Today, stomach diseases, unfortunately, are not uncommon. They are dangerous not so much because of their prevalence as because of their frequent relapses, which usually lead to the inability to lead a normal lifestyle. Failure to identify problems in a timely manner causes complications, which can sometimes even lead to death. That is why, when the first symptoms of gastric diseases are detected, a diagnosis should be made immediately. Among the most informative methods today is FGDS of the stomach.
FGDS - what is it?
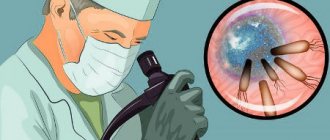
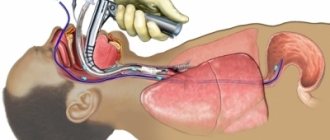
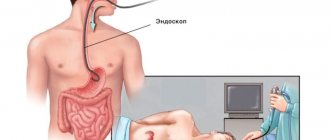
FGDS (abbreviated as fibrogastroduodenoscopy) is one of the most accessible and widespread diagnostic studies of gastrointestinal pathologies (gastrointestinal tract). To carry out the procedure, a special device is used (it is called an endoscope), which is a fiber optic tube with a mini-camera attached to the end. It is inserted into the esophagus and the stomach and mucous membrane are examined. The camera can be controlled by turning it towards certain areas.
There is another abbreviation - FGS, which stands for fibrogastroscopy. At their core, FGS and FGDS are the same thing. The difference is only in the simplified name. Another synonym is gastroscopy.
The FGDS procedure is the most informative of the gastrointestinal tract examinations. Modern devices have tubes with a diameter of less than one centimeter. Thanks to this method, you can find diseases of the esophagus, stomach or duodenum, and also choose the right algorithm for their treatment.
What you can check
Gastroscopy helps to check the stomach, during which you can perform a number of actions:
- determining the cause of the emerging pathology of the gastrointestinal tract;
- detailed examination of damaged areas of the stomach;
- stopping bleeding by administering special medications;
- suturing;
- collection of biomaterial from the desired area of the stomach;
- administration of medications;
- elimination of stenosis and other obstacles to the discharge of bile;
- alignment of the walls in the esophagus.
Indications for FGDS
Endoscopic examination of the stomach is one of the safest and most informative examinations in medicine. It is prescribed to provide a clear picture of the pathological process for the following patient complaints:
- with persistent attacks of heartburn, belching;
- with pain in the epigastric region, heaviness and sensations of bloating;
- with attacks of nausea, frequent vomiting;
- for problems with bowel movements (bowel movements).
FGDS is prescribed for suspected oncology, esophageal stenosis, gastritis, peptic ulcer, gastric bleeding and other diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopic examination, if necessary, is combined with:
- with treatment of the pathological focus with a drug (for example, chemical coagulation of a bleeding vessel);
- with testing for Helicobacter (analysis);
- with stopping bleeding (tamponade, application of ligatures/clips);
- with biopsy and subsequent histology (if cancer is suspected);
- with removal of polyps;
- with bougienage of the esophagus (expansion of the stenotic area).
Indications and contraindications
The doctor will prescribe FGS of the stomach if the patient is bothered by the following symptoms:
- heartburn, nausea, bad breath, change in appetite;
- feeling like there is a lump in the throat;
- anemia;
- decreased body mass index;
- suspicion of cancer.
In addition, the procedure allows you to control how the treatment is progressing.
The study has no age restrictions, but FGDS has contraindications. These include:
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- hypertension;
- recent myocardial infarction or stroke;
- poor blood clotting;
- enlarged goiter;
- illnesses that may make breathing difficult.
Contraindications to the procedure
FGDS is considered a safe procedure, but when it is performed by a doctor, many factors and possible risks are individually taken into account. FGDS of the stomach is prohibited:
- if the patient suffers from mental disorders;
- with angina pectoris;
- if the patient's condition is serious;
- for problems with the thyroid gland (goiter);
- during exacerbation or severe course of bronchial asthma;
- for hypertension;
- partly during pregnancy;
- with a recent stroke;
- during stenosis;
- in the first 7-10 days after myocardial infarction;
- with poor blood clotting.
- How to disable T9 on Android
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes: causes of the disease, symptoms and treatment
- Water manicure at home
How is gastroscopy done?
The examination includes several stages:
- Preparation;
- examination;
- transcript and conclusion of FGDS.
Preparation rules
Manipulation requires serious preparation. If you ignore it, the doctor will not be able to do a gastroscopy of the stomach correctly. The recommendations are as follows.
