Development mechanisms
To understand why sudden, causeless nausea occurs, it is necessary to understand the mechanisms of its development. Doctors distinguish several varieties:
- central;
- reflex;
- visceral;
- motor;
- hematogenous-toxic.
Central
The cause of the development of the central variety can be inflammatory and infectious pathologies occurring directly in the brain and/or its membranes. Provocateurs include: concussions, head injuries, benign/malignant brain tumors. Accompanies arterial hypertension and may indicate the development of a hypertensive crisis.
Visceral
Visceral nausea is a sign of problems with the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). It occurs as a symptom of stomach cancer, ulcerative pathologies, inflammation of the pancreas, cholecystitis, gastritis.
Nausea may be a sign of gastrointestinal disease
This type often develops against the background of the following pathologies:
- inflammation of the pharynx;
- pleurisy;
- myocardial infarction;
- renal colic;
- thrombosis.
Motor
Motor nausea develops during inflammatory/infectious pathologies of the ear, as well as disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
Hematogenous-toxic
Sudden nausea in this case occurs as the body’s response to exposure to toxic substances. Often found in patients diagnosed with renal failure, endocrine pathologies, all types of tumors, as well as during pregnancy.
Important! The cause of its development may be the use of certain medications. In this case, it is considered as a side effect.
Antiemetics
Special medications - antiemetics - help stop severe vomiting attacks. The drugs differ in their action. It is necessary to take them only as prescribed by a doctor so that the condition does not worsen. There are three groups of antiemetic medications:
- central action - neuroleptics, antihistamines, dopamine and serotonin receptor blockers;
- peripheral influence - local antispasmodics, painkillers;
- mixed action - with a comprehensive solution to the problem.
Medicines help cure vomiting caused by diseases:
- neuroleptics - Triphasin, Aminazine - eliminate the symptoms of drug poisoning, are effective during pregnancy, radiation sickness, and in the period after surgery;
- antihistamines - Diprazine, Diazolin - cope with motion sickness caused by disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus;
- antiseptics – Enterofuril, Intetrix – destroy bacteria in infectious diseases of the stomach and duodenum.
Medicines selected for the treatment of certain pathologies can stop vomiting:
- migraine, traumatic brain injury - dopamine receptor blockers - Motilium, Zofrom;
- gag reflex during treatment and diagnosis by an ENT doctor - local anesthetic - Lidocaine;
- chemotherapy for oncology – Sertonon, Latran, Haloperidol;
- intestinal infections – Ersefuril;
- for a neurogenic cause of urge - Tenoten, Persen;
- universal medicine - Metoclopramide.
- How to get rid of roundworm worms
- How to sew a hidden zipper into a skirt
- Motilak - instructions for use for adults and children. What does Motilak help with and contraindications
Central acting anti-vomiting agent
Drugs in this group have an inhibitory effect on the vomiting center, its chemoreceptor trigger zone located in the medulla oblongata. As a result, an impulse is not sent to the muscles that provoke the reflex effect. There are several types of centrally acting agents. These include:
- neuroleptics - Triphasin, Aminazine - used for poisoning, radiation treatment, pregnancy;
- antihistamines - Dimenhydrinate, Diphenhydramine - eliminate vomiting of vestibular origin.
Centrally acting agents include:
- Histamine receptor blockers, with a depressing effect on the central nervous system, accelerating peristalsis and bowel movements - Domperidone, Motilium. Medicines are prescribed for vomiting caused by infections, gastrointestinal dysfunction, and poor diet.
- Seratonite receptor blockers - Tropisetron, Latran - stop vomiting caused by gastric dyspepsia after surgery or chemotherapy.
Peripheral drugs
This antiemetic group of drugs acts at the level of efferent, afferent nerve endings involved in the mechanism of formation of the gag reflex. Peripheral medications include local anesthetics:
- Lidocaine, Benzocaine - used when performing otolaryngological manipulations - operations, treatment, bronchoscopy, anesthesia;
- Anestezin, Novocaine - help with vomiting caused by inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, provoked by ulcerative processes.
Among the drugs of peripheral action are local antispasmodics. They are used for retching caused by disturbances in evacuation and motor function in acute and chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary tract. Medicines include:
- Atropine, No-shpa, Papaverine, which have myotropic, anticholinergic properties;
- Bellasthesin is a combination drug that relaxes smooth muscles.
