Acute appendicitis is considered the most common surgical pathology during pregnancy, requiring surgical intervention. The disease occurs due to displacement of the cecum and constipation that occurs throughout the entire period of gestation. Appendicitis during pregnancy, consequences: diffuse peritonitis, miscarriage or termination of pregnancy, death of mother and fetus.
Can appendicitis occur during pregnancy, possible causes, etiology
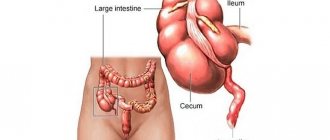
Appendicitis is manifested by inflammation of the vermiform appendix (appendix) of the cecum. The incidence of this pathology during pregnancy is 1 case per 700-2,000 pregnant patients.
The prevalence of acute appendicitis is 0.7 - 1.4%. The mortality rate of infants due to the disease ranges from 5 to 7%. The mortality rate of pregnant patients with inflammation of the appendix over the past 40 years has been reduced to 1.1% (from 3.9%).
In the 1st trimester, gangrenous appendicitis is detected in 50% of cases. In the 3rd trimester, appendiceal peritonitis is diagnosed in 99-100% of cases, which complicates treatment. With appendicular peritonitis there is a high risk of miscarriage, fetal and maternal death.
Etiology
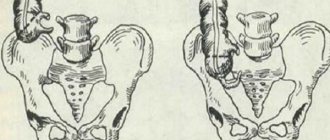
The main cause of acute inflammation of the appendix during gestation is the mixing of the appendix and the cecum upward and outward. A change in the localization of organs is noted in the period from 20-21 weeks to 37-38 weeks.
The diagram shows: 1 - appendix, 2 - uterus
Displacement of the cecum and appendix provokes bending and stretching of the appendix. This leads to deterioration of blood flow, blockage of the lumen in the appendix and the appearance of an inflammatory reaction. Ruptured adhesions from operations are also possible.
Other reasons:
- constipation;
- dysbiosis.
Another factor in the occurrence of inflammation of the appendix is constipation. During pregnancy, intestinal contractions slow down due to hormonal changes.
The uterus and intestines are innervated (supplied) by one bundle of nerves. To prevent miscarriage, hormones are released that prevent the occurrence of tone of the uterine organ. Together with the uterus, the contractility of the large intestine slows down. As a result, constipation develops.
Constipation provokes the occurrence of fecal blockages, which close the lumen of the appendix. Blockage of the appendix leads to the development of inflammation. Stagnation of the contents of the colon contributes to the development of dysbiosis, which is also considered the cause of inflammation of the appendix.
Chronic appendicitis during pregnancy occurs only when an appendiceal infiltrate has already been suffered, but not operated upon, before pregnancy. Compression of the appendix by the uterus provokes a relapse.
What is the danger of acute appendicitis during pregnancy?
Acute appendicitis during pregnancy can provoke a threat of miscarriage, as well as contribute to the development of other serious complications (occur in 17% of cases):
- intestinal obstruction
- premature placental abruption
- development of postoperative infectious and inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity
- septic shock
- right-sided pleuropneumonia
- fetal hypoxia
- disorders of contractile function of the uterus
- the occurrence of bleeding after childbirth.
Pregnancy loss occurs in 5-7% of cases. Moreover, the likelihood of a bad outcome increases with the length of pregnancy: in the second half, the risk of losing a child is 5 times higher than in the first trimester.
Signs of appendicitis during pregnancy
Signs of appendicitis in pregnant women may differ slightly depending on the period of gestation. If the disease appears in the early stages, the symptoms will be vivid. In late stages, signs of appendicitis in pregnant women are often erased, which makes diagnosis very difficult.
The longer the pregnancy, the more blurred the symptoms of appendicitis
Appendicitis in pregnant women in the early stages
In the first half of pregnancy, the main symptom of appendicitis in women is pain. The pain syndrome develops suddenly.
How does appendicitis hurt during pregnancy?
- The intensity of pain varies: severe or moderate, less often weak.
- The location of the pain at the onset of the disease is the subcostal region, the entire abdomen.
- After 3-4 hours, the pain is felt slightly above the right iliac region.
According to reviews from women, appendicitis during pregnancy is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and hyperthermia up to 38ᵒC. There may be no temperature. Possible increased heart rate up to 100 beats/min or more. An increase in neutrophil leukocytes (more than 12*109/l), an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (on day 2) is detected in the blood.
During the examination, tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall is noted. The symptom has its own characteristics. Muscle tension is weakly expressed, since the skin is strongly stretched, and the vermiform appendix is located behind the uterine organ.
