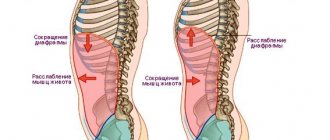
Experts consider the feeling of stabbing pain in the lower abdomen to be a sign not only of serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but also of non-dangerous manifestations of the physiology of the human body. The symptom can “wander” through the organs, as a result of which, to determine the cause of the pain, you need to consult a doctor and undergo a series of studies.
Colic in the lower abdomen is paroxysmal in nature. Sharp, severe pain indicates problems in the body. Localized in the lower abdomen, left side and right. The source is not necessarily located there; it is mainly diseases of the organs located above.
Causes of colic in the lower abdomen
The main indicators of pain in the right side, left and lower abdomen are disturbances in the functioning of the urinary and digestive organs. More serious diseases manifest themselves through the same symptom.
The main causes of colic in both women and men:
- Appendicitis. It appears on the right in the groin area, the spasm extends to the umbilical part. With some genetic abnormalities, pain appears on the left side. Body temperature rises, nausea appears. Vomiting and dizziness are possible.
- Diverticulitis. A feeling of colic may occur throughout the lower abdomen.
- Inflammatory processes in the bladder. The mucous membrane is most often affected. The pain syndrome increases over time (from aching to stabbing). Frequent urination, fever.
- Acute urinary retention. Stones and formations in the urinary stream cause sharp pain localized two fingers down from the navel. Feeling of a full bladder without being able to urinate. Surgery is required to prevent the possibility of rupture.
- Renal inflammatory process. Severe pain in the lower abdomen, chills, body temperature 38-39.5 degrees. Feverish condition.
- Cystitis. Sharp, sharp pain above the pubis. With a prolonged illness, colic moves to the central part near the navel.
- Strangulated hernia (usually inguinal). Rapid development of the symptom appears during heavy physical exertion. The pain is chaotic, accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting.
- Intestinal obstruction. Suddenly, intestinal spasm appears against the background of problems with bowel movements and increased gas formation. Location: just above the navel.
- Inflammation in the colon. Appears together with fever and difficulty in the gastrointestinal tract. Sharp, pronounced.
- Irritable bowel syndrome. Chronic pain in the lower abdomen together with sudden stomach and intestinal problems.
- Adhesive disease. Constant pain in the lower part during operations.
- Malignant neoplasms. The symptom indicates the progression of the disease to a severe form. Moves to the inguinal, lumbar, vertebral region.
They also occur against the background of hormonal changes in the body, metabolic disorders, and neuropsychic disorders. A doctor's consultation, examinations, and test results are required.
Diverticulitis
Short description
Diverticulitis refers to inflammation in the area of hernia-like protrusions of the intestinal walls (diverticula). In the bag-like protrusions, food chyme stagnates along with intestinal microflora, which potentiates inflammation of the diverticulum wall. You should consult a gastroenterologist for advice.
Localization of pain
Diverticulitis is characterized by stabbing pain in the lower abdomen. Most often, the pain is localized on the left, since the sigmoid and descending colon are located in this area, which are more often affected. The pain is localized and does not subside for several days. The intensity of pain increases after physical activity, sneezing, laughing, coughing. Due to tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, the level of pressure in the abdomen increases, and the organs compress the diverticulum, causing pain.
After defecation, the pain also intensifies due to abdominal tension.
Additional symptoms
- Defecation disorders, manifested by alternating constipation and diarrhea. Constipation is caused by the fact that the damaged segment of the intestine spasms, its lumen decreases in diameter. When the intestines relax, diarrhea occurs. This is explained by the fact that the process of fluid absorption occurs precisely in the large intestine. In the case of diverticulitis, the ability is impaired, the stool acquires a liquid consistency.
- Blood appears in the stool. The inflammatory process in the area of the diverticulum is combined with the formation of bleeding ulcerative defects and erosive lesions. Small amounts of blood can be found in stool or on underwear.
- Low-grade fever is noted. The inflammatory process potentiates the release of pyrogens into the bloodstream, causing an increase in body temperature.
- General intoxication of the body develops, expressed in nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and apathy.
