Sore throat after gastroscopy is a common complaint among people who have undergone the procedure. FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) or gastroscopy is a procedure for examining the stomach and esophagus (gastrointestinal tract). Send for analysis if gastritis, duodenitis, tumors and bleeding in the duodenum, peptic ulcer, gallbladder disease, hepatitis are suspected. The procedure is considered unpleasant, patients are afraid to undergo it, including due to painful sensations for a number of days after the procedure. In particular, a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and severe pain in the stomach.
A referral for an FGDS is prescribed by the attending physician. The basis is the symptoms of the above diseases. To carry out the procedure, the patient lies on his left side. A special mouthpiece is clamped in the teeth, through which the doctor carefully inserts the gastroscope. The device is a tube made of elastic material. At the tip there is a camera and a device for collecting samples for biopsy. Using a camera, researchers monitor the state of a person's gastrointestinal tract on a monitor in real time.
The procedure itself is unpleasant and can cause severe pain for the patient. The analysis lasts 10-15 minutes. During the procedure, the patient feels nausea, and the gag reflex is triggered due to irritation of the receptors in the throat. To minimize pain, the patient’s throat is pre-treated with a spray containing lidocaine solution. It is recommended to lie still and breathe deeply, reducing the gag reflex. Failure to follow the rules doubles the duration of the procedure. Accordingly, the risk of unpleasant pain after endoscopy increases.
In modern conditions, with the latest technology, the FGDS procedure is the least painful; local or complete anesthesia is used at the patient’s request.
Preparation for FGDS
To minimize the consequences of FGDS, a number of rules must be followed. The patient must arrive for the procedure on time or before the appointed time. It is forbidden to eat food before analysis. If the procedure is scheduled in the afternoon, doctors allow you to eat a small breakfast of quickly digestible foods. For two days, it is not recommended to consume chocolate, spicy foods, coffee, or alcohol, which affect the accuracy of the analysis results.
Smoking is strictly prohibited before the procedure. You are allowed to drink water in unlimited quantities, but stop 2 hours before the test. Do not take tablets in capsules unless prescribed by your doctor.
Restrictions are placed on gastroscopy for pregnant women. The normal course of pregnancy removes restrictions.
These rules are designed to make it easier for the patient to undergo the procedure and ensure the rapid disappearance of pain.
ESSENCE OF THE PROCEDURE
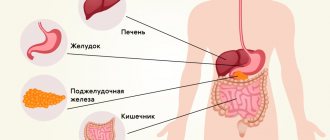
FGDS, also known as gastroscopy, is one of the most common types of diagnostics of internal organs - it can be used to identify pathologies in the esophagus, stomach and intestines. The essence of the study is the introduction of a special device, an endoscope/gastroscope through the oropharynx - this allows you to visually examine the insides and carry out simple procedures, such as a biopsy.
Harm during FGDS is unlikely, and discomfort is eliminated by anesthesia. However, sometimes the consequences of EGD can include pain.
Possible side effects
The FGDS procedure involves some complications that arise after the procedure. The duration of unpleasant sensations varies from person to person. It is influenced by the characteristics of the patient’s body, the level of pain threshold, the presence of diseases, the doctor’s experience and the degree of wear of the equipment. Side effects should go away on their own within a day or two after the endoscopy. If after this time the patient continues to complain of pain, it is better to consult a doctor.
Common Complications
After gastroscopy, your throat and stomach may hurt. Common complaints recorded:
- causing injury to the internal walls of the stomach, esophagus, and upper intestine;
- swelling and redness of the mucous membrane;
- sore throat;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- increased body temperature;
- pneumonia;
- the occurrence of ulcers;
- severe pain in the abdomen, accompanied by bleeding (during a biopsy).
Causes of complications
Most often, pain in the throat and stomach after endoscopy is caused by:
- Overdose of painkillers;
- Intolerance to medications used;
- By sharp insertion of the probe;
- Patient behavior that interferes with the procedure;
- The presence of contraindications to undergoing FGDS.
Sore throat occurs due to rough insertion of the tube with the sensor, when injuries are caused to the mucous membrane of the larynx. Likewise, injury can occur when the tube comes out. Microtraumas and scratches occur on the mucous membrane. In the worst case, damage leads to the formation of hematomas and ulcers.
The stomach may hurt if the esophagus is damaged. It is also damaged when tissue is collected for biopsy. This can even lead to organ rupture. In the worst case, the patient gets an intestinal infection.
The most dangerous complication is pneumonia. Its occurrence causes vomit to enter the lungs if the patient cannot cope with the gag reflex during the procedure. The tube is removed, after which air enters the lungs along with the vomit.
