The harmful effects of carcinogens from smoking do not affect any one organ - the heart or liver. This is a complex effect associated with circulatory disorders and many reactions from all systems. Therefore, if a person is interested in whether smoking can cause stomach pain, the answer will be in the affirmative, but not every smoker connects cause and effect with each other.
The effect of smoking on the organ
Firstly, smoking often causes the development of stomach ulcers. However, even without its formation, abdominal pain may appear. When tobacco smoke enters the body, it negatively affects the gastric mucosa. Increased irritation occurs after taking antibacterial drugs and alcohol.
Today, experts have sufficient information about whether cigarettes can cause stomach pain and why this happens. The effect of nicotine is to reduce the amount of nitric oxide synthesized by cells and lining blood vessels. Nitric oxide is involved in the protective function of the stomach, as it increases the amount of mucus produced and improves blood circulation. A deficiency of the substance leads to stomach pain.
Under the influence of nicotine, the stomach cannot regulate its functioning normally. Nicotine also affects the saturation center located in the brain, which disrupts the production of gastric juice. This affects the digestion process, since gastric juice is produced randomly, and not when food enters the body.
Due to poor circulation and vascular spasms, tension in the stomach muscles occurs. The movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract is delayed, food stagnates in the upper sections. Food is not digested properly, stretches the stomach, and pain occurs.
The effect of tobacco smoke on the oral cavity
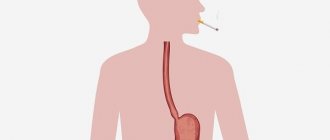
The path of food to the stomach begins from the oral cavity. It is she who is responsible for grinding food and wetting it with saliva. Smoking can lead to the fact that substances that are not intended by nature will enter the stomach. Stomach problems begin in the mouth.
The effect of smoking on the oral cavity:
- Rapid tooth decay due to smoking, including tooth loss . Due to the fact that the teeth have fallen out or are badly deteriorated, the smoker loses the ability to chew food thoroughly, including soft foods. If large pieces enter the stomach, the food may not be completely digested. That is, as a result, gases, severe pain, diarrhea, or, conversely, constipation may form.
- Tobacco tar is deposited on tooth enamel. After some time, all the settled resins turn into some kind of crystals, and a hard coating appears on the teeth. Plaque can serve as a breeding ground for microorganisms that are very harmful to the body. That is, if they get into the stomach, its activity will be disrupted. As a result, diseases and pathological changes in tissue can occur.
- Nicotine, as well as tobacco smoke, can reduce appetite and also reduce the amount of saliva during meals . This process results in the smoker having to swallow food completely dry. This may cause irritation to the mucous membranes of the mouth and digestive system.
- Irritation of the mucous membrane also occurs during smoking, resulting in copious amounts of saliva . When this saliva is swallowed, a large amount of the substance enters the body with the combustion products of tobacco. Typically these are tar, ash and nicotine. The consequence of consuming this saliva is usually the development of gastritis or ulcers.
Note that these factors are only a small part of the harm that can be caused by smoking. A very large amount of toxic substances enters the bloodstream, therefore, they are distributed throughout the body.
Reasons for deviations
Chronic exposure to nicotine leads to chronic inflammation. Smokers develop gastritis with high acidity, and eventually an ulcer. The most dangerous consequence of smoking is the degeneration of mucosal cells, i.e. the development of stomach cancer. It occurs 4 times more often in smokers than in non-smokers. Unlike gastritis, cancer does not manifest itself in any way at the initial stage.
Nicotine affects the entire gastrointestinal tract. It impairs intestinal motility, which leads to disruption of the digestive process and reduced absorption of nutrients. Symptoms of digestive disorders include constipation, diarrhea, pain, bloating, and heaviness. This occurs due to changes in the concentration of digestive juices in the intestines and stomach. The resulting stagnation provokes the onset of inflammatory processes, which result in duodenal ulcers, enteritis, and colitis.
The way smoking affects the digestive organs also affects the pancreas. This disrupts both digestive and endocrine functions. Smokers produce less bicarbonate. A decrease in their secretion leads to the development of duodenal ulcers. Due to an increase in reflux of duodenal contents into the stomach, it is damaged by bile acids. The result of disruption of the pancreas is diabetes mellitus. Chronic inflammation of the organ (pancreatitis) is accompanied by pain, weight loss, and diarrhea.
