What is FGDS
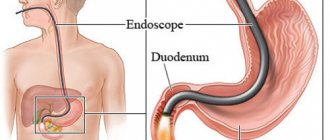
The abbreviation FGDS in medicine refers to one of the most common methods for studying the upper parts of the digestive system. It stands for fibrogastroduodenoscopy - examination of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum using an endoscope (gastroscope).
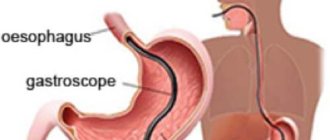
Sometimes the procedure is called EGD. The letter E in the name means “esophagus” - esophagus. However, this abbreviation is used less frequently, since FGDS itself already implies examination of the esophagus; the endoscope passes into the stomach through it.
The essence of the technique is that the patient swallows a probe, which, after passing through the mouth, enters the stomach and the initial part of the intestine. At the end of this probe is a miniature light bulb and a camera. The image from the camera is transmitted to a computer screen, after which it is deciphered by a gastroenterologist.
Types of gastroscopy
Options and methods of fibrogastroscopy are given in the table:
| View | Description |
| Classical | It is carried out without anesthesia; the patient swallows a tube after applying an anesthetic spray to the pharyngeal mucosa. Used in most subjects |
| With anesthesia support | Some categories of patients require anesthesia in order to be able to fully carry out the manipulation. A short-term general anesthesia is used, during which the muscles of the pharynx and esophagus relax, allowing the doctor to insert the endoscope |
| Planned | It is carried out by appointment, for patients who do not require an urgent diagnosis. |
| Emergency | It is carried out for vital indications, when it is urgently necessary to determine what happened to a person. The risk of complications increases due to lack of proper preparation |
| Diagnostic | Used only for examining the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and intestines, identifying pathological changes |
| Medical | In addition to the examination, the doctor can carry out the required treatment measures:
|
What diseases are diagnosed
Using gastroscopy, a doctor can diagnose the following diseases:
- various tumor neoplasms - polyps, cysts, cancer of the esophagus or stomach;
- gastritis - erosive, atrophic, hypertrophic;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- Barrett's esophagus;
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome;
- ulcers of various parts of the digestive tract;
- wounds to the mucous membrane.
With the help of endoscopic equipment, dilation of the esophageal veins can be detected, which is one of the signs of liver cirrhosis.
Photo gallery
The photo shows the main nuances of the implementation of FGDS and the detected pathologies
Position of the endoscope in the stomach
FGDS implementation scheme
Types of pathologies
Biopsy using an endoscope
What parameters are assessed?
During the FGDS, the doctor evaluates the following parameters:
- color of the mucous membrane throughout the examined area of the gastrointestinal tract;
- the presence of folds of the mucous membrane;
- integrity of all shells;
- the presence of inflammatory changes and neoplasms;
- severity of peristalsis.
If there are pathological changes for each item, they are described in the conclusion.
The video describes the FGDS procedure. Filmed by TNT channel.
What does FGDS of the stomach show?
Gastroscopy of the stomach can be prescribed to patients of any age and gender; there are no contraindications or restrictions for these parameters. The examination is carried out in a clinic or hospital, but does not require special placement in a hospital. The prescribed medical examination, namely FGDS of the stomach, shows:
- stomach diseases: gastritis, peptic ulcer, hypersecretion, achylia, esophagitis, cancer or mechanical damage;
- diseases of the inner lining of the duodenum.
A procedure is carried out to identify changes in the listed organs, including possible ulcerations or neoplasms. Your attending physician must also inform you about how to prepare for an FGDS of the stomach.
Indications
The gastroscopy procedure is prescribed if the patient has the following symptoms:
- difficulty swallowing;
- frequent vomiting for no apparent reason;
- admixture in vomited blood;
- constant pain in the stomach area, along the esophagus;
- vague abdominal pain;
- unexplained weight loss;
- sudden loss of appetite;
- untreatable anemia.
For a newborn child, gastroscopy is performed when:
- poor weight gain;
- refusal to eat;
- constant colic;
- other health problems.
Since FGDS is not only a diagnostic, but also a therapeutic procedure, it is prescribed for the following pathological processes:
- foreign body entering the stomach;
- polyposis of the stomach or esophagus;
- consequences of chemical burns of the esophagus;
- stomach bleeding;
- neoplasms of the esophagus or stomach.
