Coughing with different types of inflammation
Gastritis is a common disease that is accompanied by a pathological process in the digestive organ. It occurs against the background of regular consumption of low-quality products, lack of diet, poor lifestyle, taking certain medications and Helicobacter pylori infection.
Cough with gastritis occurs often. There are several forms of pathology that provoke the appearance of the symptom. These include:
- chronic inflammation;
- reflux gastritis;
- ulcerative process;
- atrophic changes.
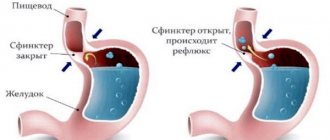
Reflux gastritis is a pathology characterized by weakening of a certain sphincter. The contents of the intestine enter the digestive organ and injure its walls. Pathology is usually accompanied by increased acidity. When sick, the cough is usually dry. There is discomfort in the larynx.
Patients often mistake the symptoms of reflux gastritis for a sore throat. The disease is characterized by sour belching. In the acute form of the pathology, coughing is paroxysmal. Appears after eating food. It doesn't take long. In the chronic type, cough is observed constantly. It disappears quickly, but intensifies after eating spicy food.
With prolonged gastritis, the inflammatory process in the stomach irritates certain receptors that are responsible for coughing. The symptom appears approximately half an hour after eating. Accompanied by severe heartburn.
Ulcerative gastritis is characterized by the appearance of defects in the mucous membrane of the affected organ. The pathology provokes the appearance of heartburn, chest pain, cough and difficulty breathing. Needs immediate treatment.
The reflex may also be present when:
- infectious diseases that affect the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysbacteriosis;
- presence of foreign bodies.
The patient needs a comprehensive diagnosis, the list of which is determined by the doctor.
Diagnostics
Cough caused by stomach pathologies is diagnosed by a gastroenterologist. To identify the causes of its occurrence and disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, the following types of examination are used:
- endoscopy of the esophagus - reveals erosions, ulcers, hernias and narrowings in the digestive canal;
- manometric study - determines changes in the tone of the lower gastric sphincter;
- impedansometry – reveals refluxes of various natures, disturbances in esophageal peristalsis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity - determines structural changes in the gastrointestinal tract.
To detect cough due to gastritis of the stomach, gastrointestinal tract and parasitic diseases, a detailed blood test is performed. The Bernstein test and coprogram (stool analysis) make it possible to distinguish reflux disease from chronic gastritis and ulcerative lesions.
If you have a sore throat or pharynx, you should consult an ENT doctor. Burns of the mucous membranes caused by gastric juice are often complicated by laryngitis or pharyngitis. When diseases are detected, patients are prescribed antacids - drugs that eliminate excess stomach acid.
Diseases-root causes
The list of reasons that provoke stomach cough is quite wide: infection, parasites, dysbacteriosis, gastroesophageal reflux and others. Chronic diseases include gastritis, gastric ulcers, problems with the liver and rectum. A common cause is gastroesophageal reflux. This disease is associated with improper functioning of the muscle responsible for pushing food from the esophagus into the stomach. Because of this, acid from the stomach enters the esophagus. This environment contributes to damage to the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract.
Regarding infection with worms and dysbacteriosis, they weaken the human immune system, thereby provoking the appearance of respiratory disorders, including cough.
At-risk groups
If we talk about the age at which this problem occurs, then it is detected more often in people after 30 years of age. Children rarely experience this because the young body copes with diseases more effectively. People who have problems with the digestive tract in general and the stomach in particular are susceptible to stomach cough. Thus, those at risk are those who have high stomach acidity (the main cause of reflux).
If a person does not adhere to a healthy lifestyle, he also runs the risk of developing gastrointestinal problems, and as a result, stomach cough. Smoking, alcohol abuse, and excess weight problems are factors in the development of the disease.
Cough with different forms of gastritis
A common cause of stomach cough is chronic gastritis. This is a disease in which inflammatory processes occur in the gastric mucosa and epithelial cells atrophy.
Depending on the causes of occurrence, gastritis is of three types:
- Autoimmune. It occurs as a result of disturbances in the body's immune response.
- Bacterial. Most often, inflammation in this type is caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. The microbe is able to survive in the hydrochloric acid of gastric juice.
- Chemical. It develops mainly when the contents of the duodenum enter the stomach, with prolonged use of selected medications or toxins.