The symptoms of an acute abdomen in women in the 1st trimester of pregnancy with appendicitis are well defined:
- Rovzinga - the pain syndrome intensifies at the site of the projection of the cecum when pressing on the left iliac region (the symptom is sometimes absent).
- Sitkovsky - pain increases if the patient lies on her left side (sometimes absent).
- Bartholomew-Mikhelson - the pain syndrome intensifies if the patient lies on the right side (the appendix is pressed by the uterine organ).
- Shchetkin-Blumberg - increased pain when the hand palpating the anterior abdominal wall is suddenly removed after pressing.
How does appendicitis affect the fetus?
Appendicitis during pregnancy is very dangerous, and its consequences for mother and child can be unpredictable. It is worth knowing about the possible negative impact of the disease on the baby.
Negative consequences:
- If there is excessive pressure on the placental barrier, uterine tone may begin.
- With a perforated form of appendicitis, toxic substances can pass through the mother's blood to the child and lead to damage to the central nervous system.
- Placental abruption, which, without urgent medical intervention, leads to the death of the child.
- Premature birth.
- Possibility of infectious infection due to insufficient attention from medical personnel and non-compliance with the rules of the postoperative period. This can lead to a missed miscarriage.
In addition to the negative effect on the fetus, a number of other complications may also occur. Among them: acute intestinal obstruction, the occurrence of bleeding, as well as side effects of anesthesia.
Complications may occur within a week after the operation. During this period, the woman is prescribed antibacterial therapy and a gentle regimen. This will not prevent all consequences, but it may minimize them.
Appendicitis in a pregnant patient - what to do
If a woman has signs of inflammation of the appendix, one cannot expect the pain to go away. You should consult a gynecologist in the first hours. The doctor will conduct an examination, rule out gynecological diseases, and refer you to a surgeon.
Don’t risk your baby’s health and yours, call an ambulance!
You should not go to the hospital on your own when the pain is very severe. In this case, you must call an ambulance. If a surgical pathology is suspected, the ambulance will take the patient to the hospital.
Symptoms of acute appendicitis in an expectant mother
During pregnancy, it is very important for a woman to know the main symptoms of appendicitis so that if they occur, she will immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms indicating the presence of an inflammatory process in the vermiform appendix of the cecum:
- Pain throughout the abdominal area;
- Increased body temperature up to 37-38 degrees;
- Vomiting and nausea.
In addition to the above symptoms, a group of particularly dangerous manifestations can be identified that indicate a rupture of the inflamed appendix and the onset of peritonitis:
- A sharp increase in body temperature above 39 degrees;
- Frequent vomiting;
- Reduction of pain followed by a sharp increase;
- Pain when touching the stomach;
- Confusion.
Diagnostics and differential diagnostics
If a woman suspects appendicitis, doctors carry out a differential diagnosis. Depending on the period of gestation, the list of diseases with which it is necessary to compare inflammation of the appendix will differ:
| 1 half gestation | 2nd half of gestation |
| Early toxicosis | Right-sided kidney inflammation |
| Inflammation of the gallbladder | Inflammation of the gallbladder |
| Renal colic | |
| Kidney inflammation | |
| Ectopic pregnancy | |
| Inflammation of the pancreas | |
| Pneumonia | |
| Torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst | |
| Inflammation of the gastric mucosa |
In the first half of pregnancy, the patient is shown the following examination:
- Determination of Pasternatsky's symptom (negative for inflammation of the appendix);
- Urinalysis (helps identify kidney and liver diseases);
- Stool analysis (to exclude pathologies of the digestive tract: gastritis, liver disease);
- Auscultation of the lungs + sometimes radiography (to diagnose pneumonia);
- Chromocystoscopy (if there is doubt about renal colic);
- Ultrasound (exclusion of torsion of the pedicle of the ovarian cyst, ectopic pregnancy).
After excluding other diseases, using this list of examinations, a diagnosis is made: acute or chronic appendicitis.
Treatment
Acute appendicitis during pregnancy quite quickly passes from the catarrhal stage to the destructive, phlegmonous or gangrenous form. Therefore, this disease can only be treated surgically.
- In recent years, catarrhal appendicitis has been removed using laparoscopy. This method is more gentle than open laparotomy and minimizes the risk of subsequent pregnancy complications.
The most common complication after surgery is miscarriage or premature birth; according to statistics, this occurs in 25–30% of cases.
- Destructive forms of inflammation of the appendix require wider access to the abdominal cavity, therefore appendicitis is removed in the usual way. The incision in the anterior abdominal wall is made taking into account the duration of pregnancy: the larger it is, the higher the appendix is located. If there is an inflammatory effusion in the abdominal cavity after surgery, drains are installed to drain the contents and infuse antibiotic solutions.
