What kind of hemorrhoids are called acute?
An acute attack of hemorrhoids is characterized by a sharp and sudden onset of symptoms of the disease, such as discomfort, pain, burning and itching in the anus. Moreover, acute hemorrhoidal symptoms can appear both in a person who has never suffered from hemorrhoids before, and in a patient with a chronic course of this disease. In the first case, they talk about the systemic form, and in the second, about an exacerbation of a chronic pathological process.
Thus, if the patient did not notice the manifestations of chronic hemorrhoids, then the pronounced symptoms of the acute stage of this disease will not allow themselves to go unnoticed.
How to treat?
The earlier treatment for acute hemorrhoids is started, the shorter it lasts, and the lower the risk of complications.
What to do with such a disease? And how many medications should I use? Typically, local remedies - suppositories, gels, ointments - are combined with oral medications.
What to do in case of thrombosis?
In case of node thrombosis, symptoms can be relieved with drugs that contain thrombolytic components, for example, heparin. Antihemorrhoidal drugs include suppositories and Gepatrombin G ointment. Heparin dissolves already formed blood clots and prevents the formation of new ones.
Another component of the product - polidocanol - is a local anesthetic, so it relieves pain well. And prednisolone, being a hormone, helps relieve swelling of the node and inflammation, if any. It is advisable to use Gepatrombin G suppositories for internal nodes, and treat external ones with ointments.
A specific antihemorrhoidal drug for node thrombosis can be combined with other drugs - heparin ointment, Troxevasin and Troxerutin gels. They are popular among patients with varicose veins of the lower extremities. However, they are also effective for node thrombosis.
How to treat infringement?
If the node is pinched, you can apply compresses to the perineal area - first cold and then hot. Cold relieves pain well in the first hours after pinching. And the heat relaxes the sphincter of the anus and allows you to fill the “external” node.
How to deal with inflammation?
If exacerbation of hemorrhoids is complicated by inflammation, preference is given to ointments and suppositories with an anti-inflammatory effect. This is, for example, Proctosedyl or Relief Ultra.
Thanks to the hormonal component, both products have a powerful anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect, so they give a quick effect. They can be combined with oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - diclofenac, Nise, Movasin, Movalis. After absorption, they act systemically and enhance the anti-inflammatory effect of local agents.
On the perineal area, if the external node is inflamed, you need to apply bandages with Levomekol ointment. It is also recommended to take venotonic drugs orally. Preference is given to Detralex. Clinical studies have shown that it gives the best effect in the treatment of acute hemorrhoids. How many days to take the drug and in what dose is decided by the attending physician. And according to the manufacturer’s recommendation, the course should not exceed 7 days.
When conservative measures do not provide significant improvement, treatment of acute hemorrhoids may end with thrombectomy. This is a mini-surgical operation during which the node is opened and the blood clot is removed from it. The surgical wound is not sutured, and it heals on its own within a few days. If there are indications, the node is removed along with the blood clot using one of the minimally invasive or surgical methods.
As for folk remedies, in case of acute illness they are not able to quickly relieve symptoms. Therefore, it is better to refuse them. Medicines in such cases act much faster and more powerfully. It is even more correct in such a situation not to self-medicate, but to seek help from a proctologist.
What are the causes of acute hemorrhoids?
The development of an acute attack of hemorrhoids is based on two main reasons, or rather pathological processes - pinching of a prolapsed internal hemorrhoid in the anal ring and anorectal thrombosis. Let's talk about this in more detail.
Pinching of hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids are a disease of the anus, which is characterized by varicose changes in the vessels of the submucous membrane of the rectum, which are located above the dentate line.
In the initial stages, the pathological process is asymptomatic, since the nodules are small and are constantly located inside the anal canal. But, starting from the second stage of hemorrhoids, varicose veins of the rectum begin to sag through the anal ring. At first, this happens only during bowel movements, and over time, when sneezing, coughing, laughing, etc.
The nodules that fall out irritate the anal ring, resulting in muscle spasm. Spasmed muscles of the anal valve compress the vessels supplying the nodes, which leads to poor circulation, swelling and increased pain.
