The situation when you immediately want to go to the toilet after eating can be caused by various factors. Loose stools are a consequence of functional disorders of the digestive process. Diarrhea after eating occurs due to the accelerated movement of a bolus of food without proper absorption.
A single bowel disorder will not harm the body. If diarrhea becomes chronic, the cause must be urgently determined. Otherwise, the heart, kidneys or other organs will suffer from systematic dehydration and demineralization.
Development mechanism
During the digestion of food, essential vitamins and minerals are absorbed into the blood. This process begins in the small intestine. Active water-salt exchange occurs here. Any irritant can disrupt the sequence of biochemical reactions and provoke increased peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract.
To quickly transport contents through the digestive tract, a large volume of liquid enters the small intestine from blood plasma. Water comes here along with salts dissolved in it. The intestines become overfilled with fluid “squeezed out” from other organs and tissues. The bolus of food with an abundance of water quickly passes into the large intestine. This process leads to an uncontrollable urge to go to the toilet, which begins immediately after eating.
The lost volume of fluid with salts leads to disruption of metabolic processes. Especially due to the emergency evacuation of food, the heart and kidneys suffer, which lose magnesium, potassium and other important elements.
Disturbances in the digestive process can occur not only in the upper gastrointestinal tract, but also in the large intestine. In this case, the body loses less fluid.
The inner lining of the small intestine is covered with many microscopic villi. Everything that is necessary and useful is absorbed into the blood through them, and the excess is formed into feces.
Diarrhea after eating: why your stomach hurts after every meal
Intestinal disorders periodically overtake every person. Loose stools combined with high body temperature, abdominal pain, and vomiting are a sure sign of infection or acute inflammatory process.
Diarrhea after eating is more likely to indicate nutritional errors. For example, excessive consumption of laxative spoiled and incompatible products.
Chronic diarrhea, without reference to the menu, can be a sign of bear disease, low-grade inflammation in the digestive organs, or dysbiosis.
What causes loose stools after eating
If diarrhea occurs immediately after eating, then it is most likely that there is a substance in the food that irritates the intestines. You need to remember what you ate the day before. The most common causes of the disorder are:
- Eating foods that loosen stool. Foods high in connective tissue, sugar, fructose, and fiber accelerate the progress of the food bolus. Defecation is painless; mild abdominal discomfort may be present.
- Dysbacteriosis. A lack of beneficial microorganisms in the intestines and disrupted microflora can also be the reason why diarrhea occurs after eating. Usually the condition is preceded by antibacterial therapy, acute poisoning or systematic errors in nutrition (mono-diets, overeating, prolonged fasting). In this case, the stool is liquid, with lumps of food, sometimes smelly, and mucous. Diarrhea alternates with constipation.
- Poisoning from spoiled foods. Mild foodborne illness is often accompanied by subtle symptoms, when the only sign of illness is diarrhea immediately after eating. The stool is usually watery, foul-smelling, and contains undigested food. Before defecation, the stomach hurts, there is bloating, and gases escape.
- Food allergies (usually to milk, gluten, citrus fruits, seafood, chocolate). Diarrhea immediately after eating is possible if you are intolerant to one of the foods. Additional symptoms: bloating, pain, mucous stool, undigested food in the stool. Allergic rashes, swelling of the larynx, and sneezing are not always observed.
- Bear disease (irritable bowel syndrome, IBS). Develops against a background of stress. The urge to defecate is uncontrollable, often with abdominal pain and cramps. The stool is the usual color, liquid or pasty, with a high content of mucus.
