There are many different intestinal diseases , and most of them are directly related to inflammatory processes. In the presence of inflammation, the intestinal mucosa is primarily affected . The lesion occurs either in a specific part of the intestine, or completely along its entire length.
Thus, duodenitis is an inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the duodenum, enteritis is inflammation in the small intestine, colitis is an inflammatory process in the large intestine, proctitis is inflammation of the rectum. Inflammatory processes in a certain part of the large intestine are also diagnosed. Typhlitis is inflammation of the cecum, appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix, sigmoiditis is inflammation of the sigmoid colon. During the process of inflammation, the intestinal mucosa swells noticeably, and mucus is actively released from it. In some cases, serous exudate or pus . If the inflammatory process becomes severe and typhoid fever, tuberculosis, dysentery , then ulcers may appear on the mucous membrane, which at times bleed.
In the process of inflammatory phenomena, not only changes occur from an anatomical point of view, but also functional disorders. Intestinal diseases disrupt the natural course of food digestion, insufficient absorption of water and nutrients occurs, and the removal of food waste from the intestines is disrupted. The excretory function of the intestines is also impaired due to the release of too large volumes of mucus, and in some cases, exudative fluid.
Diarrhea and constipation
Thanks to the reflex contraction of the muscles present in the intestinal wall, food moves through the intestines. Intestinal motility decreases if the intestines are empty, and it can also decrease or increase if intestinal diseases occur. Normally, a person has bowel movements once or twice a day. If peristalsis is too strong, stool occurs more often and the discharge becomes liquid. This occurs due to the food moving too quickly and, accordingly, the inability to absorb liquid contents into the blood. This condition is typical for diarrhea .
Excessive peristalsis can also be caused by nervous excitement . Thus, fear and anxiety can significantly increase peristalsis and provoke diarrhea. This process is also noticeably stimulated by certain foods - for example, products of plant origin, bread with bran, food that is difficult to digest. In some cases, diarrhea may occur as a protective reaction of the body to eliminate harmful products. Diarrhea can also occur due to impaired absorption of nutrients and water from food. And if the inflamed mucous membrane secretes exudate, the amount of fluid in the intestines becomes even greater. Diarrhea is often observed in the presence of inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, which arose as a result of pathological processes provoked by microorganisms entering the intestines. To prescribe effective therapy, a specialist must determine the nature of the diarrhea.
Constipation is a slow bowel movement that does not occur for several days. The cause of constipation is a significant weakening of peristalsis in the intestines. It can be triggered by weakness of the intestinal muscles, as well as atony of the intestines and peritoneal muscles . Constipation is caused by a constant sedentary lifestyle. There are also so-called habitual constipation . In such cases, the normal reflex to defecate is deliberately suppressed due to haste or other reasons, and this happens regularly. Foods that are well digested can also contribute to constipation. Thus, protein products practically do not irritate the intestines, and it works very sluggishly and slowly.
Another type of constipation is spastic constipation . They are provoked by tonic contractions of the circular muscles of the intestine. As a result, peristalsis stops. Constipation can be a symptom of intestinal diseases, for example, chronic colitis . This disease can also be provoked by mechanical obstacles - tumors, scars, hemorrhoids . If there are no morphological changes in the intestines, then diarrhea and constipation are cured once the cause of their occurrence is eliminated, as a rule, without additional medications.
Causes of pathologies
The most common causes of intestinal diseases are:
- Diet violation. Eating low-quality food products not only leads to infectious intestinal diseases, but can also cause celiac disease, and the content of carcinogens in food can lead to the development of cancer pathology. Most often, prohibited foods are excessively fatty, spicy foods, and fast food.
- Bad habits. Drug addiction, smoking and alcoholism lead to a decrease in the immune response and, as a result, the growth of pathological flora in the intestinal lumen. Alcohol and smoking can cause peptic ulcers, abnormalities in the intestinal structure in children (if consumed during pregnancy), and the development of autoimmune and other pathologies.
