- Pale skin
- Abdominal pain
- Hungry pain in the stomach
- Constipation
- Heartburn
- Sour taste in mouth
- Malaise
- Belching
- Diarrhea
- Vomit
- Weakness
- Nausea
- Heaviness in the stomach
- Deterioration of general condition
Gastropathy is a pathological process of a gastroenterological nature, manifested by changes in the gastric mucosa.
In most cases, gastropathy of the gastric antrum is caused by taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, however, the influence of other pathological processes cannot be excluded. The clinical picture does not have specific symptoms, since superficial gastropathy is a consequence of other gastroenterological diseases. A thorough diagnosis is required to make an accurate diagnosis. Treatment is determined on an individual basis. At the initial stages, it is possible to eliminate the disease through conservative measures. Regardless of the chosen treatment tactics, a diet must be prescribed.
There is no definite prognosis, since everything will depend on the underlying factor, the timeliness of starting therapy and general health indicators. The disease has no clear restrictions on gender and age, but is more often diagnosed in women, which may be due to hormonal characteristics.
Etiology
Congestive gastropathy, like other forms of this disease, can be caused by the following factors:
- long-term use of medications - anti-inflammatory, antibiotics, painkillers (reactive gastropathy develops);
- insufficient secretion of enzymes that are necessary for proper digestion;
- burn of the esophagus and other injuries;
- stagnant processes in the esophagus, bile reflux;
- improper blood supply to the gastrointestinal tract;
- chronic gastroenterological diseases;
- hereditary predisposition.
The risk group is determined by the following factors:
- age (people over 55 years old);
- the presence of chronic diseases (not only of a gastroenterological nature);
- genetic predisposition to gastroenterological diseases;
- abnormalities in the structure of the gastrointestinal tract;
- hormonal disorders.
In more rare cases, but this option is still not excluded, congestive gastropathy is caused by other systemic diseases that are not directly related to the gastrointestinal tract.
Prevention
To prevent the development of erosive antral gastritis, a number of preventive measures must be observed:
- timely treatment of gastrointestinal diseases and infectious diseases;
- maintaining sanitation and hygiene;
- avoiding unhealthy diets;
- adherence to a therapeutic diet and a regular diet (at least five times a day with an interval of 3 hours);
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcohol and drug abuse);
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- exclusion of stressful situations and strong radiation.
The condition of the mucous tissues of the stomach walls and their protective properties largely depend on a person’s lifestyle and his immune system. To prevent complications of gastritis, when the first manifestations of the disease are detected, you should urgently seek medical help.
List of references: https://sakhalinmedia.ru/news/23.11.2015/erozivniy-gastrit—kachestvennaya-diagnostika-i-effektivnoe-lechenie-za-rubezhom.html msdmanuals.com/ru/professional/diseases-gastrointestinal- tract/gastritis-and-peptic-ulcer/erosive-gastritis https://www.obozrevatel.com/health/bolezni/antralnyij-gastrit.htm https://kiozk.ru/article/cto-takoe-erozivnyj-gastrit- simptomy-i-lecenie-bolezni https://www.passion.ru/health/zhkt/antralnyy-gastrit-simptomy-i-lechenie-85966.htm https://www.promedicina.clinic/adult/gastrit-erozivnyj/ med.vesti.ru/articles/zabolevaniya/erozivnyj-gastrit-zheludka-simptomy-lechenie-dieta/ https://www.wmj.ru/stil-zhizni/zdorove/erozivnyy-gastrit-simptomy-lechenie-pravilnoe-pitanie. htm https://atvmedia.ru/materials/gastrit-antralnogo-otdela-zheludka Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/16/2020
Classification
Gastroenterological disease is classified according to several criteria:
- the nature of the flow;
- stage of development;
- clinical and morphological signs.
According to the nature of the course, the pathological process is considered in the following forms:
- initial (hyperemic gastropathy) - the mucous membrane is not changed, slight redness is possible, which indicates the early onset of the inflammatory process;
- atrophic - replacement of some parts of the esophagus with connective tissue;
- hypertrophic gastropathy - cysts form, scarring of the stomach walls occurs, the stage is characterized as extremely severe.
Regarding the degree of development of the pathological process, the classification is as follows:
- 1st degree - slight decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid, the clinical picture is absent or manifests itself in a latent form;
- 2nd degree - pronounced symptoms, significant deterioration in well-being.
