Basic information
With dyscholia of the gallbladder, the composition of bile, its physical and chemical characteristics change. Bile is a secretion of hepatocytes (liver cells), which enters the digestive tract through the bile ducts and is involved in the breakdown and absorption of food. The composition of the liver secretion is bilirubin, bile acids, cholesterol, amino acids, sodium, potassium ions, etc. If the ratio of these substances is disturbed, the composition of the secretion of the liver cells changes. In most cases, this increases the concentration of cholesterol.
Bile envelops and helps digest fats in the digestive tract. Thanks to it, vitamins and cholesterol are absorbed faster. This substance is involved in metabolic processes and in the creation of joint exudate.
Bile consists of phospholipids, bilirubin, biological compounds, cholesterol, and bile acids. If the organ functions normally, then the ratio of cholesterol and bile acid will be one to two. If the bile duct does not function properly, consequences may occur, for example, biliary cirrhosis of the liver or biliary sludge (dry sediment of bile at the bottom of the organ). Dycholia occurs when cholesterol levels in the gallbladder increase. Factors contributing to the onset of the disease include weight gain, fatty foods and diabetes mellitus.
In addition, bile regulates the motor activity of the jejunum, stimulates the formation of mucus in the intestines, and neutralizes the aggressive effects of gastric juice.
Normally, the ratio of cholic acids (bile acids) and cholesterol is 2:1. When the level of the latter in the secretion increases, cholesterol accumulates in the gallbladder (GB) and settles on its walls. As a result, the likelihood of cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis) increases. This disease develops as a result of excess weight, poor nutrition, diabetes, and hereditary predisposition.
In addition, the risk of bile ducts increases with increasing concentrations of bilirubin (bile pigment). This condition is provoked by hemolytic anemia, infectious diseases of bacterial origin in the gallbladder. Pathogenic microorganisms multiply and produce lithocholic acid, which causes JP.
The basis of this disease is a change in the physicochemical properties of the composition of bile, in which there is 3-5 times more cholates. This contributes to their deposition on the walls of the bladder and ducts, the development of inflammation and the formation of stones.
Many people find out about the presence of sediment in the lumen of the gallbladder by chance, during an ultrasound examination. If you or your child have been diagnosed with gallbladder dyscholia, do not be upset and think that this will definitely lead to the formation of stones. If at this stage you pay attention to the nature of your diet, start using soft tubes and do not let the bile stagnate, you can avoid complications.
Etiology
Violation of the properties and composition of bile occurs under the influence of many factors.
Among them:
- Infectious lesions.
- Entry of pathogenic flora into the gallbladder from the intestines. Disturbances in the composition of bile are the result of hematogenous or lymphogenous infection. The source of infection is any focus of chronic inflammation - for example, appendicitis, tonsillitis, or periodontal disease.
- Damage to the hepatocholedochoduodenopancreatic zone.
Additional factors in the development of the disease are:
- violation of the diet - the disease provokes irregular nutrition, abuse of harmful foods;
- hereditary predisposition;
- disruptions in metabolism;
- poor circulation of bile components;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hypotension of the organ;
- helminthic infestation - infection with roundworms, lamblia, opisthorchiasis;
- endocrine disorders.
Most of the etiological factors can be prevented if you are careful about your health.
What is dyscholia?
This is a pathological process in which the physico-chemical composition of bile secretion is disrupted. For example, if the concentration of cholesterol in bile increases, this creates ideal conditions for the development of gallstone disease. The secretion of the gallbladder is simply irreplaceable in the process of digesting food.
Let us highlight the most important functions of bile:
- breakdown of fats;
- absorption of proteins and cholesterol;
- stimulation of pancreatic enzymes;
- normalization of the small intestine;
- activation of mucus formation;
- protection against hydrochloric acid.
With dyscholia, bile thickens.
Often, dyscholia of the gallbladder develops against the background of diabetes mellitus and obesity. Hereditary predisposition also plays a role in the occurrence of the disorder. The disease can develop at any age, even in childhood. With dyscholia, the amount of bile in the gallbladder can rapidly increase, while its minimal amount is found in the liver.