- Stressful conditions. Frequent nervous shocks can cause cancer, the development of ulcerative defects of the mucous membrane, irritable bowel syndrome, and so on.
- Genetic reason. Most often, either the disease is inherited or the genetic code of the fetus is “broken.” Presumably this is the cause of ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, intestinal polyposis and other diseases.
- Taking certain medications. Leads to an imbalance of opportunistic and beneficial flora in the intestines; a side effect of some medications is impaired peristalsis. Medicines can be the main cause of the formation of ulcerations of the intestinal wall.
- Sedentary lifestyle. It is considered the main cause of the formation of hemorrhoids.
Be sure to read:
Appendicitis: main signs and treatment of pathology + FAQ
Flatulence
This is bloating in the abdomen that occurs due to the accumulation of a large amount of gas. The intestines are greatly stretched, and noticeable pain occurs. Gases are formed due to the influence of bacteria , as well as after consuming dairy products and carbonaceous foods, which provokes fermentation processes. If, due to a certain disease, gases in the intestines are poorly absorbed, flatulence . This phenomenon is also possible with intestinal obstruction.
Pain in the intestines
Intestinal diseases can cause very different pain sensations. This can be constant aching pain, or sharp paroxysmal pain, called intestinal colic. If a person is worried about a disease of the small intestines, then the pain will occur in the middle of the abdomen, if there is a disease of the cecum , the pain will be in the ileal region on the right, and with a disease of the sigmoid colon - on the left. Pain, as a rule, is well defined during palpation. Sharp pain occurs when gas accumulates. If the symptoms of intestinal diseases are pain before and during bowel movements, then diseases of the descending or sigmoid colon, as well as diseases of the rectum, may occur. The most severe pain will be during inflammatory processes in the peritoneum. However, the appearance of pain in the abdomen can also be caused by diseases of other organs - the liver, kidneys, spleen, pancreas.
Recommendations for the prevention of intestinal diseases
The main recommendations for prevention include the following measures:
- dietary proper nutrition;
- active lifestyle;
- eliminating bad habits;
- exclusion of stressful situations;
- Conducting rapid testing for occult blood for early diagnosis of diseases;
- Do not eat expired, unwashed or insufficiently heat-treated foods.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Rectal fissure: causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
- Rectal cancer: symptoms, stages, treatment and prognosis for life
- Details about bowel cancer: stages, symptoms, treatment and prognosis
- More about hemorrhoids: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
- Causes of bloating and increased gas formation, treatment methods
- Irritable bowel syndrome: symptoms and treatments
- Sigmoiditis (inflammation of the sigmoid colon): symptoms and treatment methods
- Diseases of the colon: symptoms and signs of pathologies, treatment
- Diseases of the anus: signs, diagnosis and treatment of pathologies
- Diseases of the duodenum: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Intestinal bleeding
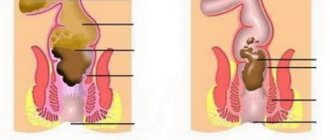
Bleeding can also be observed as a symptom of intestinal disease. These phenomena are typical in the presence of duodenal ulcers, ulcerative enteritis and colitis . Very often, patients do not notice the appearance of minor intestinal bleeding, so the presence of blood in the stool is detected only during laboratory tests of the material. If the bleeding is too heavy, the stool will be black. If bleeding occurs in the lower intestines, then blood will be noticeable in the stool in an undigested, pure form. Such bleeding occurs with hemorrhoids . Also, significant bleeding is possible in case of severe infectious diseases - dysentery, intestinal tuberculosis, typhoid fever .