Illiterate and untimely treatment of acute hemorrhoids is fraught with the development of anorectal thrombosis, since blood stagnates in the pinched lump, which thickens over time. In addition, prolonged pinching of a lump in the anal valve threatens the necrosis of its tissues, which requires only surgical treatment.
Thrombosis of hemorrhoids
Anorectal thrombosis (thrombosis of hemorrhoids) is a complication of hemorrhoids, which is based on the formation of a blood clot inside a varicose vein of the rectum. This complication can develop with both external and rectal hemorrhoids.
The blood clot that has formed inside the node puts pressure on its walls and irritates pain receptors, so the patient feels severe pain in the anus. Moreover, the pain syndrome is quite difficult to relieve and this can only be done after the blood clot has been eliminated.
Pain in the anus with anorectal thrombosis is constant. Defecation provokes increased pain, so patients specifically suppress the urge to bowel movement. But this does not alleviate the condition, but only aggravates it, because such a disservice leads to constipation.
Symptoms, signs of acute hemorrhoids
The symptoms of acute varicose veins of hemorrhoidal veins are quite varied, but the main symptom is pain. Pain during an aggravated pathological process is jerking, pulsating, and occurs with any action or movement.
Bleeding develops when a thrombosed or strangulated hemorrhoidal node ruptures.
The pain is sharp, but quickly disappears, however, even in such a short time (from a couple of seconds to several minutes) it gives the person multiple unpleasant sensations. It is painful to move, sit and even sneeze; it is impossible to go to the restroom.
Signs of worsening hemorrhoids are as follows:
- acute internal hemorrhoids are not noticeable to the naked eye, but upon palpation a tightness is felt, and the very touch leads to excruciating pain;
- acute external hemorrhoids are clearly visible upon examination, since the nodule is inflamed, swollen, dense, bluish and painful;
- bleeding develops when a thrombosed or strangulated hemorrhoidal nodule ruptures. In this case, the pain decreases, the person’s condition improves somewhat, and it seems that the illness has gone away.
When the body is intoxicated, the temperature rises, the patient develops a fever, weakness appears, and vomiting occurs. In general, the general condition is rapidly deteriorating.
At stage 3 of thrombosis, the nodes become cyanotic, ulcers appear, and a necrotic process is possible.
The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of acute pathological process. Proctologists distinguish 3 stages of thrombosis of hemorrhoidal nodules:
- first - a blood clot forms, which is accompanied by acute pain, swelling, mild redness of the anorectal area, itching and burning, but there is no significant inflammation yet;
- second - the inflammatory process affects only the hemorrhoidal node, swelling is more pronounced, spasm of the anal sphincter and redness around it appear. Touching the nodules is accompanied by severe pain;
- third, the inflammatory process spreads not only to nearby areas, but also to the subcutaneous fat. A person feels incredible pain both in the anorectal area and in the perineum. The nodes become cyanotic, ulcers appear, and a necrotic process is possible.
Similar symptoms can occur in any category of patient. This pathological condition also affects expectant mothers, since pregnancy can become another risk factor for the formation of acute hemorrhoids.
Treatment of acute hemorrhoids during pregnancy should begin immediately to eliminate possible complications and the use of potent drugs that can harm the baby in the womb.
Treatment of acute hemorrhoids during pregnancy should begin immediately to eliminate possible complications.
What provokes the development of acute hemorrhoids?
We have figured out the mechanism of development of an acute attack of hemorrhoids, but what can provoke the appearance of pronounced symptoms of the disease. Experts have been able to identify a number of factors that, individually or in combination, contribute to the exacerbation of hemorrhoids. These include the following:
- excessive physical activity. This applies to loads that are associated with lifting heavy objects, since they provoke an increase in pressure inside the abdominal cavity and overflow of blood into the hemorrhoids;
- intestinal dysfunction. Here we are talking about both constipation and diarrhea. In the first case, hard fecal lumps damage the nodules, causing an acute attack of hemorrhoids. In addition, during constipation, the patient strains strongly, which leads to active blood flow to the nodes. In the second case, liquid feces irritate the mucous membrane of the rectum and nodes, provoking their inflammation;
- errors in diet. Eating smoked meats, marinades, pickles, gifted and fatty foods helps to activate blood flow to the rectum, which is undesirable for hemorrhoids;
- drinking alcoholic beverages. Very often, gatherings over a glass of strong drink lead to an exacerbation of hemorrhoids, since alcohol increases the pressure in the vessels of the anus;
- deficit of motor activity. Sitting for a long time in one position creates favorable conditions for hemorrhoids, as blood stagnates in the vessels of the rectum.