Smoking, digestion and possible complications
In the first 5-6 years of smoking, the stomach suffers from increased secretion of hydrochloric acid, pepsin and other enzymes, the excess of which leads to duodenal and gastric ulcers. For smokers with more experience, the processes are reversed: within 15-20 minutes after the cigarette is smoked, the stomach stops contracting and producing gastric juice components. As a result, appetite disappears, a feeling of heaviness and bloating appears in the stomach, and flatulence is possible.
Impaired digestive functions are inevitable consequences after smoking. A deficiency of vitamins and microelements leads to an emaciated appearance, a tendency to depressive disorders and poor health. Nicotine and carcinogenic substances reduce the reproductive function of men and women and cause inflammatory bowel diseases and oncology.
We figured out how smoking affects the intestines. Therefore, it is not difficult to imagine how smoking affects ulcers and other existing gastrointestinal diseases. According to statistics from the World Health Organization, the risk of malignant neoplasms in the oral cavity, esophagus, stomach and intestines in people who cannot give up the addiction is 4 times higher than in non-smokers.
Ulcer
Treatment of ulcerative lesions in smokers is complicated and sometimes does not bring results if the person does not give up cigarettes.
In smokers, the process of neutralizing hydrochloric acid in the stomach is impaired. As its amount increases, the gastrointestinal mucosa suffers and ulcerative lesions can form.
Heartburn
Heartburn is a typical complaint of a smoker. An unpleasant feeling is especially disturbing after smoking a cigarette. This occurs due to irritation of the stomach by acidic contents that enter along with saliva.
Crohn's disease
This chronic, incurable disease from the IBD group is accompanied by severe pain, diarrhea, weight loss and other symptoms, which you can read more about in the Crohn's Disease section. According to research, people who smoke have a high risk of developing this disease.
Treatment of Crohn's disease in smokers rarely brings the expected effect: the body is unable to properly absorb medications, and the weakened intestines, which already suffer from disturbances in the microflora and loose stools, are deprived of the opportunity to receive normal blood circulation. Trophism suffers, metabolism is disrupted. The list of consequences of taking nicotine for Crohn's disease is endless.
Smokers are more likely to undergo surgery if diagnosed accordingly. The likelihood of disability increases significantly.
Smoking and oral organs
In addition to the fact that when smoking, poisoned saliva enters the stomach and disrupts the functioning of the entire gastrointestinal tract, it is important to understand that exposure to high temperatures harms the oral mucosa, in which cracks form over time, leading to inflammatory processes on the gums (gingivitis, periodontal disease, leukoplakia develops). , teeth may fall out). The lips, tongue and jaw of a smoker, which are the first to take the nicotine hit, are always in the crosshairs of cancer.
Liver disorders
In addition to the fact that smoking depresses the intestines, cigarettes have a detrimental effect on the liver. This natural filter in the human body works continuously, and under the influence of poisonous cigarette smoke it suffers many times more. Over time, the organ loses its ability to function fully, which affects the viability of other systems.
Gallstones
This is another side effect for people who are used to smoking. Women who smoke are especially susceptible to gallstone disease.
Possible diseases
A common complaint among smokers is heartburn. This is due to the fact that the negative impact also extends to the valve located between the esophagus and the stomach. As a result, acid flows back into the esophagus. If heartburn occurs frequently, you should consult a specialist, as it may be a sign of developing gastroenteritis.
The occurrence of stomach ulcers is caused by increased production of gastric juice during smoking, which is not used to process food. Normally, excess acid passes into the duodenum, where it is eliminated with sodium bicarbonate. However, in people who smoke, the production of this substance is reduced. Pain under the sternum that occurs in the morning or after eating will indicate pathology. When an ulcer is diagnosed, treatment must be started immediately. It should be borne in mind that smoking greatly slows down the rate of healing of damage.
Consequences of ignoring pain
The appearance of unpleasant symptoms and pain in the stomach indicates the onset of pathological processes. Timely consultation with a doctor and the elimination of negative factors will prevent the development of more dangerous diseases, often cancer, to which smokers are most susceptible.
Neglected discomfort in the stomach leads to the formation of gastritis with increased acid secretion, followed by peptic ulcer disease and pathological changes in the structure of organs.