Mixed action
The popular antiemetic drug is effective for symptoms of various etiologies. A mixed-action medicine, Metoclopramide, quickly eliminates painful urges. The drug counteracts hiccups, activates gastrointestinal motility, stops the gag reflex caused by:
- poor quality food;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- pregnancy;
- release of bile;
- kidney pathologies;
- radiation sickness;
- chemotherapy;
- taking antibiotics, anesthesia drugs, cytostatics.
Metoclopramide, a dopamine receptor blocker, is used in the form of injections and tablets. For the drug, according to the instructions, the following are determined:
- dosage – tablet 4 times a day, half an hour before meals, do not chew, wash down with water;
- contraindications – intestinal obstruction, bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, hypertension, old age, 1st trimester of pregnancy, children under 14 years of age, glaucoma;
- side effects - increased blood pressure, drowsiness, depression, tremors of extremities, diarrhea, anxiety;
- analogues - Cerucal, Clometol, Comportan, Bimaral, Primperan, Plastil.
Causes not related to existing diseases
Severe nausea sometimes occurs as the body’s response to uncomfortable conditions. Quite often, attacks occur against the background of a weak vestibular apparatus. If a person gets motion sickness while traveling, then taking special pills will help get rid of the nausea.
The causes of sudden nausea and subsequent vomiting in an adult may lie in psychological problems. Provoking factors can be a state of severe fear, being in a stressful situation, or severe nervous tension. Breathing exercises will help relieve an attack.
Mild lightheadedness with vomiting sometimes develops in a person after arriving in a new, unfamiliar place
There are other reasons. This:
- Severe physical or emotional fatigue, lack of sleep. The body needs daily rest and if it does not receive it, it responds with various uncomfortable conditions. One of these is attacks of severe nausea.
- Poisoning, development of intestinal infection. Emptying of the stomach is typical for the pathology, but sometimes the patient feels only nausea, without vomiting.
- Side effect caused by taking medications. Some drugs can cause nausea and even vomiting.
- Development of gestation. The first months of bearing a child are characterized by constant attacks of lightheadedness. Sometimes they end in vomiting.
- Migraine. For this type of headache, nausea is a typical condition.
- Brain concussion. The pathology is accompanied by dizziness and severe nausea. Sometimes the latter ends in vomiting.
The cause of lightheadedness can be a person’s diet. It is provoked by hunger, overeating, and excessive indulgence in sweets.
Causes of the problem
Nausea and vomiting without fever occurs for various reasons. These include food poisoning, the state of stress in which the patient is, and digestive problems such as diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, dysbiosis and intestinal flu.
Can cause vomiting without fever, hangover, migraine, motion sickness. Sometimes the cause can be determined independently, but if it is not obvious (as, for example, in case of poisoning or hangover), it is better to consult a specialist.
Food poisoning
Food poisoning is accompanied not only by vomiting, but also by diarrhea and fever. However, minor intoxication can cause only one serious symptom in the form of a reflex eruption of stomach contents. Although sometimes the state of poisoning of the body is also accompanied by convulsions, decreased blood pressure, and even loss of consciousness.
Poisoning is caused by ingestion of some inedible or toxic substances and ordinary food products that somehow contain toxic bacteria. Symptoms of poisoning also occur after taking certain medications. The main thing is to identify the cause in time and drink more fluids.
Stressful and neurotic state
Constant stressful situations in your personal life or during work can lead to the appearance of symptoms similar to signs of poisoning - vomiting and nausea without a change in temperature. This occurs due to the fact that the body activates protective reactions to stress. Sometimes the symptoms are accompanied by severe headaches.
Symptoms often appear in a person shortly before some important event. In most cases, nausea goes away within a few hours or a couple of days. If improvement does not occur on the third day, you should contact a neurologist. Of course, for this you need to be sure of the cause of the problem - in other situations with similar symptoms, specialist help is required much earlier.
Stomach flu
One of the most common diseases that causes vomiting without fever is intestinal flu. You can get it from another infected person - through contaminated food, unwashed hands and household items. Epidemic periods of intestinal flu usually occur in the autumn-winter period.
