What is gallbladder inflammation
This inflammation is infectious and inflammatory in nature; the causes of its formation are often hidden in the opportunistic flora that ends up in the gallbladder. In women over forty, gallbladder inflammation occurs twice as often as in men.
Inflammation of this organ is usually accompanied by a characteristic symptom - pain in the area of the right hypochondrium. The pain may radiate to the collarbone and right arm.
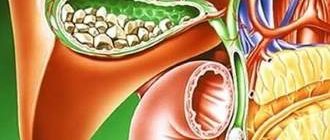
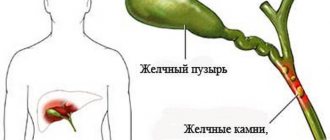
The inflammatory process (cholecystitis) has two types of course - acute and chronic, but the chronic course of the disease is diagnosed more often. Among inflammations, the calculous type is more common. This type is associated with the appearance of stones in the bladder and bile ducts. There is also an uncomplicated form of the anomaly - acalculous cholecystitis.
Etiology
There are several reasons for the formation of such a disease. Often this form of the inflammatory process develops against the background of calculous cholecystitis and subsequent phlegmonous. Thus, all three forms seem to flow into one another. It follows that such a disorder is secondary and quite rarely acts as an independent pathology. The primary form develops against the background of impaired blood flow in the cystic artery.
Very often, acute gangrenous cholecystitis is formed due to the influence of certain pathological microorganisms, which include:
- streptococcus;
- typhoid or E. coli;
- gas-forming microflora;
- other anaerobic microflora.
Pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate the walls of the gallbladder in several ways:
- with blood flow;
- with lymph;
- through the intestines.
In addition, a high probability of the occurrence of such a disease is observed in individuals with pronounced atherosclerosis of the blood vessels of the circulatory system.
Causes
Typically, inflammation of the gallbladder occurs due to infection of the organ by pathogenic microorganisms. All this occurs against the background of weakened immunity and the presence of underlying diseases. The hereditary factor plays a significant role in this.
The causes of inflammation are:
- infection by parasites, helminthic infestations – opisthorchiasis, giardiasis;
- hepatitis virus infection;
- entry into the gallbladder of staphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria;
- fungal infection;
- intoxication;
- prolonged exposure to allergens.
The onset of an active inflammatory process is influenced by the following factors:
- stagnation of bile due to dyskinesia or blockage of the biliary tract;
- endocrine disorders;
- acute infectious processes;
- physical inactivity, obesity;
- prolapse of the digestive tract;
- pregnancy;
- poor nutrition;
- constant consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking;
- regular exposure to traumatic situations.
If we talk about the development of cholecystitis in children, the factors that provoke this condition may be:
- obesity due to a sedentary lifestyle;
- hereditary predisposition;
- poor immunity;
- injuries;
- developmental anomalies.
Influencing factors that provoke complications
To make it possible to prevent all of the above consequences of cholecystitis, experts identify a number of factors that are the causes of complications. The following reasons may be prerequisites for complications of acute cholecystitis:
- secondary gallbladder infection;
- blood infection due to purulent processes;
- inflammatory process of the pancreas;
- thickening of bile consistency;
- negligent attitude towards severe symptoms of cholecystitis;
- perforation of the wall of the gallbladder and ducts;
- late diagnosis of the disease;
- untimely treatment.
The prerequisites for the consequences of chronic cholecystitis can be many factors that relate to the acute form of the disease, as well as the following factors:
- refusal of therapeutic nutrition or non-compliance with some of its points (dietary table No. 5);
- unhealthy lifestyle and excessive alcohol consumption;
- inflammatory processes and infections without timely therapy.
Almost all existing complications of cholecystitis threaten the patient’s life, and therefore require radical methods of treatment. It would be more advisable to begin treatment for cholecystitis at the first manifestations of its signs, rather than to go under the surgeon’s knife if there are serious consequences. Surgical treatment - cholecystectomy is also a risky procedure that has its own risks of complications.
Symptoms of gallbladder inflammation
Inflammation in the gallbladder occurs progressively, gradually, and often develops into a chronic, recurrent form. Symptoms of cholecystitis vary depending on the type of anomaly.
