The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
A diet for irritable bowel syndrome must necessarily be aimed at normalizing the digestion process and eliminating existing problems with the gastrointestinal tract. It must be followed for at least three months; most often, it is during this time that the body can be brought into order.
The essence of nutrition for irritable bowel syndrome is to ensure that a person receives adequate nutrition and at the same time has the opportunity to reduce the negative symptoms of the existing pathology. It is important to highlight those foods that stimulate a feeling of discomfort, provoke constipation, diarrhea or bloating. Such foods should be eliminated from the diet. This is especially true if you have intolerance to milk sugar and gluten.
The diet for irritable bowel syndrome is divided into 2 types, depending on the main symptom:
- If diarrhea predominates, you should prepare food properly, it is best to grind it. You only need to focus on the permitted list of products. Experts for diarrhea recommend taking dietary table No. 4 as the standard of nutrition. It helps strengthen the motor function of irritable intestines and reduce the urge to defecate.
- If a person suffers from constipation, then it is also important to review the diet and include foods that stimulate intestinal function. In this case, experts recommend turning to dietary table No. 3 according to Pevzner.
You should not refuse dietary nutrition if it is recommended by a specialist. From any proposed list of products, you can prepare many interesting dishes, which will also have a healing effect and improve the quality of life of a person with irritable bowel syndrome.
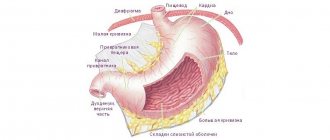
What is irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is not an irreversible disease, therefore, when the root causes are identified and eliminated, the pathology disappears without a trace.
The main causes of IBS include:
- prolonged diarrhea or constipation;
- lack of diet and daily routine;
- anomaly of intestinal development;
- neurological problems, from stress to insomnia;
- poor nutrition;
- hormonal imbalances, especially in women;
- acute intestinal diseases;
- cancerous tumors;
- hereditary factors;
- chronic fatigue.
It should be remembered that IBS does not appear as a separate disease and is always concomitant. Moreover, if the pathology becomes chronic, it provokes the development of GERD, gastritis, ulcers and other gastrointestinal pathologies.
There are 3 main symptoms that should alert a person - constipation, diarrhea or flatulence. Factors that should be a reason to contact a medical facility include the presence of mucus in the stool, a feeling of heaviness and discomfort after eating food, water, or drinks. Although such symptoms are typical for many types of gastrointestinal diseases.
Sample menu for the week
| Days | Breakfast | Dinner | Afternoon snack (snack) | Dinner |
| Day 1 | steamed omelette, bran bread, tea; | chicken broth with noodles, squash puree with boiled fish, compote; | biscuits, juice, apple; | fish baked with couscous, tea, bran bread; |
| Day 2 | cottage cheese casserole, berry juice; | beetroot soup, boiled chicken with rice, tea; | cottage cheese and berry casserole, tea; | steamed meat cutlets with buckwheat porridge, cocoa; |
| Day 3 | buckwheat porridge with milk, dry cookies, cocoa; | vegetable soup with meat broth, baked fish, tomato and broccoli salad, apple juice; | savory bun with jam, berry juice; | mashed potatoes with baked chicken and zucchini, compote; |
| Day 4 | soft-boiled eggs, whole grain bread with hard cheese and meat pate, tomato juice; | vegetarian borscht with sour cream, bulgur with veal, cocoa; | marshmallows, tea with lemon; | cottage cheese casserole with fruit, jelly. |
| Day 5 | oatmeal porridge in water with berries, weak tea, insipid bun; | mashed potatoes with butter, steamed fish, baked zucchini, compote; | berry soufflé, tea; | potato pudding with sour cream, tea; |
| Day 6 | carrot casserole with sour cream, coffee with milk; | chicken soup with egg, cauliflower puree, berry jelly; | fruit salad, compote; | steamed meatloaf, vegetable puree, apple juice; |
| Day 7 | steam omelette with vegetables, marshmallows, compote. | beef meatballs, boiled brown rice with carrots, cocoa. | dry cookies with jam and juice. | buckwheat porridge, boiled pollock, tea with cookies. |
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Treatment tables (diets) No. 1-15 according to Pevzner: food tables and diet
- Irritable bowel syndrome: symptoms and treatments
- How to eat before and after intestinal colonoscopy?
