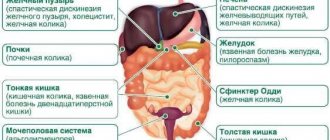
Bloating in a child (flatulence) is an increased formation and accumulation of gases in the intestines, accompanied by various clinical manifestations. It occurs frequently and is observed at different ages - from infants to schoolchildren. It is not an independent disease. This is a symptom that means that a lot of gases have accumulated in the intestines, which distend its walls and cause pain or other unpleasant sensations. Most often it accompanies intestinal pathology or occurs for other reasons not related to disease.
Causes of gas formation
Normally, gas formation occurs constantly in the intestines. This is a physiological phenomenon that does not interfere with general well-being and goes unnoticed. The reasons for it are different:
- swallowing a certain amount of gases during eating;
- digestion of food, which is a chain of biochemical reactions of the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates with the release of gases;
- diffusion (gas exchange), when oxygen from the vessels of the intestinal wall, necessary for the normal functioning of some bacteria, enters the lumen, and carbon dioxide is removed by venous blood and excreted by the lungs;
- the vital activity of the intestinal microflora itself, which releases carbon dioxide during food processing.
Gases formed in a healthy body improve the digestion process: they enhance intestinal motility, help better “digestion” of food and rapid emptying of the intestines. But sometimes the mechanisms of gas formation fail, and the child develops signs of flatulence.
How to diagnose the occurrence of a disease
Diagnosing bloating in a child is not difficult. It is enough to monitor food, behavior on the street, whether he washes his hands, picks things up from the ground, and possibly comes into contact with animals. Sometimes you need to get tested: when flatulence is a prerequisite for a serious illness.
The research will require tests:
- Feces - the presence of bacteria that cause abdominal discomfort, dysbacteriosis and other intestinal infections is detected.
- Blood – reveals signs of anemia, affects the quality of food digestion in the body.
- Probing of the stomach and colonoscopy is done if there is a suspicion of obstruction in the intestines, a dangerous disease.
Timely diagnosis allows you to quickly determine the extent of the disease. After determining the diagnosis and degree, the doctor prescribes the correct treatment. Do not forget about the influence of mental state.
Treatment depends on age. Infants are treated with infusions of chamomile and fennel; doctors prescribe Plantex, Bifiform, and Espumisan. It is recommended to wear it after feeding and place it on the tummy before feeding.
For adult children, medications are prescribed less frequently; the problem is mainly with food. Diet, walks, rest after school are the main remedies for flatulence in an adult. If preventative measures do not help, call a doctor.
Note: if the disease manifests itself, do not force it to eat. Offer more drinking non-carbonated water and tea. When the bloating decreases and the pain goes away, you are allowed to feed, but do not overfeed.
Causes of flatulence
The causes of bloating that cause poor health include various intestinal pathologies, which are divided into several groups:
- Diseases of the digestive system of an inflammatory nature (pancreatitis, inflammation in the intestines - colitis, etc./).
- Non-inflammatory (dysbacteriosis, enzymatic disorders) are diseases associated with disturbances in the digestion processes.
- Infectious diseases with intestinal damage - helminthiases, protozoal infections (amoebiasis, etc.), acute intestinal infections in which flatulence is combined with diarrhea.
- Congenital anomalies of the development and location of the large intestine - its elongation (dolichosigma) or increased mobility.
Flatulence also develops due to alimentary (food) reasons. The most common of them are: overeating, poor diet, consumption of large amounts of fat, carbonated drinks, foods that increase gas formation (legumes, brown bread, beer), and insufficient amounts of plant fiber in the diet.
Intestinal colic in premature and weakened children with signs of malnutrition occurs much more often than in healthy infants at birth.
Other factors
In addition to the above, there are other factors that lead to flatulence in infants. They are related to the nutrition of a nursing mother. Some foods cause gas in newborns:
- hot seasonings and spices;
- whole cow's milk;
- legumes, grapes, cabbage;
- black bread;
- carbonated drinks, etc.
Flatulence in children who are not breastfed, but are bottle-fed, can be caused by:
- formulas that are not adapted for feeding a child at this age;
- early complementary feeding;
- violation of the frequency and timing of the diet;
- psychogenic factors.
