Gastric gastrostasis is a diagnosis that affects a person’s quality of life and sometimes makes it unbearable. Gastrostasis, the causes of which can often be the result of serious diseases, is not easy to treat; there is no single scheme. It all depends on the causes of gastrostasis; the treatment regimen is considered as a whole. The appearance of gastrostars may be preceded by stomach cancer, diabetes mellitus, and gastric atony. Today we will talk about what gastrostasis is, why it occurs, as well as methods of treating this disease. Read the following article on the pages of gastritinform.ru magazine.
Gastrostasis what is it
Gastric gastrostasis is a serious pathology that, in the absence of qualified medical care, can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life and negatively affect his overall health. With gastrostasis, the body does not receive enough of the micronutrients it needs, a person noticeably loses weight, and unpleasant symptoms prevent him from leading a normal lifestyle.
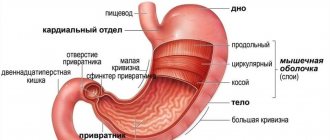
The very word “ gastrostasis ” indicates a specific problem that has arisen with human health. Everyone understands that the first part of the word, “gastro,” means stomach. Well, the second one – “stasis” – is translated as “stopping”. All together suggests that the stomach for some reason has stopped, stopped its activity in processing food. This disease is also called delayed gastric emptying syndrome. And also a disease of the operated stomach.
Gastric gastrostasis is a serious pathology that, in the absence of qualified medical care, can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life and negatively affect his or her overall health.
The diagnosis of “gastrostasis” is faced by people who have undergone operations on the stomach and duodenum, associated, for example, with the treatment of ulcers on these organs. Without going into details, gastrostasis can be called a postoperative complication when the operated patient experiences stagnation of the food mass contained in the stomach. It is clear that the operation leads to an imbalance in the functioning of the digestive organs, and efforts and medical means will be required to normalize their functioning.
Risk factors for congestive gastropathy
The etiology of this disease has not been fully explained, but liver cirrhosis to be a causative factor in its development. Organ damage leads to portal vein occlusion and hemorrhage. The risk of getting sick increases with age. A cause-and-effect factor for congestive gastropathy is also an unhealthy lifestyle, for example, a person’s addiction to alcohol and smoking. In addition, certain medications can cause portal infections. Long-term use of analgesics, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs damages the mucous membrane of the stomach and liver, which is unable to get rid of excess toxins. People with stomach ulcers, reflux disease, and chronic bacterial infections, especially Helicobacter pylori, are also vulnerable to gastric congestion.
Gastrostasis etiology
According to the etiological factor, gastrostasis is distinguished, which developed as a result of:
- functional reasons: gastric atony, pylorospasm;
- organic reasons: anastomositis, technical errors in ulcer removal;
- extraorgan changes that disrupt the gastroduodenal passage of food;
- combined reasons.
Depending on the timing of occurrence, early gastrostasis is distinguished (occurs in the early postoperative period) and late (develops 2–3 weeks after the operation).
What can you do at home?
How to provide first aid if food is in the stomach? If this happened to you due to overeating, then you need to lie on your back, unfasten the belt of your trousers or untie the belt of your robe so that they do not squeeze your stomach. Drink a cup of water, not carbonated. Do not eat for 2 hours to allow your stomach to rest. You can drink herbal tea to jump-start your digestive system.
For a child
A child may suffer from gastric atony due to drinking large amounts of carbonated drinks or overeating. Also the cause is strong feelings and stress.
How to help your child get rid of unpleasant sensations:
- bend your knees;
- lay on its side in this position;
- let it lie for up to half an hour;
- put a warm heating pad on your stomach;
- give a small amount of warm water to drink, the main thing is not to provoke nausea;
- make a light massage, stroking clockwise.
If nausea persists, it is recommended to induce vomiting. To do this, you need to drink a lot of water from 300 to 500 ml, depending on the age of the child. After the painful symptoms have passed, you should drink warm, not strong tea. Then serve a light diet meal. Even if there is no relief in this case, call an ambulance.
In an adult
If the symptoms are accompanied by heaviness, a feeling of coma, a slight aching pain, especially after eating, then you need to try to start peristalsis, increase the number of enzymes, and relieve spasms. To do this, you need to take appropriate medications or use herbs.
increase the number of enzymes with the help of drugs: Mezim, Pancreatin, Festal, Enzistal. Dry red wine also promotes digestion; for this you can drink 20-30 grams of wine.
relieve stomach and smooth muscle spasms: No-Shpa, Drotaverine. In addition, you can use mint tea, apply a heating pad, or a warm bottle of water to your stomach.
improve gastric motility : Domrid, Motilium, Motilak, Gonaton, Itomed.