For these diseases, the doctor uses a gastroscope to carry out the required medical manipulations.
Indications for the study
Gastroscopy is performed for peptic ulcers.
Gastroscopy is a high-tech method for studying the digestive system. It helps make a diagnosis:
- Cancer;
- Chronic gastritis;
- Peptic ulcer;
- Polypov.
This diagnosis is carried out if there is a need to accurately determine the source of gastric bleeding. The procedure is prescribed if the appearance of malignant neoplasms is suspected.
If an X-ray examination of the stomach has negative results, and the patient complains of gastric discomfort, then the procedure is indicated for him. Gastroscopy is performed if it is necessary to diagnose other diseases with an assessment of the condition of the mucous membranes of the stomach.
Useful article? Share the link on VKontakte
If a person has no appetite and begins to rapidly lose weight, then this requires this diagnostic method. If signs of poor food passage during swallowing appear, this research method is also prescribed.
The indication for diagnosis is pain in the upper parts of the stomach. Regular occurrence of vomiting and heartburn requires the use of this research method.
Indications for gastroscopy are quite varied. This research method is widely used in the presence of diseases of the digestive tract.
Contraindications
The gastroscopy procedure is not performed for all patients - contraindications to FGDS are:
- scoliosis 3-4 degrees;
- severe chest deformities;
- obstructive pulmonary diseases;
- obesity 4 degrees;
- multiple strictures of the esophagus;
- large goiter;
- severe blood clotting pathology;
- cachexia - extreme exhaustion of the body;
- early period after a heart attack or stroke.
The following may also be contraindications:
- the patient’s categorical refusal to undergo the procedure (in this case, the study can be rescheduled);
- state of severe drug or alcohol intoxication;
- acute psychosis.
Contraindications to gastroscopy
Gastroscopy is performed to make an accurate diagnosis of gastritis or cancer.
Despite the fact that the study makes it possible to study the mucous membrane of the digestive tract and is highly informative, it is characterized by the presence of certain contraindications.
If a patient has gastric bleeding, he needs to undergo an emergency gastroscopy.
In this case, there are practically no contraindications. This diagnostic method is carried out even if the patient is diagnosed with myocardial infarction.
Routine examination is characterized by the presence of a large number of contraindications. Diagnosis is not carried out in severe cardiovascular failure. Routine examination is not recommended for patients with acute myocardial infarction.
If acute disturbances are observed in the patient’s cerebral circulation, then he is strictly prohibited from conducting examinations. In case of severe respiratory failure, gastroscopy is prohibited.
Experts do not recommend the use of this research method during the recovery period after diseases such as a stroke or acute heart attack. A contraindication to the use of this diagnostic method is an aortic aneurysm. The procedure is not recommended for patients with carotid sinus aneurysm. It is also prohibited in case of cardiac aneurysm.
Doctors do not advise patients with hypertensive crisis to undergo gastroscopy. This research method is not prescribed for cardiac arrhythmias. During the period of severe mental disorders, diagnosis is contraindicated for patients.
Before performing gastroscopy, it is imperative to determine contraindications. Otherwise, the patient may experience negative consequences.
Preparation
In order for the patient to endure the procedure easily psychologically and physically, the doctor tells how to prepare for it.
Nutrition
A person is warned about a planned FGDS 2-3 days in advance. At this time, he follows a special diet and prepares himself mentally for the procedure.
It is recommended to temporarily exclude the following foods from the diet:
- fatty meat and fish dishes;
- mushrooms;
- baking;
- seasonings and spices;
- sausages;
- fatty cheese, milk;
- legumes;
- sweets;
- bread;
- cabbage;
- coffee;
- alcohol.
A person’s menu before an FGDS consists of:
- chicken meat;
- lean fish;
- stewed vegetables;
- porridge with water;
- weak tea.
On the eve of the study, you can eat a light dinner. Since FGDS is usually done in the morning on an empty stomach, you can drink water no later than three hours before the procedure.
