K40—K46 Hernias
- acquired hernia
- congenital hernia (except for the diaphragmatic or esophageal opening of the diaphragm)
- recurrent hernia
Note:
a hernia with gangrene and obstruction is classified as a hernia with gangrene
- bubonocele
- inguinal hernia: straight
- bilateral
- indirect
- oblique
- NOS
- bilateral inguinal hernia NOS
- inguinal hernia (unilateral) without gangrene: causing obstruction, strangulated, irreducible, strangulation
- inguinal hernia NOS with gangrene
- inguinal hernia (unilateral) NOS
- femoral hernia (unilateral) without gangrene: causing obstruction, strangulated, irreducible, strangulation
- femoral hernia (unilateral) NOS
- umbilical hernia without gangrene: causing obstruction, strangulated, irreducible, strangulation
- gangrenous umbilical hernia
- hernia of the anterior abdominal wall without gangrene: causing obstruction, strangulated, irreducible, strangulation
- gangrenous hernia of the anterior abdominal wall
- hernia of the anterior abdominal wall NOS
- Diaphragmatic hernia without gangrene: causing obstruction, strangulated, irreducible, strangulation
- gangrenous diaphragmatic hernia
- Diaphragmatic hernia NOS
- abdominal hernia, specified localization NEC
- lumbar hernia
- obturator hernia
- hernia of the female external genitalia
- retroperitoneal hernia
- sciatic hernia
- obstruction without gangrene
- strangulation without gangrene
- irreducibility without gangrene
- strangulation without gangrene
- enterocele (intestinal hernia)
- epiplocele (omental hernia)
- interstitial hernia
- intestinal hernia
- intra-abdominal hernia
- hernia NOS
Excluding:
vaginal enterocele (N81.5)
- obstruction without gangrene
- strangulation without gangrene
- irreducibility without gangrene
- strangulation without gangrene
- abdominal hernia NOS
Add a comment Cancel reply
List of classes
- Class I. A00-B99. Some infectious and parasitic diseases
Excluded: autoimmune disease (systemic) NOS (M35.9)
disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus HIV (B20 - B24) congenital anomalies (malformations), deformations and chromosomal disorders (Q00 - Q99) neoplasms (C00 - D48) complications of pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period (O00 - O99) certain conditions arising in the perinatal period (P00 - P96) symptoms, signs and abnormalities identified during clinical and laboratory tests, not classified elsewhere (R00 - R99) trauma, poisoning and some other consequences of external causes (S00 - T98) endocrine diseases, nutritional disorders and metabolic disorders (E00 - E90).
Note. All neoplasms (both functionally active and inactive) are included in class II. The corresponding codes in this class (for example, E05.8, E07.0, E16-E31, E34.-) can, if necessary, be used as additional codes to identify functionally active neoplasms and ectopic endocrine tissue, as well as hyperfunction and hypofunction of the endocrine glands, associated with neoplasms and other disorders classified elsewhere. Excluded: certain conditions arising in the perinatal period (P00 - P96), some infectious and parasitic diseases (A00 - B99), complications of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium (O00 - O99), congenital anomalies, deformities and chromosomal disorders (Q00 - Q99 ), diseases of the endocrine system, nutritional disorders and metabolic disorders (E00 - E90), injuries, poisoning and some other consequences of external causes (S00 - T98), neoplasms (C00 - D48), symptoms, signs and deviations from the norm identified in clinical and laboratory studies, not classified elsewhere (R00 - R99).Chapter IX Diseases of the circulatory system (I00-I99)
Excluded
: diseases of the endocrine system, nutritional disorders and metabolic disorders (E00-E90) congenital anomalies, deformations and chromosomal disorders (Q00-Q99) some infectious and parasitic diseases (A00-B99) neoplasms (C00-D48) complications of pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum period (O00-O99) certain conditions arising in the perinatal period (P00-P96) symptoms, signs and abnormalities identified during clinical and laboratory tests, not classified elsewhere (R00-R99) systemic connective tissue disorders (M30- M36) trauma, poisoning and some other consequences of external causes (S00-T98) transient cerebral ischemic attacks and related syndromes (G45.-)
This chapter contains the following blocks
: I00-I02 Acute rheumatic fever I05-I09 Chronic rheumatic heart diseases I10-I15 Hypertensive diseases I20-I25 Ischaemic heart diseases I26-I28 Pulmonary heart disease and diseases of pulmonary circulation I30-I52 Other forms of heart disease I60-I69 Cerebrovascular diseases I70 -I79 Diseases of arteries, arterioles and capillaries I80-I89 Diseases of veins, lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes, not elsewhere classified I95-I99 Other and unspecified disorders of the circulatory system
2Causes and risk groups
The reasons for the infringement are:
- overvoltage;
- lifting weights;
- coughing;
- long crying in children.