Diseases
Diarrhea is a symptom of many diseases. The connection to food intake can be short-term or accidental. Intestinal disorders cause infections, inflammation in the digestive tract, developmental abnormalities, endocrine and other disorders. List of diseases characterized by diarrhea:
- acute pancreatitis;
- helminthic infestation;
- viral hepatitis B, C in the acute phase;
- colitis and enterocolitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- gastritis;
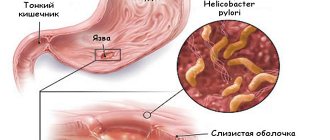
- stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer;
- dysentery;
- salmonellosis;
- diabetes;
- hormonally active tumor;
- taking medications (diuretics, cytostatics, immunosuppressants);
- congenital and secondary malabsorption into the small intestine;
- celiac disease;
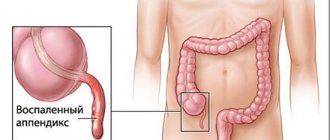
- appendicitis;
There are many options, and it is unlikely that you will be able to independently establish the cause of a chronic disorder. It’s better not to guess at the tea leaves, but to immediately contact a specialist.
First aid for diarrhea
With any diarrhea, the most important thing is to replenish the fluid supply in the body. All other measures are taken on a situational basis. If the condition is acute, you should call an ambulance.
List of medications
In case of diarrhea, the first aid kit should always contain sorbents, the most common of which is activated carbon. It is taken at the rate of 1 tablet per 10 kg of weight. It helps bind toxic substances and prevent their further absorption into the blood.
You should not take other tablets 30 minutes before and for an hour after taking the sorbent. They will not work, as they will be neutralized by the previous drug.
List of medications that can be considered as first aid for diarrhea:
- Antidiarrheal: Loperamide (Immodium). It stops loose stools by reducing the intensity of intestinal contractions. Indispensable for bear illness. It has strict contraindications: food poisoning, infections, ulcers, diverticulosis, decreased liver function.
- Sorbents: Smecta, Neosmectin, Enterosgel, Polysorb MP. They bind toxins in the stomach and intestines and then remove them naturally. Sorbents are indicated for infectious lesions, poisoning, allergies. In case of overdose, constipation is possible.
- Rehydration solutions: Rehydron, Re-sol, Orsol, Gastrolit. Help restore the water-salt balance in the body, prevent dehydration and leaching of beneficial salts. Contraindications include diabetes and high blood pressure.
- Painkillers and antispasmodics: No-shpa, Paracetamol, Analgin, Ibuprofen. Reduce abdominal pain, relieve cramps.
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, enzymes, probiotics, and antibiotics are not first aid. Taking these medications on your own can be harmful.
Starvation
If diarrhea occurs after each meal, it is advisable to unload the stomach and intestines for a while. This will allow you to interrupt frequent trips to the toilet to see a doctor.
You also need to take into account that if there is inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, the movement of the food bolus will increase irritation. Conversely, taking a break from food will speed up the healing process. The recommended period of abstinence from food is 6-18 hours.
Fasting is unacceptable during pregnancy and childhood.
Drinking regime
Together with feces, the body loses a lot of water. Therefore, during diarrhea you need to drink at least 3 liters of fluid per day. Optimally, it should be clean water without gas. A single volume should not exceed 50 ml, otherwise it will not be absorbed. It is recommended to drink every 20-40 minutes.
Diet
Adjusting nutrition is a fundamental method of healing the body. Without it, there will be no relief. Recommendations for eating rules are as follows:
- you should not fast for more than three to four hours;
- the consistency of the food should be liquid and mushy;
- choleretic drugs are excluded;
- remove salty, smoked, fatty, fried, alcohol from the diet;
- It is forbidden to create a calorie deficit in the body;
- It is advisable to drink mineral water.
The therapeutic diet should be rich in enveloping foods that are easy to digest. Includes steamed porridge, jelly, fermented milk products, lean meat (boiled). It is better to bake vegetables and fruits. Bakery products should be eaten yesterday, dried.
Main reasons
Diarrhea after eating is often caused by impaired intestinal motility. Reasons for diarrhea due to which food tends to leave the gastrointestinal tract:
- Stale or unusual food products. The body gets rid of pathogenic microorganisms if a person has eaten something spoiled. Poisoning manifests itself as pain in the abdomen and diarrhea immediately after eating. Switching to a new menu (for example, while traveling) provokes loose stools due to a lack of enzymes to break down exotic foods. In a child under 3 years old, new foods often cause intestinal upset, so their introduction into the diet begins in small portions.