Differences
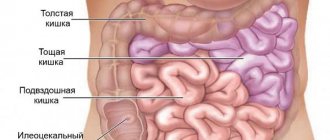
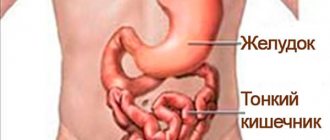
The main difference between the two sections of the intestine is the functions they perform. After all, the main function of the small intestine is the absorption of nutrients, and the large intestine is fecal formation. They also have different diameters, in thick ones it ranges from 4 to 9 cm, in thin ones - from 2 to 4 cm.
The color of the large intestine should be grayish, and the small intestine should be pink. The large intestine has outgrowths and protrusions. The large intestine is approximately 5.5 mm thick, and the small intestine is almost 2 times thinner. Based on all of the above, you can understand the principles by which the digestive system works. Now you know where the intestines are in women
, and what functions it performs.
Diagnosis of intestinal diseases
First of all, after listening to the patient’s complaints, the doctor performs a thorough palpation of the entire abdomen. The specialist pays attention to the shape of the abdomen, conducts superficial palpation to determine the soreness of certain areas and muscle tension. If superficial palpation is not painful for the patient, then the deep palpation method is used to determine the size of the internal organs, their location and pain.
The percussion method is used to determine the causes of abdominal enlargement, paying attention to the nature of the sounds. The most important method for determining the presence of intestinal diseases is laboratory testing of stool.
An X-ray of the intestines makes it possible to establish a diagnosis very accurately. If necessary, after a few days, an X-ray examination of the intestine is repeated. This method allows you to determine the presence of tumors, obstructions, study spastic contractions, and motor function. Sigmoidoscopy is performed in patients with pathology of the rectum and sigmoid colon.
Acute enterocolitis, gastroenterocolitis
As a rule, enteritis is combined with colitis and gastritis . Enterocolitis is mainly caused by Escherichia coli . It is constantly present in the intestines, but under unfavorable conditions it can turn into pathogenic and provoke inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane. Enterocolitis is also caused by streptococci, enterococci and a number of other bacteria. The toxic form of enterocolitis occurs after eating poor quality food.
The first symptom of intestinal colitis is diarrhea. If the small intestines are affected, bowel movements will be copious with the presence of mucus, but bowel movements will not occur very often. When the large intestines are affected, stool occurs frequently, and mucus comes out without having time to mix with the feces. Pain occurs throughout the abdomen, sometimes the pain is not particularly pronounced, but in some cases intestinal colic also occurs. Due to the presence of an infection that provoked the disease, the patient’s temperature may increase significantly. Symptoms of the disease also include headaches, weakness, poor appetite, vomiting, nausea .
With the correct approach to treating the disease, its signs can disappear in one to two weeks. If all the described symptoms are severe, then the patient should adhere to bed rest. If acute infectious enterocolitis is present, the patient is prescribed treatment with antibiotics and sulfonamides . In case of noticeable dehydration of the body, subcutaneous and intravenous infusion of saline and glucose . In the first days, the patient should take exclusively liquid food.
Chronic enteritis and colitis
Chronic enteritis and colitis occurs due to irrational and irregular nutrition, venous stagnation of the intestines, abuse of laxatives and enemas. Therefore, first of all it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease. Chronic colitis can be caused by regular constipation. Symptoms of the disease may include constipation, and less commonly, diarrhea. In the case of fermentation, the intestines swell and heaviness appears in the abdomen. Due to poisoning by rotting products, general weakness, headaches, and poor health are felt. In this case, a chronic disease can continue for many years.
In the process of treating a chronic form of the disease, the correct approach to diet is important. The disease should be treated, paying special attention to overcoming the problems of constipation and diarrhea. It is possible to use a mild laxative for constipation and astringents for diarrhea. If the disease worsens, the doctor prescribes sulfonamides and antibiotics .
Diseases of the small intestine
Diseases of the small intestine can be congenital, functional, inflammatory, or tumor. Congenital ones appear in children in the first years of life, tumor ones, as a rule, develop in older people.
