Does your abdominal area often swell? Does your weight seem to be increasing right before your eyes? Does your stomach hurt for no reason? Do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, you may have ascites!
COST OF SERVICES IN OUR CLINIC IN ST. PETERSBURG
| Abdominal ultrasound | 1200 rub. |
| Appointment with a urologist | 1000 rub. |
| Kidney ultrasound | 1000 rub. |
| Call free: 8-800-707-1560 *The clinic is licensed to provide these services | |
What is ascites and why is it dangerous?
The content of the article
The abdominal cavity is a separate anatomical region. It systematically produces moisture necessary to increase the efficiency of sliding of the abdominal visceral layers. During normal activities, the resulting effusion is absorbed fairly quickly.
However, it happens that free fluid begins to collect in the abdominal area. The cause of this anomaly may be a failure of blood circulation and lymphatic drainage or the presence of inflammatory processes. This disease is called “ascites,” which is better known as “dropsy.”
Dropsy of the abdomen is difficult to treat and leads to serious health problems. After all, the fluid accumulated in the peritoneal area creates ideal conditions for the formation of pathogenic microflora. It includes the causative agents of such dangerous diseases: hepatorenal syndrome, peritonitis, umbilical hernia, hepatic encephalopathy, etc.
Fortunately, today it is possible to determine the initial stage of development of ascites through the use of a non-invasive, very accurate and completely safe method - ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Thanks to the procedure, it becomes possible to begin a timely fight against the disease with the help of medications.
What are the dangers of excess mucus?
Excessive mucin formation provokes processes that in the future can lead to ulceration of the walls or cancer. They penetrate the walls of the organ very deeply, which causes discomfort and even pain. Patients often complain of pain and vomiting may occur.
As a result, mucosal hypertrophy occurs. It leads to gastritis with varying degrees of acidity or ulcerative formations. The longer this process, the higher the likelihood of stomach cancer. To prevent this, it is recommended to consult a specialist at the first symptoms of this disorder. If this factor was identified during the examination, the doctor may insist on further treatment.
What causes free fluid to accumulate?
The first and main cause of ascites is the appearance of any pathology in the pelvic organs. Initially, abdominal moisture collects in relatively small quantities (from 40 ml to 1 liter). Outwardly, it looks like swelling without inflammation.
The formation of the disease can also be influenced by a secretory disorder of proteins, the main task of which is to increase the degree of impermeability of the pathways and tissues that ensure the passage of circulating blood and lymph.
Such problems lead to the development of the following diseases:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- chronic renal and heart failure;
- portal hypertension;
- lack of protein;
- lymphostasis;
- malignant or tuberculous lesions of the peritoneum;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- diabetes.
Often the problem appears in the presence of neoplasms in the area of the ovaries, mammary glands, on the serous walls of the abdominal cavity and pleura, as well as the digestive organs.
In addition, the accumulation of free fluid can be triggered by complications of amyloid dystrophy, hypothyroid coma, pseudomyxoma and the postoperative period.
What signs indicate ascites?
At the beginning of its development, the pathology does not manifest itself in any way. The presence of a problem can only be determined by performing an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Ascites begins to show its first negative signs after the quantitative indicator of abdominal moisture exceeds one and a half liters. In this case, the following changes occur in the patient:
- total body weight and abdominal area increases;
- unpleasant sensations of “bloating” in the peritoneum;
- health worsens;
- in men there is swelling of the scrotum;
- your legs begin to swell;
- systematic belching, nausea, heartburn appears;
- it becomes difficult to breathe;
- tachycardia and flatulence are observed;
- the umbilical node protrudes forward;
- suffer from painful and uncomfortable sensations in the abdominal area;
- urination and stool are disrupted.
When too much effusion collects in the peritoneum, the patient may even feel it moving and hear splashing.
After detecting a pathology on an ultrasound, the doctor diagnoses “dropsy,” but you need to understand that this is just a symptom of one of the true reasons for the formation of fluid in the abdomen. Therefore, a new examination will follow.
How to prevent excess mucin?
It is easier to prevent a disease than to cure it. Therefore, it is recommended to adhere to proper nutrition, especially at the first symptoms of a gastrointestinal disorder.
The most effective preventive measure is a balanced diet. Food is primarily a way to obtain energy, so it should be healthy, not just tasty. Not only sick, but also healthy people are not recommended to abuse fried, fatty or smoked foods.
It is recommended to minimize alcohol intake, or better yet, abstain from it altogether. Alcohol destroys the gastric mucosa and reduces natural defenses. If you have a stomach ulcer, alcohol can cause a perforation.
The most healthy foods are low-fat soups and cereals. These are the ones you should stick to if you feel discomfort in your stomach. Pureed soups are best digested.
It is recommended to include boiled vegetables and fermented milk products in your diet. But it is recommended to abstain from whole milk: the adult body contains very few enzymes that break it down.