- Rectal fissure: causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
- Causes of bloating and increased gas formation, treatment methods
- Basic principles of a waste-free diet and preparation for colonoscopy
- Diet for diarrhea: nutritional principles, foods and menu for the week
- Diet after removal of intestinal polyps: nutritional principles, foods and menu for the week
- Diet for colitis: basic principles, products and menu for the week
- Nutrition for Crohn's disease: principles of diet and menu for the week
General rules
IBS is quite easy to overcome with the help of a special diet, but this menu should be strictly adhered to. Basic dietary requirements:
- fractional, 5-6 meals a day;
- no long breaks between meals, the feeling of hunger should be immediately dulled;
- portions must be small in size;
- any food and drinks should be at room temperature;
- you need to eat slowly, chewing everything thoroughly;
- It is forbidden to eat 3 hours before going to bed;
- You should stop drinking alcohol and smoking, or, in extreme cases, reduce the amount;
- no carbonated drinks should be present in the diet;
- The menu should not contain dishes with fat, that is, nothing should be fried.
In addition, you need to get rid of excess weight and exercise regularly, at least 30 minutes throughout the day.
If you have constipation or diarrhea, you should undergo a test that will allow you to remove foods from your diet that provoke this condition. To reduce bloating, you can eat flax seeds; it is recommended to eat porridge and oat flakes.
Remember that fast food is a provocateur of IBS, as well as any rough food containing flavorings, preservatives, and these even include chocolate and ice cream.
General principles of dietary nutrition
Nutrition when diagnosing a disease is based on the following rules:
- food intake should be fractional, in small portions;
- food must be chewed as thoroughly as possible;
- Meals should be taken at the same time;
- the interval between two meals should not exceed 3 hours;
- products should be at room temperature – neither hot nor cold;
- You need to cook dishes by steaming, boiling or baking in the oven;
- dinner should take place 2 hours before bedtime.
The diet for irritable bowel syndrome involves following treatment table No. 4 according to Pevzner, which has its own variations. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, the patient is prescribed diet No. 4B. Dishes are served only pureed. After the pathological symptoms subside, the patient is transferred to table No. 4B. Its main difference is the integral presentation of products.
Fully or partially limited products
Alcoholic drinks and fast food are completely prohibited. If you cannot refuse at all, then you should drink alcohol in minimal quantities. Spicy seasonings and smoked foods are not allowed. Fatty and fried foods are not allowed. Sweets are prohibited, especially cakes with cream, pastries and fresh pastries.
Dishes with beans and mushrooms are not the best food. They are the ones who greatly provoke intestinal irritation. The same applies to pickled and salty dishes. During treatment you will have to give up any sour berries and fruits. They stimulate the fermentation process, which leads to increased flatulence.
When creating a menu, you should always take into account the individual characteristics of the patient regarding the reaction to food.
Diet features
You should adjust your diet depending on your irritable bowel symptoms. Then the diet for IBS will bring the desired result.
Pathology and bloating
If you have IBS with flatulence, you should avoid the following foods:
- food prepared by frying and adding spices;
- fast food in any form;
- hard-boiled eggs;
- sweets (ice cream and chocolates are especially not recommended);
- coffee;
- sugar (it is not recommended to use substitutes for this product, as they often also cause increased gas formation);
- milk (in case of developing lactose intolerance);
- cabbage;
- legumes
It is not recommended to eat large quantities of overly fatty foods. The diet should be combined with the prevention of any stressful situations.
For constipation
Proper nutrition should help normalize regular stomach function. You can eat more foods containing plant fiber.
All fried, spicy, smoked dishes are excluded . You need to eat little and often, because overeating or long breaks in eating contribute to the deterioration of the digestive tract.