An elevated temperature indicates an infectious disease. The disease can be triggered by injury, surgery, smoking (especially on an empty stomach), infection, addiction to fatty or spicy foods, alcoholism, chronic stress, and certain medications. I will focus on the main diseases of the small intestine.
Enteritis
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the small intestine is caused by bacteria, viruses, and helminths that enter with food or liquid. As pathogens multiply, they release toxins, which leads to inflammation and swelling of the wall of the small intestine.
The disease can occur against the background of medication, radiation therapy, and poisoning with arsenic and sublimate. Sometimes the disease is diagnosed simultaneously with colitis (inflammation of the colon) or pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
Enteritis can appear several hours or days after the pathogen enters the intestines and lasts about a week.
Symptoms of enteritis
Pain in the navel area, mushy diarrhea up to 5 times a day, vomiting, and sometimes fever. After defecation, weakness occurs, a drop in blood pressure, tachycardia, dizziness, and tremor are possible.
The disease most often occurs in a mild form, so the doctor does not prescribe any additional examinations. For moderate enteritis, you should drink more fluids and stop taking antidiarrheal (anti-diarrhea) medications, this will slow down the elimination of toxins.
Conservative treatment of enteritis
In the acute form of the disease, it is necessary to urgently rinse the stomach with a weak solution of baking soda and take a laxative, for example, 30 ml of castor oil or 25 g of magnesium sulfate with 100 ml of water.
On the first day of illness, completely refuse food and drink plenty of boiled water and strong tea without sugar. On the second day, include low-fat broth, pureed porridge with water, and crackers in the menu. Then, taking into account the condition, the diet can be expanded.
Drug therapy includes antidiarrheal drugs rehydron or glucosolan , antispasmodics besalol, no-shpu or papaverine , antimicrobial drugs phthalazole or ersefuril .
To improve digestion, the enzymes Mezim Forte, Festal ; to normalize the intestinal flora , Hilak Forte, Linex, Bactisubtil , as well as Bificol, Lactobacterin.
Complications of enteritis
In the chronic form of enteritis, extraintestinal manifestations of vitamin deficiency, osteoporosis, dystrophy, which are associated with impaired absorption function of the intestine, cannot be excluded.
If the disease occurs with rapid loss of fluid, dehydration may develop. In this case, treatment will be in a hospital. Complications of the disease include chronic diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, lactose intolerance.
Traditional recipes for enteritis
Mix 6 tbsp. spoons of chamomile flowers, 2 tbsp. spoons of peppermint leaves and valerian roots. Pour 4 tbsp. collection spoons 1 liter of water, boil for 15 minutes, leave for an hour. Drink 150 ml 3 times a day after meals to relieve cramps and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. Store the prepared infusion in a thermos for 2 days.
Prevention of enteritis involves strict adherence to personal hygiene rules. Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly, eliminating expired products and green potatoes.
Dyskinesia
This diagnosis is made if the peristalsis of the walls of the small intestine is weakened or strengthened. The disease develops against the background of other pathological processes (cirrhosis, pancreatitis, gastritis, cholecystitis), as well as as a result of malnutrition and prolonged stress.
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia
With increased peristalsis, mild spastic pain occurs, the stool is liquid, and undigested food is noticeable in it. Weakened peristalsis leads to dull pain in the navel, bloating, and a feeling of heaviness. The diagnosis is confirmed after X-ray contrast examination.
Treatment of dyskinesia
In addition to the medications prescribed by the doctor, decoctions of cinquefoil or oak bark . Pour 2 tablespoons of raw material into 300 ml of water, boil for 15 minutes, let it brew. Drink a decoction of cinquefoil 100-150 ml 3 times a day, oak bark twice a day.
Diverticula
Bag-like protrusions of the intestinal walls, diverticula, can be congenital, resulting from connective tissue pathology, or acquired, which are formed due to poor nutrition, in particular, insufficient consumption of fiber, fruits and vegetables. Provoking factors are constipation, obesity, sedentary lifestyle.