The probable cause of gastritis is infection with Helicobacter. In a healthy state of the body, the immune system suppresses the development of pathogenic microflora in the gastrointestinal tract. But when exposed to unfavorable factors - alcohol, smoking, abuse of unhealthy foods and drinks, overeating, lack of fiber and beneficial microelements - a bacterial imbalance is provoked. As a result, Helicobacter actively develops and destroys the protective mucus. Epithelial cells become defenseless to the effects of hydrochloric acid, become inflamed and die.
Stress and hereditary factors also lead to chronic disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract.
Gastritis is an acid-dependent disease; depending on the secretion of the stomach, types develop, which are characterized by their own symptoms.
Cough with atrophic gastritis
Chronic inflammation, called atrophic gastritis, contributes to the death of cells and glands of the stomach. It is observed more often with low acidity.
The cough with atrophic gastritis is dry and prolonged. Accompanied by:
- Belching, rotten odor and bitterness in the mouth.
- Heaviness after eating, bloating and flatulence. If there is insufficient acidity in the stomach, food is not digested, but rots and becomes rotten.
- Frequent constipation and disorders accompany dysbiosis that occurs against the background of pathology.
- Weakness, dizziness and sweating after eating.
- Lack of appetite.
If food is not digested sufficiently, the body does not receive vitamins and beneficial elements. The absorption of vitamin B12 and iron is impaired, leading to anemia and the appearance of symptoms - dizziness, lethargy and fatigue, shortness of breath, pale skin, rapid weight loss.
Cough with gastritis with increased secretion
With such secretion of the stomach, erosion and ulcers more often develop.
Symptoms accompanying inflammation:
- Sour heartburn, belching and cough. Occurs when gastric juice enters the esophagus.
- Pain in the upper abdomen. More often on an empty stomach, with long breaks between meals.
- If the cause of chronic inflammation is the constant reflux of bile acids, pancreatic enzymes and other contents of the duodenal region into the stomach, the pain is not clearly localized.
- Abnormal bowel movements, nausea, and sometimes vomiting.
- Respiratory syndrome occurs immediately after eating spicy or sour foods and is often accompanied by chest pain and heartburn.
Causes of cough during exacerbation of gastritis and beyond relapse
Stomach cough is a symptom that accompanies pathologies of the digestive system. In this case, the patient does not have discharge from the nasal cavity or redness in the throat, that is, the symptom is not associated with a cold. Stomach cough is accompanied by fatigue and malaise. Additional clinic depends on the underlying pathology.
It is possible to establish the root cause using diagnostics. Typically, stomach cough is debilitating and causes great discomfort. Needs adequate treatment. Delayed therapy can result in complications.
Main reasons and mechanism of development
When coughing shocks, portions of the acidic contents of the stomach are released, some microorganisms or substances that caused a pathological reaction come out from the digestive tract.
The main reasons for the triggering of the protective reflex are:
- gastritis, stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- reflux esophagitis;
- intestinal infections causing dysbacteriosis;
- long-term use of medications that disrupt the natural microflora of the gastrointestinal tract;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- helminthic infestations;
- use of spoiled products;
- cancerous tumors;
- regular drinking, smoking;
- structural anomalies of the digestive system.
When exposed to toxic substances, a cough appears immediately. It is accompanied by nausea and severe vomiting. Food that has passed its expiration date has an unpleasant odor that causes involuntary attacks of symptoms. If a person does eat a spoiled product, then after 5–10 minutes a rejection reaction begins. Vomiting continues even when the stomach is empty.
In case of alcohol poisoning, the severity of the cough reflex directly depends on the amount of alcohol entering the blood. With severe intoxication, reactions are “inhibited” and appear in full force when the moment of a hangover occurs.
Smoking causes the accumulation of tarry substances in the digestive tract, and coughing partially clears them from the body. In case of stomach diseases (reflux, ulcers, gastritis), attacks begin about an hour after eating - they are accompanied by painful cramps and heartburn, and worsen when lying on your back.
In all cases, a chain is triggered: irritation of receptors - signal transmission to the cerebral cortex - activation of the cough center.
Rapidly progressing stomach diseases can lead to serious complications and death if left untreated.
Gastritis with high acidity
With excessive consumption of meat, spicy and salty foods, alcohol, and smoking, the stomach glands produce large amounts of acid. Normally, it promotes complete breakdown and absorption of food. If there is a lot of it, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed and degenerative changes begin. When some of the acid backs up into the esophagus, it causes heartburn. In chronic disease, gastric epithelial cells die and are replaced by connective (fibrous) tissue.
