About the problem
Diarrhea is a manifestation of the body’s ability to get rid of bacteria and viruses, of which there are a great many around the child. Neither the water that the baby drinks, nor the food, nor the air is sterile. What can we say about playing in the sandbox, crawling on the grass, on the floor, etc. Humans have several such protective “systems”: saliva is designed to destroy microbes at the stage of entering the mouth, bronchial and nasal mucus protect the respiratory organs from getting into them bacteria and viruses, gastric juice effectively destroys those microorganisms that managed to enter the body through the mouth and reach the digestive organs unharmed. Bacteria, which are the indigenous inhabitants, await “uninvited guests” in the intestines. Their task is to prevent malicious agents from taking root.
Editor's word
The first remedy for treating diarrhea in a baby is an enterosorbent (a product that absorbs particles of harmful substances in the gastrointestinal tract). You should choose a sorbent preparation for the little ones carefully so as not to harm the child’s body. According to data received from the National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Medical Products (ANSM, France), the enterosorbent Smecta®, popular among Russians, may contain lead impurities, and there is a risk of lead passing into the blood in children under 2 years of age when treated with this drug . As a result, doctors in France are not recommended to prescribe Smecta and generics to children under 2 years of age for the treatment of acute diarrhea. These medications are also not recommended for pregnant and breastfeeding women, for the same reason. The Russian Union of Pediatric Centers has already sent doctors a warning from the French regulator with a recommendation to use Russian drugs instead of Smecta for children and pregnant women. The drug of first choice is Enterosgel, which meets the main safety requirement - it works only in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract and does not penetrate through the mucous membrane into the bloodstream.
Diarrhea in a child can be caused by an intestinal infection that enters the mouth through unwashed hands, poorly washed vegetables and fruits, through water, or with food. Often these are bacteria.
Some viruses, such as rotavirus, also cause diarrhea. The intestinal mucosa is an excellent breeding ground for their reproduction, and therefore digestion is disrupted, the intestinal mucosa is irritated and diarrhea occurs.
Causes of diarrhea in children
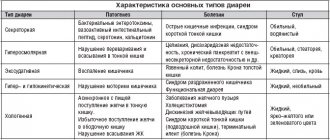
The list of possible reasons is long. Diarrhea is caused by viruses or bacterial infection.
This condition can appear as a result of the life of a parasite, taking antibiotics, or improper nutrition of the child.
- viral infection. Rotavirus, norovirus, adenovirus and astrovirus cause diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. The child may have a fever of up to 38 degrees, chills;
- bacterial infection. Bacterial food poisoning can cause diarrhea.
Common bacteria that cause food poisoning are staphylococcus, salmonella, shigella, E. coli and campylobacter. If your baby has a bacterial infection, he or she will have severe diarrhea. Less common are abdominal cramps, bloody stools in the child, and fever. There may not be any vomiting. When your baby has symptoms of a bacterial infection, make an appointment with the doctor. He will conduct an examination and may recommend testing feces for flora; - ear infections. Sometimes an ear infection (viral or bacterial) can cause a bout of diarrhea, especially in children under 2 years of age. The baby may have recently caught a cold and is now too capricious. He will pull his ears or complain of ear pain. He may also have other symptoms: nausea, vomiting and poor appetite;
- parasites. Parasitic infections can also cause diarrhea. For example, giardiasis is caused by a microscopic parasite that lives in the intestines. If a child has this infection, he will often experience loose stools, bloating, gas, nausea and painful cramps. These types of infections spread easily among children, and treatment includes special therapy, so the baby must be shown to a doctor;
- diarrhea from antibiotics. If your baby has diarrhea during or after a course of antibiotics, this is because the medicine kills good bacteria in the intestines along with infectious ones.
Talk to your doctor about alternatives and means to restore gut flora, but do not stop giving your child any prescribed medications without consulting a specialist; - drinking large amounts of juices. Drinking large amounts of juice (especially fruit juice containing sorbitol and high levels of fructose) or large amounts of sweetened drinks can upset your baby's tummy and cause soft stools. Reducing the amount of juice should resolve the problem in a week or more. Pediatricians recommend giving your baby no more than one small glass (about 150 - 200 ml) of juice per day;
- food allergy. When a child has a food allergy, it means that their body's immune system is reacting in this way to normal, harmless food proteins.
A mild or more severe reaction occurs either immediately or after a couple of hours. Cow's milk is the most common food allergen. Other foods that cause allergies are peanuts, eggs, soy, tree nuts, wheat, shellfish and fish. Symptoms of food allergies include diarrhea, bloating, abdominal pain, and bloody stools. In severe cases, the allergy causes vomiting, hives, rash, swelling and difficulty breathing. If you think your child has a food allergy, talk to your pediatrician; - food intolerance. Unlike food allergies, intolerances (sometimes called food sensitivities) are abnormal reactions that are not related to the immune system.
One example is lactose intolerance. If your baby is lactose intolerant, it means that their body does not have enough lactase, the enzyme that digests lactose. Lactose is the sugar in cow's milk and milk products. When undigested lactose lingers in the intestines, it causes diarrhea, abdominal cramps, bloating and gas. Additionally, if your baby has a severe case of diarrhea, he or she may temporarily have trouble producing lactase, resulting in symptoms of lactose intolerance for a week or two; - poisoning. Toddlers are adventurous and always want to try something new.
