– Why did I eat so much? - you think after a hearty lunch, when your stomach starts to hurt. Overeating can indeed be one of the causes of stomach discomfort. Other pain triggers include fatty, spicy, spicy foods, caffeinated foods, and alcohol. If it was just an episode, most likely it really is the ingredients or the serving size. It is much worse if you experience pain regularly after eating. Next, we will consider the most common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract that cause pain.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Pain is an integral symptom of irritable bowel syndrome . In addition to this, a person is usually tormented by bloating, increased gas production, belching and alternating diarrhea with constipation. If these symptoms are familiar to you, you will have to go to the doctor. Typically, treatment for IBS comes down to the following points:
- Proper frequent meals in small portions;
- Quitting alcohol and smoking;
- Reducing stress levels;
- Taking symptomatic medications to quickly eliminate discomfort (antispasmodics, antidiarrheals, laxatives);
- Taking gastroenteroprotectors to restore the mucous membrane and completely eliminate symptoms.
Classification of pain
Many people tend to feel pain after a tasty snack or a full meal.
The main types of pain that appear:
- Hungry. They do not become noticeable immediately, only after six hours have passed since the last meal. It’s easy to get rid of them or at least reduce their manifestation. It's enough to eat something. Drinking one glass of milk often helps.
- Late pain. They appear after a meal approximately two hours later. A common cause of such unpleasant sensations is the presence of a chronic form of pancreatitis.
- Night pain. They can signal more dangerous diseases.
- Early. The pain becomes noticeable after eating or within an hour of eating. They are characterized by inflammation in the stomach. For example, if an exacerbation of a chronic or acute form of gastritis has begun. Pain that appears an hour and a half after finishing a meal indicates damage to a more distant part of the digestive system (terminal part of the stomach or duodenum).
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach lining. The disease is caused either by the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter pylori (in 90% of cases), or by bad habits, or by taking dangerous medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, NSAIDs), or by poor diet, or, finally, by severe stress. Several aggressive factors can also act at once.
Gastritis is accompanied by abdominal pain, stool disturbances, weakness, drowsiness, etc. It is treated with diet and medications. First of all, eliminate the source of the problem. If it is Helicobacter pylori, then eradication therapy with antibiotics is first carried out, then the intestinal microflora is restored with probiotics, and the mucous membrane of the digestive tract is restored with gastroenteroprotectors.
If the cause of the disease is taking NSAIDs, then you just need to restore the mucous membrane .
In each specific case, the doctor individually prescribes a treatment strategy and dosage of drugs, so if a seditious thought has crept into your head to bypass the gastroenterologist, discard it.
Possible causes of intestinal pain on the right
The causes of abdominal pain on the right can be divided into pathological and non-pathological. The latter include overeating, food poisoning, poor diet, or intense exercise after abdominal surgery. In addition, short-term pain sometimes occurs due to strong psycho-emotional stress, such as stress. Aching pain on the lower right side may appear due to excessive gas formation.
Painful sensations on the right side of the abdominal cavity do not always occur in the intestines. The danger is that it is often difficult to distinguish them. Pathological causes of pain in the right intestine include the following diseases:
- the occurrence of neoplasms;
- Crohn's disease;
- colitis (including ischemic);
- dyskinesia;
- diverticulum;
- inflammation of the appendix;
- tuberculosis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- infectious intestinal diseases, etc.
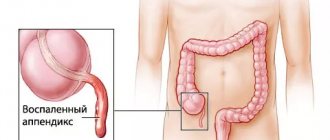
Inflammation of the appendix
Appendicitis or inflammation of the appendix is one of the most common intestinal diseases, which is localized in the right side, often in the hypochondrium. Treatment of pathology is often surgical, so you should consult a doctor at the first manifestations of pain. This will help you get by only with conservative treatment methods. Painful sensations are often confused with stomach pain. Pain can occur not only on the right side, but also in the navel area and hypochondrium. A characteristic feature is that the pain can shoot into the leg. Abdominal pain is variable in nature, usually not very intense. Over time, painful sensations can radiate down the abdominal cavity and become stronger. Patients note that discomfort increases with movement. Possible increase in temperature, nausea and vomiting.