Additional symptoms of the disease include diarrhea, the frequency of which can reach up to 10 or more times a day. In this case, the stool becomes liquid, has an unpleasant odor and may acquire a greenish tint. Diarrhea causes the body to lose large amounts of fluid, which leads to dehydration. The patient's condition may return to normal after a few days, but final recovery, even after starting treatment, occurs only within a month.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Vomiting and nausea without fever can also be caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- gastritis, additional symptoms of which include general weakness of the body, heartburn and pain in the peritoneum;
- pancreatitis, which can also be recognized by symptoms such as girdle pain extending beyond the left shoulder blade or sternum;
- gastroduodenitis, which usually occurs in an adult either without an increase in temperature or with a slight change in temperature (up to 37–37 degrees), and is accompanied by heartburn, loss of appetite and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
Sometimes enterocolitis can develop against the background of other gastrointestinal diseases. Additional symptoms include general weakness and the appearance of mucous or blood in the stool. Treatment for most of these diseases is prescribed after examination by a gastroenterologist, or less often by a surgeon.
Dysbacteriosis
In fact, dysbiosis is not a disease - rather, it is a condition of the body. Its causes are usually:
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- improper diet;
- prolonged (mainly due to lack of normal treatment) stomach upset.
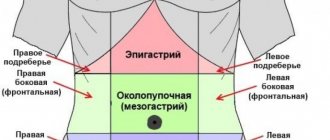
Sometimes the state of dysbacteriosis is accompanied by diarrhea; the patient may complain of discomfort in the epigastric region (approximately in the upper part of the stomach) and increased gas formation. If the problem is caused by taking antibiotic drugs, chills may be added to the symptoms.
Toxicosis or hangover
A hangover also causes vomiting without a change in temperature. Its appearance is the result of the following factors:
- poisoning of the body with alcohol products
- dehydration caused by frequent urination due to alcohol abuse;
- metabolic disorders in the body, which fights poisoning and consumes vitamins, macro- and microelements.
A hangover occurs in the morning and its symptoms disappear by the afternoon. If symptoms continue, you can try to eliminate the problem using folk remedies or by consulting a doctor.
Other reasons
Nausea and vomiting without fever can be caused by the following reasons:
- falls and blows;
- motion sickness when traveling by transport (car, bus, boat);
- migraine;
- meningitis;
- anorexia or bulimia.
In some cases, nausea occurs after taking anti-tuberculosis and hormonal medications. Similar symptoms are observed in workers of industrial enterprises whose bodies are exposed to heavy metals contained in the air. The cause of nausea and vomiting in women is toxicosis during pregnancy.
First aid
If vomiting occurs without a change in temperature and there are no obvious reasons (alcohol syndrome or pregnancy), it is advisable to call an ambulance to the patient. Before the doctors arrive, you should try to rinse his stomach by giving him 1 to 1.5 liters of water to drink. The liquid should be heated to the temperature of the human body - approximately 35-37 degrees. In addition, the patient is placed in bed, ensuring rest, and a basin for vomiting is placed within reach.
While waiting for an ambulance or if it is impossible to contact doctors at this very moment, the patient should be given an anesthetic. Suitable drugs include “No-shpu”, “Drotaverine” and “Spazmalgon”. All other medications should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor.
Attacks of nausea due to illness
Nausea occurs as a symptom of an existing pathology. Seizures can be provoked by:
What to do if your child feels nauseous and has a stomach ache?
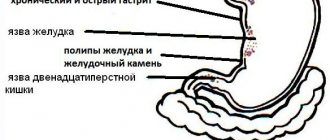
- Gastritis and ulcerative pathology of the stomach/duodenum. A typical sign of pathology is nausea after eating. The resulting vomiting brings relief to a person.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder. Frequent attacks of lightheadedness can be caused by cholecystitis. The sensations intensify while eating. It is possible that a bitter taste may appear in the mouth. A typical symptom of cholecystitis is pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). Nausea after eating and slight bloating are likely symptoms of the disease. The pathology is also characterized by weight loss and the appearance of an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Inflammation of the appendix. Nausea is one of the possible signs of a pathological condition. Additional signs include pain in the lower abdomen (left quadrant) and increased body temperature.
- Hypertonic disease. The development of an attack of lightheadedness is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure and redness of the face.