Treatment of sore throat after FGDS
What to do if your throat hurts after gastroscopy? As a rule, no special treatment is required - the discomfort goes away on its own and the pain disappears. However, if there are signs of inflammation in the throat, medication is still required. The most commonly prescribed local disinfectants are:
- Chlorhexidine solution is a good antiseptic that can reduce infection of the mucous membrane and, thereby, reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process. It is the best option for treating scratched mucosa after FGDS.
- Miramistin is an analogue of chlorhexidine that quickly destroys various types of microorganisms.
- Furacilin solution acts in a similar way, but is usually prepared independently by the patient before use.
The use of local antiseptics allows you to disinfect mucous membranes damaged as a result of the procedure and stop the progression of the inflammatory process.
If pain occurs, it is best to consult your doctor to examine the mucous membrane and choose rational therapy.
If the pain syndrome is not clearly expressed, then the attending physician may recommend the use of tablets with a local anesthetic effect (Stopangin, etc.). Their effectiveness in treating such pain with weak inflammatory components is quite high.
Lozenges with local anesthetic
What to do when your throat or stomach hurts
If, a day after the procedure, the patient continues to complain that it hurts to swallow, feels severe pain in the stomach, and his health does not improve, it is time to see a doctor. In such cases, the doctor is asked to wait a little, since the unpleasant sensations are the consequences of FGDS. Frequently used methods of treating pain are gargling and a special diet.
How to gargle
Rinsing helps relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx, disinfect and anesthetize the tracheal microtraumas received during the procedure. Doctors recommend using one of the following rinsing methods:
- Inhalipt spray is used for pain relief.
- Chlorophyllipt spray helps reduce pain and has an antiseptic effect.
- Miramistin relieves inflammation well.
- Furacilin solution helps relieve discomfort and accelerates healing.
- A solution of salt, soda and iodine, applied once every two hours, will also relieve pain.
- Chamomile solution has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect; it is recommended to use it a couple of times a day.
- Antiseptic tablets.
It is important to consult with your doctor regarding the choice of rinse and frequency of use. To achieve a better effect it is possible to combine.
In addition to rinsing solutions, doctors recommend drinking herbal teas, in particular chamomile. Drinking warm water with honey has a good effect on the throat. You can simply eat honey, even without water. The product has a rapid anti-inflammatory and soothing effect on the mucous membrane.
What to do: general tips
The first and most important advice on what to do when your throat hurts after a gastroscopy is not to ignore this symptom. It is important to minimize the likelihood of additional injury and irritation of the mucous membrane. To do this, in the first 2-3 days after FGDS, sour and spicy foods should be excluded, foods with solid particles, carbonated drinks and alcohol should be removed from the diet. To make it less painful to swallow food, on the first day after gastroscopy you need to eat pureed dishes, purees and broths.
Important! The food temperature before the mucous membranes are restored after gastroscopy should not exceed 40-50 degrees. Cold foods and drinks should also be avoided.
To reduce irritation before eating, you can drink a tablespoon of oil: sea buckthorn, olive or flaxseed. They have an enveloping, soothing and healing effect, so their use will speed up recovery from gastroscopy and prevent complications.
If FGDS results in prolonged pain that does not subside, and swallowing becomes more difficult every day, you need to make an appointment with a doctor to examine the throat and larynx for inflammation. If there are no additional symptoms, you can visit an ENT doctor, and if a cough with blood discharge appears, you should contact the gastroenterologist who issued the referral for FGDS, or the endoscopist who conducted the study.
Useful tips
Since mild and short-term discomfort in the throat after gastroscopy is considered normal, there is no need to panic and swallow all kinds of medications. Also, the probe touches the stomach muscles when taking samples for research, mucous membranes are taken for analysis and contact between the tube and internal organs simply occurs; pain can be difficult to avoid. Follow some simple tips that your doctor will tell you in detail.
This will avoid complications if your stomach or throat hurts.
- Gastroscopy is considered a safe procedure. Therefore, it is recommended to eliminate the consequences in the form of pain without the use of medications.
- If unpleasant symptoms in the oral cavity and larynx intensify, the doctor should prescribe a course of drug treatment.
- The main treatment is antiseptic gargling. In addition to pharmaceutical Chlorhyxedine, Furacilin and Miramistin, many doctors advise using regular baking soda. It is diluted in warm water and the mouth is rinsed 3-5 times a day. This remedy helps to change the acidity in the throat, due to which all pathogenic and potentially threatening microorganisms actively die. The risk of getting sick is minimized. But it is important to rinse your mouth regularly and not stop until the full course of treatment has been completed.