Smoking causes great harm to all systems of the body. With prolonged experience, irreversible processes in organs, intractable diseases or malignant tumors may begin.
Quitting a bad habit will make you feel good and improve your health.
The dangers of smoking on an empty stomach
This is perhaps the most dangerous habit of smokers. The nicotine hit falls on the completely defenseless mucous membrane. All dangerous compounds easily penetrate it, increasing the risks of the diseases listed above. Therefore, it is not surprising why your stomach hurts after smoking on an empty stomach.
Many women try to lose weight by replacing meals with a smoked cigarette. The desire to eat decreases after this, as nicotine affects the brain. In addition to the multiplied negative effect on the stomach, hormonal changes occur. Gradually, the body stops responding and weight loss is not observed, and it becomes more and more difficult to break the habit of smoking with each puff.
For women, smoking is strictly contraindicated. This is especially true during pregnancy.
Most women try to give up their addiction at the planning stage. However, some expectant mothers are unable to control themselves and reach for a cigarette even after they learn about the imminent replenishment. The harm to the baby during the period when toxins enter the body is colossal. He lacks oxygen, because of this the normal development of all systems slows down. Smoking disrupts the blood supply, and therefore the condition of the pregnant woman herself worsens. Studies have confirmed that insufficient blood flow to the pelvic organs leads to pain during pregnancy.
The terrible dangers of the passive form
Smoking is a personal matter for the smoker. But that's not true. Most studies have confirmed that others suffer more from the negative effects of smoking than even those who abuse cigarettes.
Passive smokers get the same diseases as their smoking relatives and colleagues. They are forced to absorb that part of the smoke from cigarettes that does not enter the lungs of a person who takes a drag from a cigarette. And they breathe the same toxic substances.
Families suffer the consequences. The worst harm is done to children. The baby begins to suffer even during intrauterine development. All physiological processes and functions of the fetus are harmed.
Children of a smoking mother usually lag behind their peers in development, and their immunity is weaker. They get sick more often.
Growing children develop many health problems.
These consequences include:
- The incidence of bronchitis and pneumonia in children of smoking parents is 20% higher than in their peers.
- Irreparable damage is caused to the mucous membrane of the eyes and nose, which causes diseases of these organs.
- Psychomotor functions are impaired. Attention and ability to absorb knowledge are weakened.
- Greater risk of sudden death syndrome.
Constantly staying in the same room and working together with a smoking person causes such harm to the body as if the person himself smoked from 1 to 10 cigarettes a day. More than half of passive smokers complain of eye irritation and breathing problems.
Many are susceptible to exacerbation of respiratory diseases. Some of them believe that being close to a smoker causes an exacerbation of heart and stomach diseases. Many people are allergic to cigarettes, which also prevents them from fully working and relaxing.
The effect of electronic cigarettes on the stomach
If everything is clear about the negative impact smoking tobacco has on the digestion process, then some fans of electronic cigarettes believe that they are not endangering their health.
The harm from smoking electronic cigarettes to the stomach is no less than from regular cigarettes. Steam, like cigarette smoke, passes through the oral cavity, settles in saliva, and then enters the stomach with it. Under the influence of nicotine and other additives contained in the liquid, irritation of the gastric and intestinal mucosa occurs, and the concentration of pepsin and hydrochloric acid increases. Therefore, people often complain that their stomach hurts after using an e-cigarette.
How to reduce the concentration of nicotine entering the stomach:
- Increase the nicotine concentration of the liquid. It sounds strange, but 2 puffs of liquid containing 12 mg/ml nicotine corresponds to 1 puff with 24 mg/ml. Moreover, on the second puff, with the hotter walls of the atomizer, the largest drops will settle not on the walls of the device, but in the mouth. The lower the concentration of nicotine in the liquid, the less of it enters the lungs and the more of it enters the stomach. Therefore, it is better to choose a liquid with a high level of nicotine and inhale less often.
- Choose a high evaporator power. As a result, the spraying will be small droplets, and less substances will settle in the saliva.
- It is recommended to choose atomizers with long and narrow air ducts - more droplets will settle on their walls. Side airflow is also required.
How exactly does nicotine affect the digestive organs?
The temperature of tobacco smoke is up to 60 degrees. This value is enough to damage the oral mucosa. Sudden temperature changes injure the protective shell of teeth, which in the future leads to damage to the enamel and the appearance of caries. The smoker's pharynx, tongue and esophagus are no less exposed to nicotine, ammonia and tars contained in cigarette smoke.