- Imbalance of intestinal microflora. A lack of beneficial bacteria leads to premature evacuation of food. Intestinal dysbiosis is a consequence of taking antibiotics and poor nutrition. A deficiency of beneficial bacteria leads to chronic diarrhea, which occurs immediately after eating or an hour later.
- Bacterial or viral infection. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the body with food or water. The intestinal mucosa becomes inflamed and damaged. As a result, it releases exudate, mucus, and irritating organ walls. Salmonellosis leads to severe inflammation. Bacteria damage the deep layers of the mucosa until blood and pus are released from the epithelium. In an inflamed intestine, absorption is impaired and peristalsis accelerates. Particles of excretions cause diarrhea after every meal.
- Functional disorders of the nervous system. The increased speed of movement of the food bolus occurs due to neurogenic stimulation. Since digestion is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, in a stressful situation, natural metabolism is disrupted. This leads to the fact that after eating you immediately want to go to the toilet.
- Food intolerance. The gastrointestinal tract is urgently cleared of allergens. Peristalsis increases, which leads to stool liquefaction.
- Diseases of the digestive system. In diseases of the liver and gall bladder, the secretion of electrolytes and intestinal juice increases. Gastritis with low stomach acidity is characterized by a lack of secretory fluid necessary for the primary processing of the contents. Food enters the small intestine without the necessary preparation, causing diarrhea.
- Deficiency of enzymes for digesting food. The disorder is associated with pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas.
- Hormonal imbalances. Lack or excess of active substances produced by the thyroid and pancreas glands lead to digestive upset after eating.
- Binge eating. Large portions put a strain on the digestive system. The body tries to get rid of excess fluid as quickly as possible by sending water reserves to the intestines. Diarrhea after eating in this case is a protective reaction against an overwhelming load on the gastrointestinal tract.
- Eating fatty foods. After a meal with excessive fat content, intestinal upset often occurs. Products with a high content of the substance: fried meat, lard, confectionery products with cream. A sudden urge to defecate after eating these foods may appear an hour after eating. During this period, food begins to move into the small intestine. Excess fat is poorly absorbed by its walls, causing diarrhea.
- Taking laxatives for constipation.
After eating I go to the toilet for the most part
A person may suddenly experience frequent bowel movements without diarrhea, in which case the cause of its occurrence becomes unclear.
Often the urge to go to the toilet may be false and accompanied by severe painful sensations. When diarrhea occurs, it is not difficult to find out why it happened. But in the case of frequent urge without diarrhea, determining the cause is quite difficult.
Reasons for frequent bowel movements
There are some reasons why an adult may experience frequent bowel movements, but not diarrhea. Every person should know these reasons so that an unpleasant situation does not arise.
The cause may be inflammatory processes in the rectum, the patient begins to experience quite strong pain and frequent bowel movements. At first, the urge is controllable, but a little later, bowel movements begin to occur involuntarily.
Lack of digestive enzymes
In a large number of people, there is a small production of enzymes (digestive), this deviation is directly related to the disturbances that have occurred in the functioning of the pancreas.
For proper digestion, the body needs a sufficient amount of enzymes. Due to a lack of enzymes, some of the foods consumed are not digested and this provokes frequent visits to the toilet.
Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract
If a person has frequent bowel movements, the reasons may lie in the following diseases:
A person is tormented by feelings of heaviness in the stomach, flatulence, and this contributes to a frequent urge to go to the toilet.
Irritable bowel syndrome
With this disease, stool may change its consistency, but loose stools occur infrequently.
Significant fiber intake
When consuming fiber in large quantities, the problem of frequent bowel movements may arise. When you change your diet, the number of daily urges to bowel movement will change.
Raw food diet and vegetarianism
Poor nutrition also causes this unpleasant phenomenon.