A cough with gastritis usually follows belching and involuntary regurgitation. These signs are preceded by heaviness in the epigastric region, pressure and a feeling of fullness, burning, nausea, and pain. Vomiting often follows a cough. Over time, the stomach ceases to perform its functions normally, which can lead to serious digestive disorders.
GERD
Obesity, pregnancy, poor nutrition, and bad habits negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. With reflux esophagitis, the lower esophageal sphincter does not cope with its task and allows part of the stomach contents to pass into the upper parts of the digestive tract. This causes irritation of the mucous membrane - the patient experiences heartburn attacks after almost every meal.
In this case, coughing from the stomach is a protective mechanism that gets rid of some of the contents that irritate the wall through regurgitation. Reflux is not only accompanied by the reflux of acid into the esophagus, but air can be swallowed, which is then released after eating through belching.
Dysbacteriosis
Gastroenterological cough is a typical symptom of a violation of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. Normally, the digestive organs maintain an optimal balance of beneficial and harmful microbes. As a result of poor nutrition, a weakened immune system, and previous colds and infectious diseases, this ratio is disrupted in favor of harmful bacteria. They begin to actively multiply, suppressing beneficial microflora.
The pathology is accompanied by:
- bloating (flatulence);
- rash and skin discoloration;
- nausea, belching, vomiting;
- feeling of heaviness, pressure and rumbling in the stomach;
- temperature increase;
- diarrhea.
The patient has a poor appetite, but if he manages to eat a little food, this is followed by coughing and vomiting.
Peptic ulcer
With repeated exacerbations of gastritis and reflux, inflammation of the mucous membranes intensifies. In this case, a stomach cough is an attempt to get rid of the acid that “corrodes” the lining of the organ. With repeated exacerbations of the disease, lesions form.
If left untreated, they turn into true ulcers. A cough reflex is an inevitable consequence of this phenomenon, and blood may be present in the discharge. A dangerous condition is deep damage to the walls of the organ (perforation), ending in abdominal peritonitis and sepsis.
Worm infestations
Parasite eggs enter the intestines through the oral cavity. They pass through the gastrointestinal tract to the lower sections, where the larvae then develop. Some types of parasites begin to migrate throughout the organs. They make their way into the lung tissue, muscles, heart, stomach, liver, leaving bleeding ulcers at the points of attachment to the mucous membranes.
Penetrating into the trachea, the worms are again swallowed, enter the esophagus, reach the intestines and there transform into sexually mature individuals. When parasites are found in the lungs, tissue infiltration is formed, which is accompanied by a painful cough. The latter can also occur as allergic manifestations to the waste products of parasites.
Symptoms
The symptoms of stomach cough do not coincide with the manifestations that are characteristic of a respiratory viral disease. The person does not have a fever or runny nose; fluorography does not show any abnormalities in the bronchi. Signs that may alert you are the following:
- Heartburn.
- Nausea.
- Weakness.
The main symptoms can be identified depending on the causes:
- In the presence of viral infections in the digestive tract, pain appears and diarrhea occurs periodically.
- Gastroesophageal reflux provokes a sore throat and wheezing, and sometimes respiratory arrest may occur during sleep.
- With the development of dysbacteriosis and helminthic infestations, increased gas formation is observed, which leads to bloating. In addition, joint pain occurs and skin condition worsens.
- With atrophic gastritis, a dry, prolonged cough occurs, which is accompanied by belching with an unpleasant odor.
- With gastritis with high acidity, acute pain is observed in the upper abdomen.
- The appearance of a cough in a horizontal position also indicates gastritis or other pathologies of the digestive system. This is why attacks often occur at night and do not allow for proper rest. This leads to a general deterioration in well-being.
Prevention methods
If you follow some recommendations, you can reduce the risk of developing stomach cough. Preventive measures are based on the mechanism of the problem.
If you have reflux and hyperacid gastritis, you need to carefully adhere to your diet. If the acidity of gastric juice is low, you should establish a strict diet and exercise.
Diet
The purpose of dietary nutrition is to ensure the functioning of the stomach, normalize the acidity of digestive juice, and prevent reflux. In case of hyperacid gastritis, you will need to exclude from the diet:
- fatty foods;
- smoked meats;
- canned food;
- spices;
- carbonated drinks;
- mushrooms;
- alcohol.