Inflammation of the colon
Colitis is an inflammatory process in the colon that occurs due to infection. Painful sensations are localized to the right of the navel, sometimes in the hypochondrium. The pathology affects not only the large intestine, it can also spread to the small intestine, as evidenced by pain in the right side of the abdomen. The disease also manifests itself:
- elevated temperature;
- bloating;
- frequent bowel movements;
- gagging;
- general weakness;
- headaches;
- the presence of mucus and blood in the stool.
Ischemic colitis is a disease characterized by the development of an inflammatory process in the intestines, which occurs due to obstruction of the vessels located there. The disease is accompanied by cramping pain in the abdominal cavity, which sometimes manifests itself not only on the right. The pathology is dangerous. Lack of treatment can lead to irreversible consequences.
Crohn's disease
Pain in the intestines on the right may appear due to Crohn's disease - chronic inflammation of the intestines, which spreads to the blood vessels and lymph nodes. Ulcers and scars form on the walls of the intestines. Pathology can affect other organs and systems. In this case, the patient also complains of:
- weakness;
- lack of desire to eat;
- jumps in body temperature;
- weight loss;
- diarrhea;
- bloating, etc.
IBS (irritable bowel syndrome)
Irritable bowel syndrome is a functional disorder of the organ, when there is pain to the right of the navel or lower abdominal cavity, but no physiological sign of the disease is detected. The painful sensations are aching in nature. The cause of the disease often lies in the psycho-emotional state of the patient. TFR can also manifest itself:
- flatulence;
- mucus in stool;
- bowel dysfunction;
- a feeling that the intestines have not been emptied after bowel movements;
- general weakness;
- slight increase in temperature;
- headaches;
- aching muscles, etc.
Neoplasms
The appearance of neoplasms is often accompanied by discomfort and pain in the abdominal area. The most common tumors are polyps and cancer. Pain in the intestines on the right side is not severe; they can also appear in other parts of the abdominal cavity (on the left, in the navel, in the hypochondrium, etc.). If the tumor is small in size, symptoms are often completely absent. When a tumor grows, it compresses or blocks a passage in an organ. As a result, intestinal obstruction occurs.
Tuberculosis
Bloating and heaviness in the abdomen can be a symptom of tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis most often begins in the cecum. The symptoms of the disease are practically no different from other intestinal pathologies:
- slight increase in temperature;
- loss of appetite;
- prostration;
- bowel dysfunction;
- heavy sweating;
- bloating;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach after a meal;
- mild pain in the right side, often in the hypochondrium, etc.
Other reasons
Dysbacteriosis is a disease characterized by a violation of the composition of the intestinal microflora. It often manifests itself as painful sensations in the lower abdominal cavity. The stomach is “expanding”, it is hard. The patient is bothered by frequent loose, green stools. There is a sharply unpleasant odor of feces. If the disease is not treated, the stool becomes watery. In addition, the patient's appetite worsens and intestinal rumbling appears. The cause of pain in the intestines is helminthic infestation or infection with other parasites.
Diverticulitis is a bulging of the intestinal wall. Initially, the pathology is not accompanied by any signs. Symptoms appear when complications of the disease develop. In this case, the patient is bothered by acute pain to the right of the navel, as well as:
- temperature indicators increase;
- diarrhea with impurities of blood and mucous fluids appears.
Stomach ulcer
Pain after eating is a typical sign of a stomach ulcer . You may also experience heartburn, sour belching, nausea and vomiting. An ulcer, like gastritis, in the vast majority of cases is caused by Helicobacter pylori infection and is treated with a course of antibiotics (this pathogenic bacterium cannot be destroyed otherwise). Next, antisecretory drugs are prescribed to reduce the production of hydrochloric acid, and gastroenteroprotectors are prescribed to restore the damaged mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. And, of course, diet, where without it.
Why does pain occur in the lower abdomen after eating?
As we have already said, there are a number of reasons that can cause pain in the lower abdomen after eating. Here are the main ones:
- Poor nutrition, excessive consumption of foods high in animal fats, love of fried and spicy foods, overeating, flatulence. If the pain occurs periodically and goes away on its own, then treatment is most likely not required, you just need to follow a diet for a while, limiting the consumption of foods that are “difficult” for digestion.
