Mechanism of defecation
The first bowel movement occurs in the womb. The born child produces it unconsciously. Meconium (the so-called original feces) is a black, tar-like substance. It is excreted from the mother's body naturally. Until 2–3 years of age, children do not control this process and defecate at the first urge. After this age, a person can suppress desire.
To understand how the act of defecation occurs, let's turn to physiology. Let's look at the whole process step by step:
- crushed food enters the stomach and, under the influence of hydrochloric acid and enzymes, begins to break down;
- after a certain time, the gruel (chyme) enters the small intestine, where nutrients are absorbed by its villi;
- chyme descends into the large intestine, where moisture is absorbed;
- the formed feces create pressure on the rectum, the sphincters relax, and the person feels the desire to defecate.
System of measures for intestinal slagging
Cleaning should be based on the principles of integrity and consistency. First of all, the intestinal microflora must be softened. Only after this can you begin to eliminate harmful elements that are concentrated in parts of the colon.
The variety of procedures for recreating the cleanliness and microflora of the intestine is quite large. The most important action is the process of restoring pH balance. The level of acidity is directly related to the subtleties of chemical reactions. Next, you need to pay attention to the normalization of peristalsis of the intestinal walls, because fecal stones intensively stretch the absorption organ of the gastrointestinal tract. After this, the intestines will need to be brought back to normal shape. Restoration must be done comprehensively.
At the end of the rehabilitation period, the patient will need to optimize the microflora of the colon. This solution will have a beneficial effect on the state of the entire immune system, normalizes the warm-water characteristics of the digestive organ and its energy-forming functions.
Criteria for normal bowel movements
A brief description of normal bowel movements: bowel movements ranging from 1-3 times a day to 2-3 times a week. The act occurs painlessly and does not affect the person’s well-being. To determine compliance with the standard, several criteria are important: color, weight, consistency, smell, etc.
Frequency
The amount of bowel movements depends on the age, nutrition and individual characteristics of the person.
Children under six months old can walk up to 10 times a day, this is due to the type of feeding. Babies who feed exclusively on breast milk have a bowel movement after each feeding, that is, after 2-3 hours. They may not have bowel movements for 5–7 days while remaining in good health.
Children receiving only formula poop 1-2 times a day. At 4–6 months, complementary foods are introduced and the frequency of bowel movements decreases.
It is considered normal for an adult to go to the toilet 1–3 times a day. It is not a deviation if this happens after 2-3 days, but you still feel normal.
Consistency
The norm for this parameter is well-formed masses without impurities, 70% of which is liquid, and the rest is food debris, waste products of microflora and dead intestinal cells.
- Inhomogeneous, watery stools. Appears when drinking too much fluid. The presence of foam in it indicates the presence of pathological microorganisms in the chyme.
- Liquid, mushy feces are formed when consuming large amounts of plant and dairy products. This type of stool is typical for people with a high rate of peristalsis.
- Oily, loose stools are a sign of the presence of fats in the stool. This happens with liver or gallbladder diseases, as well as with celiac disease - congenital gluten intolerance.
- Dense, tuberculate feces without breaking the integrity or in the form of individual peas (nuts) are obtained as a result of intestinal spasms, due to protein foods or lack of fluid.
Smell
Stool has an unpleasant but not pungent odor. It occurs as a result of the decomposition of fats and proteins.
The smell may be:
- putrefactive - with prolonged constipation or pathological changes in the intestinal mucosa;
- sour - with abuse of foods (drinks) that cause fermentation, and intestinal infections;
- sharp, reminiscent of acetone - with heavy loads on the liver, release of bile, for example, with long-term drug therapy or alcohol abuse.
It also happens that stool has almost no smell. This happens with rapid contractions of the intestines and a short time for food to pass through the gastrointestinal tract.
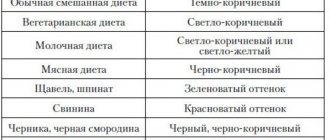
The color of stool can vary from light yellow to brown normally, depending on the food. So, for lovers of dairy products and infants it is yellow, and for meat eaters it is dark brown.
