Most people who are far from medicine know little about the purpose and methods of examining internal organs. Laboratory tests in the case of checking the esophagus are not very informative. When such a need arises, the most in demand are imaging examination methods, which allow the gastroenterologist to assess the condition of the mucous membrane, the presence of lesions and pathologies. The article describes how the esophagus is checked, basic examination methods and tips on how to avoid anxiety and pain during procedures.
List of the most informative examination methods
The most relevant examination methods today in gastroenterology:
- visual survey and examination of the patient;
- X-ray examination;
- gastroscopic examination;
- CT scan;
- Ultrasound examination of the esophagus.
Each of these methods has its pros and cons. Many patients have a question about how to check the esophagus and larynx in such a way that there is no discomfort or even pain. In fact, modern examination methods are quite painless, and if the basic rules of the procedure are followed, only mild discomfort may occur.
Research methods
If a patient has complaints about gastrointestinal disturbances, then he needs to undergo a full medical examination. There are several methods of medical diagnosis:
- Physical method. Based on a visual examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis.
- Laboratory research. Includes taking tests prescribed to confirm a preliminary diagnosis.
- Hardware methods. They provide the opportunity to examine the gastrointestinal tract and identify the presence of pathologies.
Only a doctor can select the optimal diagnostic option or prescribe a comprehensive examination. The choice will depend on the nature of the patient’s complaints, the collected medical history and preliminary diagnosis. We will talk about hardware research options.
Gastroscopy and sounding
Gastroscopy refers to endoscopic examination methods. Provides comprehensive information about the inner surface of the duodenum and stomach. The manipulation is based on the oral insertion of a probe with a videoscope and a light bulb at the end into the cavity of the organ.
The study is unpleasant, but the most informative of all diagnostic measures existing today. During the examination, the doctor may remove single small polyps or take a tissue sample for a biopsy. The procedure is prescribed for chronic forms of gastritis and ulcerative pathology to confirm the diagnosis and select a treatment regimen.
A probe study is carried out in the same way as FGS. With the help of manipulation, the specialist receives information about gastric secretion, but does not see the mucous membrane.
Oral insertion of a probe is associated with extremely unpleasant sensations for the patient, which is why many are terrified of the procedure. How can you check your stomach without swallowing your intestines? Are there other research options?
What function does the esophagus perform in the body?
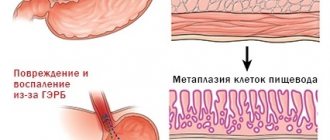
Most people don't think about the role the functioning of the esophagus plays in their overall health. Meanwhile, this is the first organ of the gastrointestinal tract, which is responsible for the beginning of the circulation of food in the human body. And if pathologies arise in the esophagus, then there can be no talk of healthy and harmonious, holistic functioning of the digestive tract.
The main and most important function of the esophagus is to move incoming food from the oral cavity and directly from the pharynx into the stomach cavity.
This is a complex process that has reflex-automatic characteristics. In some cases, the work of the esophagus may be difficult due to neoplasms, the development of erosions, etc.
What does the endoscopic method reveal?
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy rightfully refers to highly informative methods for diagnosing the organs of the digestive tract that make up its upper section, since during its implementation the specialist not only receives a visual picture of the internal state, but can also pay close attention to:
- anatomical features of the structure of organs;
- quality of mucous membranes and folds;
- the appearance of erosions and ulcerations;
- the presence of tumor-like or polypous formations;
- condition of blood vessels;
- the presence of hidden bleeding.
The procedure is characterized by a significant volume of manipulations, since it allows you to examine all organs related to the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract.
Esophagus
The organ is located at the beginning of the gastrointestinal tract and is a muscular tube approximately 25-30 cm long, hollow inside and slightly compressed on the sides. In accordance with the areas in which it is located, it is divided into three parts - the cervical region, the thoracic region, and the abdominal region. Its main purpose is to allow food to pass into the lower segments of the intestinal tract.
During the examination, in normal condition the following should be revealed:
- three physiological narrowings (at the beginning, end, and in the area of bifurcation of the trachea);
- normal light pink color of the mucous membrane and smooth surface without pathological changes.
