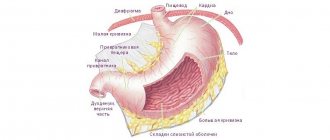
Drug treatment of gallstone disease
Drug treatment of gallstone disease is primarily aimed at eliminating the expression of a large number of unpleasant symptoms of such a disorder, which can have varying degrees of intensity.
To remove large stones, only surgery is used. However, if during diagnosis sand or small stones were found in the gallbladder or bile ducts, they are often tried to dissolve them with medications. Despite this, drug dissolution of stones is only possible if cholesterol gallstones with a volume of up to fifteen millimeters are detected. In addition, the course of the disease should be accompanied by normal contractile function of the gallbladder, as well as patency of the biliary tract.
However, there are several contraindications to drug therapy for gallstone disease. These include:
- bearing a child;
- breastfeeding a child;
- inflammation of the gallbladder or ducts;
- the presence of stones with a diameter exceeding two centimeters;
- diabetes;
- the presence of any stage of obesity;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- tumor of this organ;
- detection during instrumental diagnostic measures of multiple stones that occupy more than fifty percent of the total volume of the gallbladder.
In most cases, the following groups of drugs are prescribed for gallstone disease:
- choleretic substances;
- ursodeoxycholic acid;
- antispasmodics;
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
The danger of "stone-carrying"
Modern medicine and competent surgeons are still committed to preserving the gallbladder, which is precious in every sense. Therefore, after detecting unpleasant accumulations in the organ, be sure to check whether pain bothers you or whether there have been attacks of hepatic colic. And, at the same time, they explain that small stones (sand) are a more dangerous situation than a hardened large stone in the gallbladder.
Sharp petrified crystals can form both in the gallbladder and ducts. With active motility of the gallbladder, which persists at the initial stage of gallstone disease, the stones are able to move. This is the danger of small stones.
Biliary sludge (and stones less than 2 mm) are the most common causes of acute pancreatitis
Large stones in gallstone disease in rare cases (but they do exist) may not manifest themselves until the end of life. At this stage of the disease, as a rule, the gallbladder is no longer able to actively contract. It actually does not fulfill its function, and a “bouquet of unpleasant symptoms” arises from the gastrointestinal tract. You can live with this condition, and relatively well. Until a certain point...
However, as soon as the patient (knowingly or unknowingly) decides to crush the stones using folk methods, drive out parasites, “improve the fluidity of bile,” small stones begin to move. Sharp particles can break off from large ones, which begin to wander throughout the biliary system.
Calcified seals in the bladder or ducts move, injure tissue, cause inflammation (for example, cholangitis - infection of the bile ducts). In this case, the entire biliary system suffers: cholecystitis begins (inflammation of the gallbladder itself), the motility of the organ worsens, and dysfunction of the valve (SPHINTER OF ODDIE), which is responsible for the timely flow of bile into the duodenum, develops.
The sphincter of Oddi stops functioning correctly (pressure increases), the number of contractions decreases. And, as a result, small pebbles clog the duct from which the pancreas secretes. Then, the gland begins to digest itself, as it were, causing gradual tissue death (necrosis). By nature, pancreatic enzymes are activated only in the intestines under the influence of bile. However, for various reasons, a malfunction in the delicate functioning of the biliary system may occur.
The bile and pancreatic ducts can be anatomically located in two variants:
- Each of them flows into the duodenum separately (the likelihood of stones and sand getting from the bile duct into the pancreas is minimal);
- The common bile duct and the pancreatic duct form a single channel even before entering the intestine (the risk that stones will enter the pancreatic duct is incredibly high).
If a person’s duct structure follows the second type, then cholelithiasis is often complicated by pancreatitis. And, most often, in the acute stage, without a chronic course.
