Intestinal diseases: structure, causes and signs of diseases
Intestinal diseases and their symptoms in women often resemble the clinical picture of gynecological diseases.
Therefore, the doctor needs to be extremely careful during diagnosis, and patients should not self-medicate.
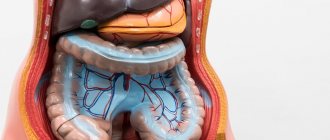
All about the intestines: its structure and functions
The intestine is the longest human organ. It looks like a hollow tube, the thickness of which varies in different sections. It consists of:
- duodenum, which is located in the chain of digestive organs immediately behind the stomach;
- small intestine - the longest section in which all useful and vital substances are absorbed from food;
- the large intestine, where water is absorbed from food debris and feces are formed.
Digestion begins
still within the oral cavity, when food begins to break down under the influence of salivary enzymes. At the same time, the brain receives a command about the entry of food into the body and gives the command to the digestive organs to prepare for work - to begin producing digestive enzymes.
In the stomach, food is broken down into a pulpy state.
, is disinfected by means of hydrochloric acid, which is part of the gastric juice. At this stage, the primary breakdown of protein foods occurs.
The ducts of the gallbladder and pancreas open into the duodenum, through which bile and digestive juices flow. Here fats are digested and absorbed (through bile), food is broken down into its main components.
All nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine
. Food moves through the contraction of its walls, which is called intestinal motility.
In the large intestine, the most indigestible component, but necessary for the human body, is absorbed - fiber.
Here vitamins are absorbed, the final breakdown of proteins occurs, and toxins are produced. Then the leftover food, along with toxins, enters the rectum, through which it is eliminated from the body.
The digestion process is completed in the large intestine: no components are absorbed in the rectum.
Causes of intestinal diseases
One of the most common causes of intestinal pathology is improper and unbalanced nutrition.
.
An excess of one or another component, a lack of fiber, constant overeating or prolonged fasting, consumption of low-quality or poorly washed foods cause both acute and chronic forms of ailments.
Also, intestinal disease in women, men and children can be caused by:
- Intestinal infection - microbes that are contained in spoiled, dirty foods or get through unwashed hands.
- Helminthic infestations are infections with intestinal parasites that adhere to the intestinal mucosa. Symptoms vary depending on the type of parasite.
- A sedentary lifestyle, which leads to impaired intestinal motility. One of the main symptoms is constant constipation.
- Stress, nervous tension, which causes spasm of the intestinal muscles. The absorption of nutritional components and the entire digestion process are disrupted.
- Diseases of other organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas), due to which digestive enzymes are produced in insufficient quantities.
- Imbalance of intestinal microflora.
- Hormonal changes.
- Hereditary causes.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, when the relationship between the brain and the intestines is destroyed.
In adults, intestinal diseases are triggered by stress, as well as bad habits. Alcohol and nicotine, especially on an empty stomach, can cause serious changes in the functioning of the entire digestive system.
Intestinal diseases in women can occur as a result of adhesions against the background of gynecological inflammatory diseases.
Disturbances in the digestive system appear during pregnancy due to the fact that the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the intestines
.
Such pathologies usually occur if a woman previously had the prerequisites for the development of the disease. Pregnancy in this case acts as a catalyst.
Signs of intestinal diseases in women
Symptoms of the disease may vary depending on the location and nature of the disease. But there are general symptoms that indicate disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract:
- Abdominal pain. How the stomach hurts depends on the degree of inflammation, the nature of the course (acute, chronic), the presence of damage to the mucous membrane, etc.
- Stool disorder (constipation or diarrhea).
- Flatulence (bloating, increased gas formation).
- "Hard belly." On palpation, you can feel a tense abdominal wall.
- Nausea, belching.
- Vomit.
- Discomfort in the abdomen - heaviness, feeling of transfusion.