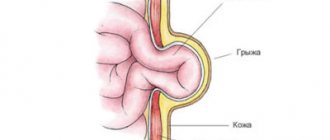
As a result of these phenomena, the pressure in the abdominal cavity increases, and the inguinal hernia is stretched more strongly, and some organs fall out. After the tension is relieved, the muscle ring narrows back, and the organs remain pinched. With this type, the contents of the hernia can include parts of the intestine, as well as the ovaries, fallopian tube, and bladder.
The fecal form occurs due to accumulations of feces in the adductor colon. The accumulation of feces begins to put pressure on the abductor muscle, and a strangulation gradually forms. In this case, the intestines end up in the hernial sac. Typically, such processes are observed in older people.
An inguinal hernia can be strangulated in 20% of 100%. Among middle-aged and elderly people, males are most often affected. In childhood, the disease occurs equally in both boys and girls.
Characteristic symptoms
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles .
The first sign is a sharp pain in the groin area, which can spread to the entire abdominal cavity. The pain syndrome occurs acutely, immediately after severe stress.
Our readers successfully use Sustalaif to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
When examining the groin, a protrusion may be detected. It is slightly swollen, hard and irreducible. When you try to straighten it with your hands, the pain only intensifies. The surrounding skin is elastic. In children, this protrusion may not be noticeable.
Another of the very first symptoms is nausea and vomiting. As the disease progresses, vomiting becomes constant. Immediately after strangulation, diarrhea may occur, followed by constipation and lack of gas. Periodically there is a false urge to defecate.
If the bladder is pinched, the patient experiences a frequent urge to urinate. The process is painful. Pain shock of 1-2 degrees (moderate and severe) may be caused. At the same time, the general condition of a person worsens. The temperature may rise.
In young children, a strangulated inguinal hernia is accompanied by anxiety and crying. Older children complain of pain in the groin.
The longer the disease develops, the stronger the pain becomes and spreads to the entire abdominal area. Symptoms develop faster and more intensely. The general condition also begins to deteriorate. For example, at the very beginning of the infringement the patient generally feels good, but a day later his condition sharply worsens. A fever and constant vomiting appear.
Diagnostic measures
The main method for determining ring strangulation in a hernia is the “cough impulse”. The doctor leaves his hand on the bag and asks the patient to cough. If the shocks are directed towards the area of compaction, then there is no infringement. If these shocks are absent, then infringement has occurred.
Palpation of the hernia can be difficult if it is small. Then an ultrasound is performed to confirm or refute the diagnosis. This is the most accurate and safe way to diagnose an inguinoscrotal hernia. Using an x-ray, you can identify the presence of loops of the large or small intestine in the area of the pouch.
Another diagnostic method is diaphanoscopy. With it, the scrotum is visible: in the absence of pathologies, the liquid inside passes the directed rays of light without any problems. The presence of denser structures in the fold will make it dull and uneven.
In boys, the doctor should also check the descent of the testicles into the scrotum, their size and shape. And also determine the possible presence or absence of varicocele. The lymph nodes of the groin area are subject to mandatory examination.
When there is a question that there may be a cyst in the spermatic cord, you should definitely take the hernial contents for examination through puncture. Its symptoms can often imitate the development of a hernia. Video of inguinal-scrotal hernia on ultrasound:
Description
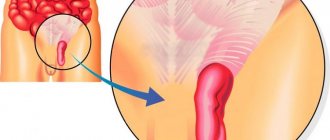
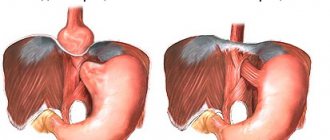
An inguinal hernia is a pathological protrusion of the peritoneum into the cavity of the inguinal canal. They occur much more often in men. The inguinal canal is a cavity of triangular cross-section, in which the round ligament of the uterus passes in women, and the spermatic cord in men. Inguinal hernias are among the most common abdominal wall hernias.