Even with the second degree of development of gastropathy, if treatment is started correctly, complications can be avoided.
The pathological process is classified according to the nature of the course as follows:
- acute - caused by exposure to medications and chemicals. Poor nutrition;
- chronic - the formation of erosions, ulcers on the mucous membrane of the esophagus (develops if treatment is not started in a timely manner).
Based on clinical and morphological characteristics and taking into account the localization of the development of the pathological process, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- antral gastropathy - pathology develops in the antrum of the stomach;
- associated or non-steroidal gastropathy - a consequence of taking medications, most often NSAIDs;
- hemorrhagic gastropathy - excessive blood supply to the stomach, which leads to swelling of the mucous membrane;
- papular gastropathy - the formation of single or multiple papules on the gastric mucosa;
- portal gastropathy, portal hypertensive gastropathy - a pathological process caused by vasodilation and increased blood pressure;
- erosive gastropathy - formation of erosions and ulcers on the gastric mucosa;
- diabetic gastropathy is a pathological process caused by diabetes.
Determining the nature of the pathological process is carried out through diagnostic measures.
Symptoms
Chronic erosive gastritis may have nonspecific symptoms. The most commonly observed manifestations are:
- moderate pain in the epigastric region;
- nausea;
- stool disorders;
- heartburn;
- poor appetite;
- bloated stomach;
- general weakness;
- increased sweating;
- vomiting with blood.
In the acute form of erosive antral gastritis, more pronounced symptoms are typical:
- Sharp pain in the abdomen.
- Periodic pain in the lower abdomen (usually after eating).
- Feeling of stomach constriction, burning and heaviness in the abdomen.
- Belching, heartburn.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Diarrhea followed by prolonged constipation.
If ulcers have formed on the walls of the antrum, the pain syndrome is similar to the pain associated with ulcerative gastrointestinal tract. Pain occurs in the morning on an empty stomach or 1-2 hours after eating. Signs of bleeding with erosive antral gastritis are:
- vomiting blood;
- melena (semi-liquid black stool);
- pale skin;
- cardiopalmus.
When an exacerbation of erosive antral gastritis occurs against the background of reflux, the following symptoms will be observed:
- Belching with a bitter taste.
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- White coating on the tongue.
Over time, the inflammatory erosive process causes atrophy of the glands. In this case, pain may not be felt. Appetite decreases, a feeling of fullness in the stomach is felt, the person quickly becomes full and loses a little weight.
Provoking factors
Age after 40 years. Chronic gastritis. Helicobacter pylori. This bacterium in the process of its life provokes gastritis and ulcers. Against this background, a polypoid formation begins to form. Gastric resection. Peristalsis is impaired. Hereditary factor.
Polyposis can cause cancer. The exact time it takes for a benign tumor to transform into a malignant one is unknown. For diagnosis, X-ray examination or an endoscope is used.
Diagnostics
A comprehensive diagnosis is required, since there is no specific clinical picture. A gastroenterologist, after a visual examination and history taking, may prescribe the following:
- general clinical and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- general analysis of stool;
- pH-metry;
- PCR testing;
- endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- X-ray of the stomach with a contrast agent;
- ELISA.
At the discretion of the doctor, the diagnostic program can be supplemented with other laboratory or instrumental research methods.
Treatment
Treatment will depend on what caused the development of the pathological process. In most cases, the disease is eliminated through conservative measures; in some cases, surgical intervention is practiced.
Drug treatment can be based on the following drugs:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antispasmodics;
- sorbents, enterosorbents;
- prokinetics;
- antacids;
- intestinal antiseptics;
- prostaglandins;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- medications to improve gastric motility and enzyme production.
A diet is required. The specific dietary table is determined on an individual basis.
Provided that therapeutic measures are started promptly and correctly, complications can be avoided. The forecast is personal in nature.
As for prevention, the only appropriate solution would be to take measures to prevent pathological processes that are included in the etiological list.
I did FGS. The conclusion is as follows:
Esophagus: Z line is uneven, there are quite numerous erosions in the upper boundaries of the gastric folds. Stomach: The mucous membrane of the antrum, body and fundus is hyperemic. Two rather large flat erosions are visible in the antrum. The lake is clean. Gatekeeper unchanged.