Acute cholecystitis is expressed by the following symptoms:
- the pain is acute, nagging in nature, sometimes bursting, localized in the hypochondrium on the right side. The pain can radiate to the collarbone, right forearm, and shoulder blade. Painful sensations in the form of attacks are typical for gallstone cholecystitis, as this is caused by blockage of the bile duct with a stone or a clot of bile secretion;
- loss or deterioration of appetite and weight loss;
- obstructive jaundice, which changes the color of the eye sclera and skin;
- heat;
- nausea and sometimes vomiting with bile in the vomit;
- bloating and problems with bowel movements (constipation).
The patient's condition may improve after a few days if there are no concomitant diseases.
The catarrhal form of pathology is one of the acute forms of cholecystitis. Its appearance is due to the presence of stones in the cavity of the gallbladder.
Symptoms for this type of pathology are:
- continuous intense pain in the area of the right hypochondrium and epigastrium, pain can spread to the shoulder girdle, lower back, neck, scapula;
- vomiting, which does not bring a feeling of relief; it may contain duodenal contents (particles of undigested food, bile, mucus);
- high blood pressure and tachycardia;
- low temperature.
Also, the development of the catarrhal form of the disease may be indicated by Ortner's symptom - a sensation of pain during tapping of the right costal arch, increased pain when palpating the gallbladder while inhaling.
Phlegmonous cholecystitis has a severe course. Its signs are:
- severe pain that increases with changes in body position or deep breathing, as a rule, pain is felt in the right hypochondrium;
- general weakness, chills;
- high temperature (up to 39);
- loss of appetite;
- nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief, repeated;
- Ortner's symptom (as with the catarrhal form of the disease).
Gangrenous cholecystitis refers to complications of the phlegmonous type of inflammation.
Symptoms of this complication will be as follows:
- intestinal paresis;
- rapid breathing of a superficial nature;
- bloating;
- tachycardia;
- dry mouth;
- general symptoms of body intoxication are fever, weakness, sweating.
Palpation determines the muscle tension of the anterior abdominal wall.
Signs of chronic inflammation are less pronounced and may appear and disappear.
With chronic inflammation, the following symptoms occur:
- mild pain in the right side, pain may intensify after consuming fatty foods or excessive physical activity. The pain can range from stabbing to squeezing and can radiate to the solar plexus and sacrum;
- nausea on an “empty” stomach;
- belching of air or food;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- salt syndrome;
- jaundice, the cause of which is a short-term increase in bilirubin;
- skin itching;
- chills, fever;
- heaviness and discomfort in the epigastric area;
- attacks of tachycardia, sleep disturbance, migraine, increased heart rate (symptoms of VSD).
Symptoms of gallbladder inflammation in women and children
The presence of inflammation in a child may be indicated by:
- belching rotten;
- bad breath;
- indigestion (alternating constipation and diarrhea);
- loss of appetite;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- low temperature that can last a long time.
Inflammation in women often occurs during pregnancy or menopause.
In addition to the main symptoms, specific ones may also occur:
- frequently changing mood;
- paleness of the skin of the legs and swelling;
- attacks of headache, which intensifies before the onset of menstruation;
- premenstrual syndrome.
Symptoms of the disease
Unlike other forms of the disease, acute gangrenous cholecystitis has pronounced symptoms.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease are:
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- severe tachycardia;
- vomit;
- muscle weakness;
- headache;
- increase in abdominal size;
- bowel dysfunction (constipation or diarrhea);
- prolonged and severe abdominal pain;
- dry mucous membranes and white coating on the tongue;
- pale skin;
- unusual sleepiness.
A rare but possible symptom of the disease can be the so-called toxic scissors, in which, against the background of extremely severe intoxication of the body and a clear inflammatory process, there is a lack of elevated temperature.
Due to the fact that during the development of gallbladder gangrene, the nerve endings of the diseased organ die, sometimes the clinical picture of the disease is characterized by a predominance of symptoms of the inflammatory process against the background of a decrease or absence of pain.