If a person consumes a large amount of raw fruits and vegetables, the intestines begin to work much faster and this provokes frequent bowel movements. This problem most often occurs among vegetarians.
For any reason, there is an increase in not only frequent bowel movements and a change in the color, consistency and smell of feces.
Psychological problems
Frequent bowel movements in an adult can occur due to frequent nervous shocks. The nervous system greatly affects the digestive system and people exposed to frequent stress suffer from frequent urge to go to the toilet.
Constant bowel movements may indicate the following abnormalities:
- feeling of fear and being in an unstable emotional state;
- schizophrenia;
- constant stress and irritation;
- a large number of difficulties arising at one time.
To eliminate this situation, you need to:
- consult a doctor (psychologist) to help get rid of stressful situations;
- Some citizens can take anti-depression pills for a while.
As soon as the problem can be identified and solved, the person ceases to be tormented by constant bowel movements.
Many patients want to find a gentle remedy for cleansing or preventing parasite infection. This preparation contains a complex of selected herbs to combat a wide variety of parasitic organisms.
The herbal drug successfully relieves inflammation, cleanses the body, neutralizes pathogenic bacteria, viruses and fungi.
What is the danger of frequent bowel movements?
When a person suffers from frequent bowel movements:
- Microelements and vitamins that are necessary for the normal functioning of the body begin to be released along with feces.
- Anemia or vitamin deficiency develops if the cause is poor enzyme production and the food entering the intestines is not processed.
- If the body does not produce enough bile acid, the number of trips to the toilet begins to increase within 24 hours. The consistency of the feces becomes oily and the color pale.
- If this pathology is not cured as soon as possible, vision may deteriorate significantly, bones will become fragile, and the anus will begin to bleed.
What should you not eat if you have frequent bowel movements?
One of the reasons for frequent bowel movements is poor nutrition. In this case, treatment begins with a detailed analysis of the products consumed.
Products that cause frequent bowel movements include:
- sugar substitutes (artificial), one of the most common additives, the use of which can lead to some problems;
- excessive consumption of dairy products;
- use of foods containing large amounts of fructose in the daily diet.
To get rid of frequent bowel movements, you need to carefully analyze your daily diet.
Until the illness stops, it is advisable to completely exclude from the menu:
- Fried and smoked food.
- Eating food that is too hot can irritate the intestinal walls and cause frequent bowel movements.
This can indicate many diseases.
Can't deal with parasites?
Helminths are dangerous to the body; their waste products are toxic and provoke inflammatory processes where they live.
Treatment should be started immediately! Protect yourself and your loved ones!
In such cases, our readers recommend using the latest remedy - Tibetan collection TIBETTEA against parasites.
It has the following properties:
- Kills more than 120 types of parasites in 1 course
- Has an anti-inflammatory effect
- Breaks down and removes eggs and larvae of parasites
- Destroys pathogenic bacteria and viruses
- Removes waste and toxins
Source: https://ParazitHelp.ru/parazity/posle-edy-idu-v-tualet-po-bolshomu.html
What diseases cause diarrhea?
Intestinal upset after eating may indicate pathologies:
- hyperthyroidism;
- colitis;
- enteritis;
- gastritis;
- stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- rotovirus;
- salmonellosis;
- norovirus;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- pancreatitis;
- hormone-dependent tumors;
- parasitic infection, etc.
In adults and older people, diarrhea often occurs due to changes in blood pressure. These two states are interconnected. When pressure increases, brain neurons responsible for regulating bowel movements are stimulated. Diarrhea can also be caused by blood pressure medications.
How to determine the source of the problem
A single diarrhea after eating is not harmful to health. If diarrhea becomes a constant occurrence, vitamin deficiency and chronic diseases may develop.
The source of diarrhea can be determined by the characteristics of the stool. The consistency of the stool, color, and the presence of inclusions play a role in making a diagnosis.