If fluid accumulates in the stomach in excessive quantities, this may indicate the development of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. A normal amount of mucus is always present in the gastric cavity, but its volume is strictly limited. Symptoms of the pathology appear gradually, but to successfully get rid of them it is necessary to eliminate the cause.
How to properly prepare for an abdominal ultrasound
One of the main advantages of ultrasound examination is that it does not have any restrictions or contraindications. In this case, ultrasound allows you to diagnose the presence or absence of many pathological processes in organs. But to get accurate results, you need to properly prepare for the examination.
The following rules must be adhered to:
- Three to four days before an abdominal ultrasound, it is prohibited to consume foods that can increase the formation of gases and include a large amount of fiber;
- A couple of hours before the procedure, you need to give a cleansing enema or use a laxative;
- To reduce gas formation the day before the ultrasound, you should take activated charcoal or Mezim.
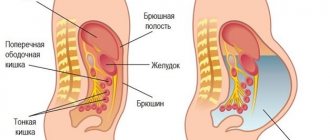
Thanks to modern ultrasound methods, a specialist will detect the accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. Most often this is:
- the upper abdominal region, located directly below the diaphragm;
- areas under the liver;
- descending and ascending colon;
- lateral canals;
- the small pelvis, into which the effusion enters through the lateral canals.
Ultrasound today is one of the most informative and effective ways to detect a dangerous disease. The physical properties of the liquid do not allow it to reflect the ultrasonic wave, therefore a spot forms in the image in this place. Or rather, effusion, even in small quantities, looks on the monitor like a moving dark lesion. If the person is healthy, the procedure time does not exceed five minutes.
However, it also happens that for one reason or another it is not possible to find a transudate. Therefore, the doctor uses additional examination techniques:
- During the process of tapping the peritoneum, the sound changes. In the lower zone it becomes more deaf, and in the upper zone it becomes tympanic;
- there is a shift of the loops of the colon.
Mucus in the stomach - why is it needed and what does its accumulation mean?
Our readers successfully use Monastic Tea to treat gastritis and ulcers. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Reading the description of the just completed FGS, patients sometimes learn about the accumulation of mucus in the stomach. For people who do not have a medical education and have a vague understanding of the mechanism of the digestive organs, such a mark raises many questions.
Mucus-bicarbonate barrier
The mucous membrane (MU) is enveloped in a continuous layer of gel. Normally its thickness is about 0.5 mm. This substance contains glycoproteins, which give it a unique property - elasticity.
As A.V. Kononov notes,
The main components of the attached gel, which provides cytoprotection of the coolant, are produced by the cells that they protect.
Bicarbonate is constantly secreted from the epithelium into the mucus, thereby maintaining an optimal pH gradient.
The mucous-bicarbonate barrier protects tissues from various negative influences - both chemical (“aggression of the acid-peptic factor” (2) and mechanical (the outer part of the mucus is easily desquamated and plays the role of a lubricant).
Glycoproteins (...) are constantly destroyed by active gastric juice, but in healthy people there is a dynamic balance between the rate of their destruction and renewal.
In the most common inflammatory diseases of the stomach, this balance is disturbed.
Pathological changes in gastritis and ulcers
In patients with Helicobacter pylori gastritis, the usual thickness of mucus on the coolant decreases: there is a noticeable shift of the gel towards the duodenum and beyond. This is a protective reaction of the body, its attempt to speed up gastric emptying and get rid of the pathogen (4).
The rejected gel no longer fulfills its protective function, and the organ becomes more vulnerable.
As the disease progresses, the situation is complicated by a significant change in the so-called rheological characteristics of the mucus: it becomes insufficiently elastic and viscous.
What should I do?
There are supposedly folk methods of clearing mucus from the body in general and the gastrointestinal tract in particular. Usually they are blatant barbarism. What is it worth at least the recommendation to swallow black peppercorns every day! Pepper is generally contraindicated for severe gastritis or ulcers, and even a healthy digestive system can be ruined in heavy doses. No less dangerous advice is to drink a strong tincture of ginger root.
Removing excess loose mucus as such is pointless. It is necessary to fight the disease as a whole, based on its pathogenesis and the present clinical picture.
In the HP-associated process (https://gastrit-yazva.ru/vidy/helikobakternoe-vospalenie/), therapy involves eradication - the destruction of HP bacteria, symptomatic treatment and measures aimed at normalizing the digestive process.
- A.V. Kononov, “Cytoprotection of the gastric mucosa: molecular cellular mechanisms”, “Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology”, T. 16, No. 3, 2006
- Ya.S. Zimmerman, “Modern methods for studying gastric functions and their diagnostic capabilities,” “RZHGGK”, No. 5, 2011
- T.K.Dubinskaya, A.V.Volova, A.A.Razzhivina, E.I.Nikishina, “Gastric acid production and methods for its determination”, Moscow, 2004
- Yu.V. Vasiliev, “Pathogenetic aspects of Helicobacter pylori”, “International Medical Journal”, No. 1, 2007
What types of ascites are there?