- Enlargement of the abdomen, which causes swelling of the intestines. A woman’s abdomen may be enlarged on the eve of menstruation, during ovulation, or in the presence of gynecological diseases. All these conditions may be accompanied by pain, upset stool, and nausea - this is important to consider when making a diagnosis.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
The NetGastritu project was created with the goal of providing people with accurate and up-to-date information on medical topics. Articles are written by professionals and, unfortunately, development costs slow down the development of the project. If you want to support us, use the form below.
Let's make the world a better place together. Thank you for your attention.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/netgastritu/bolezni-kishechnika-stroenie-prichiny-i-priznaki-zabolevanii-5aae2cf68139ba8c18ec89cf
What is an intestinal tumor?
An intestinal tumor is a pathological proliferation of cells of the intestinal wall of different size, structure and quality. Intestinal tumors grow from the muscular, glandular or epithelial layer. Neoplasms affect the duodenum, ileum, jejunum, cecum with appendix, colon, sigmoid, rectum.
Based on the nature of intestinal tumors, they are divided into benign and malignant. Benign tumors grow inside the intestinal lumen and do not spread to other organs. However, sooner or later, some types of benign tumors become malignant. Malignant neoplasms behave aggressively - they spread their cells to other organs, turning them into the same cancerous tumors.
Intestinal dyskinesia
Intestinal dyskinesia is a complex of intestinal disorders that arise due to impaired motor function of the intestine (mainly the colon).
That is, despite the fact that there are no organic changes in it, it cannot work normally.
According to the World Health Organization, intestinal dyskinesia affects almost a third of the world's population, most of them women.
The manifestations of this disease are extremely unpleasant. First of all, these are abdominal pains of a very different nature: from aching to cutting, lasting from several minutes to many hours. At the same time, it is very difficult to determine exactly where it hurts.
Various pains “in the whole abdomen” (pulling, sharp, boring, cutting, aching) most often disappear when falling asleep, gradually increasing upon awakening. For many, the pain intensifies when eating or after eating.
The pain may subside after bowel movements or the passage of gas, but may intensify with stress and emotional tension.
With intestinal dyskinesia, in addition to pain, bloating, rumbling, and stool disorders appear. And this is all against the backdrop of dislike for life, because being in such a state in public places is extremely unpleasant.
Sometimes bloating or loud rumbling may be the only symptom, regardless of what you ate. All sufferers of intestinal dyskinesia experience bowel dysfunction, most often constipation. Sometimes constipation is replaced by short-term diarrhea.
(Constipation can be considered the absence of stool for 2 days. Diarrhea is very loose stool 3 or more times a day). Often, mucus is released with the stool, which is either mixed with feces or located on its surface in the form of films.
However, stool disorder is not necessary, just like pain during diarrhea (“nervous diarrhea”), there are also painless dyskinetic constipation. But even with frequent diarrhea, those suffering from intestinal dyskinesia do not lose weight; rather, they even gain weight. Very often they have mental disorders.
They are distinguished by increased anxiety, nervousness, or, on the contrary, depression. Complaints of pain in the heart, joints, and back are possible, although these organs turn out to be healthy when examined.
With spastic (hypermotor) intestinal dyskinesia, its tone and spastic contractions increase, which leads to constipation and paroxysmal colic-like abdominal pain.
With atonic (hypomotor) dyskinesia, its tone and peristalsis are sharply weakened, which leads to constipation, dull bursting pain in the abdomen, and sometimes intestinal obstruction. With constipation, a buildup of dense stool forms in the rectum.
If products are not removed from the colon in a timely manner, dizziness, nausea, weakness appear, mood deteriorates and performance decreases. Due to the long stay in the intestines, food undergoes putrefactive decomposition, which can lead to allergies.
Chronic constipation can cause hemorrhoids, anal fissures or rectal polyps.
Description
Intestinal dyskinesias are primary, when intestinal motor disorders are an independent disease, and secondary - symptomatic, occurring in other diseases, primarily the gastrointestinal tract. True, it can be very difficult even for a specialist to distinguish them.