Watery greenish discharge in adults is a sign of infectious diarrhea. Most often, the causative agent of the disease is rotovirus, norovirus. Microbes multiply in the intestinal epithelium, which causes a decrease in enzyme activity. Microvilli on the surface of the small intestinal mucosa have the ability to absorb molecules of a certain size.
Since the activity of enzymes decreases under the influence of viruses, disaccharides are not able to break down into monosaccharides - molecules of the required size. Undigested food along with liquid quickly passes into the large intestine, causing diarrhea after eating.
Particles of blood and mucus in the stool are a symptom of a bacterial infection. Common causative agents of this type of diarrhea are staphylococci and salmonella. The infection may be accompanied by vomiting and increased gas production.
Greasy stool with a pungent odor indicates that the small intestine is not coping with its functions. Fats are not absorbed, so they are excreted directly in the feces. This phenomenon is often associated with poor nutrition and excessive consumption of heavy foods.
If the source of infection is the stomach or small intestine, the stool is always large, watery, and may contain particles of undigested food.
With exacerbation of erosive gastritis and stomach ulcers, the stool has a tarry consistency. The feces are colored black because the blood, moving through the lower gastrointestinal tract, has time to clot.
Diseases of the stomach and duodenum can worsen due to stress, poor diet, and irritation with medications. Inflammation of the mucous membrane is often accompanied by diarrhea after eating, belching, and heartburn.
When diarrhea after eating is caused by diseases of the colon, the urge to go to the toilet is difficult to control, since the lesion is located close to the anus. The stool is mushy and the volume of feces is small.
Mucus and pus in the stool indicate inflammation of the colon - colitis. Inflammation is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, localized on the left. If there is blood in the stool, this is a sign of ulceration.
Why do I have diarrhea immediately after eating and how to treat it correctly?
The situation when you immediately want to go to the toilet after eating can be caused by various factors. Loose stools are a consequence of functional disorders of the digestive process. Diarrhea after eating occurs due to the accelerated movement of a bolus of food without proper absorption.
A single bowel disorder will not harm the body. If diarrhea becomes chronic, the cause must be urgently determined. Otherwise, the heart, kidneys or other organs will suffer from systematic dehydration and demineralization.
Development mechanism
During the digestion of food, essential vitamins and minerals are absorbed into the blood. This process begins in the small intestine. Active water-salt exchange occurs here. Any irritant can disrupt the sequence of biochemical reactions and provoke increased peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract.
To quickly transport contents through the digestive tract, a large volume of liquid enters the small intestine from blood plasma. Water comes here along with salts dissolved in it.
The intestines become overfilled with fluid “squeezed out” from other organs and tissues. The bolus of food with an abundance of water quickly passes into the large intestine.
This process leads to an uncontrollable urge to go to the toilet, which begins immediately after eating.
The lost volume of fluid with salts leads to disruption of metabolic processes. Especially due to the emergency evacuation of food, the heart and kidneys suffer, which lose magnesium, potassium and other important elements.
Disturbances in the digestive process can occur not only in the upper gastrointestinal tract, but also in the large intestine. In this case, the body loses less fluid.
The inner lining of the small intestine is covered with many microscopic villi. Everything that is necessary and useful is absorbed into the blood through them, and the excess is formed into feces.
Main reasons
Diarrhea after eating is often caused by impaired intestinal motility. Reasons for diarrhea due to which food tends to leave the gastrointestinal tract:
- Stale or unusual food products. The body gets rid of pathogenic microorganisms if a person has eaten something spoiled. Poisoning manifests itself as pain in the abdomen and diarrhea immediately after eating. Switching to a new menu (for example, while traveling) provokes loose stools due to a lack of enzymes to break down exotic foods. In a child under 3 years old, new foods often cause intestinal upset, so their introduction into the diet begins in small portions.
- Imbalance of intestinal microflora. A lack of beneficial bacteria leads to premature evacuation of food. Intestinal dysbiosis is a consequence of taking antibiotics and poor nutrition. A deficiency of beneficial bacteria leads to chronic diarrhea, which occurs immediately after eating or an hour later.