The pathological process also deforms the bile itself: the active elements are dissolved, and the enzymes may have an unacceptable concentration. A violation can lead to impaired tissue motility, that is, biliary dyskinesia, cholecystitis, biliary pancreatitis, as well as the appearance of malignant polyps. Bile is a secretion of hepatocytes produced to break down food. It actively participates in the digestive process, entering the intestines through the bile ducts:
- promotes the absorption of fats and vitamins;
- helps process “good” cholesterol;
- participates in metabolic processes;
- regulates intestinal motor activity;
- neutralizes the aggressive effects of gastric juice.
The composition of bile includes cholesterol, bilirubin, bile acids, amino acids, etc. With dyscholia, it changes. Even a small violation can cause unpleasant consequences for human health.
Treatment options
To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, you must follow certain rules:
| № | Rule |
| 1 | Follow the recommended diet and nutrition regimen. |
| 2 | Do not forget about physical activity, which helps prevent the development of stagnant processes in the body. Physical activity should be moderate, the patient should not overexert too much. |
| 3 | It is important to protect yourself from stress and strong emotional experiences. |
| 4 | Drinking mineral water based on alkaline components. |
| 5 | Taking medications prescribed by a doctor. |
Drug treatment
To eliminate the manifestations of the disease, medications of the following groups are prescribed:
- Analgesics to relieve severe pain;
- Antispasmodics that eliminate spasms of the digestive system;
- Enzyme preparations to facilitate food digestion;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate inflammatory processes in the gallbladder and other nearby organs;
- Choleretic drugs to normalize the flow of bile;
- Drugs that increase the amount of bile produced. These products can be of natural or synthetic origin. The medicine has a wide spectrum of action, that is, it allows not only to normalize the process of bile production, but also to eliminate increased gas formation, normalize intestinal function, and reduce the viscosity of bile;
- Antibacterial agents if the disease is accompanied by secondary infection of the affected organ.
Surgery
If drug treatment is ineffective, and the formation of gallstones cannot be prevented, the patient is prescribed surgery. Surgical treatment involves removing the affected organ in various ways. Laparoscopy is considered the most popular method, since this operation is considered minimally invasive and less traumatic for the patient.
A small incision is made in the abdominal cavity, through which a laparoscope equipped with a camera and 2 tubes is placed inside to control the surgical instrument. Using a special instrument, the affected organ or part of it is removed. The duration of the operation is no more than an hour, the rehabilitation period is minimal.
Traditional methods of treatment
The use of traditional medicine recipes is justified if the disease is at an early stage of its development. However, these treatment methods can only be used as an auxiliary therapy that complements the main treatment prescribed by a doctor. The following recipes have worked well:
- Consumption of bran. The product can be added to cereals, yoghurts, and other foods. At the same time, at first it is not recommended to consume more than 0.5 tsp. bran 3 times a day. After 3-4 days, this amount is increased to 1 tsp. Bran helps reduce cholesterol in bile and has a cleansing effect;
- Strawberries promote the delicate removal of bile. To obtain a therapeutic effect, you can brew tea from the dry leaves of the plant, infuse its fruits by pouring boiling water over them, or eat the berries fresh (if there is no allergic reaction);
- A decoction of rose hips has a general strengthening effect . The product is poured with boiling water, heated in a water bath, cooled, filtered;
Diet
Proper nutrition involves excluding foods high in fat, limiting the consumption of spices, salt, pickled and canned foods.
Preference should be given to vegetables that have undergone heat treatment (boiling, stewing, steaming), cereal milk porridges, low-fat dairy and fermented milk products.
Characteristics of the disease
Gallbladder dyscholia is a disease in which a change in the composition of bile, its physical and chemical characteristics occurs.
Bile, necessary for digesting food, has a rather complex composition, which includes various types of bile acids, bilirubin, cholesterol and other components.