Diagnostics
After a personal examination, palpation and history taking, the doctor prescribes the following types of examination to accurately diagnose gallbladder inflammation:
- a general and extended blood test (an acceleration of ESR, a high level of neutrophils and white blood cells, an increase in C-reactive protein, bilirubin are detected);
- general urine test (it shows the presence of bile acids);
- bile analysis;
- detection of giardiasis;
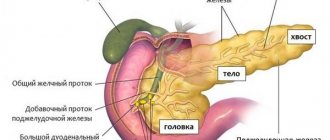
- echography of the organs of the biliary system (visible hypertrophied, compacted, layered walls of the organ, irregular shape of the organ or its compression);
- CT, MRI;
- duodenal sounding. This type of examination makes it possible to identify failures in the process of accumulation and excretion of bile.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis begins with examining the patient's medical history. Phlegmonous cholecystitis always develops from the catarrhal form of the pathology. Moreover, cholecystitis itself in 95% of cases is a complication of the presence of stones in the ducts of the bladder.
Then a physical examination is carried out and the patient’s complaints are studied. The doctor may feel bloating on palpation. When pressing on the area of the right hypochondrium, the patient experiences severe pain discomfort. The doctor can also feel the inflamed gallbladder.
Blood and urine tests are a mandatory stage of diagnosis. In the case of an inflammatory process, an acceleration of ESR and an increase in the number of leukocytes are observed. To visually assess the affected organ, ultrasound, radiographic examination, CT and MRI are performed. In particularly serious cases, a biopsy may be required.
How to treat gallbladder inflammation
Treatment for an inflamed gallbladder is usually complex.
The following medications are used to treat inflammation:
- antibiotics: Azithromycin, Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline, Erythromycin, Ampiox;
- combined antimicrobial agents (when pathogenic strains are not sensitive to antibiotics): sulfonamides (Biseptol, Bactrim), nitrofurans (Furadonin, Furazolidone);
- antispasmodics - "Drotaverine", "Duspatalin", "Papaverine", "No-shpa", M-anticholinergics - "Metacin", analgesics - "Baralgin", which relieve pain and spasms;
- prokinetics – “Motilak”, “Domperidone”. They are needed for reduced contractility of the gallbladder and its ducts;
- products with a litholytic effect - "Ursosan". Prescribed in the presence of stones, to improve liver function, strengthen the immune system, for better outflow of bile;
- drugs to stimulate bile secretion - tablets "Allohol", "Odeston", "Holagol", "Xylitol". They are not used during the acute period; they can only be used for acalculous cholecystitis;
- hepatoprotectors – “Hofitol”, “Gepabene”, “Karsil”, “Essentiale”. They are used to normalize the outflow of bile and restore liver function;
- means for normalizing the activity of the pancreas - “Creon”, “Pangrol”, “Mezim”;
- calcium antagonists – “Dicetel”, this drug serves to relax the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract;
- antiparasitic drugs - “Dekaris”, “Vormil”, when inflammation develops against the background of Giardia infection;
- medications with a sedative effect - “Novopassit”, motherwort extract. They are usually prescribed to women before the onset of menstruation.
After a period of exacerbation, physiotherapy is prescribed. Their benefit is to normalize the activity of the gallbladder and increase the tone of the bile ducts. In case of cholecystitis during remission, mud or paraffin applications to the bile duct area are also useful; ultrasound and UHF are well received by the body. Hydrogen sulfide and radon baths have an effect in relieving inflammation; they are taken in courses.
If stones are found in the gallbladder during ultrasound, cholagogues should not be taken!
Surgical intervention
Sometimes the development of the disease forces removal of the gallbladder. After organ resection, the patient may develop postcholecystectomy syndrome. You may experience soft stools for several months after surgery. Later the condition returns to normal, but in 1% of patients this anomaly can persist throughout life. To prevent the development of diarrhea, it is necessary to review the diet and completely exclude dairy products from it and increase the amount of foods containing fiber.
Diet
It is impossible to get rid of cholecystitis without diet. The diet is selected individually, taking into account the form of inflammation. In all cases, dishes with an irritating effect on the gastrointestinal tract are removed from the diet, these are:
- spicy, sour dishes;
- too hot or cold;
- fried, fatty, smoked foods;
- coffee, hot chocolate.