Small stones can block the pancreatic duct
Note that there are several scenarios for the development of acute pancreatitis. We have given an example of the so-called “primary biliary pancreatitis”. There is also a certain “reverse path”: the pancreas becomes inflamed for other reasons (stage of chronic pancreatitis), increases in size, begins to compress the common bile duct, and closes it. Chronic pancreatitis is insidious in that it is practically asymptomatic, or its signs are blurred, similar to mild disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Thus, when “stone bearing” is established, it is important:
- Get ultrasounds regularly
- Follow diet number 5
- Do not take choleretic drugs (herbal infusions, bile-stimulating drinks and foods)
- REMEMBER: small stones in the gall bladder are possible causes of BIG trouble (including from the pancreas).
- In case of acute, unbearable pain, call an ambulance. Don’t wait, don’t hope that “it’s about to let go”!
- Do not take antispasmodics or any painkillers.
- Be sure to inform the team that you have been diagnosed with gallstone disease. Because many diseases have a similar clinical picture. Acute cholecystitis, acute appendicitis, intestinal obstruction - the symptoms are almost the same. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis.
Choleretic drugs
One of the most effective choleretic substances is Allochol, which consists of the following herbal components:
- nettle;
- garlic;
- Activated carbon;
- dry animal bile.
The drug exists in several forms - syrup and tablets.
The properties of Allochol include:
- acceleration of bile secretion in the duodenum, which helps stimulate intestinal motility;
- preventing the accumulation of large amounts of cholesterol, which prevents the formation of new stones;
- elimination of the inflammatory process in the gallbladder and its ducts;
- reduction of intoxication of the body with bile acids - this medicinal effect is achieved thanks to activated carbon.
Indications for this medicine are:
- housing and communal services;
- chronic constipation, which is caused by impaired intestinal motility and insufficient bile secretion;
- inflammatory process in the bile ducts and walls of the gallbladder.
There are also several contraindications to taking Allochol for cholelithiasis:
- closure of the duct with a large stone. This is what causes obstructive jaundice;
- hepatitis;
- gastritis and gastrointestinal ulcers.
The duration of therapy with this drug is approximately one month, it is best to repeat it twice a year. It must be consumed after every meal.
In addition to Allochol, the group of choleretic drugs includes:
- Urolesan - consists of natural ingredients. Contraindications are: an allergic reaction to any component of the medication, gastritis or ulcers, stones larger than three millimeters;
- Holosas – based on rosehip. Contraindications – diabetes or allergies;
- Flamin is a drug based on immortelle. Contraindications include: high blood pressure;
- Holagol is an extract of curcuma longa rhizomes, emodin from buckthorn. Prohibited for use if there is a violation of the blood clotting process, blockage of the bile duct, patients under sixteen years of age, or the presence of renal or liver failure.
Why does pancreatitis occur?
Pancreatitis is a group of diseases and symptom complexes, the characteristic feature of which is specific changes both in the tissues of the pancreas and around it, resulting from their inflammation due to increased production of digestive enzymes. The cause of inflammation in the pancreas can be virtually any situation when the organ has to produce more enzymes than is necessary for natural digestion.
Excessive secretion of digestive enzymes is a natural reaction of the pancreas to:
1. Any alcohol 2. Fatty, fried foods, fast food, drinks with artificial colors and sweeteners 3. Vegetables and fruits “overfed” with pesticides and fertilizers 4. Tobacco smoke and tars 5. Some medications
If the effect of these factors is regular or prolonged, you are at risk of developing chronic pancreatitis!
There are other explanations for why pancreatitis occurs . They are associated with diseases of the digestive system, attacks of bacterial and especially viral infections (hepatitis B, mumps, Epstein-Barr viruses), congenital defects of the pancreas itself, liver, bile ducts and duodenum.
A certain role in the development of pancreatitis is played by disorders of the nervous system during stress and neurosis, hormonal disorders that cause spasm of the sphincter of the gastrohepatic ampulla.
Antispasmodics
A disease such as cholelithiasis in all cases is accompanied by severe pain, which often spreads to other areas of the abdomen, so taking painkillers is important.
In almost all cases, doctors prescribe No-shpa to their patients, which also has several analogues:
These drugs eliminate spasm of smooth muscles that occurs due to damage to the ducts by stones.
