What is stomach discomfort? How does it manifest? Discomfort is a feeling of heaviness, fullness, often distension in the upper half of the abdomen; sometimes these symptoms are accompanied by belching of air, food and nausea. Today, this is one of the most common syndromes associated with digestive disorders. It should be regarded as a cry from the stomach for help. The manifestations of discomfort can be variable depending on the reasons that caused this condition.
The causes of discomfort in the stomach vary from the most banal - poor nutrition, overeating, bad habits or the presence of negative psychological factors (stress) - to existing diseases, which are characterized by the presence of pathological changes in the digestive tract. To help yourself faster, it is very important not to self-medicate, but to consult a doctor to find out the cause of stomach discomfort, timely diagnosis, provide the necessary assistance and prevent complications.
Causes
The following reasons can lead to stomach discomfort:
- First of all, gastroenterologists call poor nutrition the main culprit of discomfort. In particular, the systematic consumption of fast foods, an abundance of fatty, spicy, fried, sweet, smoked foods in the diet, which leads to irritation of the mucous membrane, overeating, which causes stretching of the stomach walls, constant snacking on the go, a long interval between meals , a combination of incompatible products (milk, cucumbers). All these factors negatively affect the condition of the gastric mucosa and the functioning of the digestive organ as a whole.
- Doctors cite tobacco smoking and constant consumption of alcoholic beverages as the second cause of stomach discomfort. Bad habits provoke constant irritation of the mucous membranes, contribute to poor circulation and, as a result, cause discomfort.
- Psychological stress is also often the cause of gastric discomfort. The intense work of the nervous system directly affects the condition of the digestive tract. And if a person experiences constant stress, is nervous, and anxious, then this is more likely to lead to stomach neurosis. Constant stress on the nervous system causes unpleasant stomach symptoms. Often this is:
- nausea;
- belching;
- discomfort in the stomach not related to food intake;
- regurgitation or vomiting.
Gastric neurosis can be distinguished by the following signs: a person experiences hunger when completely full or, on the contrary, a full stomach after eating a small amount of food. All sensations in the stomach area are usually not associated with food.
In pregnant women, stomach discomfort is associated with hormonal changes and pressure on the stomach and diaphragm by the growing fetus.
If discomfort occurs in the upper abdomen, it is recommended to eat small portions of food at least 5-6 times a day. Be sure to include fiber-rich foods and still water in your diet - 1.5 liters per day.
Diseases in which there is a feeling of discomfort in the stomach
Discomfort in the stomach, including in combination with pain, is a manifestation of dyspepsia. Symptoms of the following diseases often occur:
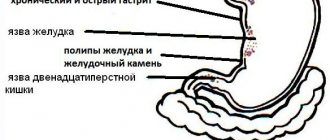
- Chronic gastritis, gastroduodenitis with varying secretory activity. When reduced, heaviness after eating is especially pronounced, “belching like a rotten egg.”
- Stomach ulcer – in the first place is still pain, followed by signs of dyspepsia.
- Stomach tumors - a feeling of discomfort appears, as with gastritis with low acidity.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease – there is constant discomfort, often accompanied by heartburn.
- Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas.
- Gallstone disease is the presence of stagnation of bile in the gallbladder with “stones”. With the last two diseases, there are more manifestations of pancreatic dyspepsia in the clinic.
The presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the body, intoxication, poisoning are also possible causes of gastric discomfort.
Feeling of a lump in the stomach
Gastritis
33336 21 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Feeling of a lump in the stomach: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
The feeling of a coma in the stomach is described when one experiences a feeling of heaviness, discomfort and fullness in the stomach, even when it is only slightly filled. Sometimes patients find it difficult to determine the exact location of the coma and point to the lower third of the sternum or solar plexus. In some cases, a feeling of a lump and cramps in the stomach may occur on an empty stomach.
Types of feeling of a coma in the stomach
A feeling of heaviness or coma in the stomach can be an independent symptom, but may be accompanied by other unpleasant sensations. Sometimes it is heartburn, sour belching, bloating, constipation.
In some cases, a feeling of a lump appears when swallowing
, making it difficult for chewed food to pass through.