With dyscholia, the cholesterol content in the bile increases, which causes the formation of solid compounds in the cavity of the gallbladder, which settle on the walls of the organ. And this, in turn, contributes to the development of gallstone disease and the appearance of corresponding symptoms.
Symptoms of the disease
Any disturbances in the functioning of the liver and gallstones are manifested by dull pain on the right side of the abdomen, under the ribs. If stones have already formed, the pain may be severe. Symptoms depend on which components of the bile are in excess or insufficient quantities. Their intensity may vary, but when pathology occurs, unpleasant sensations visit the sick person regularly.
In addition to pain, the following may periodically appear:
- heaviness in the abdomen, a feeling of fullness (especially with stagnation of bile);
- bitter taste in the mouth due to the reflux of bile into the stomach;
- nausea;
- bowel disorders - constipation, diarrhea;
- vomiting (rarely) streaked with bile;
- general weakness, lethargy due to poor digestion of food and the presence of an inflammatory process.
After eating high-calorie, fried and fatty foods, symptoms usually worsen.
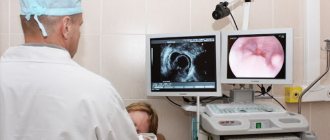
For a more accurate diagnosis, an ultrasound examination of the gallbladder is performed, and, if necessary, other abdominal organs. An analysis of the composition of the fluid taken during probing of the bladder is performed, as well as a blood and urine test. An increase in cholesterol and alkaline phosphatase is often found in the blood, and bilirubin in the urine. To identify parasites, the patient's stool is examined.
Often dyscholia is detected already at the stage of stone formation. It is very important to pay attention to pain and other symptoms in time in order to begin therapeutic treatment. This will help avoid the formation of large stones, which may lead to the need to remove the gallstone.
Small stones and sand can dissolve on their own with appropriate treatment, but large ones cannot be dealt with using conservative methods.
Functions of bile and its composition
The main function of bile is to participate in the digestion process. It is carried out in the following directions:
- breakdown of fats, absorption of cholesterol in the intestines;
- activation of enzymes for subsequent absorption of proteins;
- stimulation of pancreatic enzymes.
Its other functions are no less important:
- regulation of motor activity of the small intestine;
- stimulation of mucus formation in the intestines;
- reducing the aggressive action of gastric juice.
The composition of bile is represented by the following components:
- bile acids (cholic, deoxycholic, chenodeoxycholic);
- bile salts (glycocholic and taurocholic compounds);
- bile pigments (bilirubin, biliverdin);
- cholesterol;
- water.
Most often, cholesterol concentration increases. Normally, it should be half as much as bile acids. If cholesterol levels increase, it begins to accumulate in the gallbladder and settle on its walls. As a result, the risk of developing gallstone disease increases.
The reasons for this violation come down to:
- poor nutrition;
- being overweight;
- endocrine diseases, including diabetes mellitus;
- hereditary predisposition.
JP can also be manifested by an increase in the concentration of the bile pigment bilirubin. In this case, dietary habits are not particularly important, since this phenomenon is caused by hemolytic anemia or bacterial infection.
Pathogenic microorganisms (staphylococcus and Escherichia coli) multiply quickly and produce lithocholic acid during their vital activity, which leads to dyscholia. They can enter the body in different ways:
- from the external environment;
- through blood from any internal source of inflammation (appendicitis, periodontal disease, tonsillitis);
- through lymphatic vessels.
Diseases of the stomach and intestines can provoke dyscholia. A sedentary lifestyle also plays a negative role, as it negatively affects the neuromuscular apparatus of the gallbladder. As a result, pathologies such as hypotension (low tone) and atony of the muscles of the organ (lack of tone) develop.
All diseases of the gallbladder and its ducts are interconnected. Due to metabolic disorders, neuroses, and parasitic infestations, dyskinesia of the gallbladder develops with disruption of its peristalsis, which leads to dyscholia, which, in turn, leads to the development of cholelithiasis.
Principles of treatment
Dycholia itself does not require treatment. Problems arise when pathology leads to various diseases. In this case, treatment will be symptomatic, and the drugs and methods chosen depend on the disease.