- Bacterial or viral infection. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the body with food or water. The intestinal mucosa becomes inflamed and damaged. As a result, it releases exudate, mucus, and irritating organ walls. Salmonellosis leads to severe inflammation. Bacteria damage the deep layers of the mucosa until blood and pus are released from the epithelium. In an inflamed intestine, absorption is impaired and peristalsis accelerates. Particles of excretions cause diarrhea after every meal.
- Functional disorders of the nervous system. The increased speed of movement of the food bolus occurs due to neurogenic stimulation. Since digestion is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, in a stressful situation, natural metabolism is disrupted. This leads to the fact that after eating you immediately want to go to the toilet.
- Food intolerance. The gastrointestinal tract is urgently cleared of allergens. Peristalsis increases, which leads to stool liquefaction.
- Diseases of the digestive system. In diseases of the liver and gall bladder, the secretion of electrolytes and intestinal juice increases. Gastritis with low stomach acidity is characterized by a lack of secretory fluid necessary for the primary processing of the contents. Food enters the small intestine without the necessary preparation, causing diarrhea.
- Deficiency of enzymes for digesting food. The disorder is associated with pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas.
- Hormonal imbalances. Lack or excess of active substances produced by the thyroid and pancreas glands lead to digestive upset after eating.
- Binge eating. Large portions put a strain on the digestive system. The body tries to get rid of excess fluid as quickly as possible by sending water reserves to the intestines. Diarrhea after eating in this case is a protective reaction against an overwhelming load on the gastrointestinal tract.
- Eating fatty foods. After a meal with excessive fat content, intestinal upset often occurs. Products with a high content of the substance: fried meat, lard, confectionery products with cream. A sudden urge to defecate after eating these foods may appear an hour after eating. During this period, food begins to move into the small intestine. Excess fat is poorly absorbed by its walls, causing diarrhea.
- Taking laxatives for constipation.
What diseases cause diarrhea?
Intestinal upset after eating may indicate pathologies:
- hyperthyroidism;
- colitis;
- enteritis;
- gastritis;
- stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- rotovirus;
- salmonellosis;
- norovirus;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- pancreatitis;
- hormone-dependent tumors;
- parasitic infection, etc.
In adults and older people, diarrhea often occurs due to changes in blood pressure. These two states are interconnected. When pressure increases, brain neurons responsible for regulating bowel movements are stimulated. Diarrhea can also be caused by blood pressure medications.
How to determine the source of the problem
A single diarrhea after eating is not harmful to health. If diarrhea becomes a constant occurrence, vitamin deficiency and chronic diseases may develop.
The source of diarrhea can be determined by the characteristics of the stool. The consistency of the stool, color, and the presence of inclusions play a role in making a diagnosis.
Watery greenish discharge in adults is a sign of infectious diarrhea. Most often, the causative agent of the disease is rotovirus, norovirus. Microbes multiply in the intestinal epithelium, which causes a decrease in enzyme activity. Microvilli on the surface of the small intestinal mucosa have the ability to absorb molecules of a certain size.
Since the activity of enzymes decreases under the influence of viruses, disaccharides are not able to break down into monosaccharides - molecules of the required size. Undigested food along with liquid quickly passes into the large intestine, causing diarrhea after eating.
Particles of blood and mucus in the stool are a symptom of a bacterial infection. Common causative agents of this type of diarrhea are staphylococci and salmonella. The infection may be accompanied by vomiting and increased gas production.
Greasy stool with a pungent odor indicates that the small intestine is not coping with its functions. Fats are not absorbed, so they are excreted directly in the feces. This phenomenon is often associated with poor nutrition and excessive consumption of heavy foods.
If the source of infection is the stomach or small intestine, the stool is always large, watery, and may contain particles of undigested food.
With exacerbation of erosive gastritis and stomach ulcers, the stool has a tarry consistency. The feces are colored black because the blood, moving through the lower gastrointestinal tract, has time to clot.