If food is lumpy in the stomach of an adult, you can drink a decoction of marshmallow, fennel and buckthorn bark every time before eating. Mix all ingredients in equal parts, take a spoonful of the mixture and add 400 ml of water. Place in a water bath, bring to a boil, cool, strain through cheesecloth. Use the decoction for at least one month. You need to drink 200 ml at one time.
Another effective method is to use cinnamon. Spicy foods activate blood circulation in the body. Take 1 dessert spoon of powder, mix with a cup of boiling water and boil for about 5 minutes. Drink 1 tbsp for two weeks. l. half an hour before meals, three times a day.
If your stomach stops, you should not drink carbonated water! This is not mineral healing water from a spring. Gases in water from the supermarket will only worsen the situation, adding flatulence to the symptoms.
In all this, you should adhere to the recommendations of specialists:
- Avoid food for a while (4-6 hours after unpleasant symptoms);
- eat at a certain time;
- do not eat enough food 2 hours before bedtime;
- replace coffee with herbal tea from chamomile, St. John's wort;
- Prepare a paste of dried fruits, take 1 spoon on an empty stomach.
If your stomach is often upset and nausea is periodic, you need to think about going on a diet. The main food will be dominated by easily digestible products.
For reference! A good result comes from fasting days, which help not only cope with atony, but also lose extra pounds.
In pregnant women
During pregnancy, it is advised to avoid taking medications. You especially should not do this without the recommendation of your attending physician - this risk is not worth it. Therefore, if you feel heaviness in the stomach, dizziness and nausea, you must take the following measures:
- drink mineral water (pharmacy water);
- use low-fat kefir;
- take a few tablets of activated carbon, it does not harm even expectant mothers;
- drink mint and chamomile tea.
How to restart your stomach after poisoning?
If there is no belching, and the stomach does not want to work after poisoning, you should include porridge cooked in water with a small amount of sweeteners and salt in your diet. Chicken broth with the addition of rye bread crackers, black tea with sugar, and mineral water are suitable products during this period.
In case of poisoning, the structure of the stomach becomes intoxicated, so you should drink as much water as possible at room temperature. This will restore lost fluid. To keep it in the body, you need to take medications that restore water balance. These are such as Hydrovit or Regidron. It is also useful to drink green tea, fruit compotes, rosehip decoction, and jelly. Dairy products allowed include yogurt, low-fat cottage cheese, and kefir in small quantities. Carbonated drinks, strong tea and coffee should be avoided.
Chicory tincture normalizes the digestive system and gastrointestinal functions. You need to pour 200 ml of boiling water into 2 spoons and leave for 12 hours. Divide the drink into two doses, take before meals. Prepared food should be fresh and not too hot.
If the stomach should be stimulated, it is recommended to use pharmaceutical drugs that help restore the intestinal microflora and start its work. Often used:
- Bifiform;
- Hilak;
- Linux.
Toxins that cannot be removed by gastric lavage can be removed from the body using adsorbent agents: Atoxil or Sorbex.
Gastrostasis symptoms
Gastrostasis syndrome usually manifests itself with characteristic combinations of symptoms. Sometimes the patient may indicate only one or two signs that bother him. The most common complaints are nausea and vomiting. Some patients with impaired evacuation function complain only of belching and a feeling of fullness after eating, which is probably caused by the accumulation of food in a distended stomach. Anorexia and an early feeling of satiety are usually associated with constitutional features, but in combination with the symptoms mentioned above, they can be a sign of gastrostasis.
Still have questions? Ask your doctor for free online!
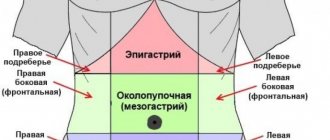
Abdominal pain is sometimes observed with gastrostasis, and is probably also associated with stretching, but their appearance should alert the doctor and prompt him to look for anatomical disorders in the stomach or surrounding organs that may be the cause of gastrostasis. Such disorders include: gastric ulcer, penetrating ulcer of the posterior wall of the duodenum, stomach cancer, indurative (pancreatitis, diseases of the biliary tract, “irritable” stomach, possibly caused by gastritis or a viral infection, as well as pancreatic cancer.
Clinical examination may not reveal any pathology or may only reveal a bulge in the epigastrium or gastric fullness. A splashing noise, characteristic of blockage of the gastric outlet, can be detected with gastrostasis, especially if there is a significant delay in the evacuation of fluid. It is possible, although rare, to detect pain on palpation in the epigastrium. Sometimes endoscopy or fluoroscopy reveals a bezoar, which may indicate a delay in evacuation.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of gastric obstruction usually appear very quickly and bring unpleasant, increasing pain. The main signs of a clogged gastrointestinal tract:
- Vomiting, diarrhea. The body strives with all its might to get rid of the food that has entered the stomach, which is why various digestive disorders occur.