Before starting to treat acute hemorrhoids, the proctologist tries to find out what exactly triggered the acute pathological process. After all, this disease can be cured using modern therapeutic techniques, but subject to the elimination of provoking factors.
Diagnosis and treatment
Symptoms of acute hemorrhoids force the patient to remember the doctor. The doctor diagnoses and prescribes treatment. Establishing a true diagnosis is not difficult. The proctologist selects therapy. Acute external hemorrhoids with visible nodes are more common.
Non-drug treatment
The early stage of the disease requires treatment at home. These are behavioral changes in life, nutrition, and increased physical activity.
Drug effects
Used for acute onset of illness. Aimed at pacifying pain, stopping bleeding and inflammation of hemorrhoids. Non-narcotic painkillers and local anesthetics are used here.
Rectal suppositories and ointments containing hormonal components help relieve pain immediately and eliminate inflammation. They have pronounced anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effects. Anticoagulants are needed to prevent the formation of blood clots in the bloodstream. Ointments are prescribed - Heparin and Troxevasin.
The basis of therapy for hemorrhoids are considered to be venotonic agents, which bring blood flow back to normal and increase the tone of the veins. But in acute cases of the disease, medications provide a positive effect for a short period of time. Refusal to diet, constipation, and excessive physical effort provoke an exacerbation of the disease, requiring repeat therapy.
In case of insufficient effectiveness of the use of drugs, treatment is supplemented with minimally invasive (less traumatic) and surgical methods.
Minimally invasive treatment methods
Ligation and sclerotherapy. Hospitalization and pain relief are not provided.
- Ligation – ligation of the hemorrhoidal node. Latex rings are used. They are applied to a vessel near the hemorrhoidal node, the node is rejected, and the blood supply vessel becomes empty. At the moment of contact of the node with the light guide and the action of infrared coagulation, the blood vessel is glued together with thermal energy. Minimum pain and no complications.
- Sclerotherapy is the injection of a medicinal composition into the hemorrhoid to glue blood vessels together.
Cryotherapy is a method of freezing a hemorrhoid for a couple of minutes. The cone dies.
Electrocoagulation - the effect of electric current on a node
The surgical method is an operation to remove hemorrhoids. If the patient has missed the chance to use minimally invasive treatment and has reached the “highest ranks” of hemorrhoids, he will have to be treated surgically. Previously, the method was painful. With modern methods, the operation is quick, safe and painless.
Types of surgical intervention
The operation is performed using cutting instruments: an electric scalpel, radio wave, ultrasound devices, and a surgical laser.
When cutting out polyps, condylomas, rectal fistulas, and hemorrhoids, general anesthesia is used. Spinal anesthesia is most often used.
- Classic hemorrhoidectomy is a radical but effective way to remove hemorrhoids. When the nodes are removed, the vascular pedicles are sutured. The mucous membrane of the anal canal is restored. Used at all stages of the disease.
- TGD (transanal hemorrhoidal dearterilization) is a method that involves suturing the hemorrhoidal arteries to empty the venous tissue using an ultrasound probe.
- Operation Longo. A circular endostapler excises the area of the mucosa above the nodules and is sutured in a circular manner. The vessels that drive blood to the hemorrhoids are sutured. The nodes, having tightened, return to their original position.
Treatment at home
Doesn't bring the desired results. Home practices have not learned how to quickly relieve symptoms of the disease during the acute phase of the disease. Home therapy is allowed as a component of complex treatment.
Traditional healers recommend drinking wheatgrass decoction before bed with an enema of 30-60 ml. Fresh juice from the aboveground part of the plant and roots is useful.
Medicines work more effectively.
A proctologist will help you avoid serious complications of the disease. Treatment of acute hemorrhoids will be complex and targeted.
