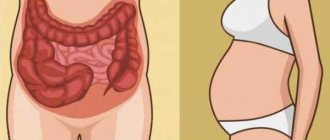
general description
There is always some fluid in the abdominal cavity of a healthy person, which is absorbed by the lymphatic vessels.
With various diseases, the rate of fluid formation increases, and its absorption worsens, fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity and ascites develops. Signs of this disease are an enlarged abdomen, pain of varying intensity, and shortness of breath. Before starting treatment for ascites, it is necessary to find out the causes of its occurrence. Symptomatic therapy consists of taking diuretics and periodically removing fluid from the abdominal cavity using puncture.
Possible complications and consequences
At first glance, it seems that pumping out fluid from the abdominal cavity is a simple and safe procedure. Like any other surgical procedure, it may result in unwanted reactions. The most harmless of them is the formation of a hematoma. It is formed in cases where the surgeon damages small and large vessels while performing a puncture.
Very rarely, careless actions of medical personnel can lead to damage to internal organs. Then laparocentesis can be complicated by massive bleeding and death of the patient.
If antiseptic rules are not followed, phlegmon of the abdominal wall is formed. This disease causes acute diffuse purulent inflammation of fatty tissue. It spreads quickly and involves muscles in the pathological process. The patient develops a red swelling in the affected area. It has severe pain. The skin above it is shiny. Palpation reveals a compaction without clear boundaries, hot to the touch, motionless. Lack of treatment leads to the formation of softening in the area of compaction and the appearance of a fistula. The development of abdominal phlegmon causes an increase in body temperature to 40 degrees. The patient feels weak and very thirsty.
The consequence of laparocentesis for ascites can be bleeding.
Causes of ascites
The disease occurs under the influence of the following etiological factors:
- Liver pathologies. As a result of the death of hepatocytes, they are replaced by scar tissue, the size of the liver increases, and it begins to compress the portal vein, which ultimately leads to the development of dropsy.
- Lack of protein.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Kidney diseases.
- Gynecological diseases.
- Myocardial diseases. Most often, dropsy develops with pericarditis or heart failure. An enlarged and weakened heart cannot cope with pumping blood, which accumulates in the vessels, which can lead to fluid accumulation.
- Pathologies of the lymphatic system.
- Systemic pathologies.
- Damage to the peritoneal surface. The development of dropsy can be caused by diffuse, fungal or tuberculous peritonitis.
- Bad habits.
- Myxedema. With this disease, swelling of the mucous membranes and soft tissues occurs, the cause of which is a violation of the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
- Polyserositis.
- Poor nutrition. Particularly dangerous are fasting and constant strict dieting.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The risk group includes the following categories of people:
- drug addicts;
- patients who have undergone a blood transfusion procedure;
- obese people;
- patients suffering from various types of hepatitis;
- hemodialysis patients;
- people who are interested in tattooing;
- people with a hereditary predisposition to the disease.
Ascites in children can be hereditary, acquired or congenital. The following are the main reasons for the development of this pathology in young patients:
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Congenital general edema, which can be caused by Rh conflict between the organisms of the mother and fetus. Children born with this pathology have no chance of survival and die within a few hours.
- Exudative enteropathy. It is a hereditary pathology.
- Damage to the liver and bile ducts in infants.
In older children, the reasons are basically the same as in adults.
Symptoms
With ascites, which accompanies cancer, heart failure and a number of other ailments, many patients complain of the following symptoms:
- Bloated, enlarged abdomen. As a result of the constantly increasing amount of fluid in the peritoneum, the patient's weight increases. Difficulty breathing and eating. Heartburn or nausea often occurs.
- Infections. If left untreated, the patient may experience peritonitis, and heart and kidney failure often develops. In such cases, doctors' forecasts are extremely negative. Patients are prescribed a long course of antibiotic therapy.
- The appearance of a hernia (umbilical, inguinal) due to constant pressure inside the peritoneum.
- Impaired urine output.
- Shortness of breath, even in a calm state, which can occur due to the accumulation of fluid in the lung area.
- Swelling of the limbs.
- Fast fatiguability.
Stages of ascites
There are three stages of abdominal dropsy:
- There is an accumulation of a small (up to 400 milliliters) amount of fluid, which is usually discovered by chance during an ultrasound or MRI for other diseases. No pathological changes are observed, all organs are functioning normally. If a patient with stage 1 ascites notices any unpleasant symptoms, they are usually associated with a concomitant disease.