Diet food
Food should not overly burden the gallbladder and liver. Therefore, patients with dyscholia are recommended diet No. 5 with some indulgences. With dyscholia, it is not necessary to completely give up foods prohibited in the diet, but it is worth limiting their use. Such foods include:
- fatty and fried foods;
- strong coffee, cocoa, tea;
- sweets, baked goods;
- heavy food - mushrooms, legumes.
Eat 4-5 times a day, in small portions. Dishes from the prohibited list cannot be included in the diet more than 2 times a week; it is not advisable to eat them at night.
Drugs
The list of medications for dyscholia depends on the severity of the provoked disease and its symptoms. May be prescribed:
- Painkillers - No-shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine for inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder.
- Choleretic drugs – Ursodeoxycholic acid, Betaine, Phenipentol.
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections are selected depending on its type.
- Hepatoprotectors to improve liver function - Essentiale, Heptral, Phosphogliv.
Operation
For dyscholia, surgery is not required. It is carried out when emergency conditions arise, for example, blocking of the bile duct with a stone. In all other cases, doctors prefer conservative treatment, since it is impossible to surgically remove the suspension from the bile.
Other methods
With dyscholia and the pathologies it leads to, it is important to change your lifestyle. Necessarily:
- Avoid nervous situations, especially before meals. Psycho-emotional arousal disrupts the production of bile.
- Quit smoking, alcohol, drugs. They injure tissues and organs, which leads to increased negative effects of dyscholia.
- Prevent stagnation in the body. A sedentary lifestyle will not bring benefits, so it is worth including sports in your daily routine. This could be walking, running, swimming, aerobics, etc. It is best to consult with your doctor before choosing a sport. He will give recommendations taking into account all existing diseases and contraindications.
The essence of pathology
Bile, which is a complex complex of substances, ensures the subsequent breakdown in the intestines of semi-digested food that enters it from the stomach. Produced in the liver, bile accumulates in the bladder. Its concentration here is several tens of times higher than in the liver. The bladder functions not only as a reservoir, but also as a regular supplier of these enzymes to the duodenum.
In a healthy person, bile contains bile acids, cholesterol, bilirubin, phospholipids and other biologically active substances. Moreover, it is important that there are twice as many bile acids as cholesterol. With dyscholia, both the chemical composition of bile and its physical properties change.
The most problematic thing is that the physiological proportion of bile acids and cholesterol is disrupted (2:1). As a rule, the amount of the latter increases many times, and it is deposited on the walls of the bladder. As a result, the normal functioning of the intestines is disrupted, and digestive disorders occur.
In addition, conditions appear favorable for the formation of stones in the bladder. Frequent complications of dyscholia include dyskinesia (weakened motility) of the biliary tract, biliary pancreatitis, and cholecystitis. The possibility of the formation of polyps, which can develop into malignant tumors, cannot be ruled out.
How to improve the contents of the gallbladder
To adjust the composition of bile in children, doctors prescribe choleretic drugs:
- choleretics with natural bile – Allochol;
- choleretics with lektravas - Holosas, Flamin, Holemaks, Chofitol, Febichol;
- synthesized choleretics – Osalmid, Nikodin, Oksafenamide;
- cholespasmolytics - Spasmonet, No-shpa, Atropine, Drotaverine, Spazoverine, Metacin, Ple-Spa, Platyfillin;
- cholekinetics – Magnesium sulfate, Cormagnesin, Valerian, Magnesia, Valerianahel.
Their dosage is calculated based on the body weight of the small patient. Drugs for dissolving stones are given to children for a long time - up to 8 months.
Among the folk remedies, the condition of the bile ducts quickly improves with tea made from wild strawberry stems. The twigs are collected during the flowering period of the crop. The raw material is brewed fresh or dry and given to children as regular tea.
To enhance bile secretion, the drink is prepared from dried strawberries. 1 tbsp. l. berries are thrown into a thermos and poured 400 ml of boiling water. After some time, the product is filtered and given to children before meals, 80 ml.