Diseases of the stomach and duodenum can worsen due to stress, poor diet, and irritation with medications. Inflammation of the mucous membrane is often accompanied by diarrhea after eating, belching, and heartburn.
When diarrhea after eating is caused by diseases of the colon, the urge to go to the toilet is difficult to control, since the lesion is located close to the anus. The stool is mushy and the volume of feces is small.
Mucus and pus in the stool indicate inflammation of the colon - colitis. Inflammation is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, localized on the left. If there is blood in the stool, this is a sign of ulceration.
Necessary tests
To find out the cause and begin treatment for diarrhea that occurs after eating, contact a gastroenterologist. Go to the doctor if diarrhea does not go away for more than 2 days. The list of diagnostic procedures depends on the accompanying symptoms.
The doctor may refer for research:
- analysis of stool, blood, urine;
- gastroduodenoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- food allergen test.
To determine the nature of diarrhea, stool samples are taken to check for bacteria, viruses, and helminthic infestations.
Drug treatment
Chronic diarrhea after eating exhausts a person, leads to dehydration and general weakness. To prevent undesirable consequences, you need to take measures immediately after detecting a problem:
- drink plenty of fluids (clean water is best);
- take medications to restore electrolyte balance - Regidron, Gidrovit;
- use sorbent agents to remove toxins from the body - Activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel;
- follow a gentle diet.
If diarrhea is caused by allergenic foods, they are excluded from the diet. In addition to saline solutions and absorbents, they take antihistamines - Zodak, Suprastin, Fenistil.
The treatment regimen for the treatment of chronic diarrhea is selected individually, depending on the type of underlying disease. Based on the results of the examination and examination of the patient, the doctor may prescribe:
- Drugs that slow down intestinal motility based on loperamide - Imodium, Lopedium, Diara. These medications should not be taken for intestinal infections, blood in the stool, or peptic ulcers.
- Anti-diarrhea medications that normalize intestinal microflora - Bifidumbacterin, Linex, Bifiform, Acipol. Such remedies are effective in eliminating dysbiosis.
- Anthelmintic drugs for parasites - Dekaris, Pirantel. They are prescribed when roundworms and pinworms are detected in feces.
- Antibiotics if diarrhea is caused by a bacterial infection. Treatment is carried out with Levomycetin, Sumamed, Amoxicillin.
- Sedatives – Novo-passit, Afobazol, Persen. They are used for diarrhea that occurs due to nervousness.
Diet for chronic diarrhea after eating
To restore intestinal functions and eliminate intestinal irritation, you need to follow a therapeutic diet. For one-time diarrhea, it is enough to adhere to a special diet for 2-5 days. Chronic diarrhea is treated with a diet for 2–4 weeks.
Fried, salted, smoked, and spicy dishes are excluded from the menu. During the diet you should not eat:
- canned food;
- sweets;
- fresh fruits;
- milk;
- insoluble fiber (seeds, nuts, muesli).
These foods can lead to renewed diarrhea because they are difficult to digest.
During the diet, they consume well-cooked porridges, broth-based soups made from cereals, vegetables, and chopped lean meats.
Folk remedies
Rice water and strong tea have astringent properties. To relieve inflammation, you can prepare a chamomile decoction - 1 teaspoon of crushed flowers per glass of boiling water. The drink is infused for 20 minutes and drunk 3 times a day.
Effective folk remedies for diarrhea after eating:
- eat buckwheat porridge with water in the morning without adding salt - such a breakfast will relieve loose stools throughout the day;
- decoction of oak acorns - thanks to its astringent properties, the drink relieves diarrhea associated with irritable bowel syndrome and nervous tension;
- black peppercorns - 4-6 pieces should be eaten before bed.
Diarrhea after eating should not be ignored. Especially if this symptom becomes a permanent occurrence.
The information on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
Rumyantsev V. G. Experience 34 years.
Gastroenterologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Prescribes diagnostics and carries out treatment. Expert of the group for the study of inflammatory diseases. Author of more than 300 scientific papers.