- Heart failure. The disease is characterized by prolonged nausea.
- Hypothyroidism. Nausea is also one of the signs of pathology of the endocrine system. As a rule, it is accompanied by weakness and lack of appetite.
- Inflammation of the renal system. The formation of nausea that does not end with vomiting may indicate the development of renal pathology. Accompanied by pain in the kidney area.
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining of the brain. The disease is characterized by nausea and high body temperature accompanied by severe headaches.
If pathological symptoms develop, in order to diagnose the pathology, consultation with a qualified specialist is necessary.
Causes of morning sickness
There are many reasons for nausea that occurs in the morning. The most common are the following: evening overeating, morning hunger, excessive intake of alcoholic beverages, taking medications on an empty stomach.
Sudden nausea in the morning may be the first sign of pregnancy
One of the harmless reasons why there are attacks of lightheadedness in the morning is pregnancy. Many women suffer from this symptom of early toxicosis. As a rule, the condition stabilizes by the beginning of the second trimester.
Attacks in the evening and at night
Most often, uncomfortable conditions for a person develop in the evening and at night, nausea is no exception. Severe evening nausea can be a sign of significant physical fatigue. The reason could be, for example, irregular working hours.
The next likely reason is overeating in the afternoon. As evening approaches, the rate of metabolic reactions decreases, which leads to slower functioning of the digestive tract. Food stays in the stomach for a long time, which causes nausea.
To avoid the development of an uncomfortable condition, it is necessary to refrain from eating foods that are difficult to digest. The food should be light and the portions should be small. Pathological conditions, in particular dysbacteriosis or inflammation of the appendix, can also be causes of evening and night nausea.
Late intake of medications can provoke an attack of lightheadedness in the evening or at night
Aminazine against vomiting and nausea
This drug is most often used only in the presence of vomiting during pregnancy and in the treatment of cancer with chemicals. In other cases, the appointment of Aminazine is possible only with severe and prolonged attacks of nausea and vomiting.
The drug is available in the form of a solution for intramuscular and intravenous administration, as well as in the form of pills for oral administration. The dosage of the medication is selected taking into account the intensity of the problem, the cause of the symptom and the current condition of the patient. Aminazine can be used after the first year of life.
Prescription of Aminazine is possible only for severe and prolonged attacks of nausea and vomiting
For intramuscular and intravenous administration, the dose of the active substance can be 25-50 mg, the number of daily doses is also selected individually. Oral use is possible only with mild attacks of vomiting, when the drug has time to act. In such cases, treatment is selected in minimal doses. The duration of treatment is individual for each patient.
Attention! Self-treatment with the described drug can be very dangerous, since Aminazine is used for very serious diseases not only of the digestive tract, but also of the nervous system.
Attack after eating
Nausea after eating, as a rule, indicates the development of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. The cause may be inflammation of the gastric mucosa. The following symptoms are typical for the disease:
- pain in the epigastric region, intensifying after eating;
- nausea;
- belching;
- increased gas formation;
- copious secretion of saliva.
In most cases, inflammation is caused by the introduction of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori into the gastric mucosa. Ulcerative pathology is also accompanied by nausea. Additional symptoms include acute pain in the epigastric area, heartburn, and vomiting.
Pain occurs 1.5–2 hours after eating. Often at night or in the morning. Signs of duodenitis, in addition to lightheadedness, include a feeling of fullness and pain in the stomach, heartburn, increased gas formation, and loss of appetite.
The cause of sudden lightheadedness may be a disease of the digestive system
Nausea can be caused by cholecystitis. Its signs:
- nausea and belching that occurs after eating;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- bitter or metallic taste in the mouth;
- bloating.
Vomiting in children
Intestinal or stomach obstruction is the leading cause of sudden, severe vomiting in young children. Pyloric stenosis is a narrowing of the opening for food to exit the stomach, which causes obstruction of the gastric canal. The condition is congenital in nature and is usually noticed within three months of birth. Requires urgent surgery.
Symptoms include severe vomiting without bile. An obstruction in the upper intestine can be caused by a foreign object that has entered the body. This is a common problem in babies and older children.
A foreign object may also be detected if the child has trouble defecating or has sudden abdominal pain after eating. It can also be caused by ingesting a caustic substance.