Inflammatory effusion (exudate) is a liquid released into tissues or body cavities from small blood vessels during inflammation.
Laparoscopic appendectomy is a gentle method of removing the appendix
Treatment in the postoperative period is carried out jointly by the surgeon and the obstetrician. In addition to eliminating inflammation in the abdominal cavity, the main task is to maintain pregnancy.
After the operation, medications are prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory;
- tocolytics and antispasmodics to eliminate uterine tone;
- infusion drugs that improve uteroplacental blood flow.
Medicines are prescribed taking into account their effect on the fetus.
After surgery, pregnant women are advised to take longer bed rest. Nutrition during the postoperative period should be as gentle as possible on the intestines. For the first day, only drinking is allowed.
Is it possible to remove appendix during pregnancy?
Patients often ask doctors whether pregnant women have their appendix removed. Treatment of the disease is aimed at eliminating the source of inflammation and infection. If a diagnosis of appendicitis is made, the patient is indicated for urgent surgery, regardless of the gestation period.
The pain suddenly went away - a sign of peritonitis (death of nerve endings occurred)
Surgical treatment is carried out if a woman experiences subsidence of symptoms of acute inflammation of the appendix. In this case, the probability of developing peritonitis is 90-100%.
If the clinical picture is unclear and the diagnosis is difficult to make, the patient is monitored for 3 hours. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is indicated for urgent surgical intervention.
Surgical treatment in the 1st half of pregnancy
Each half of pregnancy has its own surgical treatment techniques. If the gestation period falls within the first half, the patient is indicated for surgery, which is performed on women outside of pregnancy. After surgery, the wound is sutured tightly.
When complications are detected on the operating table (periappendicular abscess, appendiceal infiltrate, peritonitis), the patient is given a drainage after the operation. A drainage tube is necessary for the free release of pus from the abdominal cavity. The wound is also washed with antibacterial drugs through the drainage.
After surgical treatment, if the fetus is damaged, abortion is allowed after 14-21 days. Termination of pregnancy is carried out in the first half of gestation.
Management tactics in the 2nd half of gestation
In later stages, the operation is more difficult, since the uterus is already large. Appendicitis in pregnant women: surgery in the 2nd half of pregnancy, types of access:
- Extended McBerway-Volkovich-Dyakonov incision; at the same time, the sheath of the right rectus abdominis is incised.
- Median lower laparotomy is more often used.
After surgical treatment, the patient is prescribed antibacterial drugs. Medicines are also prescribed to reduce the tone of the uterine organ and other means to prevent miscarriage or termination of pregnancy. If there are no complications after surgery, the patient is allowed to stand up for 4-5 days.
Appendicitis can only be treated with surgery
If complicated appendicitis occurs in women during pregnancy (symptoms of purulent peritonitis) at a gestation period of 36-40 weeks, the patient undergoes an extraperitoneal cesarean section. The uterus is preserved during the operation. After suturing the incision on the uterus, the inflamed appendix is removed and the peritoneal cavity is sanitized.
In case of diffuse peritonitis, which is provoked by phlegmonous or gangrenous lesions of the appendix, the patient is indicated for a cesarean section with removal of the uterine organ. The peritoneal cavity is drained, after which the peritonitis is stopped.
Forecast
Removing the appendix in most cases does not affect the subsequent birth process. When the operation is performed in the early stages of pregnancy or at least 1.5 months before birth, the risk of complications is minimal.
After surgery, even in the complete absence of complications, monitoring the woman’s condition should be especially careful. In case of complications or a destructive form of the disease, especially when surgery is performed a few days before birth, delivery will have some features.
Such as:
- In order to reduce the risk of hypoxia, oxygen therapy is prescribed.
- Childbirth is carried out in the infectious diseases department.
- During childbirth, doctors carefully monitor the condition of the woman and child.
- During the pushing period, an additional incision is made in the perineal area to avoid excessive tension in the abdominal muscles.
- To maintain the integrity of the seams, use a tight bandage, tightening the abdominal area.
The risk of premature termination of pregnancy continues for 7-10 days after removal of the appendix. With uncomplicated appendicitis, in most cases the birth outcome is favorable. With timely detection and a competent approach to treatment, appendicitis in pregnant women does not pose a serious threat.
Ignoring the symptoms and obvious signs of the disease leads to the development of complications that can harm both the expectant mother and the child. If you suspect the onset of an inflammatory process in the body, you should immediately contact a medical institution to confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis.
Article design: E. Chaikina