As mentioned above, dropsy is not an independent disease, but a sign of one of the pathologies, indicating that the process is in the last stages of development. Depending on the cause, ascites is divided into several forms, each of which differs in the individual severity of symptoms:
- initial - in the abdominal cavity the amount of fluid does not exceed one and a half liters;
- moderate – it is characterized by swelling in the area of the legs, shortness of breath, increased volume of the chest, constipation, heartburn, and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen;
- massive - in this case, the quantitative indicator of the collected water reaches five liters.
The condition is dangerous: the patient’s respiratory and cardiac systems are disrupted, the abdominal walls become tense, and the free fluid becomes infected.
During bacteriological testing of transudate, which is mandatory, experts distinguish between:
- sterile dropsy – does not have the presence of pathogenic microorganisms;
- infected dropsy – pathogenic microbes are present.
Ascites detected in a timely manner can be treated with medications. However, there is also a so-called pathological persistent disease that cannot be cured.
Treatment of pathology
If the ultrasound showed a critical accumulation of fluid in the body, it is necessary to begin immediate treatment of the deviation. Treatment measures should be aimed not only at relieving the symptoms of the disease, but also at eliminating the cause. Timely therapy minimizes the need for surgery. For treatment, an integrated approach is used, which includes taking medications, traditional medicine and surgery at the last stage of the disease.
Medicines
The treatment regimen for each patient is prescribed based on the results of ultrasound and laboratory tests. Conservative treatment involves the use of medications that normalize stomach function and mucus production. The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
Bellasthesin will help get rid of pathology caused by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ.
- "Bellasthesin." Painkiller based on analgin. Used to treat excess fluid due to gastritis.
- "Maalox." An antacid medication that is used to restore the mucous membrane.
- "Festal". Accelerates metabolism and normalizes acidity levels in the body.
- Antibiotics. Eliminate bacteria that provoke inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
It is prohibited to use medications if contraindications are found.
Traditional methods
In addition to taking medications, alternative medicine recipes are also used. The following methods have a good effect:
- Therapeutic fasting. Once a week you need to give up food and drink only water. To relieve hunger, you can add lemon juice to the liquid.
- Black peppercorns. In the evening you need to eat 1 tsp. before meals with water. You can't chew it.
- Ginger. Infuse the crushed rhizome in 2-2.5 liters of boiling water, mix with lemon and honey and drink on an empty stomach, immediately after sleep.
Diet food
The patient should not eat smoked meats and sausages.
The most important condition for successful treatment of ascites is proper nutrition. The diet is based on maintaining the balance of sodium in the body and enriching the body with proteins. The amount of salt consumed per day should be no more than 1 gram. In addition, you must avoid the following products:
- fresh baked goods;
- fat meat;
- sausage and smoked meats;
- milk;
- spicy broths and sauces;
- coffee and strong tea;
- alcohol.
It is better to cook food by steaming or in the oven, in its own juice. Instead of salt, you need to add fresh herbs. It is better not to eat raw vegetables. It is better to eat 5-6 times a day, in small portions. The amount of liquid consumed should not exceed 1 liter. In addition, it is necessary to ensure that the temperature of the food is not too low or high.
Possible operations
If the fluid is foamy, the walls are inflamed, and medications do not help, the patient undergoes surgery. Surgical treatment is used for 10% of patients. The operation involves peritoneovenous shunting - special tubes are installed in the veins, which create additional channels for removing fluid. However, this technique causes complications, so you should consult a doctor before performing it.
What will the patient face after the diagnosis is confirmed?
If an ultrasound confirmed ascites, the course of the treatment process will directly depend on the cause that caused the accumulation of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity. To make an accurate and reliable diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe additional diagnostics. The patient undergoes:
- general clinical and biochemical analysis of urine and blood;
- research on tumor markers and electrolyte metabolism;
- general x-ray of the abdominal and thoracic cavity;
- coagulogram showing the level of functionality of the blood clotting system;
- vascular angiography;
- CT and MRI of the peritoneum;
- hepatoscintigraphy, which will make it possible to view the liver with a special gamma camera;
- laparoscopy together with puncture of ascitic water may also be required.
If the patient has liver cirrhosis, he will additionally need to undergo portosystemic intrahepatic shunting. The manipulation is carried out using a mesh metal stent. The stent affects the space between the hepatic and collar veins. If an advanced form of the disease is observed, then organ transplantation is indispensable.
What happens if you don't treat it?
The accumulation of transudate is not a disease, but a negative manifestation of complications associated with other pathologies. If treatment is not started on time, dropsy will cause dysfunction of the spleen and heart. Also, the problem often provokes the onset of internal bleeding, cerebral edema and the formation of peritonitis.
And the worst thing is the mortality statistics from dropsy - patients die in 50% of cases. Therefore, you should not be negligent about your health: you need to be examined on time and seek medical help. Inflammations and infections should be treated urgently and only in a clinic. It is also very important to be systematically examined by a doctor for preventive purposes and to strictly follow all his recommendations.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter