Feces are normal
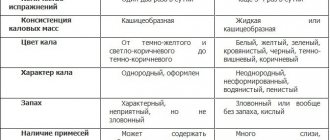
As mentioned above, feces should be yellow-brown or light brown, which is due to the processes of digestion of food in the stomach and intestines. The final color of the stool will depend on the food recently consumed, diseases present in the body, or medications taken.
In newborns, feces should normally be light yellow or greenish in color. The liquid consistency of a child’s feces does not always indicate diarrhea; moreover, it may contain various inclusions.
Causes of white feces
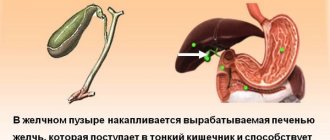
Provided that the digestive organs are functioning normally, a certain amount of bile is gradually released from the gallbladder into the duodenum, which takes an important part in the processes of digestion and assimilation of food, breaking down proteins, fats and carbohydrates into easily digestible substances.
Very light stool or completely white stool in an adult has reasons that lie in the fact that bile is not secreted into the duodenum at all, or it contains a small amount of enzymes necessary for digestion.
Among the main causes of faeces discoloration are:
- Stones or sand in the bile ducts, which prevent the complete evacuation of bile into the duodenum.
- Pathologies of the liver or gallbladder that do not allow bile to be produced in the required quantity.
- The patient's use of various types of pharmacological drugs that affect the level of bilirubin in bile or reduce its production.
- Dysbacteriosis, due to which bilirubin does not have time to act on feces in a timely manner, coloring it in the usual brown shade.
Why does stool become discolored?
If light-colored stool is found in adults, this is most likely the result of bile entering the intestines. In this case, the production of stercobilin does not occur (gives feces a brown color) and the feces are not colored. This substance is formed as a result of the conversion of bilirubin and has pigmentary properties.
Discolored stool occurs for the following reasons:
- If the functioning of the gallbladder is disrupted, the outflow of bile is disrupted. The outflow of bile is disrupted if the ducts are blocked by tumor formations or stones in the organ. Problems can arise due to inflammation in the pancreas (pancreatitis) or infectious inflammation in the bile ducts (cholangitis).
- When there is an abnormal balance of microorganisms in the intestines – dysbacteriosis. The condition occurs after an intestinal infection . The concentration of beneficial microorganisms in the intestines and the production of the coloring enzyme stercobilin are directly related. If the balance of microbes is disturbed towards harmful bacteria, enzyme production also decreases.
- With excessive loss of fluid from the body.
- When treated with certain medications that can reduce bile production. Such medicines include:
- Antipyretic drugs (Aspirin, Paracetamol).
- Antibacterial agents.
- Anti-tuberculosis drugs.
- Antiepileptic drugs.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen).
Diseases that cause white stool
All of the above reasons for problematic bowel movements almost always refer to signs of a pathological condition of important digestive organs, such as the liver or gall bladder. Such conditions include:
- Oncological diseases in the gallbladder area, which block the flow of bile and cause congestion in the organs.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Inflammation of liver of all types and forms.
- Cholangitis.
- Presence of stones in the bile ducts.
- Bend of the gallbladder of congenital or acquired etiology.
Causes
White diarrhea in adults is not so common. To understand why liquid feces may change color, you need to undergo an examination. The main reasons for the discharge of discolored feces are:
- hepatitis;
- disorders of the gallbladder and its ducts;
- intestinal infection;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- intestinal lipodystrophy (Whipple's disease);
- oncological diseases;
- taking certain medications;
- period of artificial feeding of the child.
Hepatitis
Inflammatory liver disease, most often of viral etiology. There are 3 types of disease:
- hepatitis A (transmitted through water, food, common household items, etc.);
- hepatitis B (transmitted through blood and body fluids, through sexual contact, from mother to child during childbirth);
- hepatitis C (transmitted through blood, body fluids).
In the acute stage of all three varieties, almost the same symptoms appear: slight pain in the abdomen, darkening of the urine, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, and the stool becomes white. In this case, the general condition worsens significantly, the patient loses his appetite, and he actively begins to lose weight.
In the absence of treatment, the acute stage of hepatitis turns into a chronic stage, which, in turn, is dangerous for the development of liver cirrhosis and ascites
Intestinal infection
Also called stomach flu, intestinal flu, rotavirus gastroenteritis. The cause of the disease is a virus that is predominantly transmitted through the fecal-oral route. Children who attend kindergartens and other educational institutions are most often affected.