- Stomach diseases, for example gastritis, can cause quite severe pain after eating in the lower left abdomen, or in the entire side. The pain is often accompanied by nausea, heartburn, belching, weakness, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth; as a rule, all symptoms worsen after eating or during long breaks between meals. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and start treatment, unpleasant symptoms will disappear within 1-2 weeks.
- Appendicitis, most often the pain in the right lower abdomen is of an increasing nature, intensifying after eating. Appendicitis requires immediate surgical intervention.
- Inflammation of the bile ducts and gallbladder. They can often cause pain in the lower abdomen after eating, or pain on the right side. Often, this is due to poor nutrition and consumption of large amounts of fatty foods. Also, the cause may be stones formed in the gall bladder, and the pain can be acute and paroxysmal in nature. If such pain occurs, you should consult a doctor and undergo a course of treatment followed by a diet.
- Irritable bowel syndrome. It is at this point that I would like to dwell in more detail. After all, most pain in the lower abdomen after eating is associated with irritable bowel syndrome. Next, we will look at associated symptoms, causes and treatment.
GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is what we used to call heartburn.
In addition to burning pain in the chest area, such patients often also experience abdominal pain. For GERD, you need to exclude all triggers from the diet (citrus fruits, caffeine, hot, spicy, salty, fatty, fried, alcohol, tobacco, soda) and take a combination of medications - antisecretory drugs in combination with prokinetics. The former suppress the production of hydrochloric acid, the latter normalize motility in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Diseases with symptoms of abdominal pain
If pain occurs periodically, regardless of the type of food consumed, then it is a sure signal of pathology of the internal organs.
Such diseases include:
- Pylorospasm. The disease manifests itself as spasms in such parts of the stomach as the pylorus or pylorus. The sensation of pain occurs almost within the first minutes after finishing a meal or after some period of time. Spasms are accompanied by vomiting, which prevents food from being digested.
- A disease called Irritable Bowel Syndrome. The pain is combined with diarrhea, bloating, and rumbling. Stool often occurs due to increased peristalsis. After the gas passes, the pain subsides gradually, but after eating food it appears again. Most often, such a syndrome in the intestines manifests itself in a calm state of the body, namely at night.
- Pancreatitis, characterized by dull or cutting pain in the area under the ribs. If the disease is not treated, the pain is girdling in nature.
- Ulcerative lesion of the stomach. It is most often a consequence of gastritis, sometimes duodenitis. The patient feels pain in between meals. Its location is the upper abdomen. Taking any product eliminates pain. This disease can be recognized by some other symptoms: heartburn, weight loss, feeling of overeating with minimal food consumption, loss of appetite, heaviness after eating. With gastritis, the symptoms of pain are similar to those of a stomach ulcer.
- Inflammatory process in the biliary tract, cholecystitis and dyskinesia. Pain in such diseases is observed in the area located in the right hypochondrium.
- Dysbacteriosis. This intestinal pathology contributes to the fermentation of products and the rotting of incoming food. As a result of such processes, the gastric walls become damaged and signal with pain that negative changes are occurring in the digestive system.
- Colitis, accompanied by inflammation of the large intestine. The pain is stabbing, sometimes even twisting.
- Reduced acidity. Food stays in the stomach for a long time because it cannot be digested due to a lack of gastric juice. As a result, the patient feels pain.
- Heartburn. This disease is also accompanied by difficult bowel movements.
Treatment of these diseases at home does not completely eliminate pain, but only muffles it for a short time.
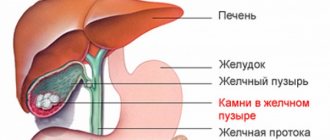
Gallstones
Gallstones can lie in the gallbladder for years, and a person will have no idea that he has them. But one terrible day they will move and stand in the bile duct. Then the patient will feel a sharp, sudden pain in the abdominal cavity. In addition to this, there is also nausea, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, and vomiting.
