February 4, 2021
In the 21st century, stomach cancer began to lose ground in incidence, but only in developed countries. Since the 1970s, the cohort of cured patients in the United States has doubled - every third person with a neoplasm can be confident of a healthy future.
Just like a hundred years ago, the main method of salvation from stomach cancer is surgery, but modern oncology is inclined towards reducing the volume of tissue removed while maximizing the functionality of the entire gastrointestinal tract.
Our expert in this field:
Sergeev Pyotr Sergeevich
Deputy chief physician for medical work, oncologist, surgeon, chemotherapist, doctor of the highest category, Ph.D.
Call the doctor
Causes of stomach cancer
It is believed that Helicobacter pylori infection contributes to cancerous degeneration. It is known for sure that the bacterium Helicobacter pylori causes peptic ulcers; with ulcers and malignant transformation, the same process occurs - proliferation or increased reproduction of cells in response to chronic inflammation.
During the process of enhanced cell reproduction, a malfunction occurs and a structural defect occurs in the cell, turning it into the progenitor of a malignant cell pool.
It is interesting that among the peoples of the Russian North, the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori is very high, and ulcers are very rare, as is cancer, because the mucous membrane is genetically adapted to process hard food.
It turns out that bacteria prepare the development of a malignant neoplasm; what becomes the main cause of cancer development is not yet known.
Heredity as a cause for the development of stomach cancer
Genetic predisposition is confirmed by a one-fifth increase in the likelihood of developing a malignant neoplasm in the stomach when a close relative has stomach cancer.
Apparently, some genes are responsible for the development of the disease, because entire nations very often suffer from it: the Japanese, Chileans and Icelanders. It is typical for black Indian and Spanish emigrants living in the United States, while in their homeland in India and Spain the incidence is not the highest.
Risk factors for stomach cancer
- No specific harmful product was found, but nutrition was also identified as a factor contributing to the development of the tumor. Thus, a change in the dietary pattern of the Japanese who moved to America leads to a decrease in morbidity.
- It is believed that chronic deficiency of vitamin B12, which occurs due to the inferiority of the mucous membrane, is to blame. It is possible that impaired absorption of the vitamin and malignant growth are caused by the initial soreness of the mucosa, and are not at all related to each other.
- It has been noted that in those who have undergone gastric surgery, the incidence of malignant tumors increases threefold.
- Working with asbestos and nickel can lead to the process, as well as high levels of nitrates, nitrites and preservatives in food.
- Chronic and severe deficiency of immunity contributes, therefore, with immunodeficiency against the background of HIV infection, malignant tumors often develop.
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse damage the mucous membrane, which causes proliferative changes, but these factors do not increase the risk of the disease.
In most cases, stomach cancer occurs when several risk factors are combined, but also often the patient does not have a single cause that could lead to a malignant process.
The role of polyps in the development of the disease
The role of polyps in the formation of malignant neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract has been well studied. Adenomatous polyps of the stomach, especially those with villi and larger than two centimeters, can also cause cancer. All polyps are removed during gastroscopy, because only examination of all benign growths of the mucous membrane under a microscope can exclude or confirm the onset of transition to cancer.
Drugs for the treatment of peptic ulcers from the group of proton pump inhibitors promote the formation of pitted polyps with a low probability of degeneration.
The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for pain relief promotes inflammation of polypous growths of the mucous membrane, and inflammation is proliferation with the possibility of cell transformation into cancer.
Symptoms of stomach cancer in the early stages, when it can be cured, are practically absent or are taken for banal and passing gastric suffering without a trace. Obvious clinical manifestations of the disease often call into question the possibility of radical treatment.
Skirrhus of the stomach: treatment
Total gastrectomy, which is a common option for gastric adenocarcinoma, produces good results in only 20-30% of patients with scirrhous cancer. The reason for this is the presence of peritoneal metastases, extensive damage to the lymph nodes and neighboring organs. However, radical resection of the carcinoma provides the best survival rates.
