Comparison
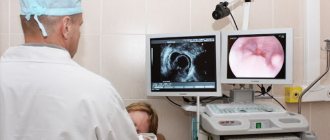
Fibrogastroscopy involves the use of a device to examine the walls of the stomach. This technique involves passing the probe no further than the portal region. Due to FGS, it is possible to identify ulcerative and other lesions of the mucous membrane, take tissue material for biopsy and scraping of the epithelial cover. In this case, the length of the probe corresponds to that from the oral cavity to the xiphoid process.
The procedure will allow examination of the upper parts of the stomach.
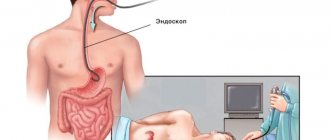
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is a more advanced way of examining the digestive organs. With it you can examine not only the stomach, but also the duodenum. The indications are broader; the difference is that, using this technique, it is possible to examine the small intestine and draw conclusions about the diagnosis and further treatment, taking into account the different structures of the digestive tract.
The study of the esophagus, stomach and upper duodenum using one technique is called esophagogastroduodenoscopy. In this case, the probe is slowly inserted into the esophagus, examining all the walls, and if necessary, a biopsy or scraping is taken. The length of the device allows it to pass down to the upper part of the small intestine. There are a number of indications for using this technique.
If choosing FGS or FGDS, doctors are inclined to choose the option that will be more informative for a particular patient.
FGS and FGDS - what is the difference
Both methods - FGS and FGDS - are varieties of the endoscopic method for studying the digestive tract. In terms of methodology and technique, the differences between them are insignificant, since both types of gastroscopy use the same device - a fibrogastroscope. It is a thin long probe with a camera installed at the end and a light bulb that illuminates the internal space of the gastrointestinal tract. A fiber gastroscope tube is inserted for FGS or FGDS of the stomach through the oral cavity and esophagus, which can cause some discomfort in the form of nausea.
The main difference between FGS and FGDS is the area of study of the digestive tract. The fibrogastroscopy procedure involves directly examining the stomach cavity, its mucous membrane and peristalsis, while fibrogastroduodenoscopy examines not only the stomach, but also the duodenum. The differences don't end there. FGDS lasts 5-10 minutes longer than FGS, and the examination itself is carried out in two stages: first, the doctor examines the stomach cavity, and then proceeds to check the duodenum.
Important! For the patient, the differences between FGS and FGDS are so insignificant that not always after the procedure he can tell what type of gastroscopy the doctor performed.
Another point in which FGS differs from FGDS is the possibility of carrying out additional manipulations. Both types of endoscopic examination allow for a biopsy of mucous membranes and neoplasms, tamponade, or coagulation of bleeding vessels. And only fibrogastroduodenoscopy can be combined with concomitant diagnostics of the bile and pancreatic ducts (retrograde cholangiography).
Indications
Procedures are prescribed for the conditions described in the table:
| FGS | EFGS | FGDS |
| Epigastric pain, discomfort, disturbance of discharge | Belching, burning in the chest | Painful sensations in the navel area and below |
| Signs of bleeding from the stomach: vomiting blood, melena | Sensation of obstruction in the esophagus during the passage of food | History of duodenal ulcer or suspicion of its formation |
| Suspicion of cancer | Tumor formations of the esophageal wall | Diseases of the pancreas, gall bladder, liver |
| Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for gastritis or ulcers | Disturbance of normal digestion of unknown etiology | Burdened hereditary history of ulcerative formations in the duodenum |
| Preventive examination after tumor removal | Biopsy of esophageal tissue and scraping of the mucous membrane to identify atypical formations | Preparing for surgery |
| Dyspeptic manifestations | Suspicion of foreign bodies in the esophagus | Annual examination of patients diagnosed with chronic duodenal ulcer |
Colonoscopy is also an endoscopic method. The meaning of the diagnosis is the same - inserting a probe into the intestine with the following examination of the wall, taking a biopsy and scraping. But during colonoscopy, a different diameter of the probe is used, which is inserted through the anal sphincter. Indications for this procedure are pathological and organic changes in the colon.
How to prepare for the procedure
Preparing the patient for FGDS must be correct, since making mistakes complicates the procedure and reduces its information content. To avoid such mistakes, the doctor must explain to the patient the order of the preparatory stages.