Causes of colic in women
For women, colic in the lower abdomen is common; this is how premenstrual syndrome manifests itself. The intensity of the symptom varies, depending on physiological processes and the phase of the cycle, but appears every day. There is no need to treat an unpleasant spasm; it is recommended to alleviate the manifestation with painkillers and antispasmodics recommended by the gynecologist.
In addition to the usual manifestations, pain syndrome is possible due to diseases that require medical intervention:
- Inflammatory phenomena in the reproductive organs (vagina, uterus, ovaries, etc.).
- Pathologies of the menstrual cycle (sharp manifestations occur in some phases, most often 1 day before the critical days).
- Intoxication, development of infections.
- Ovarian ruptures, cysts (possible hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity).
- Myoma in the uterus, necrosis.
- Endometriosis and related manifestations.
- Inaccurate installation of the device (intrauterine device).
Sometimes the reason is the use of hormonal drugs that stimulate the ovaries. When visiting a gynecologist, a woman should bring a list of medications she is taking.
What causes colic in the lower abdomen in women
In many cases, colic in the lower abdomen in women indicates a problem with one or more organs in the pelvic area, such as the uterus, vagina, bowel or bladder. Problems may include infection, inflammation, or a condition such as endometriosis.
Localization of pain will help determine the cause:
- Cramps in upper left abdomen: enlarged spleen.
- Spasms in the upper right side: gallbladder disease, hepatitis.
- Colic in the lower abdomen: diverticulitis, ovarian cyst, ovarian torsion, appendicitis, problems with the right ovary.
- The pain is localized throughout the upper abdomen: gastric ulcer, gastritis, pancreatitis.
- Pain throughout the lower abdomen: urinary tract infections, gynecological problems such as uterine fibroids and cancer.
Pain in pregnant women
Pregnancy causes stretching of the uterus, which provokes painful spasms. The early period is accompanied by minor symptoms. If bleeding occurs, you should contact a gynecologist; these are signs of a miscarriage, which can be avoided with hospital treatment.
The first trimester of pregnancy is one of the most dangerous periods. Pain syndrome in 86% indicates the occurrence of an ectopic pregnancy if it is accompanied by general weakness, dizziness and nagging pain in the rectum. Surgery is required to prevent tubal rupture.
An unpleasant sensation in the lower abdomen in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy, accompanied by heavy bleeding, indicates placental abruption, which is detrimental to the baby. Occurs after a fall, a blow to the stomach, or to the kidneys.
If women experience nagging pain at 31-36 weeks of pregnancy, then labor most likely begins. Rarely does the progression of gynecological abnormalities worsen.
Causes of pain in men
In men, the appearance of stabbing spasms indicates not only common causes, but also characteristic diseases only of the stronger sex. 70% of people over 35 years of age are susceptible to the development of inflammatory processes in the prostate. A developing case of colic in the lower abdomen indicates an exacerbation of prostatitis due to late diagnosis of the disease. It is necessary to consult a urologist to further combat the disease. Self-medication can lead to a chronic form.
The prostate is located in an inelastic, dense capsule that practically does not stretch. Inflammation of the prostate gland leads to its enlargement, which causes an unpleasant symptom.
Acting on the intestines and rectum, the inflamed prostate causes false urges to empty the bowel and discomfort. The impact on the bladder leads to a frequent urge to urinate.
Initially, the pain manifests itself in paroxysms, gradually turning into constant pain. It is possible to get rid of spasms only by relieving inflammation from the prostate gland.
In acute prostatitis, pain goes to the pubis, perineum, genitals, sacrum and inner thigh. If spasms appear in the folds of the groin, it means that the seminal vesicles, located on both sides of the prostate gland, are affected.
When inflammatory (catarrhal) prostatitis turns into purulent, the pain suddenly becomes sharp, strong, and throbbing. Intoxication of the body occurs, accompanied by fever and general weakness.
Increasing spasms in the lower abdomen, extending to the groin, may indicate inflammatory processes in the appendages and testicles. After infectious diseases of the genital tract, scarlet fever, mumps, acute form of influenza, in addition to pain in the lower abdomen, there is discomfort when urinating, an unpleasant sensation in the scrotum, and a slight leakage of pus from the urethra.