Create a menu of dietary varieties of meat and fish, cereal dishes, pasta, and dairy products. Vegetables and fruits are only non-acidic varieties; it is best to eat them boiled or baked.
For hypoacid gastritis, remove from your diet foods that linger in the stomach for a long time and contribute to the development of flatulence:
- fresh bakery;
- legumes;
- millet, pearl barley;
- fat meat;
- pickled vegetables.
It is useful to eat dietary meat, day-old bread and crackers, fermented milk products, dishes made from buckwheat and rice. For drinks, it is better to drink herbal teas.
Cough is a common symptom of gastric pathologies. It has an indirect development mechanism, that is, it is not associated with inflammation of the bronchi or lungs, but appears reflexively. To get rid of it, act on the cause - inflammation of the stomach. For this purpose, medications and folk remedies are used in accordance with the type of disease.
Associated symptoms
Stomach cough does not constantly bother the patient. The symptom appears only when interacting with certain extraneous factors. The symptom is usually associated with food intake.
Stomach coughing occurs immediately after eating or after a short period. It intensifies when the patient takes a horizontal position and at night. The symptom cannot be eliminated using traditional cold medications. It is possible to suspect the presence of a specific pathology by paying attention to the clinical picture. A description of the violations is presented in the table.
Coughing is often caused by the presence of parasites in the body. With helminthiasis, the patient complains of a significant loss of strength, anemia and deterioration of the condition of the skin. Hair becomes brittle and dull. The nail plates are peeling. There is increased gas formation, insomnia occurs, the stomach is bloated, and there is a dry cough. The patient regularly experiences diarrhea.
All of these diseases have a similar clinical picture, so it is impossible to independently determine the root cause of stomach cough.
Symptoms and treatment of stomach cough
In situations where a debilitating cough appears in the absence of signs of colds, it is necessary to pay attention to such signs as heartburn and frequent belching.
With constant irritation of the mucous membranes of the esophagus due to the entry of stomach contents into it, a cough syndrome often occurs.
In such cases, after establishing an accurate diagnosis, you have to solve the problem of how to treat stomach cough in accordance with medical recommendations.
Etiology of the disease
The list of factors that provoke the appearance of stomach cough is quite extensive and includes the following diseases:
- adenoviral infection;
- gastritis;
- reproduction of enteroviruses in the gastrointestinal tract;
- parasitic infections;
- peptic ulcer;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- liver pathologies;
- increased acidity;
- diseases of the rectum.
Cough often occurs due to reflux. This disease is a consequence of dysfunction of the muscle designed to deliver food to the stomach. A secure blockage is released and stomach acid splashes into the esophagus. This causes damage to the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, leading to the appearance of a dry cough.
Among the factors causing GERD - gastroesophageal reflux disease, the following pathological conditions of the body are noted:
- increased intra-abdominal pressure that occurs with obesity, flatulence, ascites (accumulation of fluid inside the abdominal cavity);
- duodenal ulcer;
- hiatal hernia;
- excessive intragastric pressure, manifested as a result of the consumption of gas-forming types of food products.
Another reason for the development of stomach cough is the entry of a foreign body into the esophagus, and it is also provoked by food poisoning. People over 40 years of age are at risk.
The likelihood of stomach cough increases if you are overweight. The question of interest is whether a cough can be a consequence of bad habits.
Experts say that a common cause that provokes it is smoking, drinking alcohol, and using drugs.
Characteristic symptoms
The dominant symptom of stomach cough is the absence of sputum. It can be periodic, occurring, for example, after eating or during sleep.
Among the characteristic symptoms are heartburn, belching that appears after eating, and nausea. Due to bouts of debilitating dry cough, the patient feels tired and depressed.
Symptoms vary depending on the factors that caused the development of stomach cough.
- An indicator of viral infections is frequent vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
- Symptoms of reflux are characterized by wheezing and sore throat. Cough and heartburn, bloating appear, and short-term pauses in breathing may occur during sleep.
- Signs of dysbiosis are allergic reactions to various foods, nausea, and imbalance of the digestive system, expressed in constipation or diarrhea. There may be bad breath and bloating.
- If the cough is caused by infection of the intestinal tract with parasites, then symptoms such as increased gas formation, joint pain, insomnia, diarrhea or constipation appear.
- Anemia may develop. Skin problems appear and weight drops sharply.