It is believed that the most common causes of primary dyskinesia are psychogenic factors, but its occurrence often depends on the excessive consumption of foods low in dietary fiber. There are many causes of secondary dyskinesia, especially if they manifest themselves as constipation.
These can be diseases of the digestive system (liver diseases, chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, chronic pancreatitis and cholecystitis), as well as diseases of the endocrine system - pituitary disorders, myxedema, diabetes mellitus, hyperparathyroidism.
The development of constipation may well be facilitated by uncontrolled use of drugs that affect colon motility: anesthetics, antibiotics, sulfonamides, muscle relaxants, anticonvulsants, anticholinergics, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, opiates, diuretics, psychotropic drugs.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made only by excluding other diseases with similar symptoms by examining stool for occult blood, dysbacteriosis, scatological examination, irrigoscopy and endoscopy are prescribed. A colon biopsy is required.
Diagnosis of the causes of secondary dyskinesia is based, first of all, on the study of the medical history and general clinical examination of the patient.
Treatment
Treatment for dyskinesia depends on its type. For hypermotor dyskinesia, antispasmodics of various groups, metoclopramide, are prescribed; the use of laxatives is completely contraindicated.
For hypomotor dyskinesia, drugs that enhance intestinal motility are indicated, as well as metoclopramide, choleretic drugs and enzyme agents, potassium chloride in combination with vitamin B1...
If there is no effect from therapy with the above remedies, laxatives of plant origin are prescribed: senna leaf, buckthorn bark, zoster, rhubarb.
Moreover, they should be used no more than twice a week, alternating.
But still, many experts believe that drug treatment of intestinal dyskinesias should be used as a last resort.
For example, you can get rid of intestinal atony with the help of decoctions of dry herbs (Alexandrian leaf, buckthorn, rhubarb, lingonberries), products that have a laxative effect (yogurt, kefir, melon, cucumbers (and fresh, salted), lingonberries (soaked, fresh and canned ), rhubarb in any form, prunes (dried and decoction), plums, apricots, peaches, raw or boiled water (1 glass on an empty stomach). Recommended vinaigrettes, salads, meat boiled and stewed in its own juice, fish, millet porridge, pumpkin, zucchini, squash. You cannot eat foods and berries that have a strengthening effect: bird cherry, sloe, barberry, blueberries (raw and dried), pears, smoked sausages, hard-boiled eggs. Mineral waters are taken on the recommendation of a doctor.
Lifestyle
You can get rid of intestinal dyskinesia with proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle, including getting rid of stress, playing sports, and timely treatment of various diseases. It is important to learn to empty your bowels at the same time.
In all cases, a physiologically complete diet should be prescribed, providing the body with essential vitamins, microelements and minerals, and including mechanical and chemical stimulants of intestinal motor function. It is necessary to exclude foods that cause increased fermentation and rotting processes in the intestines (apples and cabbage, including sauerkraut).
Food should be boiled or steamed, not chopped. As motility stimulants, those varieties of berries, fruits and vegetables are used that enhance the evacuation function of the intestines without causing fermentation processes and irritation of the intestinal mucosa (beets, carrots).
At the same time, the diet depends on the type of dyskinesia, since it must correspond to certain intestinal motility. For example, with hypomotor dyskinesia of the colon, the main principle is to add foods rich in plant fiber to the diet.
Among them: beets, carrots, zucchini, pumpkin, cauliflower in raw, boiled, baked form, as well as tomatoes and lettuce. White cabbage, mushrooms and vegetables such as turnips, radishes, onions, garlic, and radishes are excluded, since they contain a lot of essential oils.
Bread made from coarse rye and wheat flour with the addition of bran, porridge with water from wheat, buckwheat, pearl barley, and oatmeal are healthy.
We recommend soups with low-fat meat and fish broth, vegetable broth, boiled, steamed, and baked lean meat and fish. If protein foods are well tolerated, you can eat soft-boiled eggs (with liquid yolk) or in the form of steam omelets, but no more than 2 pieces per day.
Figs, dates, prunes, dried apricots, bananas, apples are shown - the organic acids and sugars they contain stimulate intestinal motility.