What could the color change mean? A brief description of:
- white or very light - a sign of diseases of the pancreas or liver;
- light yellow stool appears with diarrhea and gallbladder diseases;
- bright orange - with an excess of beta-carotene and consumption of foods of this color (carrots, pumpkin);
- red or burgundy color of stool may indicate bleeding on the walls of the large intestine or simply that the person has eaten, for example, beet salad;
- green stool is one of the signs of dysbiosis;
- greenish-brown appears when there is an excess of iron;
- almost black stool is a very dangerous symptom that indicates bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract, for example, in the stomach or esophagus.
Possible deviations
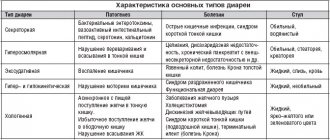
The most common abnormalities are constipation and diarrhea.
Constipation is a defecation disorder in which there is no bowel movement for more than 2 days. Associated symptoms:
- abdominal pain;
- weakness;
- irritability;
- flatulence and severe bloating;
- sleep disorders.
Diarrhea is loose stool more than 5 times a day. The disorder is accompanied by signs:
- nausea, vomiting;
- stomach ache;
- temperature increase.
Diarrhea or constipation with high fever, blood and mucus in the stool are especially dangerous in an adult. With such symptoms, it is better to go to the hospital. Medical assistance will also be needed in cases where these violations are systematic.
Many natural processes take place in the human body, including defecation. Its frequency, duration and other characteristics allow doctors to assess the patient's health status.
For various reasons, malfunctions in the digestive system occur. A person does not eat properly, suppresses the urge to have a bowel movement, and drinks little water. A doctor will help you establish an accurate diagnosis and causes of disorders.
What is defecation
Due to anatomical features, the human body gets rid of processed food through the anus. In medicine, this phenomenon is called the act of defecation.
In a healthy body, this process is carried out once a day. How often you go to the toilet affects stool consistency . The less often a person empties the rectum, the harder the stool.
The process of waste elimination is controlled by the central nervous system. When feces move from the sigmoid region into the ampulla of the rectum, a person feels the urge to empty it. He can control this process starting from 1.5 years.
Stool disorders and their causes
In medicine, cases have been recorded when the intestinal mucosa was damaged under the influence of its contents. The person was diagnosed with peritonitis, which was fatal.
Many disorders are the result of serious pathologies. Any disease requires the attention of an experienced doctor. After a medical examination and based on test results, he will make an accurate diagnosis.
- diseases of a gastroenterological and proctological nature;
- the development of inflammatory and ulcerative processes affecting the stomach, intestines, liver and bile ducts;
- intestinal infection, helminths;
- hemorrhoids or anal fissures;
- paraproctitis;
- colon prolapse;
- chronic pathological processes in the stomach and intestines.
The development of malignant cells can cause pain and difficulty in excreting feces. Persistent constipation, when a person cannot go to the toilet for a long time, is caused by diseases of a psychoneurological or vertebroneurological nature.
Against the background of developing pathological processes, muscle tone and intestinal motility are disrupted. Problems in the functioning of the neural conduction system are diagnosed.
Causes of diarrhea
In most cases, problems with bowel movements occur due to poor nutrition. But the constant nature of the disturbances indicates the development of a serious pathology. The main causes of diarrhea are:
- Infection in the intestines. Food poisoning or salmonellosis, cholera.
- Autoimmune pathologies of the digestive system.
- Cancerous tumors in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Pancreatitis in the chronic stage. The pathology is accompanied by insufficient production of enzymes that are necessary for the proper digestive process.
Irritable bowel syndrome may be the cause of abnormal bowel movements. The nervous regulation of the digestive organs is disrupted.
Causes of constipation
Rare bowel movements are observed after eating foods with large amounts of fats and refined sugar.
The diet should contain vegetables and fruits with fiber of plant origin. They facilitate the movement of food through the stomach and intestines. Thanks to them, feces are formed.
Other causes of infrequent bowel movements:
- Low fluid consumption.
- Irritable bowel syndrome. During spasms of its walls, the movement of feces slows down. This is how a person develops constipation.
- Rarely visiting the toilet. Many people ignore the urge to defecate when they are busy at work or avoid going to the public toilet. After a while they become constipated.
- Laxatives in large quantities. When the intestines become accustomed to medications, their walls stop contracting, leading to constipation.