It is worth noting! Total tumor resection is possible only in 30-35% of cases. When complete removal of a tumor poses a threat to the patient's life, the cancer is partially removed to reduce its size and associated symptoms. Palliative treatment of gastric scirrus may include gastrectomy, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
Because the 5-year overall survival rate of patients with stage II and III scirrhous gastric cancer after surgical treatment remains low, additional methods are needed. Physicians have attempted to improve survival with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hyperthermia, hormonal therapy, and immunotherapy. Unfortunately, the antitumor effect of all these methods is insufficient to improve the prognosis of patients with diffuse carcinoma. New therapy is needed based on the characteristic biological behavior of the tumor.
A clinical trial of the treatment of scirra gastric with the drug Dovitinib, which is an inhibitor of the FGFR2 gene, is currently underway. Dovitinib reduces the proliferation of cancer cells, stopping the growth and metastasis of tumors in the stomach. Another drug that has shown effectiveness in the treatment of fibrous carcinoma is Tranilast. Its antitumor effect is based on the inhibition of fibroblasts.
Such therapy may be provided alone or in combination with chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery. It can be used for recurrent carcinoma if other methods do not help.
Symptoms
Symptoms of early stomach cancer
The first symptoms of stomach cancer are vague and often there are no obvious signs of trouble at all. If there is some kind of stomach ailment, then in the early stages its symptoms are not specific to a malignant tumor. The most common is a perversion of appetite and its deterioration can be a sign of any gastric disease, not just cancer.
After making a diagnosis, you can try to retrospectively track the first manifestations of the disease, although it is impossible to say for sure that it was the tumor that caused gastric problems, and not gastritis - dyspepsia. The clinical manifestations of a malignant neoplasm are no different from the gastric complaints that trouble all adults from time to time.
The malignant process occurs under the masks of other gastric diseases; it can be detected during a routine examination; by chance, during an examination for another reason, its metastases are already found. Early cancer is usually detected during regular endoscopic examination of a chronic ulcer.
Symptoms of a common disease
Clinical symptoms depend on the size and location of the cancer in the stomach.
When the formation is localized in the inlet section, a lump is felt that interferes with the movement of food through the esophagus and belching occurs when the food is eaten. A person avoids solid food and switches to liquid food.
When cancer is localized in the outlet section, food is retained in the stomach; with minor overeating, vomiting may occur.
If a large infiltrate occupies the middle—the body of the stomach—then the patient is saturated with small, contrary to usual, portions of food. The feeling of fullness and heaviness lasts longer.
When the anterior gastric wall grows, the node can be felt in the pit of the stomach, but no obvious pain is felt. Pain occurs when the posterior gastric wall grows and spreads to other abdominal organs. Girdle pain or lower back pain is a sign of tumor growth into the pancreas.
During this period, the patient begins to lose weight, feels increasing weakness and lethargy from chronic malnutrition, hunger is accompanied by a persistent aversion to food.
Consultation with a doctor now!
Symptoms of the metastatic stage
Each malignant disease has “favorite” sites of metastases. Stomach cancer mainly spreads in the abdominal cavity - by implantation and through the lymphatic system; tumor spread to the lungs and bones is not at all typical for it.
- The appearance of icteric discoloration of the skin against the background of a moderate increase in body temperature, constant nausea and increasing weakness is a sign of metastatic liver damage.
- An increase in the size of the abdomen against the background of weight loss indicates the formation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity - ascites.
- Vomiting of brown masses and black liquid stools are manifestations of bleeding from a large gastric vessel destroyed by tumor masses.
- Ovarian enlargement and tumor conglomerates of the lymph nodes of the supraclavicular region are typical symptoms of the disease.
Diagnosis of stomach cancer has changed little in the 21st century; it is also based on endoscopic examination, only more advanced. A lot depends on the qualifications of the endoscopy specialist, because the entire history of the disease is very short.
Treatment options
The main method of correcting the patient's condition is complete removal of the stomach. This measure allows for a certain period to extend the life of every third person suffering from this type of cancer.