Dyscholia will disappear in a short time if you give your child sauerkraut juice. Let the baby drink it 3 times. per day in 30 minutes. before meals 1 tbsp. l. But if he suffers from arrhythmia, gastritis, kidney disease or stomach ulcer, such juice therapy is not carried out.
Our specialist comments
- During the treatment of the gallbladder, give children alkaline mineral waters. Natural hydrocholeretics are Essentuki No. 4 and No. 17, Borjomi, Slavyanovskie Vody.
- With bile dyscholia, it is important to strengthen the baby’s immunity. Steam rose hips by brewing them in a thermos. Proportion – 2 tbsp. l. fruits for 2 cups of boiling water.
- To detect gallstones in a timely manner, take your baby for an ultrasound examination at least once a year. Dycholia is a serious disorder. Often it begins the development of pathologies that distort the activity of the entire digestive system.
The doctor explains how to treat gallbladder diseases:
Source: LechenieDetok.ru
Types of disease
Pathology, depending on its course, can be:
- Spicy. The disease develops over several days or hours. It is characterized by pronounced symptoms. This pathology, in the case of timely seeking medical help, proceeds quite favorably.
- Chronic. If the acute form of the disease was not given due attention or the disease was treated incorrectly, then the patient develops precisely this stage. The disease may be asymptomatic. It usually develops gradually. Chronic cholecystitis (symptoms and treatment) deserves special attention. Diet plays one of the most important roles in the fight against pathology.
Chronic cholecystitis is divided into:
- to sluggish (latent);
- recurrent;
- purulent-ulcerative.
Based on the presence of stones, there are 2 forms:
- acalculous (without cholelithiasis);
- calculous.
A chronic disease is characterized by stages:
- remission;
- exacerbations.
Diagnosis and treatment
A preliminary diagnosis can be made based on clinical symptoms. An ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, gastroduodenoscopy, and a biochemical blood test will help confirm the doctor’s concerns. The specialist will certainly examine the patient, establish his neurological status, collect information about the diseases of his close relatives, and also learn about the individual characteristics of the body.
Therapy for dyscholia should be comprehensive and includes a correct daily routine, dietary nutrition, physical activity and medication. The following drugs will help relieve pain, eliminate the cause of the disease, improve the functioning of the digestive tract and cleanse the body:
- enzymatic agents;
- antispasmodics;
- analgesics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antibiotics for bacterial infections.
Preventing dyscholia is much easier than treating it. Preventive measures include the following:
- avoid stressful situations;
- periodic examination;
- a balanced diet, including the consumption of vegetables and fruits;
- playing sports;
- giving up bad habits: drugs, smoking and alcohol abuse.
Stressful situations and emotional overload can cause an exacerbation of the disease, so try not to be nervous
At-risk groups
Dyscholia of the gallbladder occurs in children and adults. If parents have liver and gallbladder diseases, in particular gallstone disease, then the risk of bile sediment formation and changes in its composition in the child increases sharply.
It is recommended to immediately contact a pediatric hepatologist immediately after detecting this disorder. The doctor will tell you what dyscholia is in children, why it occurs and how to prevent the formation of stones.
Among the predisposing factors are the following:
- any chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, especially bends and curvatures of the gallbladder;
- underweight or, conversely, a tendency to obesity;
- increased cholesterol levels;
- abuse of fatty and fried foods;
- previous intestinal infections;
- the presence of worms;
- taking certain medications (ceftriaxone, hormonal contraceptives);
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrine diseases;
- poor diet;
- rare meals;
- lack of regular physical activity.
It is worth noting that biliary dyscholia presumably occurs under the influence of several unfavorable factors. But it is impossible to say exactly what affected the composition of bile. Experts can only guess by studying the patient’s medical history, lifestyle and complaints.
Why is bile needed in the human body?
Bile is directly involved in digestion. Therefore, it performs several functions simultaneously:
- Breaks down fats and prevents cholesterol from being absorbed in the intestines.