- The amount of liquid can reach up to four liters. The patient notices that his abdomen is enlarged and shortness of breath appears, which worsens when lying down. At this stage, a specialist can already make a diagnosis based on examination of the patient and palpation of the abdomen.
- The volume of liquid can exceed ten liters. The patient's condition worsens, complications of ascites arise, and emergency medical care is required.
A separate form of the disease is refractory ascites. It does not respond to therapy, and even pumping out the fluid does not save the situation, as it quickly comes back. The prognosis for this form of dropsy is unfavorable and can result in death.
Classification
Depending on the amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity, there are several degrees of the pathological process:
- Small ascites (no more than 3 l).
- Moderate (3–10 l).
- Significant (massive) (10–20 l, in rare cases – 30 l or more).
Based on the level of infection of ascitic contents, the following are distinguished:
- sterile (uninfected) ascites;
- infected ascites;
- spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
According to the response to therapy, ascites occurs:
- transient. Disappears against the background of conservative treatment in parallel with the improvement of the patient’s condition forever or until the next exacerbation of the pathological process;
- stationary. The appearance of fluid in the abdominal cavity is not a random episode; it persists in a small amount even despite adequate therapy;
- resistant (torpid, or refractory). Large ascites, which cannot only be stopped, but even reduced with large doses of diuretics.
If the accumulation of fluid continues to increase steadily and reaches enormous sizes, despite the treatment, such ascites is called tense ascites.
Symptoms of ascites
The development of the disease can be gradual or spontaneous. The first symptoms of ascites appear when fluid accumulates in an amount of one liter or more.
The main clinical signs are a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, abdominal pain of varying intensity, an increase in abdominal volume, a dull sound when tapping the abdominal area, protrusion of the navel, swelling and cyanosis of the extremities, difficulties arising when trying to bend the body forward, rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath when walking .
In a lying position, the patient’s abdomen blurs, and in a standing position it becomes spherical. Over time, the skin on the abdomen becomes covered with stretch marks, and the navel begins to protrude.
Patients with dropsy have a decreased appetite, they quickly eat enough, and in some cases refuse to eat at all. At the same time, their abdominal volume continues to grow. In men, the legs and external genitalia may swell.
In addition, the symptoms of dropsy depend on the underlying disease that caused it. Thus, with high pressure in the portal vein, the veins under the skin dilate greatly, which is why the stomach begins to resemble the head of a jellyfish.
If the cause of dropsy is liver pathology, then in addition to fluid accumulation, the patient experiences symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and jaundice.
With tuberculosis, in addition to dropsy, weight loss, tachycardia, general weakness, and headaches are observed. If ascites occurs due to protein deficiency, then the abdomen increases in size quite slowly.
With thrombosis of the portal vein, dropsy is accompanied by severe pain, enlargement of the spleen and liver. Severe bleeding from the anus may occur.
An increase in body temperature occurs rarely (with pancreatitis, liver cirrhosis, peritonitis, various neoplasms).
With myxedema, which is one of the causes of the disease, body temperature drops to 35 degrees and below. This is due to a decrease in metabolic processes in the body due to a lack of production of thyroid hormones.
| Ascites (photo) |
Symptoms
In cancer patients, ascites develops gradually over several weeks or months. Patients feel symptoms when a significant amount of fluid accumulates. Main symptoms:
- bursting heaviness in the abdomen;
- belching after eating;
- heartburn or nausea;
- dull pain in the abdomen;
- shortness of breath at rest, especially when lying down.
These signs are associated with the rise of the dome of the diaphragm, impaired peristalsis of the esophagus, intestines, and reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus. Some patients complain of attacks of cardiac arrhythmia. Upon observation, the attending physician reveals an enlarged abdomen. In a standing position, it goes down, the navel protrudes.
Patients with “liver” ascites are characterized by a “jellyfish head” pattern due to the formation of dense dilated veins around the navel. The accumulation of fluid creates difficulties when bending over and putting on shoes.
Unfortunately, there are still frequent cases of identifying young women with an ovarian tumor in an advanced state, who for a long time were confident in their pregnancy, this was facilitated by the cessation of menstruation.
The accumulated fluid itself puts pressure on the tumor, causing decay. Metastasis through the venous system and heart failure is manifested by obstructed blood flow to the heart. This leads to swelling of the feet, legs, and external genitalia.
All the described symptoms do not develop in isolation. In the first place there are signs of a malignant tumor. Ascites requires additional treatment because living with its manifestations becomes more dangerous due to the possibility of other complications.
