What is the sigmoid colon
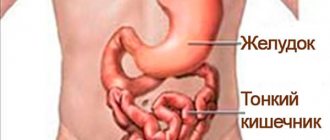
The structural unit of the digestive system is the sigmoid intestine. It is S-shaped and is the terminal part of the colon. Pathologies of such a large structure of the gastrointestinal tract organs can be detected by palpation and occur more often in women. The length of the intestine reaches 50 cm with a diameter of 4 cm. The section is located in the retroperitoneal space, mainly on the left side, with the iliac vessels located at the back. If health problems arise, the patient feels a pain attack on the left side of the abdomen.
What does it look like
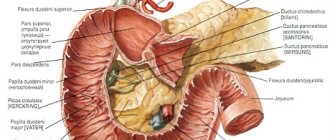
The appearance of the sigmoid section is a tube that is S-shaped. Hence the specific name. You can feel it from the left iliac region, which helps the specialist make a preliminary diagnosis. The structure of the sigmoid colon has its own characteristics: one end connects to the lower colon, the other leads to the rectum. You can view the shape of the sigmoid region on an ultrasound of the retroperitoneal space in order to promptly identify pathology.
Where is
Between the colon and rectum is the sigmoid section of the digestive system, which is responsible for the absorption of fluids and nutrients with their further distribution throughout the body. Dysfunction of the characteristic structure leads to systemic problems in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The location of the sigmoid colon can reach the level of the right hypochondrium, the mesentery is attached to the posterior wall of the peritoneum. Considering the individual anatomical features of the structure of the stomach, the palpation method is not a guide to making a final diagnosis.
Classification
The scope of therapeutic measures often depends on the characteristics of the disease, so there is a need to reflect them in the clinical diagnosis. Sigmoiditis is classified according to the following principles:
- Catarrhal sigmoiditis . Characterized by the development of superficial inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane. The clinical picture may be absent or mild, without causing severe discomfort to the person;
- Erosive sigmoiditis . Develops as a result of poorly treated or ignored catarrhal inflammation. Characteristic lesions appear that are prone to deeper damage;
- Ulcerative sigmoiditis . In this form, inflammation affects the deeper layers of the intestinal wall, which is accompanied by hemorrhages (bleeding).
- Perisigmoiditis . All layers of the wall are damaged up to the serous membrane, which leads to the formation of infiltrates and adhesions. Inflammation can spread to nearby organs and soft tissues of the gastrointestinal tract.
In some cases, the clinic of spastic sigmoiditis can be observed. This occurs when the autonomic regulation of intestinal activity is disrupted.
Functions of the sigmoid colon
With its s-shaped course, this important structure of the large intestine performs valuable tasks for the body. The main functions of the human sigmoid colon are the productive absorption of water and nutrients obtained orally. This is important for the vital activity and stable functioning of the whole organism, for example, moisture obtained from food eliminates the processes of dehydration and metabolic disorders. In this section, stool hardens, after which it moves into the rectum and is excreted naturally.
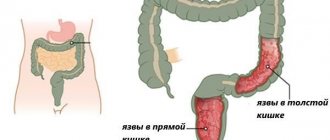
Diseases of the sigmoid colon
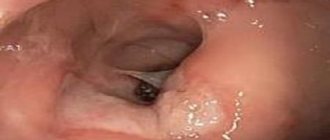
Diseases of this section of the digestive system become a consequence of fecal obstruction, arising due to a violation of the elasticity of the walls of the sigmoid intestine, with the detrimental effect of intoxication products on the gastrointestinal tract. All diseases of the sigmoid colon are accompanied not only by an internal inflammatory process and an acute attack of pain, but also by external changes in this section and its epithelial layer. Such changes can be tracked clinically - using ultrasound. Early diagnosis helps avoid serious complications in the future.