Conclusion: Reflux inflammation of the esophagus, Aphthous Gastropathy (flat erosions). Helicobacter - negative
The only treatment is omeprazole. Is this treatment enough?
A month before this examination, I drank Bismuth, 2 tablets. in the morning and before bed, for 4 weeks. She decided to drink it herself. But the erosion remained. I understand that gastritis and all these phenomena are not the cause itself that needs to be treated. Is it worth checking the cartisone level (it seems to me that I am constantly stressed because nothing is going away), or maybe take some sedatives. Well, food! What is the table for this disease?
With respect to you and your work, Tatyana
Treatment of erosive antral gastritis
Treatment should begin with the fight against pathogenic microorganisms. Symptomatic therapy is aimed at eliminating signs of inflammation, stopping bleeding, normalizing acidity and enzyme production, and healing tissues affected by erosion.
The treatment regimen for antral gastritis includes the use of medications, proper nutrition, physiotherapeutic procedures and traditional methods. Therapy is carried out in 2 stages.
The first step is a powerful drug treatment that eliminates pathogenic microorganisms and normalizes the functions of the stomach.
Antibiotics help relieve the inflammatory process and prevent the spread of infection to other parts of the digestive system.
Antacids neutralize hydrochloric acid and protect mucous membranes from destruction.
Proton pump inhibitors reduce the acidity of gastric juice by affecting the cells responsible for the production of the aggressive substance. Painkillers are aimed at relieving discomfort.
The second stage is restorative therapy, which promotes tissue healing, improves the general condition of the body, and prevents re-exacerbation of the disease.
The course of treatment for erosive antral gastritis lasts at least 2 weeks.
At the first stage, penicillin antibiotics and clarithromycin are used. Additionally, prokinetics and histamine receptor blockers are used.
If the above treatment regimen is ineffective, it is replaced by another. Metronidazole is taken in combination with tetracycline, a proton pump inhibitor and bismuth dicitrate.
Antisecretory drugs reduce the activity of gastric juice, normalize acidity and stop the process of tissue destruction.
The most effective means are:
- Almagel,
- Gaviscon,
- Maalox.
Enzymes are used to stimulate digestion processes:
- Panzinorm,
- Mezim.
In severe forms of antral gastritis, antacids and histamine receptor blockers are administered intravenously.
If gastric bleeding develops, hemostatic and blood replacement agents are prescribed. Antispasmodics help get rid of spasms: Papaverine, No-shpa.
The second stage of therapy is aimed at restoring damaged mucous membranes and normalizing stomach functions.
To protect tissues, enveloping agents are used - Sea buckthorn oil, Retabolin.
The healing of erosions is facilitated by taking Actovegin and Solcoseryl.
A disease such as erosive gastritis is an indication for the use of drugs that help saturate damaged tissues with oxygen. These include Iberogast and Trental.
With a normal immune system, the body can cope with infections on its own.
The therapeutic regimen should include vitamin preparations and immunostimulants.
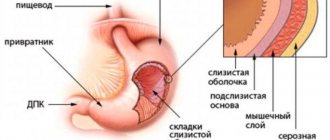
Functions of the antrum
What kind of antrum is this? It is located at the bottom of the organ responsible for the digestive process. The main functions of the antrum are to mix, grind, and then push food through the sphincter. Pieces of food larger than 2 mm do not pass through the valve. From the antrum, completely crushed food enters the duodenum. The mucous membrane produces mucus, which partially neutralizes the effects of hydrochloric acid.
The disease is predominantly caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Erosion of the antrum of the stomach: what is it?
Erosion of the antrum of the stomach is a defect in the mucous membrane that does not spread beyond its boundaries (the muscle layer is not involved in the pathological process) and is localized in the lowest part of the stomach, which passes into the duodenum - the antrum.
Erosions, unlike ulcers, heal without a connective tissue scar. Depending on the quantity, multiple (more than 3 damaged areas) and single (from one to three) are distinguished.