In addition, patients may complain that food did not enter the stomach, but stopped in the esophagus.
In such patients, vomiting of unchanged food is possible. When describing symptoms, you should pay attention to the time of onset of discomfort - before
or
after eating
.
The patient may feel heaviness in the stomach with pain or heartburn, on an empty stomach or after eating, and night pain also occurs.
Sometimes the sensation of a lump in the stomach occurs
regardless of food intake
.
In such cases, they complain of stomach spasms
, sometimes accompanied by a feeling of a lump in the throat.
What diseases cause a sensation of a lump in the stomach?
Eating more than your usual amount of food
, accompanied by a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the stomach. This condition is not a manifestation of the disease and goes away on its own after some time.
It should be noted that stomach capacity varies depending on eating habits.
People who are small or
have undergone gastric resection
can eat a small portion, otherwise they will not only experience a feeling of heaviness or fullness in the stomach, but also vomiting.
A sensation of coma may occur when consuming foods that cause excess gas.
, as well as
food that is difficult to digest
(salads with mayonnaise, fatty, fried and smoked dishes) and
highly carbonated drinks
.
When eating dry and hastily,
an unpleasant sensation in the epigastric region is caused by poor processing of the food bolus with saliva and insufficient secretion of gastric juice.
However, a feeling of coma or discomfort in the stomach, or more precisely, in the epigastric region, may appear after eating even a small amount of food
.
This condition can be caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or other reasons.
First of all, they assume indigestion, or functional dyspepsia. Its symptoms most often include pain and discomfort immediately after eating, a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach, heartburn, belching, nausea, sometimes vomiting, reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, bloating and bowel dysfunction.
Dyspepsia can be a symptom of both functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and organic diseases.
Functional causes of dyspepsia are often caused by errors in diet and medications.
Iron ions have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa, which is most pronounced when taking medications based on ferrous iron. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are systematically taken for rheumatic and non-rheumatic diseases of the musculoskeletal system, also cause undesirable effects: heaviness and discomfort in the stomach, nausea, vomiting, and dyspeptic disorders.
Neurological disorders
(neuroses, depression), psychological trauma almost always affects the state of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to impaired motility.
Functional dyspepsia is not accompanied by erosive or ulcerative lesions of the stomach; its symptoms disappear when the general state of health is normalized.
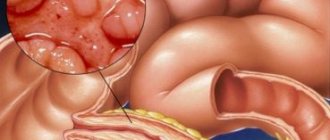
One of the common causes of discomfort in the stomach immediately after eating is
gastritis
. It is accompanied by functional and inflammatory processes that have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa. Symptoms of gastritis include heaviness and pain in the stomach, indigestion, nausea, heartburn, sour belching and bloating when eating any food. The inflammatory process leads to atrophy of the mucous membrane and disruption of the glands that secrete gastric juice.
Insufficient gastric juice and weak peristalsis of the stomach and intestines make it difficult to digest food.
Gastritis is often accompanied by dyspepsia. In addition to a feeling of heaviness and aching pain in the epigastric region after eating, poor appetite, weakness, fatigue, and irritability are noted. When pressing on the abdomen, a dull pain appears in the projection of the stomach.
Impaired motor-evacuation functions
upper digestive tract is always accompanied by a feeling of coma or a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. Disorders of esophageal motility are usually caused by incoordination of the esophageal sphincters. Uncoordinated work of the esophageal muscles can lead to a delay in the bolus of food on the way to the stomach, the reflux of food particles into the respiratory tract, and reflux (return of stomach contents into the esophagus). Impaired gastric motility leads to slow emptying, which is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and fullness even with a small amount of food consumed, pain in the epigastric region, heartburn, nausea and vomiting.
Motility disorders of the esophagus and stomach may be associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, tumors and stenoses (narrowings), metabolic disorders (hyperkalemia, hypercalcemia), postoperative complications of gastrectomy, taking certain medications (opiates, antidepressants, hormones), alcohol and nicotine .
Peristalsis worsens with a sedentary lifestyle and with age.