Dolichosigma intestinalis
Even a child can be diagnosed; it is important to treat the disease in a timely manner. Dolichosigma is a pathological elongation of the sigmoid colon or mesentery (mesocolon), as a result of which intestinal motility is disrupted. In such a clinical picture, megadolichosigma is observed, i.e. abnormal thickening of the walls. Constipation and paroxysmal abdominal pain are eloquent signs of the disease, but in order to determine the fact of damage to the large intestine, a comprehensive diagnosis is required.
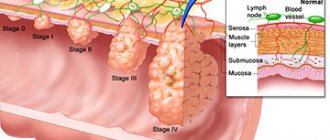
Cancer
Adenocarcinoma, neoplasia carcinoma, blastoma, distal tumor are malignant neoplasms that, with successful treatment, reduce the quality and life expectancy. For example, a villous tumor of the sigmoid colon is difficult to diagnose at an early stage; the symptoms are similar to classic food poisoning (bloating, flatulence, diarrhea, nausea). The approach to the problem is comprehensive and includes diagnostics of the body with biopsy and sigmoidoscopy. Treatment is carried out surgically - removal of the tumor with long-term rehabilitation.
Inflammation
If an inflammatory process occurs in the sigmoid part of the intestine, in medical practice this disease is called sigmoiditis, and is treated with conservative methods. Common causes of the disease are increased activity of intestinal infections and an imbalance of bacteria (dysbacteriosis). Doctors remind us of radiation sickness and intestinal ischemia, pressure of neighboring organs and impaired circulation as pathogenic factors that can provoke the first attack.
With progressive inflammation, doctors recommend taking painkillers and additionally drinking probiotics to restore intestinal microflora. To destroy pathogenic flora, treatment of sigmoiditis necessarily includes the prescription of antibiotics. Vitamin therapy and a therapeutic diet also become an integral part of an integrated approach to health problems. It all depends on the form of the characteristic disease. It could be:
- proctosigmoiditis (spastic colitis);
- focal sigmoiditis;
- bend;
- erosive sigmoiditis.
Diverticulosis
If the blood supply to tissues is impaired and improper transportation of feces to the intestines, the patient develops another disease. It is called diverticulosis and is relapsing in nature. The inflammatory process spreads to the sigmo-rectal sphincter, which connects the rectum and sigmoid colon and is responsible for the excretion of feces.
The disease starts with an acute attack of pain, which is localized in the left side of the abdomen. During the pathological process, intestinal motility is impaired, and high intraluminal pressure occurs. The patient cannot understand its cause for a long time, and the truth is revealed by ultrasound. Inflammation of diverticula of the sigmoid colon is treated conservatively in a hospital setting.
Find out in more detail what sigmoid colon diverticulosis is - symptoms and treatment of the disease.
Complications
How the disease progresses
If the patient consulted a doctor in time for medical help, underwent a detailed diagnosis and effective treatment prescribed by a specialist, then the result of such actions will be a complete recovery. However, you should not expect a quick effect of therapy. During medical procedures, patients are largely limited in nutrition.
If there is no timely treatment, then sigmoiditis most often progresses further, affecting other parts of the intestine. For example, proctitis is observed as one of the complications in patients. With the progression of ignored inflammation, proctosigmoiditis symptoms and untimely treatment lead to a violation of the intestinal tightness, which can provoke an outbreak of peritonitis. Peritonitis is an inflammatory process in the peritoneum, which is most often eliminated surgically.
Symptoms of the disease
Since the organs are located in a spacious area of the peritoneum, the patient may not feel a problem in his own body for a long time. The first signs of sigmoid colon disease are an acute attack of pain, which only intensifies with palpation of the sigmoid colon. This occurs during a progressive pathological process in which other structures of the gastrointestinal tract are involved, for example, the pancreas. The characteristic symptoms of the disease are presented below:
- upset stool, unusual color of stool;
- sharp pain during the resting stage or after defecation;
- belching leading to vomiting;
- increased signs of dyspepsia (flatulence, nausea, bloating);
- sudden weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
- loss of strength, weakness.