Consequences of ignoring therapy
- Fever. The temperature of the rectal mucosa will rise. The malaise rapidly spreads throughout the circulatory and digestive systems.
- Purulent-inflammatory process of subcutaneous tissue. The development of microflora pathology will begin. The skin and mucous membrane of the anus are tense, bluish and painful. Pustules and boils may appear, and liquid will begin to ooze from small blood vessels.
- Sepsis. Blood poisoning is a dangerous complication. The protective forces of the rectum do not resist the wounded microflora. Violation of the integrity of inflamed veins creates conditions for the penetration of microbes. Microbes will fill the circulatory system, posing a threat to the patient’s life.
- Thromboembolism. The blood clot from the hemorrhoidal vein will break away from the wall. There is a risk of getting into any organ, causing functional failure, in the brain - a stroke.
How does exacerbation of hemorrhoids manifest?
The main symptom of acute hemorrhoids is pain in the anus, and the pain is pulsating and jerking in nature, and also increases with movements, bowel movements, coughing, sneezing, sitting on a hard surface and even in a lying position.
Patients may also complain of the following:
- itching and burning in the anus;
- discharge of blood from the rectum during bowel movements;
- general weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- nausea;
- pain in the lower abdomen, tailbone and lower back.
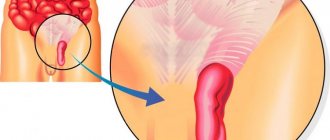
In addition, a mandatory sign of an acute attack of hemorrhoids is the presence of an external and prolapsed internal node in the anus.
Symptoms of acute external hemorrhoids
An external hemorrhoid is clearly visible to the naked eye because it is located near the anal ring. The external nodules are covered with skin and look like a round, painful lump with a bluish tint. Such bumps are characterized by severe swelling and inflammation, which can spread to adjacent tissues.
Symptoms of internal acute hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids can be seen independently only after they begin to fall out, and this is the second stage of the disease.
The internal nodules that have fallen out also hurt a lot and have signs of inflammation. Such bumps differ from external hemorrhoids in that they are covered with the rectal mucosa, and not with skin.
Classification of the disease
Acute hemorrhoids are thrombosis of hemorrhoids. The external manifestation is a dense, painful external or internal bluish-colored node filled with a blood clot.
Acute hemorrhoids are divided into three degrees of severity:
I degree – Thrombosis of external or internal hemorrhoids without an inflammatory process.
II degree – Thrombosis, complicated by inflammation of hemorrhoids.
III degree – Thrombosis of hemorrhoids, complicated by inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue in the perianal area.
Therapeutic tactics involve both complex conservative treatment and surgical treatment .
The indication for surgical treatment is acute thrombosis of the hemorrhoid. In the early stages of the disease, optimally up to 72 hours, thrombectomy is indicated - removal of thrombotic masses. Performed on an outpatient basis. The operation leads to a significant reduction in treatment time.
In later stages, either removal of the thrombosed node or conservative treatment followed by planned surgery is possible. Hospitalization is indicated for stage III of the disease, when the inflammatory process spreads to the surrounding tissues of the perianal region and anal canal.
What is the danger of the acute stage of hemorrhoids?
In a patient with hemorrhoids, treatment for an acute attack should be started immediately after the onset of symptoms, since the lack of adequate therapy or its untimeliness threatens the development of life-threatening complications.
First of all, strangulation or thrombosis of the node can result in tissue necrosis, which can only be eliminated surgically. In addition, necrosis of the hemorrhoid is dangerous due to the development of an infectious process, which in turn will lead to acute or chronic paraproctitis, and in severe cases even to blood poisoning.
How to determine that hemorrhoids have entered the acute stage?
The appearance of severe pain in the anus and the presence of inflamed nodules in the anus allows an experienced proctologist to immediately make the correct diagnosis. The specialist also performs a digital rectal examination and anoscopy, but only after pain relief.
If necessary, additional studies may be prescribed, such as sigmoidoscopy, fibrocolonoscopy, ultrasound examination of the soft tissues of the anus, abdominal organs and others.
How to treat acute hemorrhoids?
The first question that interests patients with acute hemorrhoids is what to do and how to treat it. But in this case, any amateur activity is unacceptable. At the first signs of an acute attack of the disease, you must consult a professional - a proctologist. In district clinics, this specialist is not always on staff, so his duties are performed by a surgeon.