Help at home
How to relieve an attack of nausea without using medications? There are many safe and effective options. A contraindication is an individual reaction to prescription components.
To relieve an attack of nausea, you can use the following methods:
- Cut a lemon and smell it. Relief will occur in about 2-3 minutes. The inhalation should be deep and slow.
- Pour a teaspoon of fennel seeds into a glass of boiling water and leave for 10–15 minutes. Filter and add a little honey and lemon juice to the drink. Drink in small sips throughout the day. Prevents the development of nausea. The drink is allowed during pregnancy.
- Wrap ice cubes in a soft cloth and place on the neck (back) and forehead.
- Apply 2-3 drops of peppermint ether to the fabric and breathe in the aroma. Oil can be added to the aroma lamp.
- If you have persistent morning sickness caused by lack of sleep or pregnancy, you should prepare a mint drink in the evening. To do this, brew a spoonful of herbs in 150 ml of boiling water and leave overnight. In the morning, you should drink the drink in small sips without getting out of bed.
- Ginger helps relieve nausea. You need to grate a small root and pour a glass of boiling water. Leave to brew, filter and add a little honey to it. Drink warm. The recommended norm is 3 glasses per day. Ginger drink cannot be combined with anticoagulants - heparin - and appendicitis.
- Cloves will help you quickly get rid of nausea. You need to chew a small umbrella or drink tea to which you add 1 clove. An aroma session with clove ether gives good results. Apply a few drops to any fabric and breathe in the spreading aroma a little.
Cloves are one of the remedies used in folk recipes to relieve attacks of lightheadedness and nausea.
Nausea is a very unpleasant condition that requires urgent action. If it becomes permanent and is accompanied by the development of additional pathological symptoms, it is recommended to obtain qualified medical advice and undergo a full medical examination.
Simple steps
There are quite simple tips that will help you feel much better:
- eliminate any remaining vomiting by taking a warm bath.
- clean the nasal cavity to avoid the development of infection.
- rinse to remove the taste.
- drink plenty of fluids.
What to do next?
- The first thing to do after vomiting is to remove remaining fluid from the body. This will help reduce nausea and help the body recover.
- A warm bath should be prepared to remove any remaining superficial vomit and clear out the sinuses, which may also be clogged.
- Blow your nose well before leaving the bath. The steam will clear your nose and it will be quite easy to do. To do this, keep the scarf quite close; if something goes wrong, you can always tear it out.
- Rinse your mouth to eliminate odor. You should avoid brushing your teeth right away because it may irritate your stomach.
- If the nausea is not intense, then take care of hydrating the body. Because vomiting causes the body to lose a lot of water and becomes easily dehydrated. To prevent nausea, you need to drink slowly. First, you should start with a tablespoon of water, and then increase the dose every half hour.
- Avoid strong odors, which can make you feel nauseous again. If you need to cook something, ask someone else to do it. Stay away from products with strong odors.
What can you eat?
If you have a desire to eat something, then there are some foods that are suitable for this condition. You need to start with small portions so as not to irritate your stomach.
Proven foods that prevent vomiting:
- pasta without oil,
- dry bread,
- water,
- White rice,
- potato,
- banana, only an hour after vomiting,
- soups with light ingredients such as rice and boiled potatoes,
- tinctures of chamomile or cumin.
After eating, you should remain seated or slightly reclined for at least an hour. This position will allow the stomach to digest food more easily.
If possible, you can go out into the fresh air. Also, it would be a good idea to watch TV or a movie, this can distract the brain from the urge to vomit.
Video: diet after poisoning
What to avoid
Since the stomach becomes quite sensitive after vomiting, it is recommended to avoid the following foods:
- spicy products,
- fried and fatty foods,
- very salty food
- conservation,
- dairy products,
- caffeine,
- alcohol,
- raw fruits and vegetables.
These foods should be avoided until the person feels better. If you eat raw fruits and vegetables, you may experience repeated vomiting because fiber can interfere with digestion and irritate the stomach.
Will it be difficult to sleep?
In cases where nausea is due to food poisoning, one of the recommendations is rest and sleep. In this case, there is no need to worry and you can fall asleep peacefully.
However, if vomiting is frequent and caused by reflux, it is important to be aware of possible choking or airway blockage. In such cases, be sure to consult your doctor.