General recommendations
Additional proper preparation is carried out taking into account the following nuances:
- a few days before the procedure, it is recommended to quit smoking (or reduce the number of cigarettes as much as possible);
- if a person is forced to take any medications for medical reasons, the doctor who will conduct the FGDS should be notified about this;
- If the tablet needs to be taken in the morning, it is not swallowed, but dissolved in the mouth.
Moral preparation
The moral preparation of the patient is of great importance, because if a person has a strong fear of the upcoming procedure:
- the patient will be nervous, which will prevent him from swallowing the probe;
- the doctor will not be able to fully examine the stomach.
The patient needs to understand that the procedure is painless, so the better the person relaxes, the easier it will be for him to survive the manipulation.
It is important not to be afraid of the upcoming procedure and to set yourself up positively - for this you can:
- meditate on the eve of the study;
- take a sedative;
- talk to a psychologist.
Sometimes gymnastics helps you get into the right mood.
Learning to breathe correctly
During FGDS, the patient is only required to lie still and breathe correctly, while:
- breathing should be carried out only through the nose, without using the intercostal muscles and diaphragm;
- you need to inhale the air slowly and deeply, measuredly;
- It is best to mentally count the rhythm while breathing.
Deep breathing helps you calm down, especially if you are very afraid of pain.
How to reduce your gag reflex
To reduce or alleviate the severity of the gag reflex, first of all, you must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
The urge to vomit during FGDS occurs in a person due to irritation of the root of the tongue with the gastroscope hose, therefore:
- to reduce the sensitivity of nerve endings, this area is irrigated with an anesthetic - lidocaine or ultracaine;
- reduction of muscle tension is achieved by administering muscle relaxants;
- During insertion of the tube, the person must actively swallow the probe - this will reduce the pressure on the root of the tongue.
Preparation for FGDS
Before undergoing FGDS, the patient needs to prepare for it.
For a few days, stop taking medications (especially anticoagulants - drugs that affect the blood clotting process) or you should coordinate their use with your doctor.
6-8 hours before FGDS you should stop eating, and 2-4 hours before you should stop drinking liquids.
Smokers should stop smoking several hours before FGDS, as smoking increases the secretion of gastric juice.
In case of emergency research, the procedure is carried out after gastric lavage.
Description of the procedure
Planned FGDS is prescribed in the morning. The procedure is carried out in an equipped endoscopy room.
Before manipulation, it is necessary to remove objects squeezing the body:
- belts;
- chains;
- tight clothes.
How does the procedure work?
Step-by-step process of the procedure:
- An hour before gastroscopy, the patient is given premedication - 1 ml of atropine and 1 ml of trimeperidine are administered intramuscularly.
- The person is placed on the couch on his left side. You can bend your legs slightly and wrap your arms around yourself at elbow level. Place a tray in front of your face. During the examination, you need to behave correctly - you cannot move, turn your head, swallow saliva, or talk.
- The patient is given a silicone insert to clamp between the teeth, through which the probe is inserted. It is necessary to prevent damage to the gastroscope. If it is impossible to perform the procedure due to the person’s strong tension or a pronounced gag reflex, anesthesia is performed - then it will be painless.
- Next, the doctor inserts a tube into your throat. You need to swallow it while taking a deep breath. When the tube passes through the pharyngeal ring, the discomfort stops.
- The endoscopist examines the internal organs. Sometimes it is possible to go through the intestine completely and examine the place of its transition to the next section.
- After this, the doctor carefully removes the gastroscope tube.
Photo gallery
Full insertion of the probe
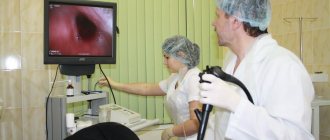
Examination directly through a gastroscope
On-screen inspection
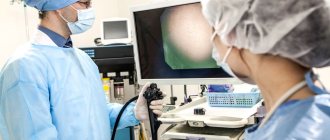
Gastroscopy with anesthesia
Is it painful to swallow a tube and tube?
The gastroscope probe has a diameter of 1.5-2 cm, so it does not cause pain when swallowing. Only discomfort appears from the presence of a foreign object in the throat.
The thickness of the tube for small children is even smaller - 5-10 mm. Therefore, there is no need to worry about pain, because the diameter of the esophagus is much larger and the tube will pass through it absolutely freely.