During diet therapy, lactic acid products are needed: fresh (2-3-day) kefir, yogurt, acidophilus, as well as drinks with the addition of a live culture of bifidobacteria. For any disease of the gastrointestinal tract, the body must receive a sufficient amount of vitamins, microelements and mineral salts.
Therefore, it is recommended to drink half a glass of natural vegetable, berry and fruit juices several times a day, as well as warm rose hip decoction without sugar.
Nutrition for constipation
Cold food is necessary for bowel movements. It is recommended to add wheat bran to food, which should be doused with boiling water (in the first two weeks, 1 tsp 3 times a day, then 1-2 tbsp 3 times a day, followed by reducing the dose to 1.5 tsp.
l. 3 times a day). They should be taken for at least 6 weeks. For hypomotor dyskinesias, it is useful to take vegetable and animal oils (sunflower, corn, olive, butter, etc.) - add to food or take 1 tsp on an empty stomach.
Not recommended: bread made from premium flour, butter dough, fatty meats, smoked meats, canned food, spicy foods, chocolate, strong coffee, tea, rice and semolina porridge, noodles, potatoes, foods that cause increased gas formation (legumes, cabbage, sorrel , spinach, apple and grape juices).
For hypermotor dyskinesia of the colon, as well as for proctogenic coprostasis (accumulation and retention of solid feces in the intestine), the fundamental difference is the prescription of a slag-free diet.
This is an easily digestible, refined food containing a minimum of indigestible substances: soups with low-fat meat broth, vegetable broths, various dishes from lean beef, veal, boiled chicken, in the form of cutlets, meatballs, soufflé; dishes from cod, pike perch, perch, pike; foods rich in calcium (low-fat cottage cheese, cheeses), compotes, jelly and juices containing tannins (blueberries, bird cherry, pomegranate, black currant, dogwood and pear).
This diet must include vegetable fats.
© Dr. Peter
Source: https://doctorpiter.ru/diseases/49/
I have a stomach ache, what should I do?
The tactics for treating abdominal pain may vary depending on the disease - different diseases require different approaches to eliminate pain. Don't take risks with your health. You should not take painkillers unless you are 100% sure that it will not make your situation worse.
If you have diarrhea or heartburn, taking the necessary medicine is often all you need. Medications can also be used to relieve intestinal spasms that cause pain. Of the drugs available to everyone, no-spa and papaverine help with spasms. Gastroenterologists often prescribe duspatalin or trimedat.
If you are not a supporter of medications, use a decoction of chamomile flowers. To do this, you need to pour boiling water over them and boil for 15-20 minutes over low heat. Cooled to room temperature and strained, the broth can be drunk.
Pain can be a sign of a fairly innocent disease, well known to the patient for a long time. But we should not forget that they can also indicate a very serious illness. It is worth understanding that taking antispasmodics, analgesics or other drugs may not bring the desired result. In this case, you should not repeat the dose or increase the dosage.
If you are worried about intense abdominal pain, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible and describe the current situation. At the same time, it would not be amiss to mention what you did on your own.
Treatment of the intestines can be carried out with medication or surgery and with the help of diets
Diet for intestinal pain
If pain is accompanied by constipation, then, first of all, it is necessary to reduce the intake of laxatives so as not to “wean” the intestines to work independently. By the way, the same applies to anti-diarrhea medications. You should first try using natural remedies and switch to drug treatment only if there is no result.
In this case, fiber is universal, which, while increasing the volume of intestinal contents, simultaneously softens it and allows for constipation to achieve increased bowel movements, and for diarrhea to normalize peristalsis. A diet for intestinal pain and dysfunction should include foods rich in fiber (although they can also cause side effects such as flatulence and bloating), or dietary supplements based on it (for example, methylcellulose and isphagula husk) .
A sick intestine also needs pectin, which contains dietary fiber. As a rule, we are talking about papaya fruits, grapefruits and oranges. It is also necessary to pay attention to sufficient water intake.