Symptoms develop only with inflammation (diverticulitis), the temperature rises, and abdominal pain appears. Diverticulitis can lead to intestinal bleeding, perforation, adhesions, or fistulas. Diverticula are removed surgically.
Dysbacteriosis
Also a very common disease, it occurs while taking antibacterial drugs, intestinal infections, and an unbalanced diet. Symptoms are general, characteristic of diseases of the small intestine. The diagnosis of dysbiosis is confirmed by testing for dysbacteriosis and stool culture.
To restore normal microflora, probiotics ( bactisubtil, enterol, linex ), as well as agents that promote the growth of beneficial microflora, so-called prebiotics ( lactulose, duphalac, normase ), are prescribed. Patients should eat properly and lead an active lifestyle and exercise.
Peptic ulcer
According to statistics, duodenal ulcers are diagnosed four times more often than gastric ulcers. The disease is caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which is able to survive in the acidic environment of the stomach, as well as drug therapy, especially the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Smoking, stress, alcohol abuse, and poor diet increase the risk of developing the disease. Gastroscopy allows you to identify not only the localization of the ulcer, but also bleeding and scar changes.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Signs of the disease are dull pain in the abdomen, which subsides after eating or taking medications that reduce the concentration of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, and intensifies after 3-4 hours. Characterized by “hungry” and “night” pain, sour belching, vomiting, and flatulence.
Peptic ulcer disease is dangerous due to bleeding, which can be hidden and is only revealed by increasing anemia. Blood may be in the vomit or stool. Minor bleeding is stopped during endoscopy by cauterizing the ulcer; severe bleeding is eliminated by surgery.
When the ulcer perforates, peritonitis develops, which is accompanied by acute stabbing pain and fever.
Treatment
Treatment involves taking medications that suppress the secretion of hydrochloric acid and prevent the proliferation of Helicobacter pylori. The patient must follow a diet.
Crohn's disease
This is the name of a chronic inflammatory disease that occurs in the inner mucous membrane and submucosal layers of the intestine. The diagnosis is made after a colonoscopy and computed tomography.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Crohn's disease, in addition to the general manifestations, are blood in the stool or hidden bleeding, weight loss, inflammation of the joints, eyes, skin, pathology of the liver, biliary tract.
Treatment
Therapy consists of reducing the inflammatory process, preventing relapses and complications. Patients are prescribed a diet, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, corticosteroid drugs, and symptomatic therapy. In emergency cases, surgical treatment.
Allergy
This immune disease is associated with changes in the intestinal mucous tissue. Symptoms are characteristic of most diseases of the small intestine; skin rash, itching, swelling, shortness of breath, weakness, and atopic dermatitis are also possible. In severe cases, anaphylactic shock cannot be ruled out.
To confirm the diagnosis, special tests are performed to identify the allergen. Treatment is taking antihistamines.
Celiac disease
Another name for the disease is celiac entropy. The disease develops as an immune response to the consumption of gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye, and barley. With pathology, damage to intestinal tissue occurs and the process of absorption of nutrients is disrupted.
Signs
Symptoms of celiac disease include stool consistency and frequency that differs from the norm, flatulence, vomiting, as well as the development of anemia and osteoporosis, headaches, and heartburn.
Children may experience delayed physical development, hyperactivity, and poor coordination. Usually the disease manifests itself by 1.5 years. In adults, the first symptoms of the disease may occur after surgery, infection, or in women during pregnancy.
Diagnostics
To determine pathology, blood tests and genetic testing are done. If necessary, endoscopy of the small intestine is performed with tissue sampling to determine the degree of villous atrophy.
Therapy
The only way to avoid exacerbation of the disease is to exclude gluten-containing foods from the diet. In severe cases of the disease, corticosteroid drugs are prescribed. To eliminate the effects of inflammation, vitamins and minerals. It may take up to 6 months for the intestinal mucosa to recover.