- The patient should eat food 8-10 hours before FGS; if there are serious deviations in the functioning of the digestive organs, then 12-13 hours before.
- A couple of days before the examination, you should refrain from smoking, as nicotine increases vascular permeability and mucus production, which significantly complicates the examination.
- On the day on which the procedure is scheduled, you should not brush your teeth. Simply rinse your mouth with clean water. Using toothpaste will strengthen your gag reflex.
- Before FGS, dentures should be removed; they may complicate the procedure.
- You should wear comfortable clothing for the examination.
- If the patient is taking any medications, this should be discussed with the gastroenterologist.
- It is very important to remain calm and not be afraid.
The doctor will recommend slightly changing your usual diet. Features of the diet are as follows:
- exclusion of foods with high acidity (tomatoes, plums), difficult to digest (melons, pears), sweets, dairy, alcohol, coffee;
- prefer to consume various cereals, baked fruits and vegetables, boiled chicken, compotes and herbal teas.
Technique and duration of the examination
FGDS is essentially swallowing a tube to check the stomach. During the procedure, the patient swallows a flexible probe (endoscope) with a diameter of no more than one centimeter (if an adult must undergo examination) and less (if we are talking about a small patient). Today, doctors use an ocular device equipped with a mini-camera. Thanks to this equipment, a specialist gets the opportunity to:
- see a color picture with high detail on the screen;
- record the process in dynamics;
- save the resulting video.
The examination itself proceeds as follows.
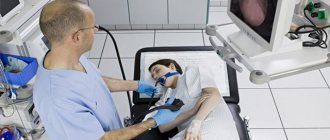
- 5 minutes before the start of the manipulation, the doctor treats the patient’s throat with lidocaine. For children and patients who cannot overcome fear, the procedure can be performed under general anesthesia (drugs are used that put the patient into a short sleep). However, the indications for gastroscopy in this way should be quite serious.
- The patient lies on the couch on his left side, a towel is placed under his head, where saliva will drain.
- Then the patient must clamp his teeth on a plastic ring, into the hole of which the endoscope passes to the root of the tongue. The patient needs to make swallowing movements, at this time the probe will move into the stomach through the esophagus. This moment is the most unpleasant thing in the whole procedure.
- When the small chamber reaches the stomach, the compressor will begin to pump air into it to straighten its empty walls. The electric suction removes excess fluid (bile, mucus).
- The examination begins. The doctor moves the endoscope to the right places and checks the walls of the stomach and duodenum.
There is another name for diagnostics - EGDS. This is the same fibrogastroduodenoscopy, the letter “E” means eso. The difference is that fibrogastroscopy involves exclusively examining the stomach, and when performing EGD, the esophagus and duodenum are also studied.
The examination lasts about ten minutes. If a biopsy is done at the same time, it takes half an hour. When all the necessary manipulations have been completed, the doctor carefully pulls out the endoscope hose, the patient can be free. If general anesthesia was used, the patient should be left under medical supervision for several hours.
Feelings after the procedure
After general anesthesia, the patient remains in the ward for some time. If local anesthesia was used, then you can wait for the examination results in the corridor. It is absolutely normal if after the procedure:
- sore throat;
- nausea is present;
- stomach ache.
After the diagnosis, you should refrain from eating and drinking so as not to provoke vomiting.
How often can FGDS be done?
FGDS is often not worth doing for young people. Repeated examination is possible if therapy does not give the expected result and the signs of the disease do not subside.
If a precancerous change in the mucosa was discovered, but surgery was refused, FGS should be performed every year.
After undergoing operations, such an examination can be scheduled no earlier than 6 months later. FGDS is advisable to carry out if the symptoms of the disease do not change.
Rules for preparing for the FGS
Preparation for gastroscopy begins a few days before the procedure itself. There are certain instructions that the patient must follow:
- in the evening before the procedure, dinner should not overload the stomach, it should be light and quickly digestible;
- before the procedure itself, eating is prohibited at all;
- smoking is prohibited;
- It is not allowed to take pills that must be swallowed.
Before the FGS procedure, the following is allowed:
- take medications that can be dissolved in the mouth;
- give injections;
- drink still mineral water or drink sweet black tea.
The last meal should be at least 10 hours before the start of the procedure, no later.
For a light dinner before the study, you can eat fish with boiled vegetables, or you can eat boiled chicken breast. In a few days, give up spicy foods and alcohol, fatty foods and smoked foods. For 12 hours it is forbidden to consume: chocolate and chocolate candies, any seeds and nuts, fresh vegetables. It is best to carry out FGS in the first half of the day. If the procedure is carried out in the afternoon, then the last meal should be before 8 am. Breakfast should also be light and quickly digestible.