The mechanism of formation of intestinal bloating and pain during gas formation is directly related to overexcitation or stress. The release of adrenaline into the blood leads to vasoconstriction, which significantly reduces the excretion and absorption of gases. Stress also increases intestinal tone, as a result: peristalsis and movement of food slows down, fermentation and putrefaction processes intensify, and, therefore, increasing the amount of gas in the child. Seething, tight abdomen, cramps and diarrhea appear.
What causes the development of bloating and flatulence in infants?
The causes of bloating in a newborn can be different. One of the common causes is underdevelopment of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract). Let me explain.
The first reason is
At the time of birth of the baby, the development of his digestive system is not fully completed. Consequently, it is difficult for the intestines to digest food due to a lack of beneficial bacteria that help digest milk. Plus, every day the child eats more and more milk, which increases the load on his intestines.
Second most common among infants
Cause of lactase deficiency. Lactase deficiency - reduced or absent lactase activity.
Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down lactose, the latter is a kind of food for the growth of bacteria in the small intestine and their entry in large volumes into the large intestine.
With an increased content of lactose in the large intestine, the child experiences diluted stool (from bright yellow to brownish-green, diarrhea), pain, rumbling, colic, and gas formation. And if lactase is not active enough, the baby’s weight gain and dehydration decrease.
Milk sugar, which is an important source of energy, is not digested. A disordered intestine does not absorb and digest many beneficial vitamins and microelements from mother’s milk.
Or formula is simply not suitable for artificial babies. As we know, a child’s immunity is located in his intestines. In this case, immunity decreases and there is a risk of other diseases.
To determine whether your baby really has lactose deficiency, you should consult a doctor and have a biopsy of the small intestine done as prescribed.
The third reason is
Perhaps one that concerns all young mothers is the incorrect position of the baby during feeding.
No offense to the girls, due to lack of experience, initially we put the baby to the breast incorrectly and the baby swallows air, which then causes him discomfort. After feeding the baby, you need to hold it upright so that the baby burps, and then it is advisable to lay it on its side.
The fourth reason is
Non-compliance by mothers with the lactation diet.
During the postpartum period, the mother needs to eat dietary foods and avoid legumes, radishes, and red foods in her diet, which increase the process of gas formation. To improve stool, mother can eat canned or dried plums, baked apples, low-fat kefir and cottage cheese, and drink uzvar.
It is advisable to take time for yourself: visit a fitness room or swimming pool, in the first months it will be enough to get a massage, it is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air.
Feeding your baby early can also lead to increased gas production.
Apple or pear purees irritate the intestinal mucosa; it is better to start complementary feeding with vegetable purees.
The fifth and very unpleasant cause of flatulence
E. coli enters the baby's body. You can catch it anywhere, in the maternity hospital, in the clinic, and even at home.
Here, first of all, the mother needs to observe hygiene, have less contact in places where children gather, and be sure to do wet cleaning at home.
Manifestations of pathology in children
Severe gas formation in the intestines leads to the appearance of a foul odor, chronic abdominal pain, and uncontrolled release of gases (more than 20 times a day).
Increased flatulence is also manifested by an enlarged abdomen, acute paroxysmal or bursting pain in the abdomen, belching or hiccups.
Children suffer from increased flatulence very often and at any age - this is a common problem. But the most troublesome thing is bloating in newborns. At the age of approximately 5 months, the child’s body is characterized by an undeveloped digestive system - the absence of normal microflora in the intestines. In addition, infants have an undeveloped enzyme system, which will improve only by 4 to 5 months.
This also leads to fermentation in the intestines, resulting in bloating, spastic contraction of some parts of the intestine and relaxation of others, which is manifested by intestinal colic - sharp paroxysmal pain in the abdomen in an infant. The causes and treatment of this condition are always interconnected; an understanding of their mechanisms is necessary in order to know what medicine to give the child for flatulence and bloating.
Treatment of children of different age groups
Treatment methods for the disease depend on age. Diet, medication, and lifestyle changes may be indicated.
What help can be provided for intestinal flatulence in an infant?