If symptoms persist even during a gluten-free diet, tests are ordered to rule out a tumor. Patients with celiac disease are at risk for colon cancer.
Ischemia
If there are circulatory disorders of the small intestine, thrombosis or narrowing of the lumen of the arteries, atherosclerotic plaques, ischemia may occur. In severe situations, when blood stops flowing to the cells, even intestinal infarction is possible.
Symptoms
Signs of chronic ischemia are abdominal pain after eating for 1-3 hours, which intensifies over several days. Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss develop. Signs of acute ischemia: sharp abdominal pain, aggravated by pressure, blood in the stool, vomiting, hyperthermia.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is confirmed using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, colonoscopy, endoscopy, Doppler ultrasound, and clinical blood tests.
Treatment
Drug therapy includes medications that dissolve blood clots and prevent them from forming again, as well as vasodilators that improve blood circulation. In acute ischemia, shunting and thrombus removal are sometimes performed.
Malabsorption syndrome
The disease develops when digestion in the small intestine is disrupted and it loses its ability to absorb nutrients. In addition to general signs of dysfunction, systemic symptoms of weight loss, weakness, anemia, osteoporosis, swelling, and dermatitis develop.
Diagnostics
A blood test indicates a lack of vitamins and microelements. The coprogram detects muscle fibers and starch in the stool, and changes in acidity. To accurately determine the cause of the disease, an X-ray examination, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, and other examinations are performed.
Therapy
Treatment is aimed at restoring the absorption function of the intestine, eliminating pathologies that led to malabsorption syndrome. The patient is given a drip with vitamins and microelements; to normalize the microflora, probiotics and prebiotics and an appropriate diet are prescribed.
If necessary, surgical intervention is performed.
Whipple's disease
This is a fairly rare disease that develops when there is a bacterial infection of the small intestinal mucosa, which leads to impaired absorption of nutrients.
Symptoms of Whipple's disease include diarrhea, cramping pain that intensifies after eating, and sudden weight loss. Extraintestinal manifestations also occur, for example, damage to the skin and eyes. To confirm the diagnosis, a biopsy of the small intestinal mucosa is prescribed.
The disease is treated with antibacterial drugs; therapy is long-term, more than a year, despite the fact that the symptoms subside a couple of weeks after starting medication.
Neoplasms
In the small intestine, benign neoplasms such as lipomas, neurofibromas, fibromas, and leiomyomas most often occur. The tumor is small and usually has no symptoms.
Signs of intestinal tumors
In other cases, blood appears in the stool, and partial or complete intestinal obstruction occurs. Then surgical treatment is performed. Small benign tumors can be removed by endoscopy.
Tumors with uncontrolled growth and the ability to affect neighboring organs develop less frequently, usually adenocarcinoma, lymphoma, sarcoma. The causes of such malignant formations are genetic disorders, celiac disease, Crohn's disease, smoking, and alcohol abuse.
Diagnostics
Older people are most susceptible to small bowel cancer, with men more likely than women. Oncology is manifested by abdominal pain, blood in the stool, and other symptoms of intoxication.
The diagnosis is confirmed by fluoroscopy with contrast, endoscopic examination, video capsule endoscopy, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. The type of tumor can be determined only after examining the biopsy specimen under a microscope.
Treatment
Treatment involves surgical removal of the tumor followed by chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Intestinal obstruction
It develops in the process of blockage of the intestinal lumen by a tumor or hernia. This pathology is called mechanical obstruction. When the cause is weakening or disappearance of peristalsis, which happens as a result of peritonitis, after surgery or injury, they speak of dynamic obstruction.
Signs
Symptoms of the disease are abdominal pain, accumulation of gases, lack of bowel movements, nausea, fecal vomiting. Fluoroscopy of the abdominal cavity helps clarify the diagnosis.
Therapy
Dynamic obstruction is eliminated conservatively; the patient is prescribed motilium or itomed, drugs that stimulate intestinal contraction. Mechanical obstruction requires surgery.