Nature and cause of pain
Most women experienced such unpleasant and painful symptoms as severe cramps in the lower abdomen. In this case, as a rule, various symptomatic medications are taken to help reduce pain. Painkillers and antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Papaverine) are used.
However, before taking any medications, you need to find out the cause of the pain. If such colic is physiological in nature, then therapy is not necessary. As for pathologies accompanied by such manifestations, they require emergency medical intervention. To avoid possible consequences, it is recommended to consult a doctor in a timely manner and begin treatment.
The reasons for the development of cramps in the lower abdomen in women are physiological and pathological. Physiological pain occurs with premenstrual syndrome. Every second woman and girl faces them. At this time, as a rule, the following accompanying symptoms are observed: aching pain in the lower abdomen, cramps, colic, excessive irritability, swelling. In addition to PMS, provoking factors for spasms can be alcohol abuse, stress, and drugs. Female colic can be a consequence of spasms of an empty stomach and a crowded large intestine. A factor such as pregnancy deserves special attention. In the first trimester, pain occurs due to spraining of the ligaments and abdominal muscles.
In addition to the physiological pain syndrome, there is also a pathological one, which is a consequence of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. Most often, severe spasms develop against the background of cystitis, inflammatory diseases of the ovaries, uterus and vagina, as well as the fallopian tubes. For example, endometriosis, ovarian cyst, adhesions, fibroids and colpitis provoke pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen. These diseases occur against a background of increased body temperature and vaginal discharge.
As for inflammatory diseases affecting the genitourinary system, they are accompanied by severe spasms and colic in the lower abdomen (cystitis, pyelonephritis). Additional symptoms include painful urination, discomfort in the lumbar region, swelling and fever. Soreness and colic accompany diverculosis, hernia and other disorders in the pelvic organs. Prolonged constipation, stool disorders are the causes of intestinal thickening and intestinal hypertrophy. Additional symptoms: lack of appetite, fatigue, flatulence. Cramps in the lower abdomen can be a signal of oncology (ovarian, uterine cancer).
Some pathological conditions require urgent surgical intervention: appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy, perforation of a peptic ulcer, torsion of uterine fibroids, rupture of a cyst and other dangerous diseases. If timely medical assistance is not provided, the risk of death increases.
Severe spasms, colic, pain, and heaviness in women in the lower abdomen occur with many gynecological pathologies:
- proliferation of uterine fibroids;
- genital tuberculosis, varicose veins;
- ovarian rupture;
- congenital pathology;
- severe pain during menstrual periods - algodismenorrhea;
- threat of miscarriage at different periods;
- incorrectly installed uterine device;
- adhesive process;
- ovarian hyperstimulation, which developed as a result of taking hormonal drugs;
- acute stage of inflammatory processes.
Each of these cases requires emergency medical care, which will help avoid unwanted consequences and complications.
Causes of pain associated with manifestations
To identify a diagnosis and draw up a complete picture of the disease, it is necessary to analyze the nature of colic in the lower abdomen. Main part:
- Paroxysmal sharp colic indicates the presence of spasms in the tubular organs. They begin to arise due to contractions of smooth muscles.
- The manifestation of aching signs of a daily nature occurs with cholecystitis and bladder diseases (presence of stones).
- The sudden appearance of strong symptoms indicates inflammation of the appendix, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, and diverticulitis.
- During inflammatory reactions in organs and systems, pain increases from a nagging nature to sharp colic.
- If acute pain is localized throughout the abdomen, but disappears after a bowel movement, then the cause is IBS.
In any case, you should consult a specialist. It is required to accurately and truthfully talk about the manifestations of pain: at what time it occurs, what is the nature, exact localization. It would be a good idea to indicate your diet on the day colic appears and on the previous day. Based on these parameters, the doctor will prescribe a set of studies, establish a complete history of the disease, and prescribe procedures and medications.
A tribute to fashion and beauty often plays a bad joke on a person. Various unbalanced diets, intense training with increased load, constant “wandering” on the Internet, unhealthy and high-calorie (or low-calorie) food lead to depletion of the body’s internal strength. Diseases appear against the background of weakened immunity; due to rare walks, vital systems suffer from oxygen starvation. Constant employment interferes with preventive examinations in the clinic. Money can't buy health. It takes time.