Doctor We recommend: What is chronic diarrhea and how to get rid of it?
Source: https://gastrot.ru/diareya/ponos-posle-edy
Necessary tests
To find out the cause and begin treatment for diarrhea that occurs after eating, contact a gastroenterologist. Go to the doctor if diarrhea does not go away for more than 2 days. The list of diagnostic procedures depends on the accompanying symptoms.
The doctor may refer for research:
- analysis of stool, blood, urine;
- gastroduodenoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- food allergen test.
To determine the nature of diarrhea, stool samples are taken to check for bacteria, viruses, and helminthic infestations.
Drug treatment
Chronic diarrhea after eating exhausts a person, leads to dehydration and general weakness. To prevent undesirable consequences, you need to take measures immediately after detecting a problem:
- drink plenty of fluids (clean water is best);
- take medications to restore electrolyte balance - Regidron, Gidrovit;
- use sorbent agents to remove toxins from the body - Activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel;
- follow a gentle diet.
If diarrhea is caused by allergenic foods, they are excluded from the diet. In addition to saline solutions and absorbents, they take antihistamines - Zodak, Suprastin, Fenistil.
The treatment regimen for the treatment of chronic diarrhea is selected individually, depending on the type of underlying disease. Based on the results of the examination and examination of the patient, the doctor may prescribe:
- Drugs that slow down intestinal motility based on loperamide - Imodium, Lopedium, Diara. These medications should not be taken for intestinal infections, blood in the stool, or peptic ulcers.
- Anti-diarrhea medications that normalize intestinal microflora - Bifidumbacterin, Linex, Bifiform, Acipol. Such remedies are effective in eliminating dysbiosis.
- Anthelmintic drugs for parasites - Dekaris, Pirantel. They are prescribed when roundworms and pinworms are detected in feces.
- Antibiotics if diarrhea is caused by a bacterial infection. Treatment is carried out with Levomycetin, Sumamed, Amoxicillin.
- Sedatives – Novo-passit, Afobazol, Persen. They are used for diarrhea that occurs due to nervousness.
Treatment of diarrhea
If diarrhea develops after eating, treatment is needed. The doctor gives the prescription after the examination. If there are any diseases, it is important to treat them first.
You need to take medications depending on the causes of the disease.
| "Regidron", "Oralit" | Restoring water-salt balance |
| "Smecta", "Atoksil", "Activated carbon" | Removing toxins from poisoning |
| "Metronidazole", "Ofloxacin" | Destroying the infection |
| "Loperamide" | Normalization of motor skills, stopping diarrhea |
| "Linex" | Normalization of microflora |
We recommend: Chronic diarrhea - why diarrhea becomes frequent and how to get rid of it
If there is blood in your stool, you should immediately consult a doctor. This may be a sign of a serious pathology and require urgent intervention.
In addition to medications, diet will help cope with the problem. You need to give up fatty, fried, smoked and pickled foods. The digestive system will not benefit from alcoholic drinks, canned food and coffee. It is important to exclude chips, soda and sweets. The diet should be dominated by porridge, boiled dietary meat, lean fish and salads with sunflower oil.
Proper nutrition and careful attention to the body will help maintain excellent health. If alarming signs appear, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination. This will protect the body and help you always feel great!
Diet for chronic diarrhea after eating
To restore intestinal functions and eliminate intestinal irritation, you need to follow a therapeutic diet. For one-time diarrhea, it is enough to adhere to a special diet for 2-5 days. Chronic diarrhea is treated with a diet for 2–4 weeks.
Fried, salted, smoked, and spicy dishes are excluded from the menu. During the diet you should not eat:
- canned food;
- sweets;
- fresh fruits;
- milk;
- insoluble fiber (seeds, nuts, muesli).
These foods can lead to renewed diarrhea because they are difficult to digest.
During the diet, they consume well-cooked porridges, broth-based soups made from cereals, vegetables, and chopped lean meats.