Stomach
It is a hollow muscular organ, which is an important segment of the gastrointestinal tract. In the upper part it connects with the esophagus, in the lower part - with the duodenum through two sphincters - the cardiac and the pylorus. If the closure of the latter is disrupted, the contents are thrown back into the stomach, causing damage to the mucous membrane and the development of inflammation. The inner shell has three layers, the first of which has many folds, the second contains blood vessels and lymph, and the third contains muscle fibers.
Normally, according to the results of the study, the epithelial layer should have a slightly pinkish color and a uniform surface.
Inside the stomach there is a “mucus lake” where digestive juice is produced. Depending on the color, you can accurately determine or refute the likely development of pathologies:
- transparent structure is the norm;
- greenish or yellow tint – bile impurities and the development of duodenogastric reflux;
- reddish color - blood impurities.
Duodenum
A horseshoe-shaped tubular organ, hollow inside, connecting at the beginning with the pylorus of the stomach, and at the end smoothly passing into the small intestine. It received its specific name because of its length, which in ancient times was measured by 12 transverse dimensions of the big toe. The actual length is 25-30 cm. A special feature of the organ is the presence of pancreatic and liver ducts. The examination takes into account the condition of the mucous epithelium, which should have a light pink tint, a smooth velvety surface and a uniform structure.
What pathologies of the esophagus can an examination show?
As a rule, the examination is carried out to identify the presence of the following pathologies and diseases:
- Reflux esophagitis.
- The presence of erosions, ulcers, injuries to the mucous membrane and muscle layer.
- Violation of the innervation of the cavity of the esophageal organ.
- Esophagospasm.
- Varicose veins of the esophageal cavity.
- Narrowing of the esophagus.
- Neoplasms of various etiologies.
- Barrett's esophagus.
- Esophagitis.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Candidal glossitis of the tongue.
Each of them requires follow-up, and some require a serious course of treatment, as they can pose a potential threat to life. You should not try to self-medicate: this can only worsen the condition. If any of the above diagnoses is present, the help of a qualified gastroenterologist is required.
Causes of development of esophageal pathologies
The reasons why certain pathologies of the esophagus develop:
- hereditary predisposition;
- abuse of strong alcoholic drinks (the esophagus is the first organ that takes the “blow” of strong 40-degree drinks);
- eating foods high in acid on an empty stomach;
- eating excessively hot, scalding foods on a regular basis;
- mechanical injuries to the walls of the esophagus;
- bulimia or other disorders in which a person regularly has to endure vomiting attacks for a long time;
- inflammatory processes that occur in the body.
How is the esophagus checked if for some reason access directly to the larynx is difficult? For this, there are methods of external examination - for example, computed tomography or radiography do not require direct access to the organ. Many patients are afraid of endoscopy and are interested in how to check the esophagus and stomach without gastroscopy. In fact, endoscopy can be completely painless if the procedure is performed by a competent specialist and the patient follows all the rules of the examination.
Esophagotonokymography of the esophagus
The essence of esophagotonocymography is to record graphic images of contractions and changes in the tone of the walls of the esophagus. Diagnoses achalasia at an early stage, other muscle diseases, hiatal hernia, the symptoms of which may not yet have fully manifested themselves. To do this, use a multichannel probe with a rubber balloon or catheter that measures the pressure inside the esophagus. Can provide comprehensive information about any violations of muscle tone and esophageal sphincters, regardless of their condition. Refers to gastroscopy methods.
Acid measurements in the esophagus are made to monitor gastric secretion and its effect on the organ.
Visual survey and examination of the patient
It would seem, what information can a simple conversation convey to a doctor? In fact, an experienced gastroenterologist can suggest one or another diagnosis based on oral complaints. The following points are important during the survey:
- whether there is pain in the esophagus and larynx;
- what kind of pain and discomfort the patient experiences;
- Is the digestion process normal?
- are there any concomitant chronic diseases;
- How long has the patient been suffering from pain and discomfort in the esophagus?
Visual examination of the larynx alone can also give an idea of the general condition of the mucosa. Of course, usually this information is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis, but in some cases it is a visual examination and oral questioning that makes it possible to form an initial and relatively accurate clinical picture of an objective examination.
Diagnostic methods
Any diagnostic examination begins with a history taking. Patients come to see a gastroenterologist with obvious signs of organ pathology. Their complaints may be associated with painful sensations behind the sternum and in the chest. There may be dysphagia of varying severity, difficulty swallowing, a feeling of a lump in the throat and other symptoms indicating problems with the esophagus. The question arises: how to examine the esophagus, what research methods to choose?