Smoking affects gastritis. Most heavy smokers suffer from this disease. At first, cigarettes do their job unnoticed, but after a while, impaired salivation and innervation of the digestive system cause bad breath, pain and a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region, as well as nausea with accompanying vomiting after eating.
Nicotine is merciless to the health of the intestines and esophagus. Once in the oral cavity, the substance acts as a powerful irritant to the salivary glands, which are forced to increase the secretion of saliva. The poisonous substance is swallowed and irritates the stomach, and can also cause infection of the digestive system.
Pain after quitting smoking
The effect of smoking on the digestive system persists for some time even after quitting the habit. This is also a reaction of the body, but you need to understand that it is not the norm. If pain occurs, you should contact a specialist to clarify the cause that caused the problem.
How smoking affects the stomach during withdrawal:
- Spasms in the intestines due to the lack of a relaxing effect on it, which was previously created under the influence of nicotine.
- General intoxication associated with the elimination of harmful substances accumulated over a long time through the kidneys and intestines.
- Withdrawal syndrome. It is observed in all smokers. Nicotine, entering the body, begins to take an active part in all internal processes. After quitting smoking, pain may be associated with changes in the body.
- Restructuring the digestive system. The full functioning of the gastrointestinal tract was actively suppressed under the influence of nicotine. After being freed from this component, the digestive system returns to the working mechanisms laid down by nature.
- Quitting smoking is stressful for the body. Against this background, an exacerbation of chronic stomach diseases may occur.
In addition to stomach pain, withdrawal symptoms may be accompanied by the following sensations:
- the appearance of pain in joints and limbs;
- the appearance of attacks of dry cough;
- the occurrence of heartburn;
- appetite disturbances (growth or lack);
- weight gain;
- decreased immunity;
- the appearance of constipation;
- emotional instability, mood swings;
- fast fatiguability;
- constant general weakness.
Why smoking affects the digestive system
Inhaled tobacco smoke, tar and nicotine enter the lungs, from where carcinogenic substances are transported throughout the body. Since the respiratory organs can be called the first instance, the erroneous opinion has taken root in society that they are the first and almost the only ones to suffer from a bad habit. To expand humanity’s understanding of the dangers of smoking, the Ministry of Health of countries has obliged tobacco product manufacturers to design the packaging of their products with visual pictures demonstrating the possible side effects of smoking. Time has passed, and today horrifying images no longer surprise smokers. Moreover, they have become familiar to the eye and therefore hardly noticeable.
Smoking affects digestion and other organs. When you inhale tobacco smoke, the gastrointestinal mucosa is irritated. The more frequent and intense such exposure, the higher the risk of developing inflammatory processes. But the harmful effects of smoking don't stop there.
In people suffering from the habit of smoking, the level of oxygen in the blood decreases and blood vessels constantly spasm. The blood circulation of a smoking person exposed to nicotine and carbon dioxide cannot a priori be normal. In conditions of oxygen and nutrient deficiency, the digestive system copes worse with its functions. Secretion decreases, the number of vital enzymes decreases, and regeneration processes slow down.
What to do if you have pain?
The best solution would be to quit smoking and consult a doctor to determine the extent of damage to internal organs. Recommendations for pain relief are as follows:
- Temporarily avoid fatty foods, carbonated drinks, foods high in salt, and alcohol. Such food creates additional stress on the stomach.
- Mandatory introduction to the diet of warm liquid dishes - soups, broths.
- Sports activities. They will help you switch and improve the overall condition of the body. You can start with light exercise - walking before bed.
- Increasing the volume of liquid consumed - ordinary still water, compotes, fruit drinks, rich in vitamins.
- If diarrhea occurs, you should add more rice-based foods to your diet. This will help normalize intestinal motility.
- If severe pain occurs, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
There are also a number of prohibitions:
- You should not take painkillers. Taking them can mask the symptoms characteristic of an ulcer or appendicitis.
- Antibacterial drugs are not allowed to be taken without a doctor's prescription.
- You should also not try to get rid of pain by applying heating pads with warm water or ice to the abdominal area. Sudden overheating or hypothermia can lead to a deterioration in the patient’s well-being and the development of complications.