Stomach cancer can also cause symptoms such as a feeling of heaviness or a lump in the stomach. Moreover, depending on the location of the tumor, its manifestations vary. If the tumor is located closer to the esophagus, problems with swallowing food occur. This is accompanied by increased salivation, nausea, vomiting, and pain in the epigastric region. When the tumor is localized in the lower parts of the stomach, closer to the duodenum, a prolonged feeling of heaviness after eating and bloating is characteristic. When burping, a putrid odor may be felt.
Which doctors should you contact if you feel a lump in your stomach?
If there is a constant feeling of a lump in the stomach or a feeling of heaviness, it is necessary to contact or to make a preliminary diagnosis. The gastroenterologist may also refer the patient to an oncologist. A consultation may also be required.
Diagnosis and examination if you feel a lump in the stomach
First of all, clinical blood and stool tests are necessary for differential diagnosis.
How it manifests itself
Actually, the feeling of gastric discomfort is a manifestation of dyspepsia, which can accompany the above diseases. In this case, dyspepsia is a collection of various symptoms of the digestive system, and not a separate disease. There is also functional dyspepsia, which refers to functional stomach disorders. It manifests itself as discomfort: heaviness in the stomach, fullness, early satiety and pain in the epigastric region.
Functional gastric dyspepsia is observed in the absence of organic lesions in the stomach and intestines. If there are changes in the gastric mucosa, they are reversible. The feeling of discomfort has nothing to do with eating or physical activity.
Previously, depending on the clinical picture, dyspepsia was divided into:
- reflux-like;
- dyskinetic;
- ulcer-like.
Functional dyspepsia manifests itself in this way:
- Reflux-like dyspepsia is characterized by heartburn, acid regurgitation, and a feeling of burning pain in the chest.
- A person complains of discomfort in the stomach immediately after eating, nausea, and bloating. Sometimes vomiting is observed, after which relief is noted. These symptoms are characteristic of dyskinetic dyspepsia.
- With ulcer-like dyspepsia, severe hunger pain is observed at night. Most often it appears after experiencing severe stress. Another distinctive sign of ulcer-like dyspepsia is a feeling of fear when pain occurs.
Important! With functional dyspepsia, blood never appears in the stool, anemia does not develop, a person does not lose weight, dysphagia (swallowing disorder) is excluded, but, as a rule, it is accompanied by many neurotic symptoms: weakness, psycho-emotional lability, irritability, unmotivated changes in mood.
Nausea
Stomach discomfort is often combined with nausea. Nausea is not a disease, it is just a separate symptom, often leading to vomiting. This sensation is directly related to decreased activity of the stomach, functional - motor changes in the functioning of the duodenum and small intestine, and nervous disorders.
If nausea along with stomach discomfort occurs after eating, you should definitely consult a doctor. This may be due to a stomach disease or a disorder in the nervous system.
In no case should you relieve stomach pain and discomfort on your own, especially if the disorders occur systematically. It is better to consult a doctor who will conduct the necessary research and prescribe effective treatment.
Diagnostic methods
Before treating stomach discomfort, it is necessary to find out the cause of its occurrence. For this purpose, they contact a gastroenterologist and undergo a comprehensive examination. It is important to find out whether the disorder is associated with pathological conditions - ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis. To do this, the following diagnostic procedures are carried out:
- ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- X-ray pictures;
- laboratory tests of blood and urine.
If there is discomfort in the stomach area, phagogastroduodenoscopy is performed using a probe. The technique evaluates the condition of the mucous membrane of the internal organ.
How to identify
The main task is to find the cause of the discomfort. Diagnosis is based on a survey and examination of the patient. The examination consists of:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- radiography of the stomach;
- esogastroduodescopy;
- ELISA, PCR - to detect the presence of Helicobacter bacteria.
In some cases, the patient will need to consult other specialists.
What not to do at home
In order not to harm the patient even more, you need to remember what not to do before the doctor arrives. The list is not that big, it’s not difficult to remember:
You should not leave the patient alone, even for a couple of minutes. You cannot give medications, with the exception of antipyretics or no-shpa. You cannot force a patient to eat. You cannot feed a person dairy products and juices. You cannot delay calling an ambulance if the person is getting worse.