Preparation for FGDS is divided into general and local measures.
General preparation for FGDS includes the following activities:
Identification of contraindications or correction of conditions dangerous to the procedure. If contraindications are detected, the doctor decides on the advisability of prescribing FGDS and evaluates all possible risks. If there are important indications, the procedure after special preparation of the patient is carried out in a hospital setting. Potentially dangerous conditions for performing FGDS are usually diseases of the heart or respiratory system (arrhythmias, arterial hypertension, respiratory failure, etc.). In such cases, the doctor will prescribe the necessary corrective treatment, and the patient will need to take the prescribed medications several days before the test. This approach avoids complications of the endoscopy procedure. Identification of possible allergic reactions to local anesthetics used and prescribed medications. When planning an FGDS, the patient must inform the doctor about all allergic reactions he has to drugs and diseases for which the use of certain drugs may be contraindicated (for example, Atropine should not be used for glaucoma, etc.). To avoid errors, it is better to provide the doctor with all medical documentation about the diseases present. Psychological preparation. Some patients are overly worried about the upcoming procedure, focusing on negative reviews from impressionable acquaintances who have undergone this study
The doctor must explain in detail to the patient the need and importance of conducting FGDS, which is one of the only highly informative diagnostic techniques that cannot be fully replaced by other types of examination. An explanation of the essence of the procedure and the details of its implementation in most cases eliminates the patient’s unfounded fears, and a favorable psychological mood reduces the unpleasant sensations that may arise during insertion of the endoscope
If it is impossible to overcome anxiety, the doctor will prescribe the patient sedatives to eliminate worries and worries.
Local preparation for FGDS includes the following activities:
The patient must inform the doctor about all medications taken. In some cases, the doctor may change the order in which you take them or stop them for a while. If necessary, the patient is prescribed treatment for inflammatory diseases of the esophagus or upper respiratory tract
Their elimination is extremely important, since it is through these paths that the gastroduodenoscope will be inserted. 2 days before the test, you should avoid eating fried foods, hard-to-digest or gas-producing foods. In some cases, to eliminate flatulence or existing problems with the evacuation of food from the stomach into the intestines, the patient is prescribed additional medications: Creon, Festal, Espumisan, Sorbex, etc. Avoid drinking alcohol. Dinner on the eve of the FGDS should take place no later than 18.00-19.00 (at least 12 hours before the procedure). You should not eat anything on the morning of the test
You can drink still water or weak tea 3-4 hours before FGDS. In the morning, the patient is allowed to brush his teeth, take dissolving tablets or inject injection solutions of drugs prescribed by the doctor. A few hours before the procedure, stop smoking, as nicotine activates the secretion of gastric juice. Wear loose and comfortable clothing. Avoid makeup and uncomfortable jewelry that may interfere during the procedure. It is advisable to refrain from using perfumes that can provoke allergies in the patient or medical personnel.
What to take with you
Before visiting the gastroscopy office, you need to take from home:
- referral, outpatient card and forms with the results of previous studies;
- water and medications to be taken immediately after the procedure;
- food (if necessary);
- towel.
Preparing for the examination
For several days before the procedure, it is recommended to eat only easily digestible foods.
FGS and FGDS require preparation of the patient for the study. More often, FGDS is performed in the morning, because it is necessary that the patient does not eat food for 6-8 hours. You should not smoke 60 minutes before the procedure. If there are no special violations, FGDS is done without anesthesia, since it is practically painless. If the patient has significant fear or concomitant diseases, general anesthesia is used. All subjects use local irrigation of the oral mucosa with a solution of Lidocaine to reduce the gag reflex and ensure passage of the probe through the digestive tube. There are no differences in preparation for the diagnostic procedure between FGS, FGDS and EFGS.
Characteristics of methods
FGS and FGDS practically do not differ from each other for a person who is not familiar with the intricacies of these procedures. However, the differences can be determined based on the analysis of abbreviations, since most medical terms reflect the very essence of research.
It is very simple to understand what FGDS and EGDS are. To do this, you need to decipher the abbreviations that reflect the following types of gastroscopy:
- FGDS – fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- EGDS – esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- FGS – fibrogastroscopy.