- You should not take laxatives or medications. It is advisable to establish all processes with the help of nutrition. Plums and prunes will have a laxative effect, and rice will have a fixing effect.
Of course, you shouldn’t return to a bad habit. As a rule, pain goes away quite quickly after quitting smoking. If they continue for a long time, you should consult a doctor.
How to quit smoking if you have gastrointestinal problems?
The most common problem for people who quit smoking and have gastrointestinal problems is constipation. In this case, it is recommended:
- adjust your diet - eat often and in small portions, give up fatty, spicy and fast food, be sure to include soups in your diet,
- drink at least 2 liters of water per day,
- play sports and walk outdoors more often.
If constipation continues for more than 7 days, and you cannot cope with the problem on your own, you should definitely consult a doctor.
If the process of quitting smoking is difficult, you need to resort to nicotine replacement therapy . It will help you cope with the pangs of withdrawal.
It is better to consult a doctor and get help with choosing nicotine replacement therapy, because certain NRT products (lozenges and gum) are contraindicated for diseases of the digestive system.
Those who quit smoking should give up coffee and alcohol . Thus, he will not only protect his stomach from the effects of caffeine and alcohol, but will eliminate situations that provoke smoking.
Consequences of smoking
All of the above confirms the fact that inhaling nicotine and other harmful substances negatively affects the condition of the stomach. Smoking significantly slows down the process of getting rid of the disease. In addition, it can lead to quite sad consequences.
Gastritis also develops in a smoker who has not previously suffered from gastrointestinal diseases. Those diagnosed with chronic gastritis regularly experience exacerbation of the disease. But the worst thing is that the superficial form of the disease can turn into atrophic, and doctors classify it as a precancerous disease. And finally, when smoking, gastritis often transforms into an ulcer.
A person who prefers to replace breakfast with a cigarette exposes himself to particular danger. The combination of smoking and coffee is no less harmful. Drinking an invigorating drink leads to increased formation of hydrochloric acid, and nicotine has the same effect on the functioning of the stomach. Gastritis occurs even in smokers who naturally have a strong gastrointestinal tract.
Thus, giving up cigarettes is necessary not only for a person suffering from gastritis, but also for those to whom the disease discussed in this article is unfamiliar. It is smokers who are primarily susceptible to gastrointestinal diseases. As for the patient who regularly suffers from stomach pain, nausea and other symptoms of chronic gastritis, but is unable to give up bad habits and switch to a healthy diet, then he has every chance of becoming a regular patient of a gastroenterologist.
What else can be said about the dangers of smoking? The imaginary pleasure that a smoker receives from acrid smoke can eventually lead to stomach or duodenal ulcers - ailments in which a person is doomed to follow strict diets throughout his life, take medications and decoctions prepared on the basis of medicinal herbs.
The provoking factors of many diseases are often harmful phenomena such as smoking, alcoholism or drug addiction. These states are listed separated by commas for a reason. They are similar, like a photo of twins, because their basis is the same - a chemical substance coming from outside replaces a similar one synthesized in a normal body. As a result, the body stops producing the chemical compound that is regularly replaced from the outside. This is how addiction is formed. Yes Yes. Smoking is the same addiction as drug addiction, and it affects all human organs and systems without exception. How are smoking and the stomach connected, can the stomach get sick under the influence of cigarettes, and what effect does smoking have on digestion? Read on.
Possible consequences
Poor chewing of food, suppressed or increased secretion of gastric juice, impaired intestinal motility causes “hunger” pain, nausea, heartburn, bloating and spasms in the intestines, as well as problems with appetite and stool. Moreover, often all this is at the same time. An experienced gastroenterologist can find out the smoking history without even asking about it - simply based on the patient’s complaints. So, in the first years of smoking - from 1 to 5 years, the motility of the stomach and intestines and the secretion of gastric juice increase, which is why abdominal pain, heartburn and diarrhea occur.
A little later - after 6-7 years of smoking, the endocrine glands begin to work much worse, less gastric juice is produced, and the gastric mucosa gradually atrophies. At this stage, sharp pains may stop bothering the patient; now his constant “companions” will be nausea, heaviness in the stomach, poor appetite and chronic constipation.
Many smokers who have been diagnosed with “gastritis” or a stomach ulcer and have not stopped smoking are happy, thinking that if their pain has stopped, then the disease has stopped or has stopped its development. But in fact, the disappearance of the clinical symptoms of the disease only indicates that the process has gone deeper and it will be much more difficult to cure it.