- Activates the production of enzymes that allow the absorption of proteins.
- Stimulates the synthesis of pancreatic enzymes.
- Regulates intestinal motility.
- Stimulates the formation of mucus in the intestines.
- Does not allow gastric juice to act aggressively on the stomach.
Having a full understanding of what it is - gallbladder dyscholia, treatment should be timely and comprehensive. The faster a person can respond, the easier and safer the therapy will be.
Symptoms and signs of dyscholia in children and adults
The characteristic signs of dyscholia in children and adults are often absent. This is the reason for late diagnosis. Complaints about well-being appear when the walls of the gallbladder become inflamed and concomitant disorders occur—cholecystitis.
Possible clinical manifestations of dyscholia in children and adults:
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- abdominal pain after eating;
- nausea, possible vomiting, especially after fatty and fried foods;
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth, heartburn;
- excessive gas formation.
It is most difficult to identify the first signs of gallbladder dyscholia in children who, due to their age, cannot clearly talk about their sensations and the location of the pain. Pay attention to your child's mood, especially after eating.
If children are capricious after eating, put their hands on their stomach, or complain of pain, it is imperative to undergo ultrasound diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract.
Parents should also be wary of increased gas formation in the intestines. In the absence of helminthic infestations and dysbacteriosis, one can suspect pathologies of the biliary tract, which are often accompanied by flatulence.
The formation of the disease depends on the level of cholesterol production. Due to a change in the physicochemical composition of bile, its uneven distribution occurs. It begins to accumulate in the gallbladder, and in the liver the concentration of bile decreases below the permissible minimum. All enzymes that are secreted by organs may also have abnormal concentrations.
Since the development of the disease is closely related to increased production of cholesterol, in addition to dyscholia, the patient may begin the process of stone formation in the bile ducts.
This pathology is divided into 2 types:
- Exogenous. Its occurrence is provoked by external factors.
- Metabolic. The cause of the disease is internal factors.
For treatment to be effective, it is necessary to find out what disease caused the pathology. Symptomatic therapy will only temporarily alleviate the patient's condition.
Dyscholia of the gallbladder in children and adults may have the following sources:
- infectious lesions of the gallbladder;
- diabetes;
- genetic predisposition;
- the presence of cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder);
- chronic diseases (periodontal disease, tonsillitis, appendicitis);
- coli;
- pathological processes in the pancreas or liver;
- helminthic infestation;
- psychoemotional disorders;
- diseases of the digestive system.
Metabolic disorders in the body, which is also one of the factors in the development of dyscholia, may be a consequence of poor nutrition.
Types and causes of dyscholia
The main cause of dyscholia is a change in the composition of bile synthesized by the liver. Depending on the cause that provoked the pathology, dyscholia can be:
- Exogenous. In this case, the violation is provoked by external factors.
- Metabolic. It occurs due to malfunctions of the body and hereditary factors.
The exact cause of dyscholia has not been established. As a rule, patients with dyscholia have a history of:
- Hereditary predisposition to the formation of suspension in the bile. A common cause of dyscholia in childhood.
- Gastrointestinal and liver diseases.
- Endocrine disorders affecting the digestive system, such as diabetes.
- Parasitic infections.
- Eating disorders, imbalance in diet.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of dyscholia manifest themselves in the same way in both children and adults. The intensity of the manifestation of signs of the disease depends on the individual characteristics of the organism, the provocateur of the pathology, the degree of severity, etc.
Characteristic of gallbladder dyscholia is pain in the right hypochondrium. Unpleasant sensations intensify after eating food, especially high-carbon food. The nature of the pain can be sharp and dull. Symptoms subside after a few hours. If you apply a heating pad to the right side, the patient will feel relief.
Other signs of dyscholia include:
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- increased gas formation;
- stomach upsets;
- constipation;
- nausea;
- vomit.
Individual intolerance to certain foods may appear that did not cause any side effects before the disease developed.
It should be borne in mind that not all of the above symptoms must necessarily be observed in a patient with dyscholia.