- Disturbed hormonal levels. For example, problems with the thyroid gland. A decrease in the production of its hormones leads to the development of hypothyroidism. When hormonal imbalances occur, people diagnosed with diabetes and pregnant women suffer from constipation.
- Pathologies associated with the functioning of the nervous system. This also applies to the spinal cord and its damage. Patients with multiple sclerosis, malignant neoplasms, and after stroke attacks complain of constipation.
- Diseases that disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. We are talking about stomach and duodenal ulcers, chronic pancreatitis.
- Vascular atherosclerosis. Pathological processes disrupt the functioning of the circulatory system in the intestinal area. Its peristalsis and movement of contents slows down.
- Hemorrhoids, anal fissures. Defecation is disrupted and spasm of the rectal sphincter occurs.
What shape should an adult's stool have?
Thin stools (pencil stools) indicate obstruction in the lower half of the digestive tract or an external pressure on the large intestine. If these symptoms occur, a colonoscopy should be done to rule out the development of cancer. Small and hard stools are clear signs of difficult bowel movements, namely constipation. This may be due to missing fiber in a person's diet. It is necessary to increase the content of dietary fiber in the diet, perform more sports exercises, eat plantain and flaxseeds to improve intestinal motility.
Stool that is too soft and sticks to the toilet means your body is not absorbing the oils as well as it should. Sometimes essential drops actually float in the toilet. With these symptoms, there are also disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas, so it is very important to immediately consult a medical specialist for diagnosis. The presence of mucous clots in stool is a common occurrence. However, if excessive mucus content is noticed in the stool, there may be some kind of inflammation in the body, granulomatous enteritis or ulcerative colitis.
Defecation standards
The frequency of stool should be at least 1 time per day. Experts warn their patients that a delay of 32 hours indicates the development of constipation.
In many ways, defecation depends on a person’s lifestyle. 70% of the population visit the toilet and have bowel movements every day, 25% of them remove feces from the intestines several times a day. There is a category of people (5%) who have stool less than once a day.
Normally, the process of bowel movements in adults and children is observed from 3 times per day to 1 time over two days. With regular disruption of normal bowel movements, constipation develops.
During the process of cleansing the intestines, a person strains. This is a normal phenomenon if it takes up no more than 20% of the total time of excretion of feces. If straining requires strong tension of the abdominal muscles or additional stimulation of the anus, this indicates the development of constipation.
One of the indicators of rare bowel movements in a child or adult is hard stool. The main cause of violations is low fluid content in the human body.
Normally, water makes up up to 70% of feces. The remaining percentage comes from processed food, dead intestinal cells and dead pathogens.
In many ways, the act of defecation depends on a person’s nutrition. The color of the colon contents should be brown. A dark shade indicates a disturbance in the digestive process or the development of constipation. Light-colored feces are a consequence of increased contraction of the intestinal walls.
As for the appearance of feces, a cylindrical shape is considered normal. The smell is pronounced, but not pungent. It all depends on the composition of the foods eaten, as well as the processes of rotting and fermentation.
Often the excretion of feces is accompanied by gases. It is a natural byproduct of the fermentation and digestion process of food .
Bowel movements are affected by diet, the quality and quantity of food, and how regularly a person eats.
When the first signs of a disorder appear, you cannot postpone a visit to a specialist. It is necessary to undergo a full medical examination and treatment to prevent the development of the consequences of constipation and complications.
What should be the daily amount of feces?
With a varied diet, the daily norm for defecation is considered to be the amount of feces in the range of 150-400 g. If plant foods predominate in a person’s diet, then the abundance of stool increases. In the case of dominance of food of animal origin, the frequency of bowel movements is much less.
Too much and active elimination of waste from the body for three days or more (polyfecality) may be a harbinger of ailments of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, gallbladder and its tracts, pancreas, or the loss of one or many nutrients entering the digestive tract due to their insufficiency absorption in the small intestine (malabsorption). Constipation can sometimes result from a decrease in the amount of stool and the frequency of bowel movements. This occurs due to prolonged retention of body waste in the colon and excessive absorption of fluid, due to which the volume of bowel movements decreases. This may also be due to the predominance of food that is digested too quickly.