Causes of erosions in the antrum of the stomach
Multiple erosions of the antrum of the stomach are found more often than single ones. They are caused by the following reasons:
- damage to the gastric mucosa by the microorganism Helicobacter pylori, which causes gastritis in 20–30% of the adult population and in 95% of cases is the cause of duodenal ulcers;
- prolonged violation of the diet: eating “dry food”, eating excessively hot and rough food, abuse of spices;
- uncontrolled long-term use of medications: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, sulfonamides, glucocorticoids;
- prolonged emotional stress, neuropsychic processes arising under the influence of chronic stress, difficult life situations;
- alcohol abuse, smoking.
Types of acute and chronic erosions
Acute erosions of the antrum of the stomach occur after a short-term stressful situation. They are defects of regular round or oval shape with a diameter of 0.2–0.4 cm and have smoothed edges. If the defects are covered with hydrochloric acid hematin, an endogenous pigment that colors their bottom black, then they are called “hemorrhagic erosions.”
Chronic erosions of the antrum of the stomach in 52% of cases are multiple and arranged in the form of a chain. They look like polypoid growths up to 5 mm in size with an umbilical retraction in the center.
Table 1. Types of erosion
| Types of erosion | Characteristic |
| Acute | They look like flat, aphthous (superficial) lesions of the gastric mucosa. There are both single and multiple. Epithelializes (heals) in no more than 2–7 days. |
| Chronic | |
| There are mature and immature types. Immature erosion can heal up to several weeks and at the top has a depression with a rim of hyperemia. In the mature type, fibrinous deposits form at the apex in the form of a round ulcer, which exists for years and periodically leads to exacerbation of the disease. Chronic erosions can turn into hyperplastic polyps - formed protrusions above the gastric mucosa, which over time can lead to complications. |
Complete erosions of the antrum of the stomach: what is it?
Complete erosion of the antrum of the stomach is localized at the top of the folds of the gastric mucosa and is a “pseudopolyp” with a depression in the center. Such a defect can persist for about 3 years, in contrast to incomplete erosion, which has a flat shape and smooth edges. The cause of formation is chronic inflammation.
Stages of the disease
Depending on the time of the disease, the quality of treatment and the condition of the stomach, the stage of development of the disease can be determined.
| On Wednesdays, Vladimir Ivanovich is on duty. Questions will be answered with a delay of 2-3 days. The site administration draws your attention! Dear patients! Don't forget to register on the site! If it is necessary to respond personally to the patient, unregistered users will not receive such a response. For repeated requests, please reproduce ALL previous correspondence in full (write the date and question numbers). Otherwise, the consultants will not “recognize” you. You can add questions or answer questions from consultants in the “Messages” under your question. They will be sent to consultants. Once you receive your answer, don’t forget to rate it (“rate the answer”). I am grateful to everyone who considered it possible and necessary to evaluate the answer! Remember that if you like the answer (consultation), you can use the special site option “Say Thanks”, where you can express your gratitude to the consultant by buying him some bonuses on our website. We hope that the proposed bonus amounts will not cause you anything but a smile due to their frivolity. |
How can hemorrhagic gastropathy be cured?
Depending on the results of tests and other studies, the doctor prescribes treatment. It will be different for each patient, as individual characteristics, type of disease, stage of development and many other factors are taken into account. Therapy includes the following drugs: antacids (Maalox) drugs to correct the acid balance (Ranitidine) acid blockers (Pantoprazole) if the gastrointestinal tract is damaged by bacteria, it is necessary to take antibiotics that eliminate parasites.
In addition, you need to drink probiotics and prebiotics in parallel so as not to completely destroy the microflora. If there is bleeding or there is a risk of its development, then the hormone adrenaline and aminocaproic acid are prescribed. It is important to additionally check other organs in order to simultaneously provide them with treatment if necessary. That is, there is no point in treating the symptoms of pathology if you do not act on the underlying cause.
Complications and consequences
If you organize treatment for gastritis in a timely manner, then you don’t have to worry about the consequences. Drug therapy in combination with proper nutrition and diets will quickly and effectively restore the condition.
If you ignore the symptoms and the condition withers, then you can provoke a number of other diseases resulting from gastritis: cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder, the functioning of which can be disrupted due to poor nutrition and the development of gastritis; stomach ulcer - a condition in which a wound appears on the mucous membrane.
Most often, as a result of gastropathy, intestinal function is disrupted and problems arise with the pancreas. Sometimes this condition can result in death, so you cannot procrastinate with problems of the digestive tract.