If you have intestinal irritation with constipation, you should avoid fast food products, refined foods, and mushrooms.
For diarrhea
The task of proper nutrition is to ensure the digestion of food and normalize intestinal motility.
In case of pathology with diarrhea, the following foods and drinks contribute to frequent bowel movements:
Therefore, such products should be banned. Diarrhea can also occur from stewed potatoes, cream pies, fish, okroshka, vegetable salad, or bean side dish. These seemingly completely combined components can cause diarrhea in a person with a weakened intestine.
The following products are recommended:
- bran bread;
- boiled eggs;
- lean meat, fish;
- jelly;
- apples;
- vegetable oil;
- compotes;
- freshes.
Teas and jelly made from bird cherry fruits are shown. They have a pronounced strengthening effect and help quickly eliminate the signs of diarrhea.
Nutrition for pain
In case of irritation with pain, all dishes should be slightly warmed up. It is forbidden to eat hot or too cold food. You should not eat food that causes increased gas formation.
Otherwise, the nutritional rules remain the same as for other types of irritable bowel disease.
Food for children
The principles of a mixed diet are the same as for adults.
The nutritionist's recommendations boil down to eating only pureed and gentle food . It will help avoid irritable bowel syndrome and restore normal functioning.
Children should get enough fluids. With dehydration, the symptoms of the pathology intensify, and the process of digesting food is disrupted.
Duration of the diet and expected effect from it
The diet lasts until intestinal functions are completely normalized. This may take from several weeks to several months. The absence of constipation and diarrhea, flatulence, and pain indicates a high result of therapeutic measures.
Diet for irritable bowel syndrome with flatulence
If IBS is accompanied by flatulence, doctors recommend using a FODMAP diet. It was developed back in 2005 in Australia. First of all, the diet allows you to identify poorly digestible carbohydrates in the diet, after which they are eliminated from the menu and thereby get rid of flatulence.
Particular attention should be paid to carbonated drinks in the diet. The situation is aggravated when a person drinks through a straw, then air enters the colon and inevitably leads to gas. Chewing gum and artificial sugars also lead to fermentation. Some fruits and green salads have a similar property. Flatulence can also be caused by dairy products and cheeses.
High FODMAP foods also include:
- some cereals, in particular bulgur, semolina, wheat and couscous;
- pistachios and cashews;
- spicy seasonings.
At the beginning of the diet, all possible provocateurs are removed from the diet for a period of 6 to 8 weeks. Then their gradual introduction begins. The patient should keep a food diary at this time and write down which foods irritate the intestines more strongly, causing flatulence. It is clear that some products will have a greater, and some less, effect on the condition. In this way, it will be possible to identify the most problematic foods that will actually have to be abandoned or reduced to a minimum in the diet.
WHAT YOU CAN EAT
- Choose low FODMAP fruits (bananas, blueberries, melon, grapes, oranges, kiwi, strawberries, red peppers, bean sprouts, carrots, lettuce, spinach, green onions, cucumber, tomato, eggplant, green beans, potatoes, olives, celery );
- Increase your calcium intake with yogurt. The beneficial bacteria found in yogurt may help relieve IBS symptoms. Instead of regular dairy products with lactose, use lactose-free cow's milk, lactose-free kefir and cream cheese;
- replace butter with olive oil;
- Avoid artificial sweeteners such as sorbitol, maltitol, and high fructose corn syrup as they can disrupt your gut microbiome and worsen IBS symptoms. The low FODMAP diet suggests maple syrup and stevia as alternatives.
A person cannot completely remove trigger foods from his life, but if he uses them to a minimum, he can make his life much easier. A diet along with drug therapy will allow you to control irritable bowel syndrome and live a full life.
Diet for irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea
Diarrhea with irritable bowels also brings many inconveniences. To cope with this problem, any foods that cause diarrhea are removed from the diet. These are fruits and vegetables high in fructose and fiber. The most common ones include apples, cabbage and beets.
