis, intestinal obstruction, and bleeding. In this case, the intervention is performed on an emergency basis. Planned operations are performed for chronic exacerbations, fistulas, ineffectiveness of conservative therapy with further deterioration of the patient's condition.
Diet features
Proper nutrition is the key to successful recovery from pathology. The table provides information about which foods are recommended to be consumed when ill and which should be avoided.
| Recommended Products | Prohibited Products |
| Porridge (oatmeal, buckwheat, brown rice, millet) | Fatty meats and fish |
| Vegetables | White rice, semolina |
| Fruits | Whole milk |
| Dairy products | Fat cottage cheese, sour cream |
| Low-fat fish and meat | Alcohol |
| Eggs in limited quantities | Drinks with caffeine |
| Dried fruits | Soda |
| Bread and pasta made from wholemeal flour | Gas-forming products (legumes, all types of cabbage, mushrooms) |
| Green and herbal teas | Strengthening products (pasta, white rice, semolina, white bread) |
| Natural juices | Fruits and vegetables that contain indigestible particles (raspberries, strawberries, kiwi) |
| Uzvary | Chocolate |
| Purified water | |
| Compotes |
During illness, it is recommended to eat food more often, in small portions, and avoid overeating. Products are prepared by boiling, stewing, and baking. Fruits are useful to eat raw with peel. It is important to establish a drinking regime. In between meals, you should drink 1 - 2 glasses of water. The total amount is 6 – 8 glasses per day.
Prevention
To prevent the worsening of the disease and its transition to a relapsing stage, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures:
- If there are existing hernias, avoid lifting heavy objects;
- eat a complete, balanced diet;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- play sports, walk in the fresh air;
- sleep should be healthy;
- take enough water.
The prognosis for cure is usually positive. Complications are extremely rare. Operations are tolerated favorably by people. It is very important to promptly identify the cause of abdominal pain and carry out treatment. And a qualified specialist can help with this.
We recommend: What is the difference between rotavirus and norovirus
Diagnosis of the disease
Diverticulosis, in which protruding formations are present in the duodenum, is detected through diagnostics, which consists of several stages.
The examination is performed in the following order:
- It is urgent to visit a therapist, surgeon, gastroenterologist and get their recommendations. Taking into account the symptoms noticed by the patient, doctors will find the root causes of the development of the disease and determine the factors that contributed to its appearance. Specialists will determine not only the disease itself, but also its type, the form in which a person has damage to the duodenum.
- After visiting doctors, an ultrasound scan is required. This study will allow you to see the presence or absence of changes in the structure of the intestinal organs. Ultrasound testing eliminates the possibility of developing a malignant tumor.
- To treat diverticulosis, proper nutrition is necessary, and the doctor will select it taking into account the specific situation and health status of the patient.
- An X-ray of the intestine will allow you to see a more complete picture. Its result is aimed at clarifying the characteristics of the disease.
- The final stage of the examination is colonoscopy and irrigoscopy, during which the condition of the intestinal walls, the exact location of diverticula, and their exact number are checked. Sometimes CT and NMR are performed.
Complications and consequences
In the parafaternal diverticulum, bile and other contents (lumps of mucus, food debris) can accumulate and stagnate, which subsequently leads to the development of an inflammatory process - diverticulitis. Complications can also manifest themselves in the form of bleeding, ulceration and perforation of the wall of the pathological protrusion. In the area where one or more diverticula are formed, the intestine becomes stenotic and becomes deformed.
The formation of an abnormal sac often leads to the development of pancreatitis and hypertension of the bile ducts, so you should not ignore the defect that has arisen and take timely measures to cure it.
Diagnosis and treatment
After examination by a specialist, instrumental and laboratory diagnostics are prescribed. Blood, urine and stool tests allow us to judge the general condition of the body. To differentiate from other ailments, as well as to clarify the location, type, degree of tissue damage and the number of diverticula, as well as to select effective treatment tactics, the following are used:
- ultrasonography;
- X-ray with contrast;
- colonoscopy.
If there are difficulties in making a diagnosis, MRI and CT are prescribed.
Treatment of the disease is most often conservative. Diverticula that are discovered by chance and occur without symptoms are treated with diet, probiotics, enzyme preparations, and anti-flatulence medications.
In case of inflammation of the protrusion, along with dietary correction, stool stabilizers, hemostatic, hemostatic agents, broad-spectrum antibiotics (course of 5-10 days), stimulants of gastric motility, enzymes, sorbents, and painkillers are prescribed.
To avoid clogging of pathological protrusions, the patient is recommended to be in a special position for better emptying of the diverticula. You need to take it for a few minutes before going to bed every day. A light abdominal massage is indicated.
If drug treatment is ineffective, complications develop, and frequent relapses are observed, then surgery is performed. To identify a diverticulum, insufflation of air introduced by probing is used. A small defect is immersed and sutured. For large protrusions, organ resection may be necessary.