Nutrition for pathology
During treatment, it is also recommended to follow the following dietary rules:
- Fractional meals - up to 6 times a day.
- Small portions.
- Eating boiled or steamed foods.
- Avoid overeating.
- Consumption of liquid and semi-liquid foods.
During the diet it is allowed:
- Lean meat, fish.
- Porridge (buckwheat, rice, oats).
- Slimy soups.
- Puree of boiled vegetables and fruits.
- Kissels, weak green tea, herbal decoctions.
Forbidden:
- Pickles, smoked foods, marinades, baked goods, desserts, chocolate.
- Fatty meat (pork, lamb), fish.
- Alcohol in any form.
- Coffee, soda.
- Canned food.
- Milk, sour cream.
- Cabbage.
- Grape.
- Fresh bread.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Legumes.
Folk recipes
Traditional recipes can complement the main treatment regimen. Some traditional medicine recipes are approved by doctors and can be used.
Herbal decoctions gently but effectively stimulate gastric motility, coat the mucous membrane, and replenish the loss of vitamins and minerals.
Sea buckthorn oil shows good results. It envelops, reduces the acidity of gastric juice, and heals erosions. A teaspoon of oil is taken orally 20 minutes before meals, 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 10 days.
The essence of pathology
In humans, the chest and abdominal cavities are separated by a muscle plate - the diaphragm. The esophagus penetrates from one cavity to another through the so-called esophageal opening of the diaphragm (abbreviated HOD). Normally, the muscles of the diaphragm and its connective tissue fibers firmly hold the esophagus in the opening and prevent the abdominal organs from penetrating into the chest.
With a classic gastric hernia, the ligaments in the area of the pancreas are weakened. With an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, the abdominal part of the esophagus, followed by the stomach, penetrates the chest cavity - this is how a hernia develops.
Symptoms of gastropathy
After clinical studies are carried out and tests are submitted to the laboratory, the doctor diagnoses the form of the disease. The epithelial layer of cells located on the inner surface of the stomach serves as a protective barrier - mucus forms on it, which prevents hydrochloric acid from corroding the tissue.
By determining how damaged the walls of the stomach are, it is possible to make an accurate diagnosis of what kind of disease the patient has.
| Hyperemic gastropathy | The mucous membrane is red, with swelling, the vessels are dilated, and increased blood flow is observed in the walls of the stomach. |
| Hemorrhagic | Damage to tissues of the vascular system, gastric bleeding is observed. |
| Erythematous | Redness is observed in individual areas or throughout the entire mucous membrane. |
| Congestive gastropathy | The motility of the stomach is impaired, small ulcers appear on the walls, and the blood supply is disrupted. |
| Papular gastropathy | Papules appear on the tissues of the stomach in the form of small swellings, they are located on the surface; When healing occurs, scars do not remain. |
| Erosive gastropathy | Ulcers appear on the mucous membrane. |
| Initial stage of the disease | The structure of the mucosa is not disturbed; minor inflammation is observed on it. |
| Chronic stage of the disease | Ulcers and erosions appear, and the secretory gland is damaged. |
| Hypertrophic stage of the disease | Adenomas and cysts form on the mucosa. The walls of the stomach take on a thickened shape and become coarser; this stage is the most dangerous. |
| And the trophic stage of the disease | The gastric walls degenerate, and connective tissue appears in some areas, indicating advanced disease. |
In an infant, this disease may manifest itself during the transition to artificial formula. If the baby's diet is not suitable, it can cause allergies. Various infections, taking medications, improperly selected diet, products with expired expiration dates - all this can cause gastrointestinal diseases. Children cannot complain of pain, so parents need to closely monitor the child's condition.
Classification of the disease
In medicine there are several classifications of gastropathy. Gastropathy is divided according to the type of course (acute and chronic), by stages, and by degrees of development.
According to the degree of development, gastropathy can be:
- 1st degree. Manifests itself in slight deformation of the gastric mucosa, in a slight decrease in the synthesis of hydrochloric acid;
- 2nd degree. It is characterized by the appearance of stronger pathological processes, in which cell damage and necrosis of the gastric epithelium occurs faster than in the first case. These processes can be reversed with timely treatment.
The stage of gastropathy depends on its duration, the nature of its course, the effectiveness of treatment, and the condition of the gastric epithelium. The following stages of gastropathy can be distinguished:
- Initial - characterized by a slight inflammatory process of the mucous membrane without transformation of its structure.