Methods for studying the esophagus
For most, the relevant question is how to examine the esophagus. For this purpose the following is carried out:
- Examination of the patient, which includes a general examination of the esophagus and larynx. Particular attention is paid to the condition of the larynx. The doctor also performs palpation of the lymph nodes in the neck, palpation of the epigastrium and other forms of general examination.
- Instrumental methods: radiography , 24-hour pH monitoring , CT and spiral tomography , esophagofibroscopy , FGS , chromoscopy , biopsy , etc.
Since instrumental methods in examining the esophagus are of primary importance, it is worthwhile to dwell on them in more detail.
Esophagofibroscopy
This highly informative research method allows you to find out the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus along its entire length. And also - to identify the cause of pain, dysphagia, determine varicose veins, the presence of tumors and bleeding.
The manipulation is carried out for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An endoscope with an ultrasound sensor is inserted through the patient's larynx into the esophagus, which examines the walls of the esophagus and collects biological material for histological examination.
The device has high performance in detecting the slightest deviations from the norm in the condition of the organ, therefore it is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods used for examining the esophagus . The procedure is performed under anesthesia - local or general. First of all, this is a thorough anesthesia of the pharynx.
There are practically no contraindications for this method, with the exception of the patient having burns of the esophagus, severe diseases of the larynx, and an aortic aneurysm. Complications during the procedure may include contact bleeding and perforation of the esophageal wall.
Daily pH-metry
Based on the results of measuring the pH level in the esophagus, the nature and severity of reflux of the organ can be determined. The manipulation boils down to installing a probe with a sensor in the lower part of the esophagus. This device remains in the organ for 24 hours. What can be revealed based on the pH results:
- the state of the acid formation process during the day under natural conditions of organ functioning;
- the effect of medications on the level of acidity in the esophagus;
- level of resistance to taking antisecretory drugs;
- functional state of the esophagus and stomach before and after surgery.
X-ray examination of the esophagus
The accuracy of this study is inferior to computed tomography. However, it is easiest and fastest to take a picture if the patient is unconscious for one reason or another. X-rays are easy to use, and if done rarely, they are safe for health (with the exception of only certain categories of patients).
How to check the esophagus and larynx without gastroscopy if there is a suspicion of a foreign body? X-ray examination is ideal for this purpose. it can also show the following pathologies:
- diaphragm hernia;
- size and deformation of the internal lumen;
- tumors (not always reliable; if suspicion arises, the patient is sent additionally for other, more accurate studies);
- diverticulum;
- ulcers and erosions.
Since the esophagus is not a radiopaque organ, the study should be carried out after the administration of a special liquid. It will allow you to see almost every part of the esophagus in the image. The liquid is diluted and taken orally immediately before the study. As a rule, it also allows you to assess the condition of the stomach.
How to check the esophagus using x-rays, is special preparation needed? Yes, there are certain rules:
- you should not eat food 12-10 hours before the test;
- do not drink liquid only in the morning; taking into account night sleep, it turns out that you should not drink anything for 8-9 hours;
- There is no need to worry or be nervous before the examination - this is a completely painless and relatively safe examination.
pH-metry of the esophagus
Allows you to determine the intensity and nature of esophageal reflux using pH level measurements. A special probe with a sensor, having from one to three electrodes, is inserted through the larynx and stops 5 cm before the cardiac part of the stomach. The sensor's task is to record daily changes in pH in the lower part of the esophagus.
pH-metry - determination of the intensity of gastroesophageal reflux using a special probe, which is installed 5 cm above the cardia. With esophagogastric reflux, there is a sharp decrease in pH in the esophagus and increased pain.
Hot Topics
- Treatment of hemorrhoids Important!
- Treatment of prostatitis Important!
Allows you to determine the intensity and nature of esophageal reflux using pH level measurements. A special probe with a sensor, having from one to three electrodes, is inserted through the larynx and stops 5 cm before the cardiac part of the stomach. The sensor's task is to record daily changes in pH in the lower part of the esophagus.
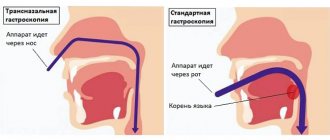
Gastroscopy of the esophagus - is it really that scary?