- Chicken liver in sour cream: recipes
- Social mortgage - who is entitled to it. Conditions of social government mortgage lending programs
- Cream for mastic
Sigmoid colon hurts
This symptom does not appear at the initial stage of the characteristic disease. Severe pain in the sigmoid colon indicates a prolonged course of inflammation, increased pressure from the source of pathology on neighboring organs. The doctor cannot make a diagnosis; differentiated diagnostics is required. For example, upon palpation, an acute attack of pain only intensifies and radiates to the hypochondrium area. Taking painkillers helps it subside, but this is a temporary effect. It is important to look for the cause in order to avoid the chronic course of this disease.
Types of sigmoiditis
As mentioned earlier, inflammation of the sigmoid colon can be acute or chronic.
- The acute form is accompanied by pronounced clinical manifestations. It develops soon after exposure to a traumatic factor, for example, an intestinal infection.
- The chronic form has less pronounced symptoms and often occurs due to dysbacteriosis.
The disease is also divided depending on the nature of the damage. Sigmoiditis happens:
- catarrhal - the mildest form of the disease, in which inflammation covers only the upper layer of epithelial tissue;
- erosive - usually develops as a result of untreated catarrhal sigmoiditis, when it forms erosions on the mucous membrane that can bleed;
- ulcerative is the most severe form of the disease, which is characterized by the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane; either one ulcer or several foci of different depths and localization can occur. Often develops with ineffective treatment of erosive sigmoiditis.
Symptoms and clinical manifestations
The clinical manifestations of the disease largely depend on the exact form in which the disease occurs.
Symptoms of sigmoiditis, which occurs in acute form, are as follows:
- intense pain localized to the left in the iliac region;
- spasmodic pain radiating to the left leg and lower back;
- bloating;
- frequent loose stools that have an unpleasant odor, and in some types of disease may be mixed with blood and pus;
- signs of intoxication (pale skin, weakness), fever;
- nausea, vomiting.
The chronic form of the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- alternating diarrhea and constipation;
- feeling of rubbing in the abdominal area;
- pain that occurs during bowel movements;
An inflammatory process of this nature leads to deterioration in the digestion and absorption of food. Because of this, with a long course of the disease, a person may begin to lose weight and experience a lack of certain substances. Long-term presence of feces in the sigmoid region can cause allergic reactions on the skin and poisoning of the body. Chronic sigmoiditis, as a rule, occurs with periods of remission, during which unpleasant symptoms subside. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, the disease usually worsens. This can lead to:
- diet violation;
- physical stress;
- stress;
- acute infectious diseases;
- injuries.
Is there always a need for hemorrhoid surgery?
What is a colonoscopy and how is it performed? Read more in this article.
How to check the sigmoid colon
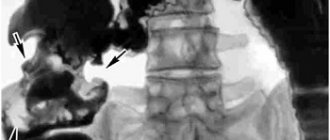
The basis of the clinical examination is ultrasound and radiography. It is obvious on the monitor screen that this section is pathologically enlarged, displaced, and exerts negative pressure on other structures of the digestive system (this is in advanced cases). Diagnosis of the sigmoid colon starts with the collection of medical history and patient complaints, and necessarily includes a study of the composition of stool and a biochemical blood test in the laboratory. Additionally, the doctor prescribes sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, followed by an intensive therapy regimen.
Palpation
During the first examination of the patient, the doctor tries to palpate the suspected focus of pathology. Pain on palpation of the sigmoid colon is sharp, disrupts breathing, and only increases with prolonged exposure. It is correct to palpate the problem area only through the anus, while checking the elasticity of the walls and their structural integrity. A rectal examination of the Rossi-Muthier sphincter is performed by a highly specialized specialist - a proctologist.
Treatment of the sigmoid colon
Inflammatory processes can be suppressed with medication, while structural changes in the department require surgical intervention. Before treating the sigmoid colon, it is necessary to identify the etiology of the pathological process and promptly eliminate the main provoking factor from the patient’s life. Then remove the pain with painkillers, proceed to intensive therapy, supplemented by a therapeutic diet and physiotherapeutic procedures for medical reasons.