It is also recommended to avoid dried fruits, bran and black bread. The menu focuses on stomach strengthening foods. These include rice, kefir with a production date of 2 days or more, and tea.
Diet for IBS with constipation
Constipation, which leads to the accumulation of feces in the intestines, leads to pain when the organ is irritated. The diet prescribed for IBS with difficult stool consists of foods that speed up intestinal motility. Plant foods do this well. To obtain a stable laxative effect, it is necessary to heat treat the products.
Bran, dried fruits and compotes based on them, Hercules porridge, fermented milk products, especially kefir are recommended.
Foods that inhibit colon motility are prohibited: baked goods, rice, chocolate, coffee, strong tea.
Diet for irritable bowel syndrome with dysbiosis
There are many reasons for the appearance of dysbiosis. To one degree or another, every person experiences this condition. A provocateur can be not only poor nutrition, but also poor environmental conditions in the area of residence and constant stress.
To cope with this condition, especially if it occurs against the background of IBS, you will have to give up spicy and fatty foods, confectionery products with a high content of sugar and its substitutes. Canned foods also additionally cause an unwanted fermentation process in the stomach. You should not eat sausages, legumes and smoked meats.
You should select foods for your diet based on their dietary content; everything must be steamed, in the oven, but under no circumstances fried. For this problem, it is useful to eat millet and pearl barley porridge, and soups made from them. The main thing is to limit the amount of spices and salt as much as possible. Probiotics will be useful, but it is better to take them as prescribed by a doctor.
List of approved products
Therapeutic nutrition for IBS involves consuming foods with a high concentration of plant fibers. The intake of fats is minimized. In this state, the body needs carbohydrates and proteins that do not irritate the intestines.
Healthy foods
Taking into account these nuances, the list of recommended products is as follows:
- Dried bread.
- Low fat meat.
- Low-fat fish: pike perch, hake, perch.
- Boiled egg - one per day.
- Low-fat cottage cheese.
- Butter – up to 30 grams per day.
- Porridge without added fat (buckwheat, rice, oatmeal, wheat).
- Boiled vegetables.
- Vegetable soups without meat with the addition of small portions of rice or pasta.
- Kissel.
- Apple and banana puree.
- Sugar in small quantities.
- Cocoa without milk, tea, coffee.
- Berry and fruit juices diluted with water.
Since the disease progresses differently in each patient, this list cannot be called universal. There may be foods that aggravate symptoms. Therefore, each new product must be introduced into the diet with caution.
When to see a doctor
If dietary nutrition does not help, and the symptoms of damage to the digestive tract only intensify, the patient should urgently consult a doctor.
This must be done if the following symptoms appear:
- severe uncontrollable vomiting;
- increased pain;
- the appearance of symptoms of an acute abdomen;
- temperature increase;
- increased heart rate.
IBS is a symptom complex that requires a very careful approach to nutrition.
Eliminating unhealthy foods helps relieve symptoms of irritation and improve bowel function. If acute symptoms of damage to the digestive tract appear, urgent hospitalization is required.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a digestive disorder that can be managed by following certain dietary guidelines. It is based on long-term avoidance of certain foods and consumption of sufficient fiber. The diet menu for IBS should be developed by the attending physician, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body and the symptoms of the disease.
The importance of diet
Dietary nutrition for IBS is considered part of a combination treatment. Since it is not a disease as such, but represents only a specific symptom complex associated with intestinal dysfunction of an organic nature, when drawing up a therapeutic diet, a specialist must determine the triggering mechanisms of the pathological disorder.
The diet for IBS is selected for each patient in accordance with his individual characteristics, and taking into account taste preferences. Here it is important to take into account the clinical manifestations of the syndrome: constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, pain.
A specially selected program is aimed at solving problems such as:
- elimination of the main symptoms;
- restoration of metabolism;
- increased regeneration of mucosal epithelial cells;
- normalization of motility of the gastrointestinal tract;
- replenishment of energy deficiency due to the supply of nutrients.