The treatment strategy for gallstone disease will depend on the severity of the patient's condition. Surgery is resorted to when the stones are too large or insoluble in composition. Cholesterol stones are classified as soluble. If they are less than 2 cm in diameter, they dissolve well with the help of drugs with ursodeoxycholic acid (ursosan). If there are more stones, then the gallstones need to be removed. As in the case of bilirubin stones, you should not even try to remove them with medication.
Right-sided anatomical structures of the abdominal cavity
If you divide the abdomen vertically in half, some of the organs end up on both sides because they occupy a central position:
- stomach (antrum and pylorus) and duodenum (flexure);
- pancreas (head and body);
- small intestine;
- bladder;
- large intestine (cecum, ascending and half of the transverse colon).
Therefore, when studying pathological changes, it is difficult to separate the right-sided and left-sided positions. Sometimes the source of pain is not located where it hurts; there are migrating sensations when a person is not able to pinpoint a specific location and talks about “pain throughout the abdomen.”
Some diseases have a “favorite” localization. The liver of the left lobe falls into the area of the left half and can cause pain throughout the upper abdominal cavity. Directly in the right area of the abdomen lie the gallbladder with ducts, the right kidney and ureter, and the appendix.
Diseases that can cause pain include:
- abdominal wall;
- vessels;
- right lower ribs.
Knowledge of the structure of organs made it possible to identify the characteristics of the pain syndrome:
- parenchymal organs (liver, kidneys) have a dense protective capsule with an abundance of nerve receptors; any unwanted effects, such as injury, inflammation, swelling, cause tension in the capsule and send pain signals to the brain;
- hollow organs (stomach, gallbladder, ureter) are equipped with receptors only in the submucosal layer, so they respond to muscle spasm, stretching, perforation by an ulcer, rupture, but rarely contribute to pain in mild catarrhal inflammation.
The kidney capsule consists of dense connective tissue
This mechanism must be taken into account by doctors in diagnosis. It is difficult to find out why the stomach on the right side hurts, since dysfunction of one organ leads to a failure of the overall digestive process.
Thyroid problems
With hyperthyroidism - hyperfunction of the thyroid gland - patients may experience disorders of the digestive system, namely abdominal pain. Patients also complain of increased sweating, muscle weakness, weight loss, anxiety, rapid heartbeat, and surges in blood pressure. In women, the menstrual cycle may be disrupted, and in men, potency may decrease. If you have these symptoms, first make an appointment with your therapist. Take a general blood test and find out whether the reason is hormones or something else
Main reasons
In healthy people who do not suffer from diseases of the digestive system, such pain may be a consequence of eating disorders. One of the main causes of pressing and bursting pain is overeating. The stomach is a hollow organ, that is, there is an empty space inside it that is filled with the food eaten. The volume of an empty stomach in a person weighing 60-70 kg is about 500-600 ml.
How much food can the stomach hold?
After eating, these numbers increase 2-3 times. If a person suffers from increased appetite (hyperrexia) or periodically experiences a feeling of psychological hunger (bulimia), he consumes more food than is required to satisfy physiological needs.
What is bulimia
In obese people prone to overeating, the volume of the stomach after eating can reach up to 3 liters (in people with stage 4 obesity - up to 4 liters). This pathology is called acute dilatation of the stomach and is accompanied by dull, bursting pain in the abdomen, which significantly intensifies after eating. For correction, the patient is usually prescribed a split diet with seven meals a day, increased physical activity to normalize the tone of the gastric walls and prevent gastric atony.
To correct the condition, fractional nutrition is required
If pain after eating is accompanied by vomiting, intestinal obstruction, or dehydration, mechanical removal of gastric contents is performed using a gastric tube. In case of severe dehydration, infusion of saline solutions and glucose solution is prescribed.
If necessary, glucose solution is administered intravenously
Overeating is not the only possible cause of pain in the right side. If pain occurs regularly, some pathologies should be excluded.
Pathologies that cause pain.
- Aerophagia. This is the swallowing of an increased amount of air during a conversation or eating, which leads to the accumulation of gas bubbles and the appearance of pain in the pyloric (lower) part of the stomach. The pathology is typical for people who eat on the run, as well as people with increased nervous excitability.