First aid for flatulence in children involves alleviating the condition. A decoction of chamomile and “No-spa” (drotaverine hydrochloride) will help relieve intestinal spasms and ease colic. You can stimulate the passage of gases with the help of Espumisan.
Important! Children under three years of age should not be given medications that have not been approved by the supervising pediatrician.
can be placed on the baby's stomach . Massage is also used to relieve discomfort: circular movements without pressure in a clockwise direction. The child's condition can be alleviated by placing him on his back and bending his legs several times, each time bending them towards his stomach and straightening them. Source: A.N. Surkov, V.V. Chernikov Symptom of flatulence in young children: causes and ways of correction // Pediatric pharmacology, 2013, v. 10, no. 1, pp. 78-82
If these measures do not help, a special gas outlet catheter can be used.
A nursing mother should be careful when consuming gas-forming foods - legumes, cocoa, coffee, chocolate, sauerkraut, baked goods, muffins, grapes, fresh vegetables and fruits.
After each feeding, you need to hold the baby upright so that excess air comes out with a burp.
You can use any medications only as prescribed by a doctor. This could be Espumisan, enterosorbents, eubiotics.
Treatment of older children
In some cases, digestive enzymes are prescribed in tablets. Changes are made to the diet, from which harmful foods are excluded: carbonated drinks, chips, legumes, potatoes, raw vegetables and fruits, chocolate, cocoa. It is important that the child does not overeat. To relieve spasms, improve motility and increase the tone of the intestinal walls, the doctor may prescribe a special drug, for example Iberogast.
It is imperative to observe what the child eats to determine what food causes bloating. Food should be steamed or boiled, and its temperature when served should be moderate. It is recommended to drink more - still water, herbal decoctions. You need to eat 4-6 times a day in small portions and chew your food thoroughly.
Authorized products:
- low fat cheeses;
- dairy products;
- lean fish;
- porridge without milk;
- rabbit meat, poultry;
- pumpkin, beets;
- egg dishes (not fried).
The child should move more, walk, play with peers. It is important to protect him from stress.
Symptoms in newborns
In general, the general condition of a child with increased gas formation is not disturbed: there are no delays in development and growth. Difficulties arise only with small children: it is impossible to find out complaints in a 1-year-old child and, even more so, in a newborn. But you can understand that your stomach hurts indirectly by the baby’s behavior:
- the child constantly passes gas;
- constantly screams, is restless, shows increased activity, does not sleep;
- does not take the breast;
- If you manage to feed it, it gets full quickly.
Due to strong gases in the intestines, the stomach swells even more. Regarding intestinal colic, which is the main symptom of flatulence at this age, there is a rule of “three”:
- appears in the third month of life;
- lasts up to three hours;
- finally disappears at the age of three months.
Symptoms
Regardless of the origin of such factors, bloating provokes discomfort and severity of symptoms in children:
- a feeling of a full stomach when the child himself feels hungry;
- abdominal pain;
- the appearance of characteristic rumbling and seething;
- an increase in the size of the abdomen, which is often noticed by parents;
- belching and hiccups;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- attacks of nausea ending with a gag reflex;
- belly hard to the touch;
- stool disorders, which is expressed in constipation, diarrhea, or alternation of these symptoms;
- high fatigue;
- decreased ability to work.
Such laboratory signs that accompany bloating are typical for children over 2 years of age. Infants and children under 1 year of age have the following symptoms:
- pale skin;
- refusal of breast or formula;
- severe anxiety and constant crying for no objective reason. It can be so intense that a baby under 1 year of age may often blush from excessive exertion;
- seething in the abdomen;
- unnatural position of the baby (knees bent to the stomach);
- frequent constipation;
- rare gas release;
- feces with a green tint, foamy consistency;
- insomnia;
- roundness of the abdomen.
The appearance of one or some of the above signs should be a signal for parents to seek advice from a specialist.
Symptoms in preschool children
In a 2-year-old child suffering from bloating, the following reasons come to the fore:
- consumption of large amounts of easily digestible carbohydrates: grapes, chocolate, baked goods, etc.;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- overweight;
- fermentopathy (insufficient production of lactase, which breaks down milk sugar);
- disturbance of intestinal microflora.