Unfortunately, it is only possible to completely eliminate the harmful effects of cigarettes and nicotine on the stomach if the smoker’s experience does not exceed a couple of years; after this, changes in the mucous membrane of the digestive organs can become irreversible.
But the sooner you quit smoking, the greater the chance that safe gastritis will become your companion for life, and not a perforated stomach ulcer or gastrointestinal cancer.
DO YOU WANT TO QUIT SMOKING?
Then you need a strategy for quitting cigarettes. With its help it will be much easier to quit.
Effect of nicotine
Smoking has detrimental effects on digestion and digestion of food. Nicotine, which enters the gastrointestinal tract, through salivation provokes a large secretion of the pancreas and rapid digestion of the contents of the stomach. There are several ways in which nicotinic acid and ammonia vapors affect the digestive organs.
- The effect of smoking on the digestive organs through the salivary glands occurs after inhaling cigarette smoke. Together with saliva, part of the tobacco fumes and nicotine secretions enter the mucous membrane of the digestive system and tightly envelop the walls of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Smoking a cigarette sends a signal to the nerve endings of the brain and dulls the appetite. The part of the brain responsible for satiating the body gives a signal to the digestive organs, after which the person does not feel hungry.
- Nicotinic acid can affect internal secretion through the blood, reducing blood flow to internal organs.
People who are addicted to smoking most often suffer from gastritis, enterocolitis and peptic ulcers, which they acquire due to their addiction.
Nicotinic acid disrupts the secretory function of the stomach, the secretion of hydrochloric acid and pepsin, which provokes the formation of erosions and ulcers.
How to quit smoking with gastritis
If a smoker is diagnosed with gastritis, then he should think about quitting cigarettes. After a person quits smoking, treatment of the disease will be more effective, and the symptoms of the disease will be less pronounced. In addition, quitting smoking is important for people suffering from a chronic form of gastritis, since very often tobacco is one of the factors in the transition of the disease to the acute phase.
However, it is important to approach this process correctly, since abruptly quitting smoking if you have an existing disease can cause more harm than good. Quitting smoking completely when you are sick can cause the following deteriorations:
- The appearance of pronounced symptoms of gastritis, which were extinguished by nicotine.
- Exacerbation of the disease due to the production of more gastric juice by the mucous membrane, which does not have time to adapt to new conditions.
- Transition of the disease into the acute phase due to unbalanced nutrition. This happens due to the fact that a person who has abruptly given up cigarettes strives to replace them with food.
- Exacerbation of gastritis due to unstable blood supply to the gastrointestinal tract, since the circulatory system does not have time to adapt to the dilation of blood vessels.
- Exacerbation of the disease due to nervousness (withdrawal).
It is necessary to get rid of this bad habit gradually, reducing the number of cigarettes smoked per day. It is best to spread out this process over a month or two. This will allow the body to prepare for changing conditions.
Is it possible to smoke on an empty stomach?
As mentioned above, smoking on an empty stomach causes great harm to the human body, especially in combination with coffee. This habit increases the negative effects of nicotine. After smoking a cigarette, a person feels lethargic and relaxed, and caffeine stimulates and excites the central nervous system.
This combination leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to the blood vessels of the brain, rapid heartbeat and cardiac arrhythmia, a feeling of anxiety and causeless agitation.
The reasons why you should not smoke on an empty stomach are associated with increased heart rate, narrowing of blood vessels and increased blood pressure, dysfunction of the liver and many other internal organs.
Tobacco cessation
Ways to solve the problem
Smoking and improving digestion are incompatible things. If you have been diagnosed with gastritis, colitis or other gastrointestinal diseases, then during treatment you will still have to give up your addiction. Ideally, quit smoking completely.
Treatment is prescribed individually by a gastroenterologist or therapist. In some cases, surgery may even be necessary. In order to prevent digestive diseases from smoking, the following actions should be taken.
- Rejection of bad habits. Not only smoking provokes enterocolitis. Together with caffeine or alcohol, the harm from each cigarette smoked increases a hundred times.
- Play sports. Meditation and morning jogging will help distract attention from a bad habit and strengthen the entire body.