This often leads them to try non-edible substances such as chemicals, plants or drugs. If your child swallows such an item, diarrhea and vomiting may occur. You need to urgently take your baby to the hospital or call an emergency room. Other symptoms of poisoning: breathing problems, loss of consciousness, painful spasms and lethargy; - functional diarrhea. When your baby poops several times a day and the stool is loose, foul-smelling, and contains undigested food or mucus, it may have a condition called functional diarrhea. There is no specific reason other than the possible introduction of new foods or another change in diet.
Danger of diarrhea
The most serious danger of diarrhea lies in the possibility of dehydration . The younger the child, the higher this risk. Potassium, calcium, and sodium salts, which are extremely important for life, are released with feces. Fluid is rapidly lost. Therefore, it is not as scary if a 3-year-old child goes to the toilet five times a day and does not show signs of dehydration as if five times diarrhea happened to a 6-month-old baby. After all, the baby’s reserves of water and mineral salts are much more meager, and he loses them at a faster rate.
Severe dehydration can cause serious problems with the nervous system and can also be fatal for an infant.
Treatment
If diarrhea is caused by a viral infection, and in addition to frequent trips to the toilet, there are all the signs of a viral illness, you should not feed the child antiviral drugs, they do not help and their effectiveness has not been clinically proven. Antibiotics are also inappropriate because they have no effect on viruses. No special treatment is required; it is enough to provide the child with the right help and prevent dehydration. If diarrhea is the result of food poisoning or intestinal infection, the treatment approach should be the same.
First of all, you should make sure that the baby is not dehydrated.
If a child does not pee for 6 hours, if he cries with dry eyes, without tears, if he has blue circles under his eyes, sharpened facial features, dry lips, tongue, dry mucous membranes - these are very alarming symptoms. Immediate medical attention is required, you need to call an ambulance.
To prevent such a dangerous condition, parents’ actions in case of diarrhea must be coordinated and clear:
- The child definitely needs to drink. And drink a lot. All drinks should be warm, about 20 degrees, so that the liquid is absorbed and absorbed by the body as quickly as possible. If a child refuses to drink from a cup, he should be fed with a spoon, little by little but often. If he does not drink from a spoon, as children under 7-9 months often do, then you need to draw the liquid into a disposable syringe without a needle and drink from it drip-wise. If the baby resists this method, you should not wait and persuade, you should immediately call an ambulance so that you can administer liquid to the child by drip.
- The child needs to restore the balance of salts and remove toxins . To do this, Komarovsky advises using ready-made pharmaceutical sachets with oral rehydration products. Regidron or Humana-Electrolyte will do . These drugs must be in every family's home medicine cabinet. If diarrhea has already occurred, and there are no such drugs, you can use a recipe that has received full approval from the World Health Organization: add a teaspoon of salt and the same amount of soda to a liter of water. You can also give your child this solution.
- Need control over secretions. What you drink should stand out. As long as the baby, who has not yet reached the age of one, wears diapers, the mother has nothing to worry about. At any time, she can measure the amount the child drinks, and after 3 hours weigh his used diaper on an electronic kitchen scale to understand whether the water is being excreted normally. If the child is already using the potty, control will also not be difficult. But a 2-year-old child, who has most likely already mastered the toilet, will have to follow on his heels.
- The child does not need food. You should not try to feed him at any cost. Diarrhea will go away much faster if the baby is hungry. You should give food only when he asks for it. If you have diarrhea, you should not eat fatty or sweet foods, drink carbonated drinks and milk. It is better to give porridge, mashed potatoes, crackers from yeast-free bread, vegetable soup with lean broth.
- Activated carbon - in the correct dosage. Another useful drug that should be in your home medicine cabinet. Parents should remember that activated carbon is dosed at 1 tablet for every 10 kilograms of body weight at a time. Thus, a child weighing 10 kilograms is given 1 tablet, and a baby whose weight is 15 kilograms is given 1.5 tablets. Modern medicine recommends modern enterosorbents, which are easier to take. If the financial capabilities of the family allow, you can buy and keep Enterosgel in the first aid kit for such cases.
Treatment of diarrhea in a 5 year old child
Diarrhea is the body’s response to the influence of pathogenic bacteria, toxic irritants, medications, etc. in the intestinal walls.
Not in all situations, the appearance of loose stools in a child requires immediate intervention and active treatment.
You should not worry when such a pathology appears only once. However, if the problem reappears and is associated with additional symptoms, this indicates a disorder in the functioning of the child’s internal organs.
Mild and short-lived diarrhea will have virtually no effect on your general well-being.
In some situations, diarrhea occurs due to eating laxative foods, such as plums, greens, beans, or any stressful situations.
Therefore, before treating a child, eliminating diarrhea, or implementing various measures, the root cause of diarrhea should be established. Based on this, appropriate treatment is selected.
Nutrition after diarrhea
When the diarrhea is safely over, there is no need to immediately cook all those cutlets for your son or daughter and carry all the cookies that the child did not eat while he was ill. You should stick to a gentle diet for a few more days. The diet of a child from 1.5 years old can include porridge, tea, vegetable soups without meat. For a child over 2 years old, you can add one small curd to tea without additives, pieces of fruit or food coloring.
Then the diet should be increased gradually, adding new products to the toddler’s menu every day, starting with boiled meat, steamed cutlets and ending (last) with a piece of chocolate or his favorite candy.