A healthy person with normal digestion can digest all these foods in 8 hours, but patients who are prescribed FGS already have digestive problems. Therefore, it is important to follow these rules.
If the rules are not followed, the procedure will not provide a complete description of the upper parts of the digestion, or you may even have to undergo FGS.
In the morning, upon awakening, before undergoing FGS, you should not brush your teeth.
Brushing your teeth and smoking cause the stomach to produce mucus, which can prolong the examination. You can't chew gum. When going to the hospital, you need to take with you a medical card with the results of tests for hepatitis, HIV and x-rays, and you should also take your insurance policy and passport. If you wear dentures, remove them. It is better to choose clothes that do not restrict movement; make sure that your trousers do not rest on your stomach, and that your top does not restrict your neck. If you must take medication for diabetics or hypertension, take the medication at least three hours before the test. The duration of the procedure is about 10 minutes; if any treatment or biopsy is performed, it takes about 20-30 minutes. Set yourself in a positive mood, breathe calmly, don’t panic. Gastroscopy can be done easily and without problems if you mentally prepare yourself for it.
Decoding the results
Making a diagnosis is exactly what fibrogastroduodenoscopy provides. The most common diseases manifest themselves differently during examination.
The norm is described in the protocol as follows:
- the mucous membrane in the upper parts of the digestive system is pink;
- moderate amount of mucus;
- reflex movements in the esophagus when swallowing;
- there is no expansion of the wall, several longitudinal folds;
- the lower esophageal sphincter is completely closed;
- no food leftovers;
- there are many folds in the stomach that straighten out when air enters through the tube;
- no blood clots;
- clear gastric juice;
- the mucous membrane of the duodenum is pink;
- there are bile impurities in the lumen;
- the large bulb has the correct shape and is not deformed.
Signs of pathologies diagnosed based on the results of FGDS are described in the table.
| Pathology | Signs | |
| Achalasia | The probe is difficult to pass through the esophagus. There are food remains in the gap. The esophagus widens just above the transition to the stomach. | |
| Barrett's esophagus | The mucous membrane of the lower section is characterized by redness 3 cm above the diaphragm. | |
| Gastritis, esophagitis, duodenitis | The mucous membranes turned red. Lots of mucus. | |
| Gastritis | Atrophic | Thin pale mucous membrane with faint folds. Little mucus. Reduced acidity. |
| Erosive | On the surface of the mucosa there are many damages - erosions. They may bleed and then crusts form. | |
| Hypertrophic | The folds of the gastric mucosa are enlarged and red in color, tightly adjacent to each other. Mucus accumulates between them. | |
| Ulcer | The mucous membrane has changed shape. The tissues are swollen. There may be blood clots. | |
| Malignant formation | Heterogeneous, growing. The mucous membrane around it is always inflamed. Tissues die and hemorrhage is possible. | |
| Benign formation | There are clear boundaries between healthy and altered tissue. There is no inflammation around. Looks like a small overgrowth. | |
| Celiac disease | Atrophy of folds. Mucous membrane is smooth. Lots of mucus. | |
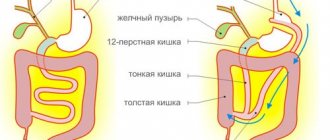
| Duodenogastric reflux | Yellow-green bile in the stomach | |
| Crohn's disease | Hyperemia and minor erosions | |
After the information is deciphered, the doctor can make a diagnosis, recognizing the disease by its signs.
Feasibility of carrying out
Gastroenterology considers the procedure as the most informative study, which usually cannot be excluded. Gastroscopy makes a final diagnosis; the examination results are important. Considered:
- Stomach.
- Esophagus.
- Duodenum.
Data from the patient’s body is supplied by an endoscope, demonstrating the peculiarities of the condition of the listed organs. Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is performed by inserting a probe into the patient’s esophagus through the oral cavity; the probe-manipulator has dimensions of 8-11 cm. Optical equipment provides a clear, detailed image, magnifying it and presenting the mucous membranes of the organs being studied for examination. It is possible to photograph images and record what is happening on a medium. FGDS is not associated with severe discomfort due to the design features of the device, slight rigidity and flexibility.