Diagnosis of ascites
A doctor can diagnose dropsy at the first appointment by examining the patient and palpating the abdomen. To confirm the diagnosis and identify possible causes of the disease, the following studies may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound - determines the size and current condition of organs, the presence of tumors or other pathologies, the amount of fluid;
- - carried out if, using an ultrasound, the doctor was unable to find out everything he needed to make a final diagnosis;
- Dopplerography - detects blood flow disturbances;
- radiography - detect the presence of fluid and its location;
- blood analysis;
- esophagogastroscopy;
- puncture followed by examination of ascitic fluid;
- Analysis of urine.
Treatment of ascites
Removing fluid from the abdominal cavity is usually quite simple, but if the underlying disease that led to the onset of ascites is not treated, dropsy will occur again and again.
Therefore, together with the removal of fluid, therapy for the underlying pathology should be carried out.
General recommendations for patients with hydrops are:
- bed rest;
- limiting salt intake, which causes fluid retention;
- limiting fat;
- introducing a sufficient amount of protein food into the diet;
- if the development of ascites is associated with cirrhosis, then limit fluid intake to one liter per day.
The choice of drug treatment depends on the underlying disease that caused the development of dropsy. All patients are advised to take diuretics.
In addition, the following medications may be prescribed:
- hepatoprotectors (for liver pathologies);
- means for maintaining the functioning of the heart muscle - in case of heart failure;
- protein preparations.
Surgical methods are indicated when there is a large amount of fluid, as well as in the absence of results from conservative treatment.
The main methods of surgical treatment of ascites are:
- Abdominal puncture. It is performed to remove fluid in the abdominal cavity. Using this method, up to 5 liters of liquid can be removed. The procedure requires hospitalization of the patient and may take several days. If the fluid needs to be pumped out regularly, the patient is given a special catheter, which greatly facilitates the procedure.
- Deperitonization of the peritoneal walls. During this operation, the surgeon cuts out areas of the abdominal cavity in order to create additional passages for the outflow of fluid.
- Peritoneovenous shunting. Used to treat recurrent ascites.
- Omentohepatophrenopexy. The operation is performed to reduce the amount of fluid leaking into the abdominal cavity.
- Reinfusion. The essence of the operation is to re-inject the pumped out liquid after it has been filtered. This is necessary in order to prevent the development of complications caused by a sudden loss of a large amount of fluid. Thanks to this technique, it became possible to pump out up to 15 liters of fluid per day without endangering the patient’s life.
Causes and mechanism of development of ascites in oncology
The abdominal cavity is formed from two sheets. Parietal - lines the inner surface, and visceral - directly contacts the organs located in the abdomen. With the help of special glands, they produce a small amount of fluid, which prevents friction of organs and eliminates minor inflammation.
Excess fluid is constantly absorbed by the tissues. At the same time, the secretion produced by the peritoneal glands is periodically renewed. The reasons for the development of ascites are a violation of the outflow of fluid against the background of pathological conditions occurring in the body.
The main reasons for the accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum
In 75% of patients with dropsy, liver cirrhosis is detected. Moreover, this pathological condition has many other etiological factors:
- increased vascular permeability due to the presence of inflammation near metastases in the presence of cancer;
- damage by metastases to blood or lymphatic vessels, this leads to stagnation of lymph and leakage of plasma into the abdominal cavity;
- decreased albumin levels due to the presence of a malignant tumor in the liver;
- production of exudate by neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature located in the peritoneum;
- the occurrence of oncological processes in organs that participate in the regulation of the water-salt balance of the body (kidneys, adrenal glands).
The development of ascites after chemotherapy occurs if the patient has carcinomatosis or peritoneal sarcoma. A similar complication is often encountered by cancer patients with cancer of the uterus or ovaries, lungs, stomach, or pancreas. Typically, the accumulation of water in the peritoneum occurs in the last stages of the disease in the presence of metastases in the lymphatic system.
Ascites prognosis
It is quite difficult to give an accurate prognosis in the case of dropsy, since it is necessary to take into account a large number of different factors (the causes of the disease, its severity, the rate of development, the presence of concomitant diseases, the effectiveness of treatment, and so on).
Complications of the disease definitely worsen the prognosis, the most dangerous of which are peritonitis, umbilical hernia, respiratory failure, and intestinal obstruction.
The two-year survival rate for ascites is about 50%. The prognosis for the refractory form of the disease is even worse. About 50% of patients die within a year.
Unfavorable factors that can worsen the prognosis are a lack of proteins in the body, age 60 years and older, diabetes mellitus, low blood pressure.