Conservative therapy
Drug treatment is aimed at removing the cause and consequences of inflammation, and is additionally monitored by clinical methods. The intensive therapy regimen involves a combination of representatives of several pharmacological groups to enhance the overall therapeutic effect. This:
- antispasmodics to relax smooth muscles: Spazmalgon, No-shpa;
- enzyme-containing preparations: Mezim, Creon, Festal;
- antibiotics to kill bacteria: representatives of the fluoroquinolone group;
- antihistamines against allergic reactions: Fenistil, Suprastin, Tavegil;
- immunosuppressants: Daclimusa, Cyclosporine, Azathioprine;
- anti-inflammatory drugs: Prednisolone and its analogues;
- adsorbents to prevent stomach ulcers: Smecta;
- probiotics to normalize intestinal microflora (Enterol, Linex);
- enemas, rectal suppositories with a favorable prognosis for the disease.
- multivitamin complexes to restore the immune system after long-term treatment of the sigmoid colon with medications.
Surgical methods of treatment
If conservative methods are ineffective, doctors recommend a radical approach to the problem. The patient requires surgery on the sigmoid colon with preliminary radiation therapy. Such surgical intervention is appropriate for oncology of the sigmoid colon. First, its size is reduced by an acceptable dose of radiation, and then completely removed. An additional course of chemotherapy and radiotherapy is necessary to prevent the spread of metastases to healthy parts of the digestive system. For polyps, resection of the pathological focus is recommended.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of a sigmoid colon tumor is made by oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital taking into account the medical history, complaints, objective examination data and the results of additional studies. The most informative methods for sigmoid colon cancer are endoscopic methods (sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy). They allow you to visually assess the volume and location of the tumor and take material for subsequent histological examination.
In the process of examining patients with suspected sigmoid colon cancer, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use irrigoscopy (X-ray examination using a barium suspension) and stool analysis for occult blood. To detail the stage of the tumor process, magnetic resonance and computed tomography are performed. All instrumental research methods are performed using the latest equipment from leading manufacturers in the USA, Japan and European countries.
Other diagnostic techniques are used to detect metastases:
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- X-ray of the spine;
- Chest X-ray.
Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital make the final diagnosis based on the results of histological examination. Differential diagnosis of malignant neoplasms of the sigmoid colon is carried out with precancerous and inflammatory bowel diseases, fixed tumors of the retroperitoneal space and mobile neoplasms of the mesentery.
Traditional treatment
If sigmoid colon disease is identified at an early stage, alternative medicine methods promise positive dynamics. It is important to coordinate the use of folk remedies in advance with the attending physician, undergo diagnostics and determine the nature of the pathology. More often this is an auxiliary therapy. Treatment of diseases of the sigmoid colon with folk remedies is long-term and not always successful. Below are recipes that many patients note as the most effective in a given direction. This:
- To relieve inflammation from the sigmoid mesocolon, you need to grind 20 grams of alder cones and boil them in 300 ml of boiling water. Simmer over a fire, then strain, take 100 ml when cooled throughout the day. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Watermelon rinds are an effective folk remedy for the treatment and prevention of inflammation of the sigmoid colon. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over 100 grams of dried raw material and simmer for 15 minutes. Infuse, strain, drink 3 times a day.
- Plantain helps with bending of the sigmoid colon. You need to take 300 grams of dried raw materials per 400 ml of boiling water, boil, infuse, divide the portion into three approaches. Take each dose before meals. The prognosis is favorable.
Diet for sigmoid colon disease
It is very important to reduce the load on the intestines, and for this we need to review and somewhat diversify the daily menu with new food products. Fatty, fried, salty, smoked and spicy foods that disrupt normal bowel movements become forbidden. The therapeutic diet for sigmoiditis provides a favorable prognosis for the disease, the main thing is to strictly follow it. The list of useful products against the expansion of the pathological focus is as follows:
- light soups with vegetable and lean meat broth;
- skim cheese;
- boiled or steamed vegetables;
- brown rice;
- baked or boiled potatoes.