If you are bothered by regular pain in the lower intestines, then you need to take up to eight glasses of water at room temperature during the day. This will help increase the volume of stool and allow it to move more vigorously. Eliminate dairy products and wheat flour and cereals, as they often cause pain.
Pain on palpation
Palpation of the digestive organs is of great diagnostic value. The formation of a symptom is influenced by a number of factors and nuances (infection, structure of the reproductive system).
Features of pain on palpation
The process of palpation of the stomach and intestines is important in terms of diagnostic examination of the human body.
Monitoring of the digestive organs is carried out as follows: at the first stage, a qualified specialist carefully palpates the sigmoid colon - this is the most common landmark and the most accessible organ for palpation.
Next, the doctor proceeds to study the condition of the cecum and transverse colon. The ascending and descending sections of the suction organ are quite problematic to palpate.
In practice, during palpation, fingers must be carefully immersed on the surface of the body area and gently pressed onto the organ being examined (toward the posterior abdominal wall). Using sliding movements, you can clearly determine the contours, density, and the presence of various neoplasms and abnormalities.
When you touch (feel) the sigmoid colon, you get the impression that there is a smooth, dense and mobile cylinder in the human body. The size of such a “geometric figure” does not exceed the thickness of a person’s thumb.
The formation parameters are directly related to the condition of the walls, which are densely filled with gases and decay products (feces/feces).
During the inflammatory process of the infiltrating walls, a significant thickening of the membrane occurs. Ulcerative manifestations form a lumpy and uneven surface of the suction organ.
Acute inflammation of the sigmoid colon is accompanied by the formation of a dense consistency of painful manifestation. Due to the dense overflow of gases and liquid contents, motor inhibition occurs. The spasm is felt in the form of a cord and cord.
The patient experiences systematic rumbling + false urge to defecate (false diarrhea).
In normal condition, the cecum is easily palpable. A specialist can detect a cylinder up to 3 cm that is moderately active in movements. Its mobility in a pathological disorder is significantly increased.
The internal consistency becomes significantly thicker during coprostasis and chronic inflammation. The volume and shape of the cecum directly correlates with the contents. In a normal functional state, the intestines do not growl.
The patient should remember that the presence of pain upon palpation in the area of the cecum indicates the development of a pathological process. The digestive organ requires systematic and comprehensive treatment.
In practice, after examining the cecum (+ appendix), it is possible to examine the less accessible parts of the large intestine. Palpation is carried out from the ascending to the transverse colon and descending colon.
The transverse colon part of the suction organ can be qualitatively palpated only in the case of chronic inflammation. Tone, consistency, volume, shape depend on the tone and degree of muscle tension.
For example, an inflammatory process of the ulcerative type forms serious preconditions for the transformation of the transverse colon. At the same time, the muscles of the organ thicken significantly, and its configuration changes.
Today, chronic colitis and percolitis are quite common. With these ailments, the wall of the suction organ begins to painfully contract. Due to the lumpy surface, palpation is accompanied by sharp pain. For example, with pericolitis, respiratory and active mobility is lost.
Palpation of the abdomen allows you to feel an intestinal tumor, which is often confused with the pathology of various organs. Oncology of the cecum and transverse colon is distinguished by already known mobility. The pain is activated during the act of breathing (tumors below the navel are motionless). Palpation of the abdomen during enterocolitis is accompanied by rumbling in the navel area.
The disease has specific signs and symptoms: painful diarrhea (mushy, mucous stools, abdominal pain, hard colon). Palpation of the abdomen is carried out in combination with a digital examination of the rectum (sigmoidoscopy + radiography). These actions make it possible to predict the formation of rectal cancer and the formation of various syphilitic structures.
It will also be possible to clearly determine the presence of inflammatory processes, cracks, fistulas, hemorrhoids and all kinds of tumors. The specialist can get a clear vision of the sphincter tone and the level of filling of the colon ampulla. In some cases, it is rational to palpate adjacent organs (bottom of the bladder, prostate gland, uterus with appendages).