The incubation period of rotavirus infection can range from 24 hours to 5 days. The main symptoms of the disease are: nausea and vomiting, increased body temperature, loose stools with white foam or a yellowish tint, but on the 4th–5th day, when the recovery stage begins, the color of the stool becomes even lighter in color.
If the mucous membrane and blood vessels are damaged, streaks of blood may appear in the stool. The general condition of the patients is poor; they complain of headaches and weakness, lack of appetite and apathy.
Pathologies associated with gallbladder disease
Significantly affect the color and consistency of stool due to the content of bile pigment.
Rumbling stomach and diarrhea
If there are any disturbances in the transportation of this pigment, the stool becomes whitish or white-yellow. The most common cause of blocked ducts is the presence of stones in the lumen.
In this case, diarrhea may occur every 60–80 minus with a strong foul odor, a bitter taste in the mouth, belching, nausea and vomiting. With biliary dyskinesia, diarrhea appears after eating, and feces take on a putrid odor.
Intestinal dysbiosis
Sometimes accompanied by white diarrhea mixed with mucus, which looks like snot. The smell of feces is very strong and foul. In addition, the patient is bothered by abdominal pain, increased gas formation, and itching of the skin. Intestinal dysbiosis most often occurs in children of the first year of life.
Whipple's disease
A systemic disease characterized by damage to the small intestine and some other organs. The cause of the disease is damage to immune cells by Tropheryma whippelii bacilli.
The initial manifestation of the disease is pain in the joints and muscles, the skin over them turns red and swells, the temperature rises to 38 degrees, chills appear and the lymph nodes become enlarged.
A few days later, other signs of the disease appear: frequent diarrhea (yellow-white stool of a foamy consistency up to 10 times in 24 hours), bloating, loss of appetite and weight loss, cramping pain around the navel, signs of vitamin deficiency (plaque on the tongue and its swelling, peeling of the skin and their pigmentation, seizures, neurological disorders).
Pathologies of the visual organs may be observed: unilateral ptosis, anisocoria, uveitis, retinitis, iridocyclitis.
Gastrointestinal cancer
Difficult to recognize at the very initial stage of development. That is why it is worth paying close attention to the color of the stool. In the presence of cancerous tumors, the color becomes discolored and has a white coating, an aversion to food appears, a sharp loss of body weight and diarrhea.
Taking certain medications
Often causes a change in the color of stool. This most often occurs with the use of antibiotics, antifungals, NSAIDs, oral contraceptives, antiepileptic and antituberculosis drugs.
In a good situation, after completing the course and treatment, the color of the feces is restored and acquires a brownish tint. If the feces remain white for a long time, then you should immediately contact a specialist.
Breastfeeding period
This can also cause the stool to change color to a lighter color. Normally, a baby who receives only breast milk will have yellow stool with white lumps or flakes. Do not be alarmed, because these inclusions are undigested breast milk, which comes out unchanged.
When switching from breastfeeding to artificial feeding, the color of stool may change one-time to a lighter shade and this will be an indicator of the norm; nothing needs to be done.
White-yellow color of stool
Yellowish coloration of stool in adults does not always occur due to pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract; it may be an incorrect diet, or abuse of too fatty or low-quality foods. In cases where white discharge is not accompanied by pain or discomfort, it is enough for a person to change his diet. A short diet, for just a few days, returns the stool to its usual color and structure.
If the white-yellow discharge continues for a longer period, you need to seek help from a doctor. A yellowish tint often develops due to the use of certain medications (antibiotics, antifungals, birth control pills). Every doctor should warn patients about a possible side effect before starting treatment.
Light diarrhea with fever
If light diarrhea is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, this indicates an infectious lesion of the liver or a radically changed intestinal microflora. In this case, feces for analysis and blood from a vein are given as soon as possible (for an extended examination). In the future, antiviral drugs, antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Temperature with any diarrhea is a rather serious and dangerous symptom that requires prompt identification of the cause of the digestive tract disorder.
In summary, light diarrhea in an adult most often indicates problems in the functioning of the liver or pancreas, when food is not digested normally, and bile enters the intestines. Often this symptom is caused by excessive stress on the gastrointestinal tract or by eating foods with dye. If the patient does not feel worse, and after 1-2 days the color of the stool becomes normal, then there is no reason to panic. If he has a fever or diarrhea is accompanied by pain in the abdomen or stomach area, he should immediately consult a doctor. Until this point, a gentle diet is used.