This test usually frightens patients. The very fact that a tube with a tiny camera will be pushed into the larynx all the way to the stomach causes psychological rejection. Therefore, patients often ask the question of how to check the esophagus without gastroscopy. In most cases, the doctor manages to persuade the patient to perform it, since EGDS is by far the fastest and easiest way to assess the condition of the esophagus and stomach.
Carrying out an endoscopy takes only about 10-15 minutes, taking into account all the preparations. If the patient follows the instructions of the gastroenterologist, the procedure will be painless and will not entail negative experiences.
Capsule gastroscopy
This research method is based on replacing the probe with a special capsule equipped with a video camera. The device allows for a thorough examination of the gastric mucosa and detects the disease in the early stages of development.
To make a diagnosis, the patient must swallow the capsule. For the inspection to be successful, you should prepare for it:
- The patient must adhere to a diet for 2 days before the procedure. It is recommended to exclude fatty, heavy foods, alcohol and dishes that cause flatulence from the diet. Food should be well chopped and steamed or boiled.
- The study is carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach. The capsule can be taken with ½ glass of plain liquid.
The process does not take much time and does not cause any discomfort to the person. During the examination, the patient can return to normal life, limiting physical activity. After 7–8 hours, the patient visits the doctor’s office again, where the doctor transfers the indicators recorded by the capsule into the computer and makes a diagnosis.
After a certain time, the device leaves the body naturally. The advantages of this procedure are obvious, but the method has not found wide application due to the rather high price of the device. In addition, such an examination does not allow you to perform a biopsy, remove polyps, or stop bleeding.
You can see how the stomach is examined using the capsule method in the video:
Desmoid test
Gastroenterologists often use a desmoid test to determine the degree of gastric juice activity. During the test, the patient swallows a bag filled with methylene blue powder and tied with catgut thread.
After the thread dissolves, the dye is gradually absorbed into the blood and no later than 18–20 hours later it is eliminated from the body. The study is based on assessing the intensity of urine staining. If the first portion of urine acquires a bright blue-green color, it means that the acidity of the stomach is increased.
Radiation research methods
Of the radiation methods, X-ray is the most widely used. Equipment for examination is available in almost every medical institution, so the examination is available to all segments of the population.
MRI and ultrasound are more modern research methods and pose less of a threat to the health of patients.
You can learn about the differences between these procedures from the video:
X-ray
Using radiography, a stomach ulcer is detected, its configuration is checked, and its size is assessed. R-graphy is carried out using a contrast agent - barium suspension. It is prescribed when the patient complains of rapid weight loss, the appearance of blood in the stool, frequent and debilitating diarrhea, and constant pain in the gastrointestinal tract.
The procedure is completely painless and not very complicated, but requires compliance with some rules:
- For 2–3 days before the examination, you should exclude alcohol, thick, fatty and solid foods from your diet.
- On the eve of the test, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines using an enema or special means with a laxative effect.
- Before the procedure, the patient is prohibited from eating or drinking colored drinks.
An X-ray of the stomach lasts 30–40 minutes. All this time, the doctor asks the patient to take certain positions and takes six pictures of the gastrointestinal tract in different projections.
How to avoid pain during gastroscopy?
How can you check the esophagus during gastroscopy? To begin, the doctor writes down the patient’s data. Then he examines the larynx and sprays a portion of a special spray on it, which has a local anesthetic effect. Thanks to the use of this spray, the procedure is completely painless and the patient does not suffer from gagging, which occurs when the area of the larynx is irritated. How is the esophagus checked using a tube and camera?
After the spray has taken effect (usually within a few minutes), the patient lies on his side on the couch. It is covered with a diaper, separating the face area. A plastic holder is placed in the mouth to prevent teeth from damaging the tube. The doctor inserts a thin tube with a tiny special camera into the larynx. As the chamber descends, the condition of the esophagus can be assessed. As a rule, the study is carried out not only for the esophagus, but also to assess the condition of the mucous and muscular layer of the stomach.