The diet should include foods prepared in gentle ways: stewed, boiled, steamed, baked. You can eat vegetables without coarse fiber, cereals, steamed omelets, lean meat, puddings, fermented milk products, but not fatty, cereal bread, white bread croutons. It is recommended to exclude fresh baked goods from your diet.
It is good to drink a lot of liquid, it is better if it is: still mineral water, rosehip decoction, sweet juices diluted with water.
If the gallbladder is inflamed, you need to eat small meals at least 5-6 times a day. Overeating or irregular eating provokes the appearance of dyspeptic disorders and pain.
Treatment with folk remedies
Inflammation of the gallbladder can also be treated using traditional methods. Herbal medicine can speed up organ recovery and relieve pain and discomfort in the problem area. For the best effect, treatment with traditional methods is best combined with drug treatment.
You can relieve painful spasms and improve bile secretion with an infusion of corn silk. Take 10 g of stigmas (dry), brew with boiling water (250 ml) and leave for an hour. Drink 50 ml before meals.
For women suffering from inflammation of the gallbladder, peppermint infusion is useful due to its anti-inflammatory and soothing effects. To do this, take 20 g of leaves, pour boiling water (1 glass) and leave in a water bath for 25 minutes. This infusion is drunk three times a day before meals.
Parsley infusion helps improve digestion and has a slight choleretic effect. Parsley (finely chopped) - 10 g, pour boiling water (1 glass), leave and drink 50 ml before meals.
In acute cholecystitis, elecampane helps. To do this, pour its crushed roots (10 g) into 220 ml of cold water and leave for 8–10 hours. Add 50 ml of honey to the infusion, or propolis. This mixture is divided into 4 servings, which are drunk during the day three quarters of an hour before meals. Course duration is a week.
At home, pears are considered an affordable method of treating gallbladder inflammation. Unsweetened compote is made from them and drunk daily.
Ordinary foods, for example, beets, also help in therapy against inflammation of the gallbladder. It is grated on a fine grater, poured with water 3-4 cm above the vegetable, cooked over low heat until smooth and pureed, and used before meals, 50 g.
You can prepare a mixture of juices of carrots, black radish, beets, horseradish, lemon (200 ml each), add 125 ml of alcohol. Place the mixture in a dark place for 10 days, drink 15 ml 3 times a day before meals.
Grind 30 dried laurel leaves, pour in 200 ml of sunflower oil, leave for a week, filter. Add 15 drops to milk, kefir, tea 3 times a day.
If the disease worsens, you can prepare a mixture of olive oil (150 ml), cognac (100 ml) and menthol (50 ml). Drink 15 ml per day, after applying a warm compress to the area of the right hypochondrium.
Cabbage juice helps well with this disease - you need to drink 100 ml warm before meals every day.
What is gangrenous cholecystitis
In essence, this is a pathological process with the formation of a focus of inflammation and death of gallbladder tissue, as well as destructive changes in the bile ducts. As the disease progresses, it provokes severe intoxication of the body, promotes the development of infection and inflammation in the abdominal cavity. The anomaly develops against the background of deterioration of microcirculation of lymph and blood to the localization of the organ.
About 90% of patients are susceptible to one of its most dangerous consequences - as the disease progresses, it provokes gangrene. As a result, necrosis of local foci develops, with damage to the entire wall of the gallbladder, necrosis of tissues and cells of the organ.
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish several categories of this pathology, which differ in the following characteristics:
- Etiological factors. The disease comes in primary and secondary forms. In the first case, it occurs rarely and is usually a consequence of impaired blood flow in the vesicular artery.
- Course of the disease. There is a sharp and erased form. With the first, the intensity of progression and spread of pathological processes throughout the tissues of the organ is higher. The erased form is characterized by more pronounced symptoms, not severe pain.
Forecast
The prognosis is generally favorable, but strict adherence to the doctor's instructions is required. If inflammation is not relieved with medications in time, pancreatitis, cholangitis, and hepatitis may develop. The formation of stones in the cavity of the gallbladder is also likely.