White mucus in stool
The epithelial layer that lines the intestinal walls constantly produces mucus. Thanks to this mucus, feces move freely through the intestinal lumen, and in addition, it protects the intestines from the irritating effects of digestive enzymes.
In the feces of a healthy person, a small amount of mucus is acceptable, which is very difficult to notice. An increase in white mucus in the stool may indicate errors in nutrition. This can result from overeating bananas, dairy products, watermelons or melons.
An increase in the amount of mucus secreted by the intestinal walls develops against the background of a disturbed internal level of intestinal microflora (predominance of pathogenic microorganisms), which can be explained by the following pathologies:
- Food poisoning of any nature.
- Personal lactose intolerance.
- Intestinal polyposis.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Enterocolitis.
- Proctitis or paraproctitis.
- Allergic reactions to foods.
- Tumors in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Diverticulitis.
Among the main reasons for the appearance of light mucus impurities in stool, a disease of genetic origin – Cystic fibrosis – stands out especially clearly. During this illness, the patient experiences increased mucus secretion: both in the respiratory system and in the intestines.
Diet
A color change in stool is a direct reason to reconsider your diet. Patients should reduce or completely eliminate fatty foods, everything fried, salty, spicy or pickled. Mushrooms and a lot of chocolate are strictly contraindicated.
Special herbal mixtures, tinctures, herbal tea from sage, chamomile or drinks from sprouted oats help normalize the functioning of the liver, bile ducts and stabilize intestinal function.
The main task of the diet is the gentle effect of foods on the body without loss of saturation. You need to eat in small quantities, the last meal should be 3 hours before bedtime. Products must be thoroughly crushed, preferably even ground. Food is cooked better by steaming.
At the first signs of the appearance of colorless feces, you need to seek help from specialists. Only they will help identify the exact reasons that caused these phenomena and select the ideal treatment plan to restore the functioning of the digestive system.
Clinical picture
Considering the main reason for the lightening of feces, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- Painful cramps in the abdominal area.
- Hyperthermia.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Unpleasant smell of discharge.
- Darkening of urine output.
- Yellowing of the sclera.
- Intense thirst.
- Bleeding from the gums.
- Muscle pain.
- Tachycardia, etc.
All the described signs indicate interruptions in the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnosis of pathology
During the initial examination by the doctor, he should ask the patient about the duration of light diarrhea, the presence of nausea or vomiting, the presence of pain and other causes of discomfort. After collecting anamnesis, the specialist conducts a visual examination: palpation of the abdomen to determine the location of pain, as well as percussion and auscultation.
In some cases, a number of additional laboratory and instrumental studies may be required, among which stool caprogram occupies a special place. Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to determine the exact composition and structure of the patient's stool.
During the diagnostic process, stool tests are often prescribed to determine the presence of pathogens. At the same time, clinical and biochemical blood tests are performed to find the cause of the change in the color of the stool.
What to do, how to treat white diarrhea, white diarrhea?
If, while following the previously described dietary recommendations, diarrhea with white stool does not stop, you need to undergo a diagnosis from a specialist to determine the cause of the disease. Based on the results of laboratory tests, the doctor will prescribe the necessary therapy. Very often, the source of diarrhea is the medications the patient takes: Allopurinol and other drugs for gout; antifungal medications (Augmentin); medications to combat epilepsy that contain valproic acid; anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen); oral contraceptives; steroid drugs; medicines for tuberculosis; acetylsalicylic acid.
In cases where diarrhea is caused by medication, it will stop within two or three days after completing therapy. Although in such a situation it is necessary to take into account all the risks that may arise when refusing the drug. The doctor will advise you to replace the medication you are taking with a similar one that does not affect the frequency and color of stool. Indigestion due to liver dysfunction should be treated as follows: bed rest; diet; taking medications that stimulate the functioning of the diseased organ; injections of blood replacement solutions; use of hormonal drugs; detoxification procedures; if necessary, take antipyretic medications.
If diarrhea occurs as a result of viral infections, then the main drugs for therapy are antibiotics. For pancreatitis, enzymes and painkillers are prescribed. Cholecystitis is fought with the help of choleretic agents and antispasmodics. Gastrointestinal dysbiosis is eliminated with enzyme preparations that normalize intestinal function. For example: Creon, Bifiform, Lmnex, Hilak forte.