Similar reasons cause belching in a 3-year-old child, in addition to other manifestations of increased gas formation. But at this age, flatulence develops much less frequently than in children under one year old.
In a 4-year-old child, signs of flatulence appear from the first days of attending kindergarten. This is due to changes in diet, due to which the intestines undergo adaptation processes. A child’s hard belly, belching of air, and frequent passing of gases lead to stress, which in turn increases the process of gas formation.
In such cases, a mandatory consultation with a doctor is necessary to establish the causes of this condition and know how to deal with flatulence and bloating.
In a 6-year-old child, the causes and clinical manifestations differ little from those in the previous age category. May play a role:
- expansion of the diet, when more sweets and soda, raw vegetables are eaten;
- incorrect combination of products;
- chewing gum use;
- Great psychological stress and stress if the child starts attending school.
If a child develops a hard stomach and complains of rumbling, pain, and belching after eating, it is necessary to adjust the diet for gas formation.
Flatulence in children 6-10 years old
In children 6 years old, the main causes of bloating have the same symptoms as in preschoolers:
- swallowing air;
- microflora disturbance;
- unbalanced diet;
- constipation (including psychological).
The psychological factor is especially important for a 7-year-old child. It is during this period that the children's age crisis occurs. Children at this moment are especially susceptible to neuroses that affect the functioning of the digestive tract.
Bloating is also a common symptom among students at school. In children 8 years old, as well as in schoolchildren 10 years old, the following signs of flatulence are observed:
- binge eating;
- eating unhealthy foods (chips, cereal);
- drinking carbonated drinks;
- unbalanced diet (it is at this age that children begin to “choose” food);
- dysbacteriosis;
- violation of peristalsis;
- overuse of medications;
- neuroses;
- intestinal infections.
First aid and treatment
First aid for bloating, which can be provided to a child at home, consists of the following:
- massage the abdomen clockwise;
- give the child dill water or Plantex - a herbal anti-flatulence preparation based on fennel;
- in case of ineffectiveness - simethicone (Espumizan, Infacol, Bobotik, Bebinos), which is a symptomatic remedy for bloating, removes gases from the intestines, but does not cure flatulence;
- if a child has constipation, leading to pain during gas formation, a glycerin suppository can be administered;
- as a last resort, use a tube to remove gases;
- in an older child with constipation leading to flatulence, a cleansing enema may be performed.
Important! Treatment of flatulence should be carried out exclusively under the supervision of a doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable, because often increased gas formation in a child occurs due to the development of serious diseases of the digestive tract (pancreatitis, colitis, dysbacteriosis), in the presence of helminthiasis, congenital intestinal pathology. Medicines that need to be taken for bloating are prescribed only by a doctor.
Therapeutic measures depend on the age of the child and the causes of the pathology. After determining the etiological factor (the reason that caused flatulence), anti-inflammatory treatment is carried out, and, if necessary, antibiotic therapy. Drugs are used to restore normal intestinal microflora, symptomatic therapy (antispasmodics for pain, laxatives, drugs that actively absorb gases).
First aid for flatulence
In case of flatulence, parents are able to provide immediate assistance to alleviate the condition. These are simple methods of control that do not require medical intervention. It is worth doing simple exercises to prevent discomfort in the baby’s abdomen.
Basic methods of combating flatulence in infants:
- Place him on his stomach and let him move his arms and legs. When moving, the baby does self-massage on his own. This promotes the release of gases.
- A warm diaper is a remedy known since the time of our mothers. It is necessary to check the temperature before contact. The diaper is heated with an iron and applied to the stomach. It is better to place the cloth between your own body and the baby, and carry him in your arms in an upright position.
- Massage. A great way to massage your tummy in a circular motion is to make a bicycle - pressing your legs to your stomach. Simple movements promote the release of gases.
- Tube for exhaust gases. A special drug is inserted into the anus. Sold in a pharmacy, administer carefully so as not to damage delicate skin.
- Dill water, Plantex. Treatment is prescribed by a pediatrician.