An unfavorable outcome can be observed in severe purulent forms of cholecystitis and multiple stones. In this case, the solution is complete resection of the gallbladder.
Video on the topic:
Treatment
After confirmation of the diagnosis, emergency hospitalization of the patient and immediate operation are necessary. Any delay can cause a complication such as rupture of the gallbladder, which entails the development of peritonitis, which, in turn, can cause the death of the patient.
The basis of surgical treatment is removal of the gallbladder - cholecystectomy. This operation is performed using several methods:
- laparoscopically – excision of the affected organ is performed using special instruments through several small incisions on the abdomen;
- laparotomy - removal of the gallbladder occurs through a large incision in the anterior abdominal wall.
In addition to surgery, patients are advised to take medications to relieve symptoms, as well as follow the rules of dietary table No. 5.
There is no specific prevention of the disease - it is only necessary to promptly eliminate conditions that can lead to gangrenous cholecystitis. With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable; with the development of peritonitis, there is a high risk of death.
Prevention
To prevent the development of inflammation, negative causes that can lead to damage to the gallbladder should be eliminated:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- try to reduce excess weight;
- normalize your diet;
- treat viral and bacterial diseases in a timely manner;
- If there is a hereditary history of the disease, it is important to systematically carry out ultrasound diagnostics for timely detection of the disease.
List of references: https://www.msdmanuals.com/ru/professional/liver-and-bile-duct diseases/gallbladder-and-bile-duct diseases/acute-cholecystitis https://www.smclinic. ru/diseases/kh/kholetsistit/ https://www.gmsclinic.ru/gms/press/articles/art-gallbladder https://www.nrmed.ru/rus/dlya-vzroslykh/urologiya/lechenie-holecistita/ https ://www.nrmed.ru/rus/dlya-vzroslykh/urologiya/hronicheskiy-holecistit/ https://unionclinic.ru/gastro/holecistit https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecystitis https://rg .ru/2012/07/05/zhelch.html https://www.kp.ru/putevoditel/zdorove/khronicheskij-kholetsistit/ https://medsi.ru/articles/kholetsistit-chto-eto-takoe-prichiny- priznaki-simptomy-lechenie-u-vzroslykh-dieta-i-profilaktika/ odrex.ua/treatment/kholecistit/ https://fnkc-fmba.ru/zabolevaniya/kholetsistit/ https://yandex.ru/health/turbo/ articles?id=4372 https://aif.ru/health/life/holecistit_kak_poymat_i_lechit_vospalenie_zhelchnogo_puzyrya https://astery-med.ru/whatailsyou/pishevarenie/zab_jelch_puzyrya.php https://www.emcmos.ru/articles/ostryy-i -hronicheskiy-holecistit https://minzdravao.ru/site-page/holecistit Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/18/2020
Possible complications and treatment methods
Acute gangrenous cholecystitis is an extremely dangerous disease that, if not treated promptly, ends in rupture of the gallbladder wall. This situation can be dangerous for the patient, since the pus that comes out of the gallbladder spreads throughout the abdominal cavity. In this way, infection occurs, resulting in complications such as peritonitis or an abscess.
The main treatment for gangrenous cholecystitis is surgery to remove the gallbladder. In modern medicine, there are two methods of performing it - laparotomy and laparoscopy. Laparotomy is a conventional abdominal operation, while laparoscopy is considered a more gentle method of removing the gallbladder, which does not involve large incisions with a scalpel, and the diseased organ is removed through small holes.
Additionally, patients diagnosed with gallbladder gangrene are prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics with a low hepatotoxic effect. For example, Erythromycin, Oxacillin, Ampicillin or Lincomycin.
Detoxification therapy is also carried out, aimed at removing toxic elements from the body. For this purpose, it is advisable to use rosehip decoctions, alkaline mineral water, prenatally administer an isotonic sodium chloride solution and a 5% glucose solution.
In case of severe vomiting and the development of concomitant pancreatitis, aspiration drainage of the stomach and treatment with Trasylol or Contrical are performed. To eliminate pain, painkillers are used (No-shpa, Spazmalgon, Ketanov and others).