The main task of treatment for hemorrhoids, which is in the acute stage, is to relieve pain, which in turn will alleviate the patient’s condition.
Treatment of hemorrhoids in the acute phase can be medicinal, surgical or combined, that is, a combination of the first two methods. Also, with the permission of the treating doctor, the main antihemorrhoidal treatment can be supplemented with the use of folk remedies that will speed up recovery.
Drug therapy
To relieve pain in the anus, specialists use drugs that contain anti-inflammatory substances and local anesthetics. The choice of medicine is made based on the type of hemorrhoids.
For external hemorrhoids, ointments, gels or creams are used, and for rectal localization of the pathological process, rectal suppositories. Tablet drugs are also prescribed to treat an acute attack of the disease, but local dosage forms allow you to quickly achieve the desired result.
For internal hemorrhoids, the following suppositories are most effective:
- Proctosan;
- Procto-Glyvenol;
- Relief Advance;
- Anestezol.
The listed rectal suppositories contain local anesthetics, which quickly relieve pain, itching and burning in the anus. Rectal inserts can also be used, which contain belladonna extract, which has pronounced antispasmodic and analgesic effects.
In case of severe inflammatory process in the anus, preference is given to suppositories that contain hormonal substances, since they have strong anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and decongestant therapeutic effects. Such drugs are Proctosedil M suppositories, Relief Ultra and Ultraproct.
With anorectal thrombosis, there is a need to use drugs with heparin, which is an anticoagulant, that is, it resolves blood clots. In this case, the suppositories of choice may be Hepatrombin G and Nigepan.
For acute external hemorrhoids, it is more convenient to use antihemorrhoidal ointments, although most ointment products can also be administered into the rectal canal.
For anorectal thrombosis, ointments such as Hepatrombin G, Troxevasin or heparin ointment are prescribed. If an attack is accompanied by severe pain, you can use Relief Advance, Proctosedyl, Ultraproct, Aurobin and others ointments.
Local antihemorrhoidal therapy is combined with the use of tablet drugs that have phlebotonic and angioprotective therapeutic effects, namely:
- Detralex;
- Troxevasin;
- Venarus;
- Phlebodia 600.
The listed drugs increase the tone of the veins of the anus and act directly on the cause of hemorrhoids - venous insufficiency.
In case of severe pain, to alleviate the patient’s condition, the proctologist may prescribe painkillers such as Pentalgin, Nimesil, Ketanov, Ibuprofen and others. If painkillers are ineffective, novocaine blockades can be performed.
If an acute attack of hemorrhoids is accompanied by constipation, laxatives are used, the most effective of which are Dufolac and Normaze.
Surgical methods of treatment
In cases where conservative therapy fails, the specialist considers surgical intervention. When choosing a surgical method, preference is given to minimally invasive techniques, since they are painless, quickly performed and do not require a long rehabilitation period.
For anorectal thrombosis, a thrombectomy operation is performed, during which the hemorrhoid is opened and the clot is removed.
After stopping the acute inflammatory process, the following minimally invasive operations can be performed:
- sclerosis of nodes, when a substance is injected into the hemorrhoid using a needle, which glues its walls;
- ligation of nodes with latex rings, when a latex ring is placed on the neck of the nodule with a ligator, which compresses the vessels supplying the formation, as a result of which it dies;
- cryodestruction of a hemorrhoid, when it is destroyed using liquid nitrogen;
- disarterization of the hemorrhoid, when the vessels that supply it with blood are tied with threads;
- photocoagulation and laser coagulation, when nodules collapse under the influence of infrared/laser rays.
In advanced stages of hemorrhoids, the only way to get rid of the disease is radical surgery. The classic operation for hemorrhoids is the Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy.
Unlike minimally invasive surgical techniques, hemorrhoidectomy is performed only in a hospital setting under general anesthesia and requires long-term rehabilitation. Therefore, there is no need to take your condition to extremes and seek help from specialists in the early stages of hemorrhoids.