- Chronic - at this stage, ulcers and erosions appear, the glands of the organ are affected. This stage occurs with advanced gastropathy - when the diagnosis was delayed or the treatment was incorrect.
- Atrophic - manifests itself in the degeneration of the gastric walls, replacement of certain areas with connective tissue, and poor health.
- Hypertrophic is the most severe stage, during which thickening and coarsening of the gastric walls occurs, adenomas and cysts form.
Physiology of the antrum
The specific function of the antrum is to finally grind food into a pulp state so that the maximum size of a food particle is no more than 2 mm. During mechanical grinding there is also constant mixing of food. After receiving a portion of uniform consistency, the food mass rushes through the pyloric sphincter and undergoes further processing in the duodenum.
The mechanical function of the antrum is not the only one. If the main section of the stomach produces more hydrochloric acid, then the task of the antrum is reduced to neutralizing acidity by producing alkaline mucus, concentrated in the pylorus area. This action is necessary to prepare the food mass for processing in an alkaline environment that will be created in the duodenum. The transition from acidic contents to an alkaline environment should not be too abrupt.
Another function of the antrum should be considered endocrine: individual cells produce the hormone gastrin, which has an effect on hydrochloric acid.
Insufficient gastric peristalsis contributes to food stagnation, fermentation and rotting, which causes the acidity of the environment to increase to a greater extent. The gastric mucosa is designed for a certain acidity level, corresponding to the normal production of hydrochloric acid by the parietal cells. When acidity increases, the mucous membrane is destroyed, which is accompanied by diseases of the entire digestive system of varying degrees of severity. If the effect of too acidic gastric juice is not stopped in a timely manner, the pathological condition becomes chronic.
Erosive gastropathy - what is the disease
Erosive gastropathy is a disease that can cause gastric bleeding ; Erosion and ulcers form on the walls of the stomach. The causes of the disease are long-term use of medications that irritate the stomach tissue.
Bacterial infections can trigger an exacerbation. Bile effusions and injuries can negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract and provoke disease. Sometimes the disease goes unnoticed, sometimes pain appears under the right rib.
Complications
The development of acute and chronic erosive antral gastritis often leads to bleeding resulting from the destruction of the walls of blood vessels in areas with erosion. In this condition, the following symptoms appear:
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- cardiopalmus;
- liquid black feces with clotted blood;
- vomit;
- confusion;
- increased sweating.
The more intense the bleeding, the more severe the patient’s condition becomes. In the absence of timely treatment, ulcers form and gastric bleeding develops. This is a serious condition that is difficult to treat and increases the risk of developing malignant tumors. In addition, erosive antral gastritis can cause the development of stenosis and deformation of the pylorus. If you do not pay attention to the symptoms of massive blood loss, anemia and shock may develop.
Congestive gastropathy - causes of the disease
The disease manifests itself as a disturbance in the activity of the gastrointestinal tract . Erosion and ulcers appear in the upper intestine and stomach, resulting in a deterioration in the blood supply to the affected areas.
Congestive gastropathy can develop against the background of liver disease, kidney pathology, or inflammation of the pancreas. Often the disease appears from the constant use of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs. These medications have the properties of relieving fever, reducing swelling, reducing inflammation in the body, and reducing pain.
Such drugs are often prescribed by doctors, and patients themselves use them without control in order to quickly get rid of pain, and as a result they get congestive gastopathy.
Causes of the disease
- Taking anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs.
- Disease of the liver, kidneys, pancreas.
- The return of bile or intestinal contents back into the stomach.
Poor nutrition plays a big role in the occurrence of congestive gastropathy in middle-aged and older people. In order not to provoke the disease, they need to adhere to a certain diet.
Development
How does antrum gastritis appear? What is it really? The development of this disease occurs due to the development of a large number of microorganisms in the stomach cavity. The most important role is played by the microbe Helicobacter pylori, which penetrates the stomach, causing atrophy and inflammation of mucosal cells. Due to the proliferation of bacteria, the production of bicarbonates by the glands of the antral zone is reduced. This is why the acidity of gastric juice increases.