- Make it a habit to eat right and have breakfast in the morning. A morning breakfast with light food will avoid problems with exacerbation of gastritis and peptic ulcers.
- Eliminate fermented products from your diet - these are bakery and confectionery products, they provoke fermentation in the stomach and heartburn.
Mechanisms of influence
A person harms his gastrointestinal tract very seriously when smoking, and it all starts from the stage of placing food in the oral cavity. When chewing, the secretion of saliva increases. The latter acts as the primary conductor of all elements into the body. That is why the patient places many medications under the tongue to quickly penetrate the bloodstream.
Alas, along with useful elements, various toxic resins, flavors and other harmful elements contained in a cigarette are also quickly absorbed. Penetrating into the stomach and intestines, they cause inflammation and irritation of the mucous membranes. Cigarette smoke and its evaporation lead to increased secretion of gastric juice, and at the same time the acidity of the environment inevitably increases.
It should be remembered that even one cigarette is enough to disrupt the functioning of blood vessels. Moreover, the electronic version of cigars or hookah is no less evil, and sometimes even greater. The negative effect of smoking is such that the vessels of the abdominal walls contract extremely, as a result of which more and more secretions accumulate, and when smoking, the pressure increases. At the same time, toxic elements penetrate into the cavity through the bloodstream. All this leads to spasms of the outlet region of the stomach, and the central nervous system does not receive signals about the feeling of hunger. The natural result is pain and decreased appetite.
Regular release of toxic elements into the bloodstream causes the development of such ailments as:
Such diseases can be manifested by nausea, belching, diarrhea or other stool disorders. The pancreas, epigastrium and the entire intestinal tract (rectum, etc.) are also affected.
What gastrointestinal diseases can be caused by smoking?
Smoking has a negative impact on the gastrointestinal tract, provoking the development of many dangerous diseases. Nicotine irritates the valve connecting the stomach to the intestines. As a result, stomach acid enters the esophagus, causing severe heartburn. If this unpleasant sensation bothers you frequently, you should definitely consult a gastroenterologist, since heartburn is a common symptom of gastroenteritis.
Harmful effects on the gastrointestinal tract
Nicotine significantly increases the risk of gastritis and stomach ulcers. Under the influence of tars and combustion products, the production of stomach acid increases. Normally, it enters and is neutralized in the duodenum. When smoking, this process is disrupted, acid remains in the stomach, which causes the development of ulcers.
In addition, the addiction increases the risk of developing liver pathologies, causes intestinal dysbiosis, stool disorders, and deterioration in the absorption of vitamins and minerals from food. As a result, the smoker deteriorates not only his health, but also his appearance.
In some cases, a full breakfast is replaced with a cigarette in order to quickly lose weight and reduce hunger. But you should never skip your morning meal, because it saturates the body with strength and energy for the whole day. To dull the feeling of hunger, it is better to replace smoking on an empty stomach with a glass of clean still water.
Major organs
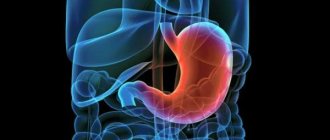
Work of the stomach
Negative effects of tobacco smoke on the stomach:
- Affects the acidity of gastric juice, blood vessels contract. This leads to disruption of the blood supply to all digestive organs. Ulcers form in the digestive tract, and gastric bleeding may occur.
- With short periods of smoking, hyperacid gastritis occurs, and with long-term smoking it develops into chronic gastritis with secretory insufficiency.
- When smoking, adrenaline is released, the walls of the stomach become tense, and food is not properly digested.
- Accumulated nicotine in the esophagus causes cell mutation and malignant formations appear.
- Smokers constantly suffer from heartburn. Tobacco weakens the valve that is responsible for releasing acid into the esophagus. A cigarette smoked on an empty stomach is harmful to the entire body.
Liver function
The liver cleanses the blood of toxins, while smoking there is an additional load on the organ, the bile ducts begin to suffer and the bile stagnates.
The consequences of these processes are chronic cholecystitis and cholelithiasis . By constantly loading and poisoning the liver, a smoker runs the risk of developing cirrhosis.
Pancreatic function
The action of nicotine leads to the cessation of the production of enzymes produced by the pancreas. They function as biological catalysts and accelerate biological processes.
Without the functioning of enzymes, the functioning of the entire organism is impossible. Atherosclerosis may develop in the vessels of the pancreas.