The mother should adjust the baby’s diet to prevent illness in the future. More walks in the fresh air, movements, active games. Walk immediately after discharge from the hospital from the first month of life. Don't wait for your belly button to heal for a couple of months. Walking is good for a baby's health. A visit to the pool is recommended.
How to deal with flatulence in older children?
Preventing the disease in older children includes proper nutrition, avoiding soda, bread, chips, and fatty foods. Parents must balance the diet. Steam vegetables, meat and fish. Limit your consumption of sweets. Monitor the internal state of children.
It’s not just food that causes discomfort in the body. Stress affects adults causing disruption. What can we say about children? Children 4 years old often suffer from the disease due to stressful situations. A change of environment, trips to kindergarten, a change in diet are provocateurs of disruptions in the child’s body. From the first days, symptoms of flatulence are observed. The intestines enter a new phase and undergo a period of adaptation after the start of trips to the garden. The body is rebuilding to a new rhythm of life. It is difficult to imagine what is happening inside the child.
The situation is similar with school-age children. The body adapts to the school regime, heavy loads, sometimes poor nutrition, and communication with peers. At this time, you should remain especially careful. At the first symptoms, you should consult a doctor and take medications that can balance the intestinal tract.
An additional reason is an intestinal infection. It is necessary to require hygiene from the baby when he comes from the street, after using the toilet. If an infection occurs, take Acipol. Grown-up children are also susceptible to flatulence.
Useful products for flatulence:
- Dairy products.
- Cheeses with low fat content.
- Porridge without milk.
- Dietary meat (white poultry, rabbit).
- Steamed fish.
- Beets, pumpkin, carrots.
- Omelettes.
Treatment will go faster, and in the future it will be possible to prevent recurrence if you feed according to the list of healthy foods. Proper nutrition means a healthy baby. The desire to breathe more fresh air and lead an active lifestyle is welcomed. Parents should show by their own example how healthy this is.
Prevention
Watch the video of Dr. Komarovsky - what to do if a child has a stomach ache:
Prevention of gas formation in the intestines, on the advice of Dr. Komarovsky, must begin long before the development of flatulence. A background correction of the measure is used to avoid the accumulation of gases in the intestines in 15% of children, if certain rules are followed:
- breastfeeding;
- strict adherence to the diet by a nursing mother;
- placing a small child on his stomach after feeding.
Older children need regular walks with active games, a favorable psychological environment at home, in kindergarten, at school, avoiding overeating, and following a diet. Following these simple tips will allow children not to encounter problems with flatulence.
Disease prevention
The child should eat in a calm environment. While eating, you should not turn on the TV, because it is distracting and encourages the swallowing of air with food. Meals should be spaced throughout the day and always be at the same time. You can’t eat hastily and on the go. It is recommended to place the baby on his stomach for 5 minutes before feeding. After eating, place it in an upright position for a few minutes.
Sources:
- P.L. Shcherbakov. Flatulence in children // Difficult Patient, 2006, vol. 4, no. 9, pp. 66-72.
- N.L. Pakhomovskaya, M.M. Venediktova. Flatulence: causes and ways of correction // Consillium Medicum. Pediatrics, 2021, No. 2, pp. 32-36.
- A.N. Surkov, V.V. Chernikov. Symptom of flatulence in young children: causes and ways of correction // Pediatric pharmacology, 2013, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 78-82.
Grek Elena Anatolyevna Clinic
Author of the article
Grek Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor of the highest qualification category
Specialty: gastroenterologist
Experience: 23 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
When a newborn has gas, what should parents do?
Sometimes attacks of gas formation in a baby are inevitable. This condition of the child can cause concern among parents. But there are several methods that often help newborns from gas.
Massage
Many parents prefer this non-invasive and relaxing technique for getting rid of gas.
Massage can be applied approximately 30 minutes after feeding or when symptoms appear:
- Step 1: Place your baby on his back. You can start by moving your legs in a few circles, similar to how a baby rides a bicycle. This will help the baby release gases;
- Step 2: Massage your baby's belly.
Make gentle stroking circular movements in a clockwise direction. Your touch will help soothe the baby and move gas along the intestines. The intestines “work” clockwise, so this is the best direction for massaging movements. Don't press too hard. This should not cause pain to the child; - Step 3: Place baby face down, stomach on lap. Gently move your legs to massage your belly. This slight pressure will help move the gas. You can also gently pat the back.