How to find out about the disease?
It is not at all difficult to understand that a person has a disease such as gallbladder dyscholia. The symptoms speak of this more than eloquently. But it’s still worth seeing a doctor – a specialist who can conduct a full diagnosis. As a rule, the main diagnostic methods are:
- Blood donation.
- Ultrasound.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Of course, the doctor will be able to not only interview the patient, but also examine him by palpation. As soon as the test results are ready, the specialist will be able to get a complete picture of the disease and begin therapy. The doctor must select individual treatment for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Treatment of dyscholia
After the root cause of dyscholia, the severity and damage to the body, provoked by a combination of pathological processes, have been established, the doctor makes a final diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment.
The therapeutic course includes several basic provisions:
- Treatment of the disease that caused dyscholia.
- Dieting.
Elimination of stagnant processes in the bile ducts. The patient is prescribed medications, the action of which is aimed at increasing the production of bile and improving its outflow.
Normalization of emotional state. Mental health has a great impact on the functionality of all organs and systems.
A diet that will reduce the symptoms of the disease and help normalize bile production involves avoiding fatty foods. Proper nutrition means introducing into the diet only those dishes that are steamed, boiled or baked. For cooking, use only olive or vegetable oil. Fatty fish and meats are excluded from the diet. Spicy seasonings, smoked meats and other products that can negatively affect the functionality of the digestive system should also be avoided.
The patient is recommended to eat frequently (5-6 times a day), but in small portions. You should also follow a routine, i.e., eating should happen at the same time every day.
In order for the treatment to be successful, in addition to following all medical recommendations, the patient is recommended to normalize his physical activity.
ethnoscience
Conservative treatment of gallbladder dyscholia is supplemented with traditional medicine. With the correct choice of medications and their dosage, such therapy is considered gentle. It is precisely because of the mild effect on the body that folk recipes are recommended for children.
Anti-inflammatory and choleretic drugs include:
- Wheat bran. They are poured with boiling water, infused, and then added to food. Bran helps reduce cholesterol levels.
- Wild strawberry. Has a mild choleretic effect. Not only the fruits of the plant have healing properties. Tea is made from strawberry leaves.
- Sauerkraut juice. For dyscholia, which is combined with an ulcer or gastritis, this therapy is carried out.
- Rose hip. A decoction of berries helps strengthen the immune system. This remedy helps lower blood pressure. Therefore, if the patient has hypotension, rose hips are contraindicated.
- Decoction of immortelle inflorescences. It has a choleretic effect and normalizes its composition.
- Mint. Soothes pain in the right hypochondrium and relieves inflammation. Peppermint tea will help cope with bouts of nausea.
- Boiled beet juice. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and normalizes bile secretion.
- Tincture from angelica roots. Improves the functioning of the endocrine system and has an analgesic effect during an attack of pain. It has a positive effect on the digestive system and the body.
- Corn silk. The decoction promotes the outflow of bile and normalizes its concentration in the organs.
Traditional medicine recipes are good assistants in the process of basic treatment. But you cannot try to cope with the disease on your own using only such treatment methods. Incorrect dosage or the presence of contraindications to the use of a particular drug can only worsen the patient’s situation. Self-medication is especially dangerous for children. To prevent the development of complications, you should consult your doctor before using any folk remedy.
In order to prevent complications in the future, patients whose dyscholia has been treated in a timely manner are recommended to undergo regular scheduled examinations for the purpose of prevention and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Diet for dyscholia
For dyscholia, treatment table No. 5 is prescribed. But there is no need to follow a strict diet if there is no pain or other complaints about your health. The main thing is to give up fatty and fried foods, which, even in a person without signs of dyscholia, cause pathological changes in the gall bladder and liver.
But remember that the composition of bile and its lithogenicity can be influenced by other factors, for example, taking contraceptives causes the formation of sludge (sand) in many women. Pregnancy also contributes to this. But nutrition still plays a key role in the timely outflow of bile and maintaining the functionality of the biliary tract organs.