- Increased gas formation, flatulence. As a result of intestinal blockage, fermentation occurs, then rotting of food masses.
- An increase in general body temperature as a sign of intoxication. This symptom most often leads to loss of appetite: at high temperatures, digestive enzymes lose their activity, so appetite reflexively decreases.
- Severe sharp pain in the abdomen. Gastrostasis, or blockage of the stomach, is usually accompanied by very unpleasant pain that occurs due to spastic contractions of the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Tendency to bleed. With this pathology, the vessels supplying blood to the organs of the digestive tract experience enormous pressure, as a result of which they can be damaged. This results in intraintestinal bleeding, a sign of which is dark stool.
Important! If any symptoms of gastrostasis occur, you must immediately consult a gastroenterologist who will examine the patient and make an accurate diagnosis.
In terms of diagnosis, patients are prescribed electrogastrography.
Causes of gastrostasis
Gastrostasis occurs in some patients after truncal vagotomy, especially with inadequate pyloroplasty. Main symptoms: nausea, regurgitation, vomiting, dull pain or heaviness in the upper abdomen. X-ray examination reveals a long-term retention of contrast in the stomach. For treatment, continuous nasogastric aspiration of gastric contents, enteral tube feeding, and prokinetics are recommended. If pyloroplasty is adequate, then with conservative treatment the symptoms of gastrostasis disappear as gastric motility is restored.
In addition to abdominal surgery, the cause of gastrostasis can be a narrowing, or, to use the medical term, “stenosis,” of the pylorus (the junction of the stomach and duodenum) due to an ulcer. Often, delayed gastric emptying is due to hypertrophic stenosis, which occurs in both children and adults. It can occur in newborns, which is explained by congenital pathology and requires a surgical solution.
Gastrostasis can also accompany cancer of the antrum of the stomach (the part of the stomach where swallowed food is ground and processed before entering the duodenum).
Diabetes mellitus can also be a cause of the disease. Thus, gastrostasis can develop not only after operations, but also accompany or be a consequence of certain diseases.
Often, gastrostasis and duodenostasis can occur as a result of pyloroduodenal stenosis and cicatricial deformation of the stomach, which occurs after PPV as a result of ulcer healing by scarring or due to compression, bending, deformation after stomach drainage operations and vagotomy. This can cause reflux esophagitis, reflux gastritis and peptic ulcers. Gastric stenosis and hourglass deformation are observed predominantly after PWS. The complication is extremely rare.
Treatment and preventative actions
Treatment of gastric atony should be carried out under the supervision of a specialized gastroenterologist, nutritionist, psychotherapist and physiotherapist. Accordingly, treatment consists of several blocks:
- classical (medicinal);
- diet;
- physiotherapy;
- control over the psycho-emotional state.
The primary action after diagnosing the pathology is the installation of a gastric tube. The stomach should be cleansed before the tube is inserted to avoid rupture and damage. Based on the tests obtained, the doctor determines the root cause of the disease and selects the appropriate drug complex. Drug therapy includes taking medications aimed at:
- improvement of gastric motility (normalization of muscle contraction);
- enrichment with vitamins and minerals;
- regeneration of damaged mucous tissues;
- general strengthening of the immune system and all body systems.
In severe cases, proteins (due to limited independent synthesis), anabolic steroids, potassium, and calcium are prescribed. Gastric atony requires the following preventive actions:
- normalization of diet (in the absence of proper nutrition, the possibility of relapse increases);
- taking prescribed medications;
- moderate physical activity;
- rejection of bad habits;
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, erosion, ulcer);
- strengthening the nervous system;
- eliminating the root cause of the disease;
- additional therapy such as treatment with mineral water, etc.
Gastrostasis treatment
It is carried out comprehensively, taking into account the causes of gastrostasis. Continuous or fractional temporary (2-3 times a day) gastric decompression is used. The timing of decompression is determined by the rate of restoration of the motor-evacuation function of the stomach. Patients are recommended to lie on their right side, which promotes “dependent” gastric emptying. Cerucal (1 ml intramuscularly 1–3 times a day), benzohexonium (0.5–1 ml of a 2.5% solution intramuscularly 1–3 times a day), pituitrin (1 ml subcutaneously 1–3 times a day), proserin are prescribed (1 ml of 0.05% solution 1-3 times a day). Polyionic solutions, potassium salts, chlorides, 10% xylitol solution (0.5 g per 1 kg of body weight) are administered intravenously. Effective methods of treatment are stimulation of the motor activity of the stomach with diadynamic and sinusoidal modulated currents, iontopheresis with acetylcholine.