Human fibrogastroduodenoscopy
The device is equipped with backlight, images are visualized accurately. The procedure does not exclude additional manipulations; it is possible to take materials for a biopsy if a suspicious area is detected. The method ensures the performance of minimally invasive surgical operations; the device stops bleeding by stopping damaged vessels. The equipment irradiates with a laser, performs cryodestruction, providing assistance immediately. The design includes small forceps. By examining the patient, the doctor detects obstructions, neoplasms, ulcers and erosions. There are scar formations, protrusions, and narrowings. The operation of the gastric valves and the composition of the juice are checked - the probe takes a sample for testing in the laboratory. Bacterial diseases, the type of pathogen, the nature of the ulcer, and its origin are detected.
Indications
FGDS is resorted to in a planned, urgent manner. Planned duodenum skopeo identifies problems of the mucous membrane and is prescribed for its detailed consideration. Carry out for regular pain, belching, nausea, problems with swallowing. Allows you to find out the cause of vomiting, discomfort, and reluctance to eat. An examination of the duodenum and adjacent organs is prescribed to search for neoplasms and control their treatment. They are examined for chronic diseases, after 45 years - an examination of the body according to age. Performed for cholecystitis, chronic pancreatitis.
Urgent treatment is carried out when foreign bodies and small tumors are detected and removed, followed by sending the materials for biopsy. Realizable for applying clips in case of urgent stopping of bleeding, stenosis - for the purpose of expanding the esophagus.
The procedure is successfully used for diagnostics and minor manipulations, the value is high. But they prescribe it selectively.
Contraindications
Duodenofibroscopy is easily tolerated, but there are contraindications and complications. Injury to the mucous membrane and infection are possible. If inflammation of the organs is successfully treated with medications, the event is postponed. Can be done during pregnancy, with caution, correctly. Acute erosive gastritis is a reason to postpone the procedure.
A categorical refusal for FGDS is given in cases of severe mental illness, severe narrowing of the digestive tract, and atherosclerosis. It is impossible to carry out in case of atherosclerosis, aneurysm, pulmonary insufficiency. Dangerous if you have an enlarged thyroid gland or problems with cerebral circulation.
Possible consequences and complications
Complications after FGDS are rare. Usually the most unpleasant consequence is a sore throat, which goes away after two days.
However, there is still one percent of those surveyed who complained about:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- discomfort caused by the air that the compressor has caught up with;
- infection;
- damage to the walls of internal organs.
Sometimes those undergoing the procedure become allergic to the local anesthetic.
You cannot do without medical help if the following symptoms are observed within 24 hours after the procedure:
- hyperthermia – 38 degrees and above;
- pain and pain in the abdomen;
- vomiting blood;
- loose stools, colored black.
These manifestations most often signal internal bleeding.
Special tools
FGDS is performed by an endoscopist using a special device called an endoscope. It is represented by a long (up to 1 m) tube, inside of which there are fiber structures and a channel for the introduction of surgical instruments or medicine.
At the end of the tube there is an optical system. This allows the doctor to examine in detail the mucous membrane of the walls of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. In addition, modern endoscopes are equipped with a small video camera, which allows the visible image to be displayed on a large monitor screen. The video is recorded on an information medium; if necessary, it can be watched to track the course of the disease over time.
Fiber optic endoscopes differ significantly from their predecessors. They have improved optics, a lighting bulb, and a high-quality video camera, which makes it possible to quickly and accurately determine the localization of the pathological process. Their thickness is 4-6 mm, which reduces discomfort for the patient.
Endoscope tip
Advantages and disadvantages of the survey
Like any medical intervention, FGDS has its pros and cons. The advantages include:
- information content;
- quality of the resulting images;
- no radiation;
- short duration;
- quick results;
- the opportunity to carry out additional manipulations - biopsy, test for Helicobacter pylori and others.
Diagnostic disadvantages:
- discomfort when swallowing the probe and after its removal;
- possible complications (especially after a biopsy).
The biggest problem is damage to the gastrointestinal tract (usually due to insufficient qualifications of the doctor).
What should you take with you?
Typically, the list of documents required in the FGDS office is specified by the doctor who ordered the endoscopic examination. In order not to forget what you need in the bustle of getting ready, you should collect in advance:
- outpatient card;
- referral for research;
- results of previous FGDS and biopsy (to record the dynamics of treatment);
- constantly taken heart and anti-asthma drugs;
- highly absorbent towel/diaper;
- sterile gloves;
- shoe covers.
Are there alternative diagnostic methods?
Today, gastroscopy does not have a 100% alternative. X-rays, ultrasounds or MRIs provide only partial information about how the stomach works. Fibrogastroscopy is the most informative and safe examination method.