The drug exists in several forms - tablets and solutions for injection. It can be taken during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Among the undesirable situations for use it is worth highlighting:
- individual intolerance;
- acute nature of renal or liver failure;
- low cardiac output syndrome, which causes heart failure.
Another effective remedy for treating gallstone disease is Duspatalin. It acts selectively on the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract. You should take it one tablet at a time.
Causes of the disease
Pancreatitis, as well as cholecystitis, are diseases of the digestive system, and their development can be triggered by poor nutrition.
The main reasons for the development of pathologies:
- obesity;
- helminthic infestation;
- sedentary, passive lifestyle;
- endocrine disorders;
- heredity;
- frequent food poisoning;
- hormonal disorders;
- alcohol intoxication;
- cystic fibrosis;
- abuse of toxic drugs;
- Housing and communal services
Separately, it can be mentioned that pancreatitis often develops against the background of cholelithiasis, gastritis, hepatitis, diabetes, cholecystitis, duodenitis and colitis.
Pancreatitis in combination with cholelithiasis is called biliary, and excessive formation of stones leads to the calculous development of pathology. Calculous pancreatitis always ends with surgical intervention.
It is important to know that cholecystitis can also appear with cholelithiasis, when the ducts are blocked by stones. This leads to stagnation of bile secretion and causes severe inflammation. Sometimes cholecystitis first appears during pregnancy, and the acute form of pancreatitis occurs when cholecystitis is advanced.
Anti-inflammatory and painkillers
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory substances are used to treat gallstone disease. They are often prescribed for relapses of the disease.
The list of such drugs includes:
- Paracetamol and its analogues;
- Ibuprofen and Nurofen;
- Analgin;
- Diclofenac;
- Indomethacin.
In cases of exacerbation of the symptoms of the disease, you can take any of the above substances, but always after meals.
Strict contraindications include:
- ulcerative lesion;
- liver or kidney failure.
Ursodeoxycholic acid
Ursofalk is a fairly new drug based on ursodeoxycholic acid (a natural component of bile). Analogues of such a substance can be:
The action of the substance is aimed at:
- decreased cholesterol formation;
- prevention of stone formation;
- dilution of bile;
- splitting existing stones;
- improving the functioning and protection of the liver.
Contraindications include:
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- allergic reaction to the components of the drug;
- acute cholecystitis;
- liver damage by cirrhosis;
- obstruction of the ducts;
- presence of cholangitis.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics should be used only when indicated. In preventive measures against cholelithiasis, such medications are not only ineffective, but can also be harmful.
Indications for the use of antibacterial agents are:
- development of an inflammatory process in the gallbladder or duct;
- recovery after surgery to remove the gallbladder.
The course of antibiotic therapy ranges from five to nine days. In such treatment, it is very important not to skip taking the drug.
Treatment of acute pancreatitis in cholelithiasis
Acute pancreatitis requires hospital treatment.
The first step is to remove a person from toxic shock. Various drugs are used to relieve pain, rehydration and antibacterial therapy are carried out. At this stage, complete fasting is indicated.
Further, the treatment strategy depends on the patient’s condition. If infection of the retroperitoneal space does occur, then surgical methods are used: these can be minimally invasive operations or full-fledged open operations to remove the affected areas.
If signs of bile duct blockage are detected, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) can be used. The procedure allows you to expand the narrowed areas of the bile ducts, remove stones (tumors), and also diagnose the condition of the bile ducts, or collect tissue from the gallbladder and pancreas for biopsy.
After the necessary manipulations to save the patient’s life, when the cause of acute pancreatitis is established as cholelithiasis (GSD), cholecystectomy is prescribed. In each specific case individually (emergency or planned).
Questions about cholecystectomy here.
CONCLUSIONS
- Acute pancreatitis is a severe disease caused by many causes.
- With the increase in the incidence of cholelithiasis, cases of acute pancreatitis have also increased proportionally.
- In women (as the main carriers of cholelithiasis), cases of acute pancreatitis due to the damaging effects of gall bladder or duct stones predominate compared to men.
- “Stone carriage” significantly increases the risk of severe inflammation of the pancreas with tissue death.