Strangulated inguinal hernia (ICD - 10 K40.3 - K 45.8) is a common complication, occurring in 10-20% of all cases of the disease. In this case, compression of the abdominal organs or peritoneum occurs in the hernial orifice, in the inguinal canal. This is the anatomical space in which the round ligament of the uterus is located in women, and the spermatic cord in men.
A predisposing factor for the appearance of hernias is weakness of the muscles of the groin area, increased stress, trauma, and often the formation of hernias during pregnancy or with prolonged crying in infants. Strangulation of inguinal hernias in men in adulthood occurs more often than in women. A strangulated inguinal hernia in children and newborns occurs with the same frequency and is formed, as a rule, already in the prenatal state.
The good news is that the operation is usually successful.
If you discover symptoms of an inguinal hernia strangulation, call an ambulance immediately and don’t even think about refusing the operation.
Strangulation is the most common and most dangerous complication of any hernia. From 10% to 40% of patients with hernias are first examined by a surgeon already in a state of strangulation; up to 60% of all strangulations occur in the inguinal canal.
This is a non-infectious disease that can affect older men and young boys. In representatives of the stronger sex, a hernia most often develops after 50 years. At this age, the natural elasticity of connective tissues decreases, and any physical activity creates additional pressure in the abdominal cavity, causing organ prolapse.
Prevention
Since congenital inguinal hernias are mainly observed in children, the main preventive measure for their occurrence is the timely identification of risk factors for the disease and regular examination of the child by pediatric specialists, primarily a pediatric surgeon. Prevention of acquired inguinal hernia in children is achieved by rational nutrition, regulation of intestinal function, treatment of constipation, and exclusion of heavy physical activity.
- https://ZhivotNeBoli.ru/neotlozhnye-sostoyaniya/gryzha/ushhemlennaya-pahovaya-gryzha.html
- https://kiberis.ru/?p=32736
- https://spina.sustav-med.ru/narodnyie-sredstva/pravostoronnyaya-pahovaya-gryzha-mkb-kod-10/
- https://diseases.medelement.com/disease/%D0%BF%D0%B0%D1%85%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D1%8F-%D0%B3%D1%80% D1%8B%D0%B6%D0%B0-%D1%83-%D0%B4%D0%B5%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%B9/15077
Localization
Paragraph K40 contains several subparagraphs that determine the types of pathology by location, for example, the following:
- double sided;
- one-sided;
- unspecified;
- oblique;
- scrotal;
- straight;
- indirect.
The second digit of the International System of Disease Classification code characterizes the localization of the protrusion of the abdominal cavity, which can be determined by a competent specialist anywhere in the world.
Causes
Many reasons for the development of an inguinal hernia of this type are associated with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which can be caused by constipation, sneezing due to allergies, and frequent coughing due to diseases of the lungs and bronchi.
The occurrence of infringement is facilitated by:
- abdominal injuries;
- pregnancy;
- excess weight;
- weak muscles of the abdominal wall;
- surgical intervention;
- atony (impaired bowel movement).
The development of pathology is influenced by physical activity (heavy lifting), difficult childbirth, difficulty urinating in men due to prostate adenoma, severe crying and sobbing.
Signs of an abdominal hernia. Selection of postoperative brace for the abdominal cavity. Ring in the stomach: what to do? Read more>>
Rehabilitation
During the recovery period it is recommended:
- provide bed rest for 24-48 hours;
- feed the child light food that does not cause fermentation;
- use antibiotics to help prevent bacterial infections;
- change the bandage regularly;
- limit any physical activity in the first days after surgery.
During the recovery period, it is recommended to use antibiotics to help prevent bacterial infections.
- Breathing exercises
Performing special exercises in the early postoperative period prevents dysfunction of the cardiovascular system and eliminates fluid stagnation in the lungs. In the future, breathing exercises are used to strengthen the abdominal muscles, preventing the prolapse of internal organs.
- Bandage
Wearing a bandage after surgery helps keep organs in the correct position, helps strengthen the abdominal muscles, and prevents the recurrence of a hernia.
The device is put on in a lying position, when the child is as relaxed as possible.
The use of the device should not be accompanied by unpleasant sensations. The bandage is worn for 12-16 hours a day, and after removal, massage of the abdominal area is performed.
Characteristic symptoms
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles .
The first sign is a sharp pain in the groin area, which can spread to the entire abdominal cavity. The pain syndrome occurs acutely, immediately after severe stress.