Traditional medicine
As we have already said, folk remedies can only be used in consultation with the treating doctor and only as a supplement to the main antihemorrhoidal treatment, since it is impossible to get rid of hemorrhoids only with the help of traditional medicine.
The following folk remedies will help alleviate the condition and speed up recovery during an acute attack of hemorrhoids:
- sea buckthorn oil . This natural remedy can be used as an ointment on the external bumps, or applied rectally by soaking a cotton swab in it;
- ice candles . To prepare such candles, use ordinary water or decoctions of medicinal plants, such as nettle, yarrow, oak bark, chamomile, kidney herb and others. The effectiveness of using herbal infusions in this case will be higher;
- Rectal inserts made from raw potatoes . Small cylinders cut from potatoes are inserted into the anus 1-2 times a day. The starch released from such suppositories perfectly stops bleeding and relieves inflammation;
- cool baths . For baths, you can use cool solutions of potassium permanganate, sea salt, mumiyo or infusions of medicinal plants. With this procedure you can quickly stop bleeding, relieve pain and inflammation in the anus.
There are many more traditional methods for treating hemorrhoids, but remember that they can only be used after consultation with a professional.
First stage of hemorrhoids
With grade 1 hemorrhoids, slight bleeding from the anus is observed - the patient may notice it on toilet paper after bowel movement. At rest, bleeding is rarely a concern. Defecation may be accompanied by shooting pain.
The clinical picture depends on the type of hemorrhoids. With external pathology, a small lump appears right at the anus. The lump is not painful or large in size. With internal pathology, only minor bleeding is observed.
Treatment methods
First stage of hemorrhoids
Therapy at the first stage is carried out using the most gentle methods possible. Efficiency shows conservative
therapy, including drugs:
- painkillers;
- wound healing;
- anti-inflammatory;
- hemostatic;
- venotonic.
They can be either systemic or local, in the form of suppositories and ointments. Local drugs eliminate the symptomatic complex, and systemic drugs eliminate the cause of hemorrhoids. Among the instrumental techniques, proctologists prescribe sclerotherapy and photocoagulation. These techniques promote gluing of nodes and their walls to prevent thrombosis and bleeding.
How to eat with acute stage hemorrhoids?
Since errors in nutrition are a provoking factor for an acute attack of hemorrhoids, diet is a mandatory component of anti-hemorrhoids treatment.
When drawing up a menu, a patient with hemorrhoids should be guided by the following rules:
- Smoked meats, pickles, marinades, fatty and fried foods are excluded from the diet, and sweets, baked goods and pasta are also limited;
- It is not recommended to consume foods that support fermentation processes in the intestines - white cabbage, grapes, radishes, fatty cottage cheese and others;
- Most of the menu should consist of foods that are rich in plant fiber. These include cereals, vegetables, fruits, bran;
- Be sure to include fermented milk products with a low fat content in your diet;
- a single serving of food should not exceed 300 grams;
- compliance with the drinking regime - 8-10 glasses of clean water per day;
- complete abstinence from alcohol.
It is also important to follow a diet - 5-6 times a day at the same time.
Following these rules will help relieve acute symptoms, prevent constipation and speed up recovery.
Complications
Untimely provision of medical care, lack of positive dynamics in eliminating constipation and diarrhea, pain, anal itching lead to complications of hemorrhoids:
- infectious diseases;
- strangulation of the hemorrhoidal nodule;
- blood poisoning;
- thrombosis formation;
- inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- formation of pus in the anorectal region of the rectum.
Acute hemorrhoids do not occur with a balanced diet for the natural functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, abstaining from alcohol and smoking, performing physical therapy, and observing hygiene procedures. If symptoms of the disease appear, therapy should be started immediately.
We recommend: How to quickly and effectively cure internal hemorrhoids at home?
How to prevent aggravation of hemorrhoids?
Prevention of the appearance of acute symptoms of hemorrhoids is not at all difficult and consists of the following:
- increasing physical activity through sports (swimming, walking, running, gymnastics), as well as performing warm-ups during active sedentary work;
- healthy and balanced diet that complies with the rules described above;
- rejection of bad habits;
- observing the rules of anal hygiene, and in particular replacing the use of toilet paper by raising water to room temperature;
- timely contact a proctologist at the first signs of hemorrhoids.