Acid enters the intestines and irritates it. The digestion process is upset, which leads to diseases of the small intestine. The pyloric region is oxidized, and atrophic changes occur. As a result, the stomach glands die. Instead, scar tissue appears.
Antrum gastritis can progress against the background of autoimmune processes in the body. The activity of the glands is disrupted, the cells of the mucous membrane become inflamed and destroyed. This can contribute to the development of a chronic disorder of the secretory function of the mucous membrane. Very often, antral gastritis causes the appearance of ulcers and erosions in the cavity of the duodenum or at the exit from the stomach.
Treatment
Treatment for gastropathy depends on the type and extent of the disease. General recommendations that apply to all patients are as follows:
- do not drink alcohol and do not smoke;
- lead a healthy lifestyle - play sports, walk a lot, follow a daily routine, develop a diet for yourself and eat, sticking to it;
- do not take medications that can aggravate the disease.
Apart from these recommendations, all others are given by the doctor. As mentioned above, treatment of gastropathy depends on the severity of the disease. If the disease occurs in an acute form, you should rinse the stomach, because an exacerbation can be caused by food poisoning from low-quality food. If the patient has a chronic disease, treatment is prescribed after examination.
Radical measures
Surgery is prescribed if bleeding begins in the stomach that cannot be stopped. Sometimes surgery is recommended if drug treatment does not give the desired result and the patient feels unwell.
Diet for stomach disease
The diet is prescribed by the doctor - it depends on the severity of the disease. Here are some recommendations that will be useful to patients who have problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
| 1. | The daily amount of food is divided into small portions; the breaks between meals should not be long. |
| 2. | Food must be steamed or boiled; fried foods are prohibited. If an exacerbation occurs, take only liquid, pureed food. |
| 3. | Extremely hot or cold food should not be consumed. |
| 4. | To restore the tissue of the gastric mucosa, you need to balance the consumption of proteins and fats. Such proportions will speed up recovery. |
| 5 | You should not eat spices, rich broths, canned food, fresh bread and buns, fatty and fried foods. |
| 6. | Legumes, rye bread, radishes - products containing coarse plant fiber should also be excluded. |
| 7. | To avoid irritating the walls of the stomach, you should limit your salt intake. |
Such recommendations will help the patient slow down the disease process and help him recover.
Treatment of the disease
Antibacterial drugs are selected for the patient only by the attending physician.
Treatment of erosive gastropathy will be successful if the patient strictly follows the diet and takes medications prescribed by a specialist. Drug therapy for stomach pathologies is prescribed if significant or bacterial damage to the mucous membrane has been detected. It includes complex combinations of 3 or 4 drugs, which are selected by the doctor individually for each patient.
General recommendations for eliminating the disease:
- fractional diet;
- refusal of fatty and fried foods, smoking and alcohol;
- avoiding stress;
- amount of sleep 7-10 hours;
- moderate mode of work activity;
- control of the course of chronic diseases.
Following simple rules and diet will help avoid complications, significantly reduce the manifestations of the disease and speed up recovery. The appearance of any pathological symptoms from the digestive organs should be a reason to visit a gastroenterologist and conduct a full diagnosis. Changes in the mucous membrane detected in the early stages are easily eliminated with diets and herbal decoctions.
Treatment with folk remedies
An erosive stomach can be cured with a collection, which is recommended to be brewed and drunk warm. Each herb must be prepared following the recipe.
Below is a list of plants that herbalists recommend:
- Oak bark
- Chamomile
- Plantain
- Calendula
- Thyme
- Sage
- St. John's wort
- Flax seeds, etc.
Gastropathy can masquerade as other diseases such as: -acute gastritis-, -bulbitis- or -intestinal dysbiosis-. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Gastropathy is a disease that many people have, so you cannot ignore it in the hope that it will go away on its own. This is a disease that can be treated, but it is important not to let it get worse. By following a diet and leading a healthy lifestyle, you can maintain good physical condition and minimize symptoms.
Prognosis and survival
The prognosis of a patient with antrum cancer is determined by the stage of the process at which treatment was started. However, in the majority of cases the outcome is unfavorable. There are no statistical data on 5-year survival among cancer patients with tumor localization in the antral zone.
According to general statistics, on average, only 20% survive for any form and location of stomach cancer, which is associated with the detection of the tumor process in the final stages, when the cancer cannot be treated and is considered inoperable.