Our readers successfully use Sustalaif to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
When examining the groin, a protrusion may be detected. It is slightly swollen, hard and irreducible. When you try to straighten it with your hands, the pain only intensifies. The surrounding skin is elastic. In children, this protrusion may not be noticeable.
Another of the very first symptoms is nausea and vomiting. As the disease progresses, vomiting becomes constant. Immediately after strangulation, diarrhea may occur, followed by constipation and lack of gas. Periodically there is a false urge to defecate.
If the bladder is pinched, the patient experiences a frequent urge to urinate. The process is painful. Pain shock of 1-2 degrees (moderate and severe) may be caused. At the same time, the general condition of a person worsens. The temperature may rise.
In young children, a strangulated inguinal hernia is accompanied by anxiety and crying. Older children complain of pain in the groin.
The longer the disease develops, the stronger the pain becomes and spreads to the entire abdominal area. Symptoms develop faster and more intensely. The general condition also begins to deteriorate. For example, at the very beginning of the infringement the patient generally feels good, but a day later his condition sharply worsens. A fever and constant vomiting appear.
Diagnostics
METHODS, APPROACHES AND PROCEDURES FOR DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
Diagnostic criteria
Complaints:
for a tumor-like protrusion in the inguinal, inguinal-scrotal area.
History of the disease:
The reason for the examination is a clinical examination of children or complaints from parents about the periodic appearance of a tumor-like formation in the groin area or an increase in the size of the scrotum.
Physical examinations:
Upon examination:
the clinical picture of an uncomplicated inguinal hernia is manifested by the presence of a tumor-like formation in the groin area, which increases with screaming and anxiety and decreases or disappears in a calm state.
The protrusion has a round (for inguinal) or oval (for inguinal-scrotal hernia) shape. On palpation,
the elastic consistency, painless, hernial protrusion disappears on its own when the patient moves to a horizontal position, or as a result of finger pressure. At the same time, a characteristic rumbling sound is clearly audible. After reduction of the hernial contents, the enlarged external inguinal ring is palpated.
In girls, the protrusion with an inguinal hernia has a round shape and is located at the external inguinal ring. If the hernia is large, the protrusion may descend into the labia majora. Older children are examined in a standing position, with abdominal muscle tension and coughing.
Laboratory research:
No.
Instrumental research (UD - B):
· Ultrasound examination of the groin area, scrotum.
List of necessary studies for planned hospitalization:
· general blood analysis; · general urine analysis; · biochemical blood test (total protein and its fractions, urea, creatinine, ALT, AST, glucose, total bilirubin and its fractions, amylase, potassium, sodium, chlorine, calcium); · coagulogram (prothrombin time, fibrinogen, thrombin time, INR, APTT); · blood test for hepatitis B, C; · blood test for HIV; · feces for worm eggs · ECG - to exclude heart pathology before the upcoming operation; · Echocardiography - if congenital heart disease is suspected; · consultation with specialists - according to indications (anemia - hematologist, heart pathology - cardiologist, etc.).
Indications for consultation with specialists:
· consultation with narrow specialists - according to indications.
Diagnostic algorithm:
Localization
Paragraph K40 contains several subparagraphs that determine the types of pathology by location, for example, the following:
- double sided;
- one-sided;
- unspecified;
- oblique;
- scrotal;
- straight;
- indirect.
The second digit of the International System of Disease Classification code characterizes the localization of the protrusion of the abdominal cavity, which can be determined by a competent specialist anywhere in the world.
Congenital
The following reasons contribute to the occurrence of an inguinal hernia in a child:
- The appearance of pathological folds after the uterus assumes a physiological position. After 24 weeks, the internal genital organs of the fetus begin to move down, taking the correct position. Sometimes this process involves peritoneal tissue, which forms a fold. After the birth of the child, it becomes a hernial sac.
- Complicated pregnancy. Toxicosis, gestosis, psycho-emotional overload, depressive disorders, and unhealthy diet are dangerous for the fetus. The girl develops congenital weakness of connective, muscle and fatty tissues, as well as other anomalies that provoke incompetence of the abdominal wall.
The following reasons contribute to the occurrence of an inguinal hernia in a child: complicated pregnancy.