Nausea, vomiting, weakness and dizziness can indicate various diseases. In most cases, the patient guesses what caused this condition; in other cases, the help of a doctor is needed to make a diagnosis.
Attacks of abdominal pain, especially in combination with other symptoms, always carry certain risks. An alternative arises: limit yourself to the means of a home first aid kit in order to prevent a rapid deterioration of the condition, or resort to medical help. Understanding the possible causes of alarming symptoms will allow you to assess their danger and take timely, effective measures.
How to get rid
Treatment for stomach discomfort will depend on the cause. If the source lies in gastrointestinal pathologies, then the doctor will prescribe appropriate medications to treat the diseases.
As for functional dyspepsia, the main focus of therapy is lifestyle changes and nutritional correction, as well as taking sedatives.
To normalize your daily routine, you need to avoid situations that lead to stress, emotional and physical overload, and worries. It is definitely recommended to give up bad habits.
It won’t hurt to systematically engage in simple outdoor sports, which will help strengthen the nervous system.
Much attention should be paid to nutrition and diet selection. You need to eat in small portions, chew food thoroughly, avoid long intervals between meals and do not overeat.
After eating, you should not immediately go to bed to rest - it is better to move around for a while.
When treating functional dyspepsia, it is recommended to completely stop taking anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, since they have a negative effect on the condition of the gastric mucosa.
Therapy must necessarily include taking sedative medications - motherwort, valerian, and, if necessary, antidepressants (Sedariston).
General principles of treatment and preventive measures
No-shpa - to eliminate colic.
If, during the examination of the patient, diseases of the abdominal organs are revealed, then their treatment is carried out first.
Colic, as an accompanying symptom, may go away on its own. It is possible to prescribe painkillers to alleviate the patient's condition.
If the etiology of gastric colic is not clear or it is established that their cause is a functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, complex therapy is prescribed. This does not include a therapeutic diet, lifestyle modification if necessary, and drug treatment.
Read: Why do many women constantly have stomach pain during menstruation?
The diet includes avoiding heavy foods, foods that cause flatulence and bloating: complex dishes, smoked meats, pickles, spices, animal fats, legumes, cabbage, sweet fruits, strong tea and coffee, carbonated drinks.
Dishes need to be steamed, boiled or stewed. Food is consumed in small portions, divided into 5-6 meals. It is advisable to adhere to a certain regime - eat at approximately the same time. Dishes are eaten warm. Food must be chewed thoroughly.
You need to drink a sufficient amount of liquid per day (up to 2 liters), mainly clean water. The lifestyle should be quite active. It is recommended to take walks in the fresh air more often and do simple physical exercises. Drug therapy covers several areas:
- Relief of pain (antispasmodics - No-Shpa, Drotaverine).
- Relieving tension (antidepressants - Amitriptyline).
- Stimulation of digestion (prokinetics - Domperidone).
- Normalization of secretion (H2-antihistamines - famotidine).
As an aid, you can take decoctions of medicinal plants. Calamus root, chamomile flowers and angelica herb are mixed in equal proportions. 3 tbsp. l. The mixture is poured with boiling water, brought to a boil, cooled and filtered. Drink half a glass of the decoction before meals.
Another option: chamomile flowers, valerian root and knotweed root in a ratio of 3:4:4 are mixed, poured with boiling water at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. mixture in a glass of water and infused in a thermos for 6 hours. Drink a glass of the infusion before meals 2 times a day. Lavender, oregano, and motherwort also have a healing effect. They are brewed with boiling water and taken before meals several times a day.
To prevent stomach colic, it is recommended to simply lead a healthy lifestyle: give up bad habits, move more, eat properly and nutritiously, and avoid stressful situations.
Knowing the symptoms of stomach colic and the principles of first aid, a person faced with this situation will not be confused and will do everything possible to alleviate the condition. It is important to remember that in any case, consultation with a specialist is necessary, even if you did not call an ambulance.
This video will tell you about abdominal colic:
Read along with this article:
- Hepatic colic: symptoms, causes and first aid for the patient
- Spasmodic pain in the stomach: what causes it and how to treat it
- What to do if your stomach hurts? What could be the reasons?