- Small stones, fossils, sand (biliary sludge), with preserved motility of the gallbladder, are more likely to cause acute pancreatitis.
- Timely treatment of cholelithiasis (at this stage it is only cholecystectomy) can significantly reduce the risk of complications in the development of diseases of the entire gastrointestinal tract, including inflammation of the pancreas.
Treatment regimens
All of the above drugs are used for exacerbation and remission of the disease.
In case of exacerbation, a regimen from the following groups of drugs is prescribed:
- antispasmodics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antibiotics.
During the remission phase, the treatment regimen will consist of:
To prevent the disease, such enzyme substances are used, in particular Mezim and Festal.
It is worth noting that patients should not expect a positive effect from drug treatment of cholelithiasis in cases of addiction to junk food or addictions.
It is important to remember that it is best not to make independent attempts to eliminate symptoms and small stones, but rather to consult a specialist in a medical facility. Because only after laboratory and instrumental diagnostics will the doctor be able to establish the daily dosage and duration of taking a particular drug individually for each patient.
source
Drug treatment of gallstone disease: list of drugs
Gallstone disease is a pathology in which a calculus forms in the gallbladder. There are 4 types of stones - cholesterol (composed of lipids), bilirubin (formed by the pigment bilirubin), calcareous (made of calcium salts), mixed.
The pathology is accompanied by acute paroxysmal pain in the right hypochondrium, dyspeptic disorders, bitterness in the mouth, and elevated body temperature. These signs usually occur after consuming fatty foods, alcohol, and sweets. With cholelithiasis, angina pectoris and disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system are possible.
Gallstones are treated either with medication or surgery, depending on the size and type of stone. In the first case, the patient is prescribed antispasmodics, naturopathic choleretic drugs, anti-diarrhea drugs, enzymes and ursodeoxycholic acid.
Sample menu for cholelithiasis and pancreatitis
For a patient suffering from a combined pathology of this kind, various diets are used, depending on the phase of the disease.
For the remission period, for example, the following menu is suitable:
- Breakfast: steamed meatballs combined with carrot salad.
- Lunch: rice or cottage cheese casserole with vegetable salad.
- Lunch: steamed fish cutlets with rice.
- Afternoon snack: white omelet.
- Dinner: potato soup with pumpkin-apple salad.
- jelly,
- compotes,
- tea with milk,
- various juices,
- decoction of rose hips.
Drinking liquid after meals is allowed no earlier than a quarter of an hour (with the exception of lunch and afternoon snack) in the form of:
As soon as one week of such nutrition has passed, the patient should arrange a fasting day with a reduced calorie content: for breakfast, lunch, lunch, afternoon snack and dinner, 0.9 liters of kefir and a mixture of 0.15 kg of sugar with 0.3 kg of cottage cheese are equally divided.
In the summer-autumn season, the optimal solution would be a fasting day, during which the only food product is fruit.
In cases where the disease has worsened and there is severe pain, eating food is prohibited. The patient should limit himself to drinking water for two to three days. During this time, the pancreas and vesica biliaris have time to rest, and the release of bile becomes less. On the 4th day, the patient can be transferred to table No. 5. In this case, food should be divided into small portions, and meat and broths should be excluded.
Antispasmodics
Antispasmodics for cholelithiasis are used without fail, especially if the patient periodically experiences attacks of biliary colic.
Specific funds are selected on an individual basis. Antispasmodics can be combined with analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For gallstone disease, it is allowed to use medications produced in the form of capsules, tablets, solutions for intravenous or intramuscular administration.