This will reveal an ovarian cyst, a tumor of the genital organs, the degree of constipation, etc.
Mechanism of the procedure
Palpation is the last stage of a full and objective examination of the abdominal area. The patient will need to cough vigorously before the procedure. In practice, a person with developed peritonitis manages to do this only superficially (holding his stomach with his hands).
It is allowed to make a small impact on the couch on which the patient is located in a supine position. The vibration impulse will provoke the manifestation of pain in the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, it is quite easy to establish the diagnosis of peritonitis without touching the hand.
To identify symptoms of peritoneal irritation, it is allowed to gently shake the patient after grasping the crests of the ileum (or jumping on one leg).
The palpation procedure begins with the patient being asked to clearly indicate the area where the first pain formed (the primary localization of the disease).
The specialist needs to closely monitor the actions of the patient himself. This is how you can identify the causes of peritoneal irritation.
Diffuse visceral pain in the abdomen is easily determined using circular movements of the palm. Your hands should be warm.
The procedure begins as far as possible from the main source of pain. This helps to avoid unplanned pain at the very beginning of the study. Children, and sometimes adult patients, sometimes prevent a quality examination due to pain.
First of all, the doctor must perform gentle and careful palpation (superficial). An experienced specialist moves gently, methodically and consistently. The fingers make a minimum number of movements.
It is strictly forbidden to palpate the abdomen randomly! The pressure on the body surface should not be high. Otherwise, protective tension in the abdominal muscles will occur.
Touching the sore spot must be done until the patient says that it really hurts.
A qualified specialist can always determine the degree of tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. The physician must distinguish between voluntary and involuntary muscle tension. To clearly determine this factor, during palpation a person takes a deep breath and exhales. If muscle activity persists, this indicates the development of peritonitis.
It is rational to carry out deeper palpation if peritonitis was not detected during a superficial examination. This makes it possible to detect various tumor formations, hepatosplenomegaly, and aortic aneurysm. It is very important for a physician to remember the optimal sizes for normal structures so as not to confuse them with malignant ones. Pain on palpation of the abdomen and intestines has two types:
- immediate local pain – the patient experiences sharp pain at the test site;
- indirect (referred pain) – pain sensations are formed in a different place when palpated. For example, during acute appendicitis, pain accumulates at McBurney's point on the left side of the iliac fossa. This symptom is called “Roving” and is a reliable sign of peritoneal irritation.
It is easy to carry out comparative palpation of a patient with tense abdominal muscles. For this, the patient, who is in a supine position, is asked to gently lift his head above the pillow.
The classic symptom of parietal peritoneal irritation is not difficult to identify.
To do this, at the time of the examination, the doctor must sharply remove his hand from the surface of the body and observe the patient’s reaction. In most cases, patients experience a significant increase in pain.
This classic examination technique is quite crude; some scientists classify it as a barbaric method of study.
With the development of various pathologies in the digestive organs (for example, acute appendicitis), hyperesthesia of the skin in the abdominal area is observed.
It is for this reason that if you pinch or lightly prick a patient, a painful reaction of the body will immediately occur.
This is a fairly common clinical symptom, but its establishment is not enough to firmly diagnose acute appendicitis and other diseases of the abdominal organs.
An integral part of the palpation examination is gentle tapping on the lumbar region (+ sides of the abdomen) to determine the degree of pain in these areas. Quite often, pyelonephritis and urolithiasis correlate with severe pain in the abdomen (costovertebral region).
In doubtful clinical situations, examination alone is not enough. An accurate assessment of the dynamics of the disease is established by repeated palpation of the abdomen by the same doctor.
Causes of pain in women
Today, medicine identifies two types of fundamental causes that affect pain when palpated. Organic factors include:
- inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system (cyst, endometritis, fibroids);
- using the IUD as a contraceptive;
- formation of various pathological formations;
- the presence of inflammation in the gall bladder (including appendicitis, pyelonephritis);
- sharp pain during pregnancy (placental abruption, miscarriage).