Prevention
The main preventive measures are:
- timely treatment of diseases that can lead to the development of dropsy;
- regular sanitation of foci of chronic infection in the body;
- proper nutrition - you need to give up fast food and other junk food, introduce foods that are healthy for the body into your diet, eat in small portions (5-6 times a day, in small portions);
- giving up bad habits (tobacco smoking, alcohol abuse);
- timely surgery for congenital heart defects, which will help avoid the development of heart failure, which is one of the main causes of dropsy;
- proper nutrition for chronic pancreatitis;
- normalization of work and rest regimes;
- refusal to take uncontrolled medications;
- refusal of a sedentary lifestyle, which leads to the development of congestion in the abdominal cavity;
- Regular preventive examinations will help identify possible pathological conditions of the body in the early stages, which will significantly facilitate subsequent treatment and improve the prognosis.
Good health to you!
Treatment
Therapy for dropsy is carried out depending on the degree of development of the disease, the characteristics of its course, the age of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs in the treatment of ascites are used only if they help alleviate the course of the disease.
The use of the technique will also reduce the size of the malignant neoplasm and prevent the spread of metastatic lesions.
Drug therapy
For the first or second degree of ascites, the use of medications with a diuretic effect is recommended. In addition, experts recommend drinking as much water as possible if you have cancer. This is due to the fact that the fluid removes the decay products of the tumor from the body. As a result, the symptoms of intoxication become less pronounced.
But if there is an accumulation of exudate in the abdominal cavity, you should not drink a lot of water. The possibility of using medications is determined by the doctor, who selects the drug, sets the dosage and duration of administration.
For ascites, which is a complication of cancer, the most effective are Veroshpiron, Diacarb, and Furosemide. They are used in various combinations.
On this topic
- Oncogastroenterology
How does colon cancer hurt?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 3, 2021
"Veroshpiron" belongs to the group of drugs that allow you to preserve potassium in the body, since it contains the adrenal hormone. It is he who gets rid of excess fluid. The medicine begins to act 2-5 days after the start of administration. Its effect continues for three days after the end of treatment.
"Diacarb" is a targeted remedy. It is used to prevent the development of cerebral edema, but is ineffective in removing excess fluid. The activity of the drug is noticeable already on day 3. The mechanism of action is to block enzymes that make up the tissues of the brain and kidneys.
Furosmid belongs to the group of diuretics. The drug blocks the process of reabsorption of fluid. But its disadvantage is its ability to remove potassium from the body.
Surgical methods
Abdominal ascites due to cancer in severe cases requires surgical intervention. The procedure for removing exudate is carried out in several ways.
Laparocentesis
Abdominal puncture is considered a full-fledged surgical intervention. The technique is carried out using a puncture.
The patient should sit on a chair. The puncture site is treated with novocaine to reduce pain.
Using a special instrument, a puncture is made in the abdominal wall. Then a tube is inserted, pumping out the accumulated fluid. In one procedure, up to 10 liters of exudate can be removed. To prevent collapse, the abdomen is covered with a sheet.
On this topic
- Oncogastroenterology
Does ultrasound show colon cancer?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 3, 2021
But it is not always possible to remove all the fluid in the abdominal cavity in one session. If it is necessary to repeat the procedure, a drainage tube is inserted into the puncture site. The puncture is performed a few days later.
The main condition is sterility, since there is a high risk of infection through a puncture. As a result, a purulent process begins.
Contraindications to puncture are removal of a hernia and the recovery period after surgery, severe flatulence. Laparocentesis cannot be performed if there are adhesions in the abdominal cavity.
Peritoneovenous shunting
The operation is performed by connecting the superior vena cava to the peritoneum using a tube. When breathing, fluid is directed into the venous channel.
Surgical intervention is complex and can only be performed in the absence of thrombosis and other contraindications.
Omentohepatophrenopexy
The technique is aimed at removing the fused abdominal wall and omentum. It is sutured to the liver or diaphragm.
The procedure is prescribed when the location of the omentum does not allow puncture.
Diet
For abdominal dropsy, patients must follow a special diet. It is aimed at restoring metabolic processes and accelerating the process of fluid removal.
A balanced diet helps maintain the vitality of the body. Experts recommend avoiding salty, sweet, fatty and smoked foods. It is also not recommended to consume acidic foods, as they overload the liver.
To maintain the digestion process, it is important to eat cottage cheese, drink milk, fermented baked milk, and yogurt. Dried fruits, vegetables and gray cereals are useful, as they contain a sufficient amount of potassium.
The number of meals per day should be at least four, the portions are small, since overeating is prohibited.