The best antispasmodics are discussed in the table below.
| Name. | Description. | Dosage. |
| Dicetel. | This medicine is used quite often for gallstone disease. It can be prescribed in preparation for surgery to remove gallstones, as well as in cases where cholelithiasis is accompanied by chronic cholecystitis. Dicetel is a medicine based on pinaveria bromide. The substance has myotropic and antispasmodic effects. The effect is based on a weak m-anticholinergic effect and selective blocking of calcium channels, which are located on the cells of the digestive tract and urinary tract. The drug eliminates spasms of the smooth muscle structure and improves blood flow to the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. | Take 150-200 mg per day, divide the dose into 2 doses. |
| Galidor. | Also a good antispasmodic medicine. Its active ingredient is bencyclane. Halidor has antispasmodic and vasodilating effects. Its main component blocks calcium channels, has an antiserotonin effect and creates a blockade of sympathetic ganglia. Bencyclane has an antispasmodic effect on the visceral muscles of the gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract. | Use 100-200 mg at a time, the maximum permissible daily dosage is 400 mg. |
| No-Shpa. | This drug is on the list of the most effective antispasmodics. No-Shpa is widely used as part of complex treatment of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. The active ingredient is drotaverine hydrochloride. The substance reduces the tone and motor activity of the smooth muscles of the internal organs, which helps relieve spasms and pain in the right hypochondrium. | You need to take 40 mg of No-Shpa at a time. The maximum permissible daily dose is 240 mg. |
| Baralgin M. | This drug is used very often for gallstone disease, as it is fast-acting, relatively inexpensive and well tolerated by patients. The active substance of Baralgin is metamizole sodium. The substance has analgesic, antipyretic and antispasmodic effects. The mechanism of action is largely similar to non-narcotic analgesics. | Single dose – 500 mg. Baralgin M solution is administered intramuscularly or intravenously, a single dose is 2-5 ml. The rate of intravenous administration is 1 ml per minute, heart rate and blood pressure levels are monitored. |
| Spasmalgon. | Widely used for diseases of the liver, hepatic ducts and gall bladder. It helps cope well with pain associated with pancreatitis and other gastrointestinal diseases. Spazmalgon contains 3 active components at once - metamizole sodium, pitofenone, fenpiverinium bromide. The drug has antispasmodic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic effects. The active components relax the smooth muscles of the gallbladder and its ducts. | Drink 1-2 tablets 2-3 times a day. When using Spazmalgon in ampoules, administer 5 ml at a time, the daily dosage is 10-15 ml. |
Antispasmodics are not recommended to be taken on an ongoing basis. The course of treatment should be 3-5 days. If there is a need to extend therapeutic measures, medical supervision is required. All of the above drugs are available without a prescription.
Principles of diet for joint illness
The combination of cholelithiasis and pancreatitis requires adherence to fairly strict nutritional principles:
- exclusion from the menu of foods containing high amounts of cholesterol,
- minimizing bile concentration,
- selection of products containing a fairly large amount of magnesium salts and unsaturated fatty acids in order to remove excess cholesterol,
- increasing the share of fresh vegetables in the menu,
- replacing all methods of heat treatment of food with one - steaming.
Meals should become fractional - food should be taken up to 6 times a day, but in small portions. Fluid intake should be increased to at least 2 liters per day.
What products should be included in the diet?
The recommended diet for a combination of cholelithiasis and pancreatitis should include foods containing plant fiber, vitamin complexes, and magnesium salts. In this case, the food must be pureed and the drink heated. This diet provides:
- stimulation of intestinal peristalsis,
- reduction of inflammatory phenomena,
- weakening of spasms.
The table below indicates which products and in what form are acceptable for people diagnosed with gallstone disease in combination with pancreatitis:
| Food group | Permitted varieties |
| Meat | Chicken, rabbit, lean beef, lean river fish. |
| Eggs | Protein omelet, whole, hard-boiled. |
| Fats | Vegetable, without exacerbation - butter. |
| Flour | Cookies based on rye bread. |
| Pasta, cereal | Buckwheat and oatmeal porridges, pasta, except durum varieties. |
| Soups | Vegetables. |
| Milk | Whole milk, low-fat cottage cheese, kefir. |
| Vegetables fruits | Any, except greens and sour varieties. |
Drinks include teas, compotes and juices. If you are overweight, the patient should greatly limit sweets, cereals, and baked goods.