Infant massage can relieve your baby's tummy troubles and it won't take much time.
Use of medications
There are three types of antigas medications, and each works differently:
- Simethicone .
Simethicone is a drug that is marketed as a gas reliever. The medicine binds the gas bubbles together, which, in theory, makes it easier for them to escape. Simethicone preparations typically contain synthetic ingredients such as artificial colors and flavors, as well as emulsifiers and fillers. Simethicone was not particularly effective in several studies; - homeopathic remedies . Homeopathic medicines contain natural active ingredients that provide safety for newborns and provide effective relief. Unlike simethicone, homeopathic remedies do not require constant dosing;
- probiotics. New research suggests that supplementing with an infant probiotic will alleviate some infant gastrointestinal problems when given over a period of several weeks.
If your baby is introduced to complementary foods, give him some yogurt. It will fill your baby's intestines with various strains of beneficial intestinal bacteria.
Bloating in children: causes and treatment
05/11/2017 children 58,541 Views
Bloating in a child (flatulence) is an increased formation and accumulation of gases in the intestines, accompanied by various clinical manifestations. It occurs frequently and is observed at different ages - from infants to schoolchildren. It is not an independent disease. This is a symptom that means that a lot of gases have accumulated in the intestines, which distend its walls and cause pain or other unpleasant sensations. Most often it accompanies intestinal pathology or occurs for other reasons not related to disease.
Possible reasons
The child's digestive tract is sensitive, the structures are not yet formed. The stomach, intestines and digestive glands are not adapted to digesting “adult” food, so improper nutrition provokes various disorders.
The transition to adult food should occur gradually.
Closer to the year, from 11 months, it is necessary to switch from homogenized food to pieces. This is porridge cooked with adapted milk, soup with pieces of vegetables, finely chopped meat. Before school age, special attention must be paid to the nature of food preparation so that there are enough pancreatic enzymes to break it down.
Symptoms of tummy troubles in children can be caused by:
- flatulence;
- constipation;
- excess sweet foods;
- allergy to milk.
Bloating occurs because air accumulates in the intestinal cavity and does not escape. Increased gas formation is caused by the intake of appropriate products.
This category includes legumes, cabbage, onions, pears, and apples. There is always some food left in the intestines that ferments . Sweets enhance this process. Bacteria feed on glucose, and digestion promotes gas formation.
Another reason for a bloated belly is constipation. If the food is predominantly solid in nature, then the feces are compacted in the intestines.
Even when the urge to defecate appears, difficulties arise, and intestinal peristalsis does not help release excess contents. If this does not happen for several days, then the stomach begins to ache, and when palpating along the intestines, pockets of compaction are identified.
In infants
A newborn's digestive tract is sterile; it will begin to be populated with flora in the following months, and by 6 months it will be able to move on to more solid foods. Until six months, the only food a baby should have is breast milk or an adapted formula.
During this period, the nursing mother must follow a strict diet with the exception of allergenic, fatty, spicy, alcoholic and gas-forming foods. If she violates the diet, then intestinal colic occurs.
In addition, due to immature digestion, children often experience infant colic. They begin at about 1 month of age and continue until 3 years of age.
The onset of each attack occurs in the evening and at night.
In a newborn, dysbiosis can be caused by lactase deficiency. Signs of this disorder are diarrhea with a characteristic sour odor, a bloated stomach, belching, and lack of weight gain.
What to do - bloating in a child at 2 years old?
Hello. Girls, something strange is happening here. A 2 year old child has bloating. It started this morning. I thought it was normal because he didn't poop yesterday. But this afternoon I pooped 2 times, but the bloating did not go away. By the evening, belching was added. I gave Subsimplex, but it doesn’t help yet. Tomorrow morning I will call the doctor, but now what else can I give a 2-year-old child for bloating? Or what to do?
Similar articles:
If the stomach is bloated, then this means increased gas formation as a result of fermentation. These are all nutritional errors. In such cases, you need to take carminative herbal medications. An excellent means for removing gases is ukrained water.