Esophagofibroscopy
It is carried out both for the purpose of diagnosing the esophagus and for providing first aid. The gastroscopy method is reliable. Helps to accurately determine the cause of dysphagia and odynophagia. Determine pathologies and locations of lesions and bleeding. Esophagofibroscopy will make it possible to view the condition of the esophageal mucosa, conduct histological studies, biopsy, and obtain smears. The procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia and only by a highly qualified specialist. Requires preliminary preparation of the patient.
Esophagofibroscopy allows you to examine the mucous membrane of the esophagus along its entire length, perform a targeted biopsy from suspicious areas (with histological examination), and make smears for cytological examination.
Psychological state of the patient during gastroscopy
If the patient is as relaxed as possible, he will not feel pain - only mild discomfort. Fear and anxiety play a disservice in such research. Judging by the reviews, usually, the more nervous the patient is, the more he stresses himself out, the more he fidgets on the couch, the more excited the doctor who performs the gastroscopy experiences.
So there is no need to worry, this procedure has been carried out for many years, and during this time no one has yet suffered from the actions of a gastroenterologist.
How is an ultrasound of the stomach performed?
Preparation for an ultrasound of the stomach is similar to an ultrasound of the intestines: the patient adheres to a strict diet for 3 days, and the night before does not eat any food from 18.00. If there is a tendency to form gas, the patient drinks 2 capsules of Espumisan before bed. In the morning, half an hour before the procedure, you should drink a liter of water so that the walls of the stomach straighten.
There is also a method of ultrasound examination with contrast. Water is an excellent conductor of ultrasound, and without it, scanning an organ is somewhat difficult.
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. The doctor assesses the condition and thickness of the walls on an empty stomach, looking for the presence of free fluid. Then he asks the patient to drink 0.5-1 liter of liquid, and uses an ultrasound machine to evaluate changes in the expanded stomach. A third ultrasound scan is performed 20 minutes later when the stomach begins to empty. The doctor evaluates the motility of the organ and the rate of fluid loss. Normally, a glass of water (250 ml) comes out of the stomach in 3 minutes.
The patient lies on the couch on his side, the specialist applies gel to the peritoneal area and moves the sensor over the surface. Periodically, he tells the patient to change position or change his position slightly
The doctor pays attention to the following indicators:
- position of the stomach and its size
- Has the mucous surface of the stomach expanded?
- is there thickening or thinning of the walls
- what is the state of the circulatory system of the stomach?
- contractility of the stomach
- are there inflammations and neoplasms?
The entire examination takes a maximum of 30 minutes and does not cause discomfort or pain. Ultrasound, unlike FGDS, is much easier to tolerate for children and the elderly.
Computed tomography of the esophagus
How to check the esophagus without gastroscopy? Computed tomography is a method that does not require additional insertion of any instruments into the larynx and esophagus. In addition, this method is suitable for those who are looking for an answer to the question of how to check the esophagus for cancer.
This is a modern diagnostic method that requires special equipment and a specialist who knows how to use it. Most large hospitals have had CT scanners for a long time.
A number of photographs are taken, layer-by-layer sections of the human body in the area of the esophagus. As a result, we can draw a conclusion about the quality and ability of the organ to function normally. The method allows you to see even beginning pathological changes, the initial stages of cancer
Radioisotope research
The method is not so widely used, but it has advantages, because it helps to obtain clear contrast data that is not available with other methods and is at the same time relatively harmless. Another advantage is the lack of preliminary preparation. Radioisotope research is based on the use of radioactive phosphorus, which accumulates in malignant tumors and is detected by specially designed sensors. This is a differential method for diagnosing cancer.
The appearance of unpleasant symptoms during the digestion process, such as pain when swallowing, dyspepsia, odynophagia, indicates the presence of diseases of the esophagus. Don't expect them to go away on their own. It is better to contact a specialist who will examine and prescribe a diagnosis.
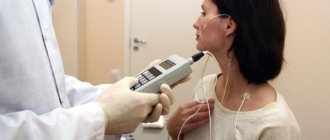
Ultrasound examination of the esophagus and larynx
Ultrasound has been known to all of us since childhood. The method is simple and safe, but in some cases it can cause incorrect diagnosis - it all depends on the experience and qualifications of the ultrasound specialist.
This method is often used as a starting method in diagnosing pathologies, especially in children. Using ultrasound, you can assess the condition of the tissue structure of the esophagus, its peristalsis, the condition of the vessels and adjacent lymph nodes.