Products prohibited for pathologies
With this combination of pathologies, the diet should not include the following food items:
- salo,
- coffee,
- greenery,
- pork,
- sausages,
- alcohol,
- margarines,
- smoked meats,
- offal,
- fat milk,
- sour varieties of berries,
- rich broths,
- fatty preserves,
- smoked cheeses,
- carbonated drinks,
- hard pasta varieties,
- baked goods, pies, varieties of white bread.
But food should also not contain seasonings such as pepper, vinegar and mustard. It is not recommended to eat immediately before going to bed, and the lunch meal should be leisurely.
Diarrhea medications
Diarrhea due to gallstone disease is commonplace, so antidiarrheal drugs are often included in complex therapy.
If diarrhea was caused by an intestinal infection, then antibiotics are used. Thus, patients are mainly prescribed Rifaximin, Intetrix, Zanotsin, Tsiprobay, Tarivid. Antibiotics for diarrhea are used short-term - usually the course lasts no more than 1-2 weeks.
If there are no intestinal infections, then diarrhea is treated with other drugs:
- Probiotics. Helps with cholelithiasis, intestinal dysbiosis, dyspepsia. The best probiotics are Lactobacterin, Bifidobacterin, Florin Forte, Bificol, Linex, Acipol, Atsilakt, Hilak Forte, Florok, Bak-Set. These drugs are available in the form of capsules, solutions and tablets for oral use. Probiotics are the safest medicines for diarrhea and can be taken even by children. By the way, drugs from this segment are recommended to be used in preparation for surgical interventions.
- Drugs that slow down intestinal motility - Loperamide, Imodium, Diara, Lopedium, Enterobene. Such medications slow down the passage of stool through the intestines. The tablets also increase the tone of the anal sphincter, slow down intestinal motility, and reduce the urge to defecate.
- Enterosorbents. They help eliminate diarrhea due to gallstone disease and speed up the process of removing toxins from the intestines. Enterosorbents can be taken even over long courses and in cases where cholelithiasis is accompanied by intoxication. The best enterosorbents are Smecta, Enterosgel, Polysorb, Activated Carbon, Sorbex, Carbactin.
- Plant-based antidiarrheal medications. The best help is: Bird cherry fruits, Blueberry fruits, Burnet rhizomes.
Enzymes
With cholelithiasis, the pancreas is often affected.
Cholelithiasis is accompanied by chronic pancreatitis, that is, an inflammatory process in the pancreas. In case of exacerbation of the disease, hospitalization is indicated. If pancreatitis occurs without exacerbation, then it is treated conservatively. For cholelithiasis and inflammation of the pancreas, enzyme agents are used. They contain enzymes from the pancreas of pigs or cattle.
Enzymes have a positive effect on digestion, reduce the severity of pain, help get rid of spasms, and promote the absorption of vitamins and minerals in the intestines.
Enzyme preparations are available in the form of capsules and tablets for oral use. The basis of these drugs are digestive enzymes, namely amylase, lipase and protease.
The best products in this segment:
- Pancreatin. The cheapest drug of domestic origin. The medicine is good, but it contains a fairly low concentration of enzymes. As a rule, Pancreatin is used to prevent inflammatory processes in the pancreas, as well as in the presence of dyspeptic disorders against the background of cholelithiasis.
- Mezim.
- Creon.
- Panzim Forte.
- Hermital.
- Mezim Forte.
- Panzinorm Forte.
Enzymes for gallstone disease should be taken after meals. The course of treatment lasts from 2 weeks to 3 months, depending on the presence of concomitant complications from the pancreas.
How to treat cholecystitis and pancreatitis
Acute or chronic pancreatitis and cholecystitis are treated comprehensively. Therapy includes a diet plan, medication, and physical therapy.
Therapeutic diet
Diet is the first and main therapeutic measure.
To cure cholecystitis and pancreatitis during an exacerbation, you need to follow 3 principles: cold, hunger and rest.
If in the acute course of the disease hunger, cold, and rest are prescribed, then in chronic pancreatitis it is recommended to eat properly:
- Eat small portions up to 7 times a day. Food should be warm.
- Avoid fatty foods, fried foods, smoked foods, hot spices, alcohol, chocolate, and soda.