Of course, with bloating and colic, examination and consultation with a specialist is necessary. He will prescribe appropriate treatment to avoid pathologies and complications. I can offer this option: mix St. John's wort, cucumber and yarrow in equal volumes, pour boiling water at the rate of 3 tablespoons per liter of water, leave for 4 hours and take 3-4 cups during the day. But this recipe was tested on a three-year-old child, so it would be better for you to also consult a doctor first...
Treatment
Flatulence is not considered a life-threatening symptom, although if it persists for a long time, it can affect the absorption of nutritional components and contribute to the emergence or aggravation of inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. And this, in turn, matters for the growth and development of the child, and at an older age - social adaptation in the team.
Diet requirements
If the child eats on his own, his menu is adjusted; if he is breastfed, the mother’s diet is adjusted. You should not use:
- Legumes.
- Fatty meat and lard.
- Spicy seasonings.
- A large number of rich pastries.
- Smoked meats, pickles, canned food.
- Garlic.
- Mushrooms.
- Semi-finished products (dumplings with pepper, etc.).
- Cabbage, radishes, turnips, raw onions.
- Whole milk, full fat sour cream, cream.
- Nuts.
- Pearl barley.
- Fatty broth on meat or fish.
- Melon, grapes, pears.
- Raisins, prunes.
- Chocolate, chips, crackers.
- Potato.
- Fried foods, including eggs.
- Soy products.
- Alcohol, beer, kvass.
- Coffee, cocoa, carbonated drinks.
A child or nursing mother is allowed porridge with water, lean meats and fish, stewed, boiled or steamed, thermally processed vegetables and fruits. During periods of intense manifestations, fresh plant foods should be limited. Children can be given yesterday's bread, crackers, low-fat cottage cheese, plain yogurt or yogurt. It is also allowed to include soft-boiled eggs, steam omelettes in the menu, and drinks - weak tea, rosehip decoction, compote of seasonal fruits without excess sugar.
Daily regime
What can you do to help your child get rid of bloating? Necessary:
- learn to eat in small portions at the same time, chewing food thoroughly;
- normalize sleep patterns;
- take your time and give yourself enough time to eat;
- monitor the regularity of bowel movements - it is better if the child visits the toilet in the morning, this creates conditions for the release of accumulated gases;
- avoid wearing tight clothing;
- Do not allow children to go to bed immediately after breakfast, lunch, dinner or a snack;
- Avoid eating large amounts of food at night.
The baby should be given the breast or bottle in a semi-upright position, and not placed on his back immediately after eating - this will allow “extra” air to escape from the stomach.
Frequent sucking of lollipops and chewing gum are contraindicated for older children. You should not force a child to eat if there is no appetite or if he is overexcited or stressed - the resulting spasm contributes to the development of flatulence.
Drug therapy
If a child experiences bloating, it is worth giving medication to help cope with the adverse symptoms. The following drugs are used:
- "Espumizan L".
- "Simethicone".
- "Infacol".
- "Bobotik".
- "Colikid."
These are liquid forms (suspension, syrup) that can be given to a child from the first weeks of life, as well as tablets or capsules intended for older children who control the act of swallowing. They belong to the group of defoamers - drugs that destroy gas bubbles accumulated in the intestines.
In the presence of pain, drugs that can affect the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract are indicated. Children are allowed the medicine "Riabal", available in the form of tablets and syrup. Sometimes the combined drug "Meteospasmil" is also prescribed, but in pediatric practice it is permissible to use it only for an older child under the supervision of a doctor.
If your body temperature is high (more than 38°C) and you have a painful fever, give an antipyretic. Children may be prescribed active ingredients such as Ibuprofen or Paracetamol (Imet, Nurofen). They can adversely affect the liver and other organs and should be taken sporadically, as they do not have a therapeutic effect and only temporarily eliminate hyperthermia.
If an intestinal infection develops, the body loses fluid, and therapy for bloating should be combined with taking saline solutions (Regidron) or administering them intravenously (0.9% sodium chloride). To maintain strength, rice water is given, and if necessary, antibacterial agents (Nifuroxazide) are used.