Today, endoscopy in medicine has reached a new level. It is possible to conduct a gastrointestinal examination without swallowing the probe. There are several such techniques.
- Capsule endoscopy - you swallow a single-use capsule that takes pictures of your organs and displays them on a computer. The patient can work, and the diagnostician will examine the esophagus. The capsule is eliminated naturally.
- Transnasal FGS - a gastroscope is inserted through the nostril, it shows an image on the screen.
- Virtual FGS is a study using X-rays.
Each method has a number of contraindications, so you need to consult a specialist.
Proper preparation and adequate behavior of the patient during the study are the key to its successful completion. You should not pay attention to the stories of people who have already done FGDS. The most important thing is to tune in and listen to the doctor’s recommendations, then everything will go without problems.
Is it dangerous?
Endoscopy is not the most pleasant, but it is an easily tolerated procedure, so there is no need to panic. The study will show the duodenum, intestines, and stomach will be studied in detail. Duodenoscopy accurately identifies the diagnosis, simplifies the diagnosis, and ensures 100% accuracy. You should not refuse the need to examine organs, conduct an examination, or get help.
There will be no negative cost for the examination in the form of infection; the method does not transmit HIV, hepatitis, or other infections. The examination of the patient ends with complete disinfection of the equipment in washing machines designed for this purpose. The mucous membrane may react, belching, nausea, and minor pain may occur - temporary phenomena that do not require treatment. A simple method to relieve the discomfort that gastroduodenoscopy brings is to rinse your mouth and drink water in small sips.
The examination is completed - you should avoid heavy, fatty foods for a day. A temporary diet will eliminate bloating and disorders. There will be no pain. Statistics show that complications and illness after examination are observed in less than 1 percent of cases. The body will immediately show an unfavorable outcome. If the membrane is damaged, infection occurs and the temperature rises within hours; normally, this does not occur after the procedure. Vomiting, diarrhea, pain are reasons to consult a doctor immediately; diagnostics of the duodenum and stomach normally do not give such symptoms.
It is better to take tests and undergo duodenal testing at a certain time. If you go in the morning, it will be easier to prepare. Proper preparation for the event is important for success, it can make the doctor’s work easier and minimize risks for the patient. You need to prepare for the examination 3 days in advance.
The technique is specific; when preparing for the test, it is wise to choose a worthy performer. The experience and qualifications of the doctor play a big role; a professional will provide an accurate result and carry out the procedure faster. The risk for the patient is minimized, the mucous membrane will not be affected. Doctors will be able to look at a detailed picture, the stomach and intestines will be detailed in detail. The latest equipment is important, technology increases accuracy, comfort, and allows you to examine the duodenum in detail. It is recommended to be examined in private clinics, where imported equipment, highly qualified personnel, the result will be more accurate, the process will be more comfortable. Turning to private traders will eliminate queues and ensure the accuracy of the result. But they also turn to government clinics for urgent and routine work. Public services are free, the quality of provision depends on the staff, equipment, and status of the hospital.
After the procedure is completed, the patient goes home. FGDS is simple and safe, the accuracy of the result is close to one hundred percent. The painless approach makes it possible to diagnose dozens of diseases of the stomach and adjacent organs, and allows you to quickly provide assistance using a minimally invasive, non-invasive method. Treatment, emergency assistance, and examination of organs are possible for children, pregnant women, and the elderly. Contraindications are minimal and temporary; there are few permanent prohibitions. The technique guarantees accurate diagnosis and formation of a competent course of treatment. You should not abandon the method of accurate diagnosis; this is the only way to cure and defeat the disease. The health of the digestive organs is the key to the well-being of the body, a comfortable life, and a positive mood.
What diseases can be detected using FGDS?
The most common finding during this study is the inflammatory process of the gastric mucosa - gastritis. In fact, after 20 years, almost everyone has it. A more serious finding is an ulcer. Its danger lies in the fact that it can bleed and even perforate the stomach wall completely. In case of signs of such complications, an emergency FGDS is performed. Stomach ulcers, among other things, can degenerate into more serious diseases.
Much more alarming is the discovery of a tumor process in the stomach cavity. A stomach polyp is also an unpleasant discovery. If something similar or simply an inflamed area of the mucous membrane with signs of changes in structure is detected, the doctor will most likely, with the patient’s consent, take a biopsy. Subsequently, samples of the removed tissue are sent for pathocytological examination. The result will allow us to say exactly what this or that modified area of the gastric mucosa is.