These complex words have several roots that reflect both the essence of a certain type of endoscopy and the organs being examined, which is their main difference. They are interpreted as follows:
- The root “fibro-” (from the Latin Fibra - fiber) means the use of a special flexible fiber optic probe;
- The root "gastro-" (from the Greek Gastros) indicates the examination of the stomach;
- The root “egophago-” (from Latin oesophago) indicates examination of the esophagus;
- The root “duodeno-” (from the Latin Duodenum) indicates examination of the duodenum;
- The root "scope" (from the Greek skopeo) means the process of visual inspection.
Thus, the expression “FGDS of the stomach” is incorrect, since the study ends in the duodenal bulb and the initial parts of the small intestine.
Therefore, if a person cannot understand how FGDS differs from EGDS, it is enough to simply clarify what is behind the definition of these words. All of these methods are endoscopic, and are primarily carried out to study the anatomical and physiological state of the stomach.
The gastroenterologist prescribes a study of the gastrointestinal tract that will confirm the expected diagnosis or assess the dynamics of the disease.
Carrying out
The patient's position should be lying on the left side. After treating the oral cavity with an anesthetic, an FGDS probe is inserted. Before carrying out the procedure, you need to decide on its purpose - is it diagnostic or therapeutic - in order to carry out all the stages one by one. Esophagogastroscopy for diagnostic purposes includes 2 points: first, examination of the esophagus, then the stomach.
There is esophagoscopy - insertion of a probe only into the esophagus.
A biopsy will allow for more detailed studies.
The purpose of gastroscopy is to examine the inner wall of the stomach and, if necessary, to take material for a biopsy or scraping. With FGDS, 2 stages are carried out: first, as in FGS, with the next advancement of the probe into the duodenum and examination of its walls, the large and small papilla. It is more painful because the stomach is separated from the small intestine by a sphincter through which the machine must pass. They also use a method to study the release of bile into the duodenum. To do this, the patient consumes a choleretic breakfast, after which an FGDS is performed and the reactivity of bile secretion is studied.
What can gastroscopy of the stomach do?
During the procedures, it is possible not only to identify various pathologies of the digestive system, but also to carry out therapeutic manipulations. Modern gastroscopes are equipped with useful functions and allow you to do without surgery in some cases.
With gastroscopy you can:
Taking a biopsy during FGDS or FGS
- Removing polyps is a potential cancer threat. If the doctor discovers these tumors during the procedures, they are cauterized using a gastroscope.
- To carry out bougienage is an expansion of the narrowed esophagus. The device moves deformed shells apart and restores patency.
- Spray the medicine - a gastroscope is capable of spraying medicines over a specific area of the mucosa. This option is widely used to eliminate hidden bleeding.
- Take a biopsy to determine the bacteria Helicobacter pylori or to check for tumors.
- Take a stomach acid test.
Contraindications
Before conducting a study, it is important to take into account the limitations - ignoring contraindications is dangerous for the health, and sometimes even for the life of the patient.
We list when gastroscopy cannot be done:
- problems with blood pressure are noted;
- history of stroke or heart attack;
- there is a risk of bleeding ;
- the patient has bronchial asthma ;
- mental disorders are noted.
What do the studies diagnose?
When performing FGS, pathological changes in the stomach of an inflammatory and traumatic nature are revealed, which caused the appearance of symptoms. The doctor examines the epithelium and takes the necessary photographs. A biopsy is taken to exclude oncology.
FGDS diagnoses the conditions listed above, and additionally identifies diseases of the duodenum in the form of ulcerative lesions and various injuries . Based on a visual examination, the functioning of the biliary system and pancreas is assessed.
Preparation
In order for the examination to be successful and the results to be reliable, it is necessary to properly prepare for gastroscopy. In a few days, you need to change your usual diet, start sticking to a diet excluding heavy foods, alcohol, strong tea and coffee. The diet includes only easily digestible foods. 8-12 hours before the study, eating is prohibited to minimize the risk of a gag reflex during the procedure. Drinking liquid (plain water without gas) is allowed 3 hours before the start of the diagnosis. Smokers should avoid cigarettes because nicotine causes increased gastric acid secretion.
If possible, you should stop taking medications. This is especially true for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and blood thinners.
If the patient experiences severe anxiety immediately before the procedure, a subcutaneous injection of a mild sedative can be given.
Remaining calm during the procedure is very important. Otherwise, the person begins to make involuntary sudden movements and makes it difficult to conduct research
If you have an allergic reaction to anesthetics, you should notify your doctor in advance.