- Medicines for colic in newborns, causes of the condition,…
- Stomach medicine for children: how to help and not harm
- Right side hurts, what could it be and how to deal with it
- How to relieve stomach pain: first aid
- Abdominal pain after eating: features of development and...
- Spleen diseases: symptoms and causes
Diagnostic “hide and seek”
Sometimes the pain spreads beyond the diseased organ, and to very distant parts of the body. For example, disturbances in the blood supply to the heart muscle (ischemia, threatening a stroke) can cause pain significantly above (or below) the chest, in the abdomen, left shoulder, arm and even palm. Pain during an ectopic pregnancy often radiates to the shoulders, and an ovarian cyst to the pancreas, causing symptoms similar to those of acute pancreatitis (Kocher's symptom).
Abdominal pain is sometimes caused by spinal injuries, fractures of the ribs and pelvic bones. An inflamed appendix is the main simulator of pain in any (!) point of the abdominal cavity. In this regard, diagnosing appendicitis sometimes requires “aerobatics.”
Painful sensations in the absence of organic changes that could cause them are called psychogenic pain. Most often, the background for their occurrence is mental disorders: depression, anxiety, and various phobias.
Doctors note that sharp, intense pain in the abdomen is sometimes caused by ordinary flatulence, and prolonged dull pain that a person ignores is usually a sign of a serious illness.
Possible causes of abdominal pain depending on their location
These tables are quite conditional. The innervation of the abdominal cavity of each person is unique, like fingerprints, therefore the manifestations of pain are strictly individual.
| Right hypochondrium | Acute cholecystitis, hepatic colic (with stone movement), radiculitis, attack of acute appendicitis |
| Left hypochondrium | Acute pancreatitis, radiculitis, acute appendicitis |
| Epigastric region (above the navel) | Gastric or duodenal ulcer, “posterior” myocardial infarction, consequences of overeating, initial stage of acute appendicitis, strangulated umbilical hernia |
| Left (or right) side | Inguinal hernia strangulation, intestinal diverticulum, intestinal obstruction, ovarian inflammation, ectopic pregnancy, acute appendicitis, renal colic (with stone movement), irritable bowel syndrome |
| Lower abdomen above the pubis (suprapubic joint) | Ectopic pregnancy, cystitis, strangulated inguinal hernia, intestinal obstruction, urological diseases of men, acute appendicitis |
Sometimes a complete examination of the patient does not reveal organic causes of abdominal pain; in such cases, we may be talking about chronic pain syndrome, a problem of a neurological nature.
Organic causes of pain
Pathogenic microbes and toxins affect the regulation of blood circulation, excretory and respiratory functions of the body, and the formation of hormones. Therefore, the most common causes of abdominal pain are:
inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract and pelvis; stagnation of fluids (for example, ascites), leading to excess pressure in hollow organs or the peritoneum (internal bleeding is especially dangerous); tissue swelling, impeding the blood supply to the organ and causing necrosis (death); spasm of the muscular walls of hollow organs; trauma to the mucous membranes by foreign bodies (during the passage of stones).
A sharp increase in abdominal pain, accompanied by bleeding, vomiting, dry mouth, headache and dizziness, requires immediate medical attention.
Causes of dizziness
Dizziness is a serious sign of oxygen starvation of the brain, often accompanied by nausea, and a dangerous factor in injury from a fall that cannot be ignored.
Organic causes of coordination problems may include:
stroke; tumors of the brain and cervical spine, causing pinching of the nerves and blood vessels supplying the brain; delayed consequences of concussion; cerebral aneurysm; osteochondrosis of the cervical spine; increased intracranial and/or intraocular pressure; cerebral edema as a symptom of meningitis, encephalitis; inflammatory diseases of the middle ear; vascular spasms leading to surges in blood pressure.
Oxygen starvation of the brain and dizziness cause a number of metabolic disorders:
anemia; unbalanced diet causing vitamin deficiency; intoxication of the body; a sharp change in body position, leading to a redistribution of blood volume (for example, when standing up from a squat), weather dependence.
Often the cause of dizziness is prolonged stay in smoky rooms.