How often can you do it
Initially, healthy people do not often need to undergo gastroscopy. FGDS is carried out only according to indications, on which the regularity of the manipulation will depend. It is prescribed when appropriate symptoms appear; the further number of examinations depends on the established diagnosis.
If you have uncomplicated gastrointestinal diseases, the test can be taken once a year. Severe pathologies - with complications, rapidly progressing - require gastroscopy every 3-6 months. In most cases, the frequency of FGDS is determined individually.
How is FGDS performed?
The procedure begins with the written consent of the patient. This stage scares many, but in fact, it is nothing more than a legal formality. According to modern laws related to medicine, consent is required for any “intrusion.”
Then the patient is asked to take off his outer clothing, sometimes it is expected to undress completely in order to change into a special hospital gown, which, on the one hand, is clean, and on the other hand, you don’t mind getting dirty.
The next stage is anesthesia. This is why all the stories about terrible pain are not particularly believable. Doctors performing the procedure do not need the patient to experience discomfort at all, and the gag reflex can completely interfere with the FGDS, at the same time distorting all the results. Therefore, the patient is sprayed with lidocaine in the throat and entrance to the esophagus, or given a tablet of falimint with a similar effect.
How is the FGDS procedure performed?
Next, you need to lie on the couch in a special position: on your side, hands placed on your chest or stomach. After this, the doctor will ask you to clamp a rather voluminous tube made of hard plastic with your teeth. There is no need to be afraid of it: this is not the probe itself, but a protective mouthpiece that protects the thin rubber wire from accidental biting.
A fiberscope is a thin elastic wire. The doctor brings him to the root of the tongue, the patient can only make a swallowing movement. Then they ask you to lie still and not move. As the probe is immersed, the discomfort will decrease, because irritation and gag reflexes are more characteristic of the esophagus than of the stomach and upper gastrointestinal tract.
When the fiberscope reaches the duodenum, the urge to feel sick should stop completely. On the other hand, this is the last “stage” of testing: first comes the esophagus, then the stomach, and only then the intestines. The inside of the probe feels slightly itchy or scratchy. Patients describe the sensation as uncomfortable, but not painful and quite easily tolerated.
FGDS from the inside
The procedure takes from five minutes for a simple examination to half an hour if you need to take a piece of tissue for a biopsy or remove a polyp. The probe is pulled out with the same care so as not to damage the walls of the intestines, stomach and esophagus.
Possible complications
The procedure is considered safe, but sometimes unforeseen situations arise. Doctors note that they are most often associated with improper behavior of the patient himself - eating before swallowing the probe, restless behavior during an examination using FGDS. The most common problems that occur are:
- damage to the walls of the stomach or esophagus - especially dangerous with severe ulceration or bleeding tumors;
- bleeding in the esophagus;
- infection.
All complications are extremely rare, but the patient will still be warned to monitor their condition for two to three days. If you experience vomiting, especially with blood, chills or fever, or tarry stools, you should immediately go to the hospital.
Video - About the FGDS procedure
Testing without swallowing the tube and probe
If it is absolutely impossible to perform a classic gastroscopy, if the patient has contraindications, there is an alternative method of visual examination of the gastrointestinal tract. This is a capsule FGDS - the patient swallows not a tube, but a small chamber in the form of a capsule. It sequentially passes through all parts of the gastrointestinal tract and leaves the body naturally. The data recorded by the camera is then transferred to a computer where the doctor can study it.
This lightweight method is no less informative than classic gastroscopy; it allows you to study not only the upper gastrointestinal tract, but also the entire intestine from the inside. However, it is not performed on all patients. The cost of such a study is very high - together with the capsule itself, the price of the procedure is within 50 thousand rubles.
As with classical gastroscopy, there are several contraindications:
- swallowing disorder;
- installed pacemaker;
- epilepsy;
- intestinal obstruction.
The preparation required is the same as for conventional FGDS. The capsule passes through the entire gastrointestinal tract in 12-14 hours, so the test result is issued the next day.
Capsule FGDS
Is the procedure dangerous or safe?
Now you know how to prepare for gastroscopy. It's time to find out how safe this diagnostic method is.
This procedure should be performed by a qualified specialist who has experience in such matters. Therefore, before gastroscopy, you should ask how competent the doctor is and whether you should trust him with your health.