Bowel function
When smoking, the absorption of beneficial substances necessary for the body in the intestine slows down, and the affected epithelium ceases to function properly. Over time, the intestines may stop absorbing nutrients necessary for human life, and all internal organs will deplete.
Tobacco obstructs the outflow of blood in the intestinal vessels, resulting in hemorrhoids that can bleed.
A lack of oxygen in the body due to smoking leads to a malfunction of the intestinal tract, food souring and rotting, and diarrhea or constipation. Consequences of smoking:
- lack of vitamins;
- haemorrhoids;
- ulcerative colitis;
- gastritis, stomach ulcer;
- pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- cholelithiasis;
- primary sclerosing cholangitis;
- liver cancer;
- diabetes.
Due to frequent abdominal pain, irritability and dissatisfaction appear. Tobacco reduces the pungency of taste; people who smoke may have difficulty distinguishing between sweet, bitter, sour, etc.
Effects of nicotine on the gastrointestinal tract
In the process of smoking, nicotine enters the human body, which destroys many vitamins that are actively involved in the regeneration of the gastric mucosa. With gastritis, inflammation develops on the walls of the organ, provoking a change in the secretion of gastric juice, as well as the process of cell restoration.
It is worth noting that in the chronic form of the pathology, it is smoking that often provokes an exacerbation. If a patient smokes on an empty stomach, then he risks soon encountering a new, more serious problem - ulcerative pathology of the stomach or duodenum.
A cigarette smoked by a person begins its negative effect, provoking the occurrence of stomach diseases, already in the oral cavity. Any smoker, even one with little experience, will have their teeth very quickly destroyed.
The result of this is its poor digestion. Each portion of nicotine contained in a smoked cigarette hits the stomach in the following way:
Substances contained in tobacco smoke disrupt the normal nervous and humoral regulation of the stomach. Because of this, a smoker may feel a “wolfish” appetite after smoking a cigarette or, conversely, lose it completely, which leads to the production of bile and gastric secretions at the wrong time when food is in the digestive organ.
Cigarette smoke in the stomach causes spasms of smooth muscles and thereby disrupts peristalsis. The result of this negative process is the stagnation of food in the upper parts of the digestive tract.
“Thanks to” nicotine, the stomach does not receive enough oxygen from the blood, which leads to oxygen starvation.
Such harmful consequences caused by tobacco smoke entering the digestive organs provoke the rapid development of gastritis in smokers.
Is it possible to smoke if you have gastritis? Everyone who has a combination of a bad habit and a disease is interested. This issue will have to be resolved individually, but it is still worth finding out exactly how nicotine acts on the body.
Everyone knows that tar and nicotine are very harmful to the entire body, but the first “gate” to smoke is the lungs and stomach. Due to the penetration of smoke into the gastric mucosa, it becomes irritated and inflamed.
Nicotine from cigarettes enters the stomach in other ways:
- First, nicotine is absorbed into the blood.
- With the bloodstream, it spreads throughout the body and enters the gastrointestinal tract tissues.
The substance leads to vasospasm, disrupting blood circulation in the tissues of the stomach.
Nicotine, through its effects on the central and peripheral nervous system, contributes to disruption of gastrointestinal motility and nervous regulation of gastric juice secretion.
Among other things, harmful substances from cigarette smoke settle in abundance in the oral cavity, after which they also enter the stomach with saliva. The result of these processes is the same: inflammation of the mucous membrane, irritated by the poison from cigarettes, intensifies, the secretion of hydrochloric acid increases, all functions of the stomach decrease due to vasospasm and changes in motility.
Taking into account the decrease in local immunity and the rate of tissue regeneration, the consequences of smoking can be:
- The development of gastritis of the stomach in a previously healthy person without the presence of other risk factors.
- Exacerbation of gastritis in those who had a chronic form of the pathology.
- The transition of superficial gastritis to atrophic, recognized as precancerous, or to deeper, more extensive forms of the disease.
- Transformation of gastritis into erosion or ulcer of the gastrointestinal tract, including perforated one.
Those who replace breakfast or another meal with a smoke break are especially at risk, and also like to wash down cigarette smoke with another stimulant of hydrochloric acid formation - coffee. Usually, smokers, even with the strongest digestive tract, develop gastritis and a host of other gastrointestinal problems.