The lack of a chance for a complete cure of the tumor is explained by the too rapid occurrence of metastases in the abdominal cavity and the rapid penetration of cancer cells into the lymphatic system, from where they spread throughout the patient’s body.
And yet, it is complete resection of the stomach that gives the best results in the fight against scirrhoses of its form. Treatment is usually supplemented with chemotherapy and x-rays. Immunotherapy is also used.
Experimental methods include the use of Dovitinib or Tranilast , which prevent the rapid proliferation of tumor cells. The drugs have a cytostatic effect and inhibit its spread beyond the stomach. Experiments demonstrate fairly high rates of effectiveness of these medications.
Diagnostics
The first stage of diagnosing stomach cancer
Diagnosis does not begin with an oncologist; gastric cancer is primarily detected by a therapist or surgeon, to whom the patient turned with complaints of gastric discomfort. It is also possible that pathological changes are discovered completely by accident during an examination for another disease, and these changes are metastases, because gastric pathology can only be identified with a targeted examination; with an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, neither the stomach nor intestines are visible.
A patient comes to an oncologist with a suspicion of a malignant tumor, with an endoscopic examination performed in the clinic and “slides” of histological preparations that were obtained from a biopsy of a piece of the tumor. At this stage of diagnosis, the prevalence of the malignant process is not assessed and, accordingly, it is not yet possible to choose the optimal treatment for stomach cancer.
Second stage of diagnosis
The examination is necessary to develop treatment tactics for stomach cancer. It is necessary to find out the size of the tumor in the organ and determine how far it has managed to spread throughout the body. Therefore, the endoscopic examination will be repeated; it is not possible to find out the true state of affairs by other means.
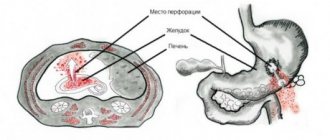
Today, a more modern esophagogastroduodenoscopy combined with ultrasound - endosonography allows you to see how the tumor is located inside the gastric wall, where the boundaries of the cancer lie, and whether the tumor conglomerate penetrates into neighboring organs.
During the study, the possibility of removing the stomach is not only assessed, but also life-threatening complications are predicted: bleeding and wall breakthrough - perforation.
Diagnostic methods
EGDS is the most informative diagnostic method.
Scirrhus is a multifactorial disease. And yet its nature can be established on the basis of competent and detailed collection of anamnestic data. The doctor studies data on the presence of an atrophic form of gastric inflammation, anemia, surgical interventions, benign gastric tumors and gastroesophageal reflux disease in the patient. As background factors, lifestyle, the presence of bad habits, cases of malignant neoplasms of the gastrointestinal system in close relatives, and the nature of the diet are studied. A number of laboratory and instrumental examination methods are also performed, such as:
- General blood analysis. With a serous malignant tumor, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases and leukocytosis occurs.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy. With this instrumental method, changes in the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract, their thickening and proliferation are noted. Noteworthy is the narrowing of the lumen of the organs.
Ways to clarify the condition of scirrhous cancer
A number of the following instrumental methods make it possible to clarify the depth of infiltration and the degree of metastasis:
- Taking a tumor site for biopsy. The samples are preserved, cut on a microtome, stained with special dyes and examined under a microscope. Based on these actions, a conclusion is made about the degree and form of dysplasia.
- Endoscopic ultrasonography. This method allows you to examine the gastrointestinal tract from the inside and monitor the extent of cancer invasion.
- CT scan. It signals the depth of infiltration of the tumor, the degree of damage to the lymph nodes and neighboring organs.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy. This is a technique with direct intervention in the abdominal cavity. It provides the most accurate data about the condition of the cancer tumor. But the method is dangerous due to the risk of damaging the tumor with further aggressive metastasis.