- In addition to soda or as an independent remedy, throat lozenges are used to soften the throat and restore the mucous membrane. The soreness is eliminated and the patient feels relief within a few hours.
- If your throat continues to hurt and dryness is actively manifested, eat 1 small spoon of sea buckthorn oil before meals. Its enveloping properties will relieve dryness and help eliminate discomfort.
- Honey is a good folk remedy, which doctors themselves recognize. But you need to take only high-quality honey, dissolving it in your mouth. It is recommended to do this before bed and before each meal. If you are allergic to this product, you should not use it for treatment.
- Eat right. You should not eat any solid foods, fried, salted, smoked, spicy, sour, etc. Choose food that is as soft and light as possible. Spicy foods are considered the most dangerous for the stomach and throat after gastroscopy. The temperature should be average. Too hot or very cold food can aggravate your condition.
Before and after the procedure
Any gastroenterologist will tell you that it is impossible to completely avoid discomfort during the procedure of inserting a probe with a camera. But if you follow the rules prescribed by your doctor, all consequences will be minimized. They are prescribed on an individual basis, depending on the patient’s condition, the presence of certain diseases, contraindications, etc.
There are general tips that everyone should take into account.
- Bile in the stomach. It is there if there is undigested food. To prevent bile from being in the stomach and its particles from entering the throat or esophagus when removing the probe, you should not eat anything for at least 8 hours before the examination.
- Cervical spine problem. It hurts and swells because it is not easy to relax while the tube is inserted. If the patient experiences problems in this area, the doctor may prescribe a special muscle relaxant.
- Don't worry, don't panic. Stress often provokes pain. There are a number of tips that doctors give to their patients before the procedure and during manipulations with the tube. The specialist’s ability to interact with the patient has a positive effect on the percentage of successful gastroscopy procedures.
- Antiseptic treatment. Since pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate through damaged areas of internal surfaces, it is better to use antiseptic agents before inserting the probe and after completing the procedure to consolidate the effect.
- No smoking, alcohol or carbonated drinks before gastroscopy. They provoke a gag reflex, disrupt the mucous membrane and do not allow the probe to enter the cavity normally.
- If you are being treated for any diseases using medications, be sure to tell your gastroenterologist about them. For some diseases, gastroscopy is contraindicated until complete recovery. Also, do not forget to talk about chronic diseases and intolerance to anesthesia.
By following simple recommendations and strictly following all the doctor’s instructions, you will easily undergo the gastroscopy procedure with minimal consequences. We wish you all good health! Don't forget to subscribe, leave comments and invite your friends to join us!
Source
The FGDS procedure (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) is carried out to examine the esophagus and stomach using special instruments. This is a modern and quite informative method, but it has its negative consequences, for example, the throat often hurts after FGDS.
Such an examination is carried out if the following diseases of internal organs are suspected:
- duodenitis;
- the presence of a tumor in the duodenum or inside the stomach;
- gastritis.
To determine the diagnosis and to determine the extent of damage to internal organs, an elastic probe with a built-in camera is used. It also has a built-in special device that allows you to pinch off a piece of tissue for a more detailed study (biopsy). To facilitate the introduction into the patient’s throat, as well as for the purpose of pain relief after FGDS, the patient’s throat is treated with drugs with an analgesic effect.
When performed correctly, the procedure is considered safe. However, many patients complain of discomfort during FGDS examination. In some cases, your throat may hurt.
Typically, such negative consequences arise when using old equipment or due to poor professional training of the specialist who conducted the research.
CAUSES OF STOMACH PAIN
The most common cause of pain after gastroscopy is quite simple and straightforward - the pain is provoked by the air that is pumped into the stomach. This is necessary to “smooth out” the mucous membrane. There is nothing wrong with this soreness; it usually goes away in a day or two without any treatment. Also, with such pain, quite active belching occurs, which is one of the most characteristic indicators that everything is in order.
Moreover, deliberate belching in this case will alleviate the condition somewhat, as it will release air from the body, so patients are often recommended to resort to it.
But the reason that your stomach hurts may be more dangerous. If the procedure was carried out incorrectly - or the patient did not allow it to be carried out correctly enough, for example, did not remain motionless. In this case, other quite dangerous options are possible, although there are not many of them:
- Traumatization of the walls of organs was carried out - the esophagus, stomach or rather thin areas of the upper stomach.
- The stomach or esophagus was perforated.
- There was an infection. In general, before FGS, the endoscope is processed in a special way using special saline solutions and using a certain technology. Also, patients are always checked for infections before the study. But if the doctor was sufficiently negligent or incompetent, then in very rare cases it is possible that the body was infected.
All measures are taken to ensure that this does not happen - therefore, cases when something similar happens during the procedure are isolated exceptions.