Basic principles of nutrition for dyscholia:
- try to eat at least 4-5 times a day, but in small portions;
- do not drink immediately after meals so that there are enough digestive enzymes and bile to digest food;
- avoid overeating;
- limit not only fatty fried foods, but also spicy foods, marinades, and sour juices.
The diet should be as varied as possible. For dyscholia, fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs and all dishes that contain plant fiber are useful. It cleanses the intestines, stimulates the growth of beneficial microflora, and prevents constipation, which plays a key role in the development of cholelithiasis and cholecystitis.
Prohibited Products
A diet for dyscholia requires limiting the following foods:
- fatty fish and meats;
- alcohol;
- smoked meats, sausages;
- spices, marinades, all canned foods;
- sour juices;
- extractive substances contained in garlic, onions, radishes;
- gas-forming products (cabbage, corn, legumes);
- carbonated drinks.
To prevent complications of dyscholia, it is recommended to steam, boil or bake food. It is not advisable to fry, even if there are no complaints. With this diagnosis, you can quickly and deliciously cook in a slow cooker.
The daily diet must include porridge with water or milk, vegetable and fruit salads, low-fat fish and meat. It is recommended to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day, preferably, in addition to clean water, use infusions and decoctions of rose hips, which have a mild choleretic effect.
Discholia #8212; Why do abnormalities develop in the gallbladder?
The gallbladder is an important organ of the digestive system that receives bile from the liver and continuously distributes it into the duodenum in a certain amount, which depends on food intake.
Bile performs an equally important function, because it contributes to the normal digestion of coarse and fatty foods that enter the human body, crushing large particles for normal absorption. If for some reason a certain malfunction occurs in the biliary system, unpleasant diseases arise, fraught with some complications.
There are several diseases associated with the biliary organ, one of which is dyscholia. This term characterizes provoked disturbances in the composition of bile, which can occur due to an incorrect lifestyle, as well as due to developed diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
If any abnormalities in the functioning of the gallbladder are detected, you must urgently seek help from a gastroenterologist! Treatment in the early stages of the disease is more gentle and short-lived, and in case of advanced disease, surgical intervention and sometimes death cannot be ruled out.
Causes of dyscholia
Bile contains different components: phospholipids, bilirubin, biological compounds, cholesterol, bile acids and other elements. With normal organ functionality, the amount of cholesterol and bile acids is in a 1:2 ratio.
Any negative changes can lead to an increase in cholesterol levels several times, and this phenomenon provokes favorable conditions for the formation of gallstones.
When the level of cholesterol in the biliary system increases, dyscholia occurs. As a rule, several factors contribute to this, for example, excessive consumption of fatty foods, obesity, and advanced diabetes mellitus.
In some cases, dyscholia occurs against the background of hemolytic anemia, which provokes a sharp increase in the level of bilirubin in the bile. The action of pathogenic microorganisms in the bile organ negatively affects lithocholic acids, which can also cause the development of dyscholia.
Features of the development and treatment of JP in children
Dycholia can occur at any age. The causes of gallbladder dysfunction in children are approximately the same as in adults:
- nutritional and metabolic disorders;
- parasites;
- infectious diseases;
- congenital pathologies.
Children, especially young ones, do not always understand what hurts them. If a child complains of abdominal pain, flatulence, stool problems and nausea, a full diagnosis and ultrasound of the digestive tract is performed.
If abnormalities in the functioning of the gallbladder are detected, safe medications are prescribed. Many doctors recommend Gepabene as the most effective herbal remedy based on milk thistle. The course of its administration is 1-2 months.
Decoctions of medicinal plants - yarrow, immortelle, corn silk, rose hips, angelica root - are effective in the treatment of liver and gall bladder diseases. Drinks promote the outflow of bile and increase the tone of the organ. Do not forget about following a diet and moderate physical activity.
To prevent dyscholia, you first need to adhere to proper nutrition. Not only during illness, but also after recovery, it is worth following a light diet. It will help to avoid other disorders in the digestive system.