Reviews from our patients
- Feedback on the treatment of stomach cancer
Feedback on stomach cancer treatment January 13, 2021The patient was admitted to the clinic for diagnosis and treatment of stomach cancer. The tumor was verified as soon as possible. A central venous port system was installed. The first of four courses of chemotherapy was completed. After completing this stage of treatment and reducing the size of the tumor, a surgical operation for gastric resection is planned.
read more
- Feedback on the treatment of stomach disease
Feedback on the treatment of stomach disease December 8, 2021
The patient was admitted in serious condition with symptoms such as repeated vomiting, severe weakness, and increased abdominal volume. The cause is a stomach disease. Other clinics refused to treat the patient due to the complexity of the diagnosis. During hospitalization at the Medicine 24/7 clinic, fluid from the abdominal cavity was evacuated, which led to an improvement in the general condition. At the second stage of treatment, stenting of the gastric outlet was performed. Thanks to this, the patient...
read more
- Feedback on the treatment of stomach cancer 10/20/2020
Review of treatment for stomach cancer October 20, 2020 October 20, 2021
The patient was admitted to the Medicine 24/7 clinic with a stomach disease aggravated by somatic diseases. To date, treatment tactics have been selected, including courses of chemotherapy.
read more
- Feedback on the treatment of stomach cancer 09.23.2020
Feedback on the treatment of stomach cancer September 23, 2020 September 23, 2021
A patient's wife talks about her husband's treatment. Diagnosis: stomach cancer. At his place of residence, he was denied treatment. The Medicine 24/7 clinic was able to help. The patient’s wife notes the efficiency of the entire staff, their mobility, and professionalism. In particular, she thanks the attending physician Milana Khanlarovna Mustafaeva.
read more
- Feedback on photodynamic therapy
Feedback on photodynamic therapy July 21, 2020
Mikhail Lvovich is 92 years old. He went to the Medicine 24/7 clinic for treatment of stomach cancer. Surgery and chemotherapy courses are not indicated at his age, as they can lead to significant complications. An individual treatment plan has been developed for the patient, including sessions of endoscopic photodynamic therapy. A positive effect has been achieved. In addition, molecular genetic diagnosis of the tumor was carried out, which in the future will make it possible to select…
read more
- Successful treatment of stage IV gastric cancer with metastases at the Medicine 24/7 clinic
Successful treatment of stage IV gastric cancer with metastases at the Medicine 24/7 clinic November 21, 2021
Here is an example of the effectiveness of properly selected treatment. Even when there seems to be no chance and no one can help. Elena was diagnosed with stage IV gastric cancer with metastases. Treatment included gastrectomy and targeted selective therapy. It gave results. According to the latest examination, the patient has no signs of the disease. Despite this, treatment continues until complete victory. "Thanks a lot! You gave...
read more
- Anna Sergeevna about the treatment of stomach cancer
Anna Sergeevna about the treatment of stomach cancer June 29, 2021
Anna Sergeevna was admitted to the Medicine 24/7 clinic in serious condition. Due to stomach cancer, the patency of her esophagus was impaired. At the clinic, her condition worsened, any food intake was impossible, and continuous vomiting began. During the examination, an inoperable stenosis was discovered. A decision was made to perform stenting. During the procedure, a unique stent was installed, 70 centimeters long. Thus, the clearance...
read more
Diagnostic laparoscopy
Endoscopic examination of the abdominal cavity - not all patients need laparoscopy. It is certainly necessary for a large tumor or a cancerous node growing through the wall of the stomach. With a high degree of malignancy, laparoscopy will reveal peritoneal carcinomatosis - metastatic nodules along the mucous membrane lining the internal organs. No other methods, except for direct eye examination using optics, can detect contamination of the peritoneum.
Detection of metastases in the peritoneum radically changes treatment tactics. With such metastases, only palliative surgery is performed to relieve painful symptoms; radical intervention is no longer possible.
If you refuse laparoscopic examination, then at the first stage of abdominal surgery the surgeon will conduct a revision, hidden metastases will be detected and the initial surgical plans will change. In case of stomach cancer, laparoscopy avoids unnecessary intervention, therefore it is included in the standard of mandatory preoperative diagnosis.