- Steam dietary meat and chop before use.
- Include low-fat fermented milk products, vegetable stews, cereal soups and porridges in the menu.
- After eating, you should move for half an hour to increase the flow of bile and improve the digestion of food.
Dietary nutrition helps reduce the load on the gallbladder and pancreas, get rid of pain and heaviness in the abdomen.
Drug treatment
List of drugs to treat cholecystitis and pancreatic insufficiency:
- Kontrikal, Antagozan - inhibitors of pancreatic enzymes. Drugs are prescribed in acute cases of the disease to suppress the secretory function of the gland.
- Methyluracil, Pentoxyl are anabolic agents indicated for improving metabolic processes in the body.
- Omeprazole, Cimetidine - to reduce gastric secretory function.
- Festal, Pancreatin are enzyme preparations necessary for the breakdown of food mass in the intestines into nutrients.
- Bactrim, Biseptol - these antibiotics for cholecystitis and pancreatitis are indicated to be taken to eliminate inflammation, especially if it was caused by an infection.
- Holosas, Cholenzym are choleretic agents that improve the outflow of bile from the bladder and its ducts.
- No-shpa, Papaverine, Motilium - relieve muscle spasms, relieve pain.
Folk remedies
Herbs for pancreatitis and cholecystitis improve the functions of the digestive system. Healing infusions for the treatment of gallstones and pancreas most often include chamomile, plantain, wormwood, immortelle, marigold, yarrow and other medicinal plants.
Effective folk remedies for pancreatitis and cholecystitis:
- Mix 1 tbsp. l. wormwood, immortelle flowers, yarrow and fennel seeds. Brew one tablespoon of raw material with 500 ml of boiling water, let it brew for 8 hours. Strain. Take 1 tbsp. l. during the day. The need and duration of treatment for an inflamed bladder must be agreed with a herbalist.
- Mix in equal parts crushed burdock and elecampane roots, marigolds, wormwood, St. John's wort, chamomile, string, sage and horsetail. Pour a large spoonful of the mixture into a thermos and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. After 2 hours, strain. Drink the medicine for pancreatic insufficiency daily, 100 ml 30 minutes before meals.
Additional Methods
It is impossible to completely cure chronic pancreatitis. Ultrasound heating of the abdomen helps to enhance the effect of drug treatment and accelerate the onset of remission. For inflammation of the gall bladder, electrophoresis is also prescribed (an easily digestible form of the drug penetrates the skin under the influence of direct current) to the liver area. This enhances the production of liver secretions and improves blood supply to the organ. About 10 sessions are required.
To facilitate the functioning of the digestive system, patients are prescribed to drink medicinal mineral waters of Borjomi, Essentuki, and sea water baths saturated with carbon dioxide. After the inflammation has been relieved, mud therapy and medicinal applications are prescribed for the area where the liver and pancreas are located.
When is surgery necessary?
Surgery on the gallbladder is prescribed if there are large calcifications in it that cannot be broken down by medications. Large stones can completely block the lumen of the excretory duct, which will lead to liver and pancreas diseases. In such cases, emergency surgery to remove the stones is required.
You cannot do without the help of a surgeon if pancreatitis is complicated by a purulent-necrotic process. In this case, the affected part of the gland is removed and drainage tubes are placed.
Choleretic agents
In order to normalize the functionality of the gallbladder, medications with a choleretic effect are used.
They should be taken in long courses - from 1 to 3 months. Please note that products in this segment cannot be used if there is a blockage of the bile ducts. When choosing a specific drug, the physician takes into account the pathogenesis of cholelithiasis and the presence of associated complications, including cirrhosis, fatty hepatosis, bile duct dyskinesia, cholangitis, etc.
The list of the best medications with a choleretic effect includes:
- Lidan Paishi. Chinese homeopathic remedy, has many positive reviews. The composition includes the following plants and naturopathic components: Banks's rose, wormwood, desmodium, skullcap Baikal, root tubers of curcuma longa, rhubarb, betel nut, magnolia, Glauber's salt.