How is the treatment carried out?
Pathology therapy consists of eliminating the cause that caused the stagnation. The treatment regimen includes pharmacological drugs and diet therapy. Medicines will require analgesics, means to improve motor skills, antiemetics, vitamins, and in case of infection, antibiotics. In case of severe dehydration, droppers with electrolyte solutions are indicated, and siphon enemas are indicated to ease stool. A very important element of therapy is the development of a diet. The patient is advised to consume protein foods, fruits and vegetables, as well as frequent split meals with easily digestible dishes and small portions. You can use dietary table No. 2. Among traditional medicines, tincture of blueberries, chamomile flowers, and mint tea will help improve your condition.
In the absence of results of conservative therapy and in advanced form, gastric obstruction can only be treated surgically. During the operation, resection of defective areas, dissection of adhesions and removal of other mechanical barriers are performed. In the first days after the operation, the patient can only drink warm tea or rosehip decoction. After the first stool, you can gradually introduce ground, liquid food, puree. The stitches are removed after 10 days.
To alleviate the patient's condition during long-term stagnation, gastric lavage using intubation is indicated.
Gastrostasis treatment with drugs
There is no single treatment regimen for gastrostasis. The choice of treatment tactics depends on the cause of the pathology. An important role in this is played by diagnostics and determination of the causes of impaired evacuation of food from the stomach. Treatment methods common to all patients include following the diet prescribed by the doctor.
Of the medications prescribed to most patients, it is worth highlighting antiemetics. They relieve nausea and make eating possible. Antiemetic drugs are prescribed in the form of rectal suppositories and injection solutions.
Among medications for delayed gastric emptying, prokinetic drugs are prescribed. Most often, intravenous injections of Erythromycin and Cisapride solution are prescribed. Metoclopramide may be prescribed in tablet form. It also has antiemetic properties. The drug Domperidone and its analogues: Motillium, Passazhix, Motilak are considered effective.
If eating naturally becomes impossible, nutrition is delivered to the patient through a small intestinal tube. In difficult cases, when conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment of the pathology is resorted to.
Glycemic control in patients with diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a common cause of slow gastric emptying. It has been suggested, but not proven, that effective glycemic control will improve gastric motility. This hypothesis is based in part on the following observations:
- Hyperglycemia caused in healthy individuals causes a decrease in antral motility, stimulates pressure in the pylorus and increases distension of the gastric fundus, all of the above slows down gastric emptying [4,5].
- Acute hyperglycemia can also affect gastric myoelectric activity and slow gastric emptying in patients with diabetes mellitus [6,7].
However, the role of chronic hyperglycemia is less clear. In one of the largest studies, for example, there was no significant difference in the rate of gastric emptying between patients with blood glucose levels above and below 270 mg/dL (15 mmol/L) [8]. Another potential concern is that glycemic control may be impaired in patients with delayed gastric emptying, even asymptomatic ones. Two factors may be responsible for this: variability in glucose absorption in patients receiving intensive insulin treatment and impaired absorption of oral hypoglycemic drugs [9]. However, there is no reliable data showing that treatment of gastrostasis improves the course of diabetes and prevents its complications.
Gastrostasis nutrition
Gastrostasis is a condition that prevents a person from eating normally
Due to the fact that liquid food leaves the stomach cavity more easily than solid food, with gastrostasis it should prevail in the patient’s menu. To do this, broths, liquid porridges, and liquefied foods are introduced into the diet. You can take protein supplements diluted in milk.
Multivitamin complexes in liquid form can be a source of vitamins and minerals. For gastrostasis, a diet with a reduced amount of fat and plant fiber is recommended. Fatty foods stay longer in the stomach, which slows down the emptying process, and fiber is not digested in the body.
Gastrostasis is a condition that prevents a person from eating normally. If it is impossible to eat food, the body loses strength, there is a lack of energy and nutrients. This leads to many other health problems. Pathology requires qualified medical care.
Symptoms
An enlarged stomach is one of the signs of the disease. The symptoms of this disease are similar to infectious/inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity (gastritis, ulcers, erosion, etc.). The main complaints of patients are as follows:
- an increase in the volume of the stomach (intragastric pain, which seems to stretch the organ);
- frequent manifestations of heartburn;
- nausea/vomiting (contains green substance);
- belching air;
- increased blood pressure;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- increasing the level and time of saturation;
- pallor of the epidermis;
- cold sweat;
- sensation of a large amount of fluid upon palpation;
- circulatory disorders (in the later stages of the disease in the absence of medical care);
- stagnation of food in the body (provokes the development/exacerbation of gastritis);
- moderate increase in acidity or complete absence of changes in pH levels.