Detection of cancer metastases
- An X-ray polypositional examination of the stomach from several angles will reveal cancer metastases up to the esophagus and down to the duodenum, which cannot always be seen even on a CT scan.
- In the abdominal cavity, ultrasound determines the involvement of the liver and peritoneum in the process, and determines the size of visible lymph nodes.
- The diagnostic standard is CT of the abdominal cavity, which allows you to find very small metastases in secluded corners where ultrasound cannot penetrate.
- Stomach cancer, in addition to the liver and peritoneum, has typical areas of metastasis in the lymph nodes of the supraclavicular areas, ovaries, and navel. Therefore, an ultrasound of the cervical-supraclavicular areas and pelvis is performed with an examination by a gynecologist.
- A CT scan is performed to detect metastases in the chest.
Get a stomach cancer treatment plan
Additional diagnostics
To ensure that anesthesia does not bring unpleasant surprises, you need to know the state of the cardiovascular system and consult an anesthesiologist.
A malignant tumor of the stomach greatly disturbs the biochemical balance; you will need to take a detailed blood test with coagulation factors and determine from the blood elements which nutrients - nutritional support is necessary before and after surgery.
Stomach cancer was first successfully operated on by the Austrian Billroth at the end of the 18th century. Over the past century and a half, therapeutic approaches to most malignant neoplasms have changed, many antitumor drugs have appeared, but only surgery provides hope for curing stomach cancer.
Treatment of stomach cancer
Principles for choosing treatment for stomach cancer
For stomach cancer, treatment tactics are determined by the prevalence of the malignant tumor. All patients are divided into three groups according to a treatment strategy aimed at maximizing life expectancy with acceptable quality:
- The first group can hope for a long life; nine out of ten will live more than five years, because they have been diagnosed with early cancer, which can only be cured surgically, in some cases even saving the stomach.
- The second group is the largest, it includes patients with a fairly extensive tumor, but localized only in the stomach and affecting the lymph nodes closest to it, which can be removed with the loss of part or all of the organ.
- The third group consists of patients for whom it is impossible to radically remove all existing tumors, or whose general condition is so weak that it does not allow undergoing surgery.
Surgical treatment of stomach cancer
Only surgical removal of the tumor gives hope for a cure; the range of interventions recommended by standards includes resection - removal of part of the stomach and complete removal - gastrectomy; with minimal damage to the mucous membrane, innovative endoscopic operations are used to preserve the organ, and with it a good quality of long life.
For small cancers, the generally accepted and most often used tactic is gastric resection; for widespread tumors, gastrectomy is used.
In case of metastases, radical treatment is excluded; during this period, cancer cells are spread throughout the body by blood and lymphatic fluid, a process called dissemination. Surgery is absolutely contraindicated for several metastases of gastric cancer in the lung tissue and liver. In case of single and slowly growing tumor nodes, the council should discuss the advisability of removing part of the lung or liver affected by metastases, only if it is possible to completely “free” the body from cancer - not a single tumor should remain.
It will not be possible to remove cancerous lymph nodes outside the abdominal cavity or tumor screenings in the peritoneum, so surgery is contraindicated.
Treatment
The only treatment for scirrhous gastric cancer is removal of the tumor. Depending on the volume and extent of the lesion, the surgeon performs a resection of part of the organ or removes it completely.
The use of conservative methods of therapy is ineffective, since medications do not completely destroy cancer cells. In order to reduce the risk of complications, chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be prescribed.
Drug treatment is used during the recovery period after surgery to relieve pain, restore immunity and the general condition of the body after radiation or exposure to chemotherapy drugs.
During and after therapy, it is important to follow a special diet. Carbonated and alcoholic drinks, harmful foods containing many chemicals and carcinogens should be completely excluded from the diet. Dishes must be steamed or consumed boiled, baked, or stewed. Smoking is strictly prohibited.