- Lecithin. Contains 1200 mg soy lecithin. Indications for use are cholelithiasis, fatty liver, gestosis, atherosclerosis, acute hepatitis, toxic liver damage. Lecithin for gallstone disease should be taken for at least 1-2 months.
- Karsil. The active component is milk thistle extract. The drug has hepatoprotective, choleretic, immunomodulatory effects. Karsil perfectly helps to dissolve small cholesterol stones and maintain normal liver function.
- Choleretic collection No. 2. The composition includes sandy immortelle flowers, peppermint leaves, and yarrow herb. It is recommended to drink the medicinal mixture after meals. Indications for its use are the initial stage of cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, varicose veins, hepatitis.
Please note that it is strictly forbidden to take any choleretic drugs if the diameter of the stone in the gall bladder is more than 1 centimeter.
Formation of stones
As a result of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, disorders of hormonal or metabolic processes, as well as cholelithiasis (GSD), diffuse changes in the pancreas appear. This leads to inflammation and, in some cases, the formation of stones. They contain insoluble calcium compounds with metal salts or organic components.
Most often, the stones are located in pairs or large clusters. Their sizes range from 0.5 mm to 5 cm, and their shape can be round, oval or irregular.
Formation of stones in the pancreatic ducts
Stages of formation
Clinicians distinguish three stages of development of stones in the pancreas:
- The first phase is characterized by an increase in the concentration and viscosity of pancreatic juice, leading to the appearance of insoluble conglomerates of a protein nature.
- During the second phase, thickening of pancreatic juice continues, and calcium salts are adsorbed on the formed protein structures. Similar processes occur in the parenchyma of the organ; foci of necrosis appear, affecting the islets of Langerhans. This leads to a decrease in the pancreas' production of hormones and enzymes involved in the breakdown of food. Of particular danger is the inhibition of insulin synthesis, leading to the manifestation of secondary diabetes mellitus.
- At the third stage, an inflammatory factor joins the process of calcification formation. The outflow of gland secretions is disrupted, and clinical signs of pancreolithiasis appear. Often during this period, infection of the organ occurs, aggravating the course of the disease.
The greatest danger is posed by stones stuck in the pancreatic duct and impeding the free passage of secretions, which begin to digest the tissues of the organ itself.
Reasons for appearance
Diffuse changes in the pancreas are provoked by: cholelithiasis, hepatitis, mumps, ulcerative colitis, gastritis and other diseases of various natures.
Also, the causative factors causing stagnation of pancreatic juice and the formation of stones include:
- benign and malignant tumors;
- inflammation of the duodenum;
- pancreatic cysts;
- disturbance of calcium-phosphorus metabolism;
- infectious diseases;
- dysfunction of the parathyroid gland.
Scientists have conducted research into how gallstones affect the pancreas. It has been found that cholelithiasis is a common cause of pancreatitis, which contributes to the thickening of secretions and the formation of calcifications.
A significant role in the appearance of stones in the pancreas is played by poor diet and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
A lot of fatty, fried, spicy and sweet foods create an increased load on the organ, disrupting its normal functioning, and creating favorable conditions for the progression of inflammatory processes and the formation of insoluble compounds.
Ursodeoxycholic acid
To maintain normal liver function and dissolve small cholesterol stones, it is customary to use products based on a compound called ursodeoxycholic acid.
UDCA is an active component of such drugs as Grinterol, Ursofalk, Urkliv, Ursodex, Ursolak, Choludexan, Ursosan, Ecurohol, Livodex. Medicines are produced in the form of tablets, capsules and suspensions. By the way, suspensions are mainly used in the treatment of hepatobiliary disorders in children.
- Reduces the saturation of bile with cholesterol and the production of cholesterol in the liver.
- Dissolves cholesterol stones.
- Has a membrane-stabilizing effect.
- Increases immunity.
- Reduces the lithogenicity of bile, normalizes its physicochemical parameters.
When using products based on ursodeoxycholic acid, it is customary to regularly undergo ultrasound and monitor the activity of liver enzymes. You also need to take into account the fact that UDCA can cause decompensation of biliary cirrhosis.
source