What is aerophagia
- Stomach hypotension. Hypotension is a violation of the motor function of the walls of the organ, as a result of which their contractile activity weakens, and food remains in the stomach for a long time, causing sharp or stabbing pain.
- Xerostomia. With xerostomia, the functioning of the salivary glands is disrupted, so the oral cavity produces an insufficient amount of saliva necessary for the primary digestion of food. Pain after eating in this case will occur simultaneously with other symptoms, the main of which is dryness of the mouth and lips.
Xerostomia
It is equally important in what mood a person eats. It has been proven that stress and emotional tension negatively affect digestive function and contribute to the appearance of unspecified pain in the epigastric and epigastric region. Prevention of abdominal pain in neurosis is the correction of psycho-emotional status (sedatives, long walks, exercise therapy, refusal to watch TV and read magazines while eating). If you can’t cope with a bad mood, or the person is in a depressed, depressed state, it is better to refuse to eat altogether and postpone it for a couple of hours.
Due to stress, food is poorly digested
What to do if there is pain in the lower abdomen
If you feel chronic, regular colic in the lower abdomen, aching pain, sharp cramps, then with such problems you need to contact a gastroenterologist who will conduct the necessary tests and examinations. For one-time manifestations of the disease, you can take medications that improve the functioning of the stomach and intestines. Antispasmodics help well with cramping pain; it is better to take tablets containing enzymes before/after meals. There are general recommendations that will help avoid the need for treatment:
- You should not frequently take laxatives or do enemas.
- Add more foods that contain fiber to your diet. If you experience flatulence after taking them, try replacing them with nutritional supplements.
- If you use a laxative, change the drug periodically so as not to cause your body to become addicted to a particular medicine.
- Doctors recommend adding foods containing pectin (most citrus fruits) to your diet.
- To improve peristalsis (pushing mass), it is recommended to drink more water.
- Eliminate coffee, hot peppers and other hot seasonings from the menu that irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, and stick to your diet.
How to diagnose pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen
If the cutting pain in the lower abdomen lasts more than 3 days, home medication therapy does not lead to the desired result, you need to consult a doctor who can accurately determine the causes of these sensations and prescribe an adequate course of therapy. To determine the source, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Visual inspection. The specialist assesses the patient’s condition based on external signs.
- Palpation. This palpation technique helps determine the degree of inflammation, location, nature and intensity.
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound examination provides the opportunity to obtain the most complete information about the condition of all parts of the intestine.
- Colonoscopy. A special device that is used only to study the condition of the colon.
What treatment is needed if the lower abdomen hurts severely?
When the pain is chronic and occurs regularly, you need to consult a specialist and conduct a study. Most people prefer to relieve spasms and pain on their own without seeing a doctor. To reduce discomfort in the intestines, drugs that can relieve pain are more often used:
- antispasmodics;
- analgesics;
- anti-inflammatory medications.
When a person suffers from diarrhea, it is necessary to take antidiarrheal medications. These can be medications or folk remedies (decoctions, infusions). For constipation, you need drugs from the group of laxatives; preference should be given to options that increase not only peristalsis, but also improve the condition of the gastrointestinal microflora. Strictly follow the dosage for adults and children indicated on the package.
When to call an ambulance
In many cases, a person manages to cope with abdominal pain on his own, but there are certain accompanying symptoms for which an ambulance should be called:
- temperature rises to 39;
- the person is unable to sleep or do any other activities;
- diarrhea with bright red blood;
- vomiting blood;
- stomach hard as a board;
- loss of creation due to pain;
- Along with diarrhea and vomiting, severe dehydration is observed.
Possible intestinal diseases
Depending on the nature of the sensations, spasm may be a sign of the following conditions:
- Aching pain accompanies chronic inflammation of the lower gastrointestinal tract, tumor processes, and obstruction.
- Acute discomfort is one of the points in the clinical picture of ulcerative colitis, appendicitis, and intestinal infection.
- Colic - cramping spasms are present during mechanical damage, poisoning, or parasitic infestation.