If everything is in order, then this procedure is considered completely safe and does not cause any complications.
But there are different situations, and you should know for which symptoms after diagnosis you need to urgently call an ambulance:
- if you have severe abdominal pain;
- the person coughs continuously;
- basal temperature has risen;
- nausea and even vomiting appeared;
- chest pain occurred.
If any of these symptoms are present, you should immediately call emergency services. Because these signals may indicate internal bleeding or even rupture of the esophagus.
Now you know how to prepare for gastroscopy, and you also understand what complications may arise after this examination method.
Advantages and disadvantages
Fibrogastroscopy has a number of positive and negative aspects, taking into account which the need for it is determined.
The pros and cons of gastroscopy are presented in the table:
| Advantages | Flaws |
|
|
What do the reviews say?
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is an extremely common procedure. People who have suffered it report that they were much more afraid than it deserved. Unpleasant urge to vomit is softened by anesthetic drugs, pain is practically eliminated even during the removal of polyps and small tumors. Patients note that in the first minutes after swallowing the probe it is a little difficult to breathe, but this feeling quickly passes. In any case, people who have undergone FGDS agree that the benefits of the diagnostic and treatment procedure justify all possible unpleasant effects. What hurts on the left under the ribs you will find the answer in the link.
What diseases can be detected during diagnosis?
Using capsule endoscopy, you can evaluate the condition of all parts of the gastrointestinal tract, but the greatest diagnostic value is found when examining the small intestine . Diseases of other parts of the digestive tract (stomach, esophagus, large intestine) can also be detected in this way, but it is still inferior in information content to the conventional endoscopic technique and colonoscopy.
The small intestine is quite difficult to access for other research methods, but is perfectly visualized in pictures taken by the capsule camera. Each organ has its own capsule, and devices have also been developed that can record images from all parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Capsules vary in size: the smaller it is, the greater the safety of the procedure. The speed of recording images and the viewing angle of the camera are of - the diagnostic value of capsule endoscopy depends on these indicators.
Many companies produce capsules. Some of them are Given Imaging (Israel), IntroMedic Co. (Seoul, South Korea).
Given Imaging capsule
Using the capsule, you can detect polyps in the intestines, neoplasms, hidden bleeding, Crohn's disease , establish celiac disease and other changes in the gastrointestinal tract that are difficult to see with other research methods.
Price for gastroscopy of the stomach and small intestine
In Russia, capsule endoscopy is carried out at the expense of the patient himself, that is, it is not paid for under the compulsory medical insurance policy. The cost in Moscow and St. Petersburg varies from 35 to 100 or more thousand rubles. This variation is due to the cost of the capsules, which differ from each other in many respects.
Also, the price of the study may include the work of a specialist to conduct and decipher data, hospital stay and meals. The procedure is not cheap: the reason for this is the high cost of the video capsule.
What it is?
The procedure is a method for studying the small and large intestines, differs from others in its lack of invasiveness , and is extremely informative. This requires a special capsule with a built-in camera.
The patient swallows it, and the device moves sequentially through the gastrointestinal tract and records images after a certain period of time ( from 1 to 35 images per second ). All this is recorded on the device (receiver) thanks to the presence of sensors that are located on the patient’s body. The doctor then works with the images, analyzing the results of the study. The capsule is often used instead of FGDS with an endoscope, which helps to avoid complications and fear of the procedure.
FGS stomach video
FGS of the stomach or gastroscopy is carried out by inserting a special probe with a camera at the end into the esophagus and then into the stomach. The results are displayed on the monitor screen. The doctor carefully examines all areas of the esophagus, stomach and, if necessary, duodenum. In addition to the camera, the probe can be equipped with a special device for taking a sample for biopsy. Instead of centimeter lamps of the last century, an almost microscopic apparatus is installed on the probe, so the examination does not cause significant inconvenience to the patient. The procedure is painless, leaving minor discomfort for a short time after the analysis. For easy passage through the larynx, doctors inject a special spray with an anesthetic and a freezing agent into the throat. You can watch a video about FGS of the stomach, how the analysis is done from start to finish, it is clearly visible that the patient does not feel discomfort or pain.
To provide complete clarity about the procedure, we suggest you watch the video.