Symptoms of the disease
Inguinal hernias in girls have the following symptoms:
- The presence of a seal in the perineum, pubis or labia majora. It has a dense elastic consistency and a round shape. When the child takes a lying position, the size of the hernial sac decreases. With small hernias, the seal completely disappears. When the girl stands up or sits down, the protrusion appears again.
- Increased swelling in the perineum. It is observed when pressure in the abdominal area increases (during coughing, crying, sneezing or vomiting).
- Pain in the perineal area. Characteristic of large and strangulated hernias. With uncomplicated protrusion of internal organs, the child does not experience any inconvenience.
- Rumbling in the stomach. This sign indicates prolapse of intestinal loops. In rare cases, children complain of flatulence and pain in the navel area.
- Signs of intestinal obstruction. Gases and solid feces accumulate in the intestines, the child loses appetite and becomes restless. This is typical for strangulated hernias.
Diagnostics
To identify inguinal protrusions, the following diagnostic procedures are used:
- Examination and interview of the child and parents. Specific signs of the disease help to easily make a preliminary diagnosis. If an inguinal hernia is accompanied by an adhesive process, the patient tries to be in a special position, slightly leaning forward.
- Palpation. Used to determine the type of protrusion - reducible or irreducible. To determine the symptom of a cough impulse, the girl is asked to cough, the doctor evaluates the vibration that appears. It is transmitted to protrusion.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs. Helps obtain information about the condition of internal organs, which helps plan the course of future surgical intervention.
Treatment method
It would seem that with such destruction of the disc as an intervertebral hernia, there is nothing to hope for. However, it is not.
Our body has a huge resource for self-healing. When diagnosed with an intervertebral hernia, treatment using integral medicine methods consists of helping the body recover as much as possible, stimulating and strengthening the mechanisms for restoring damaged disc tissue.
To do this, it is necessary, firstly, to eliminate the causes of destruction of the intervertebral disc - congestion in the back, vascular edema, pinched nerves, muscle spasms. And secondly, enhance the nutrition of the disc tissue - improve blood supply and oxygen delivery, normalize metabolic processes.
It takes time, but the results of such treatment for intervertebral hernia are incomparable to anything else. Today, integral techniques make it possible to successfully treat and eliminate intervertebral hernias up to 12-14 mm in size without surgery.
When diagnosed with an intervertebral hernia, treatment includes the same methods as the treatment of osteochondrosis and disc protrusion (with the exception of manual therapy) - acupressure, special massage, acupuncture, hirudotherapy, physiotherapy, but the nature, intensity and sequence of effects have significant differences.
There are cases in which it is possible to treat a scrotal hernia without surgery. As a rule, this is done at the stage of early development of compaction.
Surgery is contraindicated if:
- Severe health condition of the patient;
- Intolerance to anesthesia;
- Anemia;
- Acute infectious and inflammatory processes.
In these cases, doctors focus all their efforts on conservative treatment of the patient, since he may not tolerate surgery. There are cases in practice when the patient himself refuses to undergo any surgical procedures.
Non-surgical treatment also involves wearing a special bandage. With its help, organs are retained. Outwardly, it looks like swimming trunks. You can strengthen your abdominal muscles through light physical exercise. To relieve pain and inflammation, painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed.
Surgical intervention
In cases where taking medications does not produce positive dynamics or the disease is at a stage where medications no longer help, surgical intervention is required. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and takes about half an hour.
The patient is made an incision through which access to the hernia is made. The sac with it must be removed, and the prolapsed organs must be reduced. Plastic surgery is performed on the inguinal canal damaged during surgery.
Stitching of the layers of wounds occurs sequentially with the installation of drainage. In the postoperative period, there is a risk of a ligature fistula.
Rehabilitation after surgery
Approximately 3 months after surgery, the patient can begin to move. A bandage is applied to the incision site, on which purulent discharge may accumulate.
There's nothing wrong with that. After the manipulation, this is the norm.
The stitches are removed after 1-1.5 weeks. During the first 20 days after this, heavy lifting is prohibited.
It is better to avoid physical activity for six months from the date of the operation.
The healing process will proceed faster if the patient follows medical recommendations during the rehabilitation period. These include:
- Wearing a compression bandage;
- Refusal of increased physical activity;
- Taking antibacterial drugs.
If these conditions are met, the prognosis for recovery is very favorable. Subsequently, the man or boy can return to his usual lifestyle. But the influence of factors that provoke the appearance of an inguinal-scrotal hernia should be controlled.