If the intestines in the lower abdomen hurt for a long period, two diagnoses are in question - ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. Another option is mesenteric thrombosis, which is fraught with necrosis. A feature of most of the listed pathologies is discomfort in the groin.
Pain in the lower abdomen on the right
This symptom indicates an impaired outflow of bile and inflammation of the bladder. The reason is the formation of stones blocking the lumens of the canals. In addition to right-sided spasm, cholecystitis is accompanied by heaviness in the lower back, discomfort in the shoulder and shoulder blade, fever and high temperature, nausea, vomiting, and itchy skin. Eating food contributes to increased discomfort on the right side.
Pain in the left lower abdomen
This symptom is included in the clinical picture of several pathologies:
- Gastritis. The disease occurs with a pronounced dyspeptic syndrome - increased gas formation, stool upset, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, unpleasant taste in the mouth, malaise, drowsiness, pale skin.
- Inflammation of the sigmoid colon.
- Impaired functioning of the pancreas. With pancreatitis, the clinical picture is complemented by bloating, stool retention, green vomiting with bile, and confusion.
- Stomach ulcer. In addition to the spasm on the left, there is belching with a sour taste, heartburn and nausea, and sudden weight loss.
Pain near the navel
This malaise is typical for the following conditions:
- Inflammation of the small intestine due to enteritis or helminthiasis.
- Appendicitis. The pathology requiring surgical intervention is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen on the right, but exceptions are possible. The reason is the anatomical location of the process. If the malaise is accompanied by loose stools, fever, nausea and vomiting, you should visit a surgeon.
When unpleasant spasms occur in several parts of the abdominal cavity at once, the question arises of a complex inflammatory process that requires prompt treatment.
Which doctor should I contact?
Pain on the right side of the abdomen can be caused by various diseases, the treatment of which is within the competence of different specialists. The choice of doctor should be made depending on the accompanying symptoms. If the pain is acute, does not subside over time, is accompanied by severe weakness, fever, a sharp deterioration in general health, a decrease in blood pressure or fainting, you must urgently call an ambulance. The patient is hospitalized in the hospital. The symptom complex indicates an acute emergency condition that can threaten not only the health, but also the life of a person. If help is not provided as soon as possible, there is a risk of death.
If the pain is moderate, you can visit a specialist as planned. First of all, you should consult a therapist. He will conduct an initial examination and perform diagnostics. Based on the information received, he can redirect the patient to other specialists
- Gastroenterologist - in addition to pain, the patient complains of constipation, bloating, flatulence, frequent bowel movements and soft feces, rumbling in the abdomen, nausea. Such symptoms indicate intestinal diseases.
- To the surgeon, the pain is nagging in nature and intensifies with stress, physical activity, sudden movements, but is in no way associated with digestive disorders, fever or general weakness. Such symptoms may indicate the appearance of adhesions in the abdominal cavity formed after surgery or inflammatory diseases of the digestive system.
- To the urologist - the pain radiates to the groin and lower back. It is combined with urination problems and forces a person to constantly move. The woman tries to find a position in which the pain will not be so severe. Symptoms indicate urolithiasis or renal colic.
- Neurologist - the pain is localized in the center and radiates to the right side of the abdomen. The unpleasant sensation is accompanied by frequent urination, which increases the pain. There is some blood in the urine. Symptoms indicate that the woman most likely has developed cystitis.
- For an infectious disease specialist - pain is combined with frequent initial loose stools, bloating, rumbling, lack of relief after defecation, and is accompanied by vomiting. The last symptom does not always occur. A set of signs indicates the development of an intestinal infection.
- To the gynecologist - the pain is dull or aching in nature. It occurs after stress, physical exertion or hypothermia. Most likely we are talking about inflammation of the uterine appendages. Associated symptoms include pain in the rectum, lower back or sacrum.
Unpleasant sensations also occur when urinating. The woman becomes hot-tempered and irritable. The menstrual cycle occurs irregularly. Fatigue increases. The discharge becomes greyish, greenish, yellowish, with flakes, pus or mucus. An increase in body temperature may occur.
A highly specialized specialist may prescribe additional diagnostic measures. Based on the results obtained, treatment is prescribed.