The functional reasons are as follows:
- systematic disruptions in cycles during menstruation;
- discharge of uterine bleeding;
- ovulation + uterine inflection.
Inflammatory processes are the main cause of pain during palpation of the stomach and intestines. The disease begins with classic acute manifestations and is supplemented by various signs of intoxication of the body, namely:
- Endometritis is accompanied by aching pain in the abdominal area. Their manifestation can be determined by light palpation. The patient experiences heaviness in the area of the appendages + hardening of the uterus;
- Endometriosis is a pathological disorder that affects the uterus and appendages. Severe pain is observed when palpating the middle of the abdomen;
- Ovarian apoplexy correlates with ovulation. In this case, some of the blood penetrates into the abdominal cavity due to strong physical exertion;
- Uterine fibroids. The pain syndrome is localized in the lower abdomen (compression of neighboring organs);
- Appendicitis requires surgical medical intervention. Pain on palpation in the area where the appendix is located;
- Cholecystitis is an inflammatory process of the gallbladder. The pain radiates clearly to the lumbar region and back;
- Cystitis is a lesion of the bladder. Pain is observed both during palpation and during urination.
What types of tumors are there by location?
A tumor of the small intestine is found in 4-5% of cases of intestinal neoplasms. Tumors of the small intestine occur in adults over 40-50 years of age and are rarely diagnosed in children. Benign tumors of the small intestine are found inside the duodenum and the initial parts of the ileum. Among benign tumors of the small intestine, polypous formations predominate.
The final section of the ileum and the beginning of the jejunum are more often subject to cancerous degeneration. Intravital tumors of the small intestine are diagnosed very rarely. Such neoplasms occur secretly and mimic other diseases.
Tumor formations of the large intestine occur in the vast majority of cases. Among the sections of the large intestine where neoplasms are diagnosed, the rectum predominates. The predominant localization of malignant tumors in the large intestine is explained by prolonged contact of the intestinal wall with feces and the abundance of opportunistic microflora of the large intestine.
Benign tumors of the large intestine are represented by polyps. Polyps are initially benign neoplasms that develop from the epithelial tissue of the intestinal wall. A common type of polyp is adenomatous, which has a high probability of oncogenic degeneration.
How is intestinal palpation performed?
Intestinal palpation involves two types of palpation of the abdominal cavity: superficial and deep.
If the patient has painful areas, an important rule that the doctor follows is the following: in no case should palpation begin from the place that hurts. Usually the doctor starts from the opposite part of the abdomen.
Most often, palpation begins from the left iliac region and involves feeling the intestines in a circle and counterclockwise.
Video about the intestinal palpation technique:
Surface method
With the superficial palpation method, the doctor needs to relax the patient as much as possible. For this, the patient is placed in a horizontal position with his knees slightly bent. This way the abdominal muscles relax as much as possible.
If the patient is still too tense, the doctor can distract him from the procedure by forcing him to perform breathing exercises.
The palpation occurs very smoothly and accurately. The area that hurts is palpated last, since if you start the procedure from the painful area, the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall will tense, which will not allow a full examination.
Deep
A deep type of palpation is performed to diagnose serious changes in the structure of the intestine. The most important condition for deep palpation is the doctor’s clear knowledge of the projection of the internal organs onto the anterior abdominal wall.
Causes
There are a number of main reasons that cause colon cancer. Ailments of the colon, which include ulcerative colitis, adenoma, polyp, Crohn's disease and inflammatory bowel disease, can lead to cancer. Patients who have a history of such a diagnosis are required to undergo systematic diagnosis.
Heredity. In cases where there were people suffering from cancer in the family, it is important to undergo regular examinations. The presence of a genetic predisposition can increase the risk of tumor formation. Age exceeding 50 years can cause a neoplasm.
Incorrect diet, which contains a large amount of meat products, animal fat and baked goods. If the body lacks plant foods that are rich in fiber, pathological processes may occur in the intestinal area. Regular consumption of alcohol and smoking tobacco products can cause cancer.