- Infectious diseases of the stomach and intestinal tract manifest themselves as a long, painful dry cough.
- Enterovirus infection, along with a cough, causes abdominal cramps and general weakness.
- With a stomach ulcer or gastritis, the appearance of a cough is usually associated with food intake and is observed several hours after a meal.
If a person rolls over on his back during sleep, the cough intensifies, provoking a gag reflex. Only a specialist can determine the causes of stomach cough and prescribe treatment, so if you experience characteristic symptoms, you must consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
Without identifying the relationship between a debilitating cough and the main cause that provokes it, it is impossible to prescribe effective treatment.
The initial stage of a gastroenterological examination includes identifying the patient’s complaints and examining him. The palpation method is used, which consists of feeling the abdomen.
Tapping - percussion and listening to sounds - auscultation are also performed. If necessary, the following diagnostic measures are prescribed.
- Donation of urine and blood for general analysis. With its help, the presence of an inflammatory process is determined.
- Stool analysis. Allows you to detect intestinal infections and the presence of parasites.
- Fibrogastroscopy. It is prescribed to evaluate the mucous membranes of the digestive organs.
- Endoscopy of the esophagus.
- Intraesophageal pH monitoring. It is carried out throughout the day and allows you to determine the nature, stage of development, and duration of reflux.
- X-ray. This examination is necessary to detect pulmonary pathologies.
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
The obtained diagnostic results serve as a reason for additional consultations with specialists. This could be an infectious disease specialist, a gastroenterologist, an allergist.
Therapeutic drug techniques
Based on the diagnostic results, complex therapy is carried out as prescribed by the attending physician. Its task is to eliminate a specific disease, relieve pain, and bring general well-being back to normal. The drug complex may include the following drugs.
- Prokinetics. Their action is aimed at stimulating gastrointestinal motility. This group of drugs, often prescribed for stomach ulcers, includes Motilak, Motilium.
- Antacids. They help fight high acidity by reducing concentration. Taking medications such as Maalox, Almagel, Alka-Seltzer
eliminates damage to the gastric mucosa caused by hydrochloric acid. They also serve as good preventative agents. - Antisecretory drugs. They inhibit gastric secretion, neutralizing excessively high concentrations of hydrochloric acid. This group of drugs useful for heartburn includes Famotidine, Omeprazole, Ranitidine.
- Antimicrobial drugs. Prescribed for infectious diseases in order to eliminate the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Foaming agents. Gaviscon
, a remedy that neutralizes the destructive effects of hydrochloric acid, will help - In case of dysbiosis, it will be necessary to restore the intestinal microflora with the help of prebiotics and probiotics. If a connection between dysbiosis and a fungal infection is identified, then Nystatin, Levorin, Mycoheptin are prescribed.
In order to eliminate discomfort in the throat - soreness, dryness - antitussive medications are prescribed, for example,
Mucaltin.
If treatment is started too late and the development of the disease is detected in the final stages, then surgical intervention may be prescribed for the patient according to indications.
Prevention
One of the areas of preventive methods is maintaining a special diet that includes several rules. The practice is to switch to five split meals a day, which involves eating in small portions. In order for the stomach to function normally, excessively fatty, spicy foods, and alcohol are excluded from the diet.
Daily inclusion of vegetables, fresh herbs, and fruits in the menu will be beneficial. Daily walks and physical activity are recommended. You should also adhere to the norms of a healthy lifestyle during the treatment process if you cough heavily due to gastrointestinal problems.
Possession of information about the symptoms and treatment characteristic of stomach cough should serve as a motive for timely seeking medical help.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/lor/simptomy-i-lechenie-jeludochnogo-kashlia-5a8979277ddde84a9e268ed1
Features
A cough due to gastrointestinal diseases can be easily distinguished from a common cold, bronchitis or pneumonia. These ailments are preceded by catarrhal phenomena - inflammation of the throat mucosa, runny nose. There is almost always an increase in temperature. Stomach cough occurs without previous symptoms and is very rarely accompanied by fever. Even with prolonged bronchitis or pneumonia, the cough lasts no more than 2-3 months.
If a person has gastritis or an ulcer, coughing has bothered him for years. In pulmonary diseases, attacks occur without connection with meals or changes in body position. With reflux gastritis, a sore throat appears after eating and during sleep. Stomach cough does not occur with sputum, because there is no inflammation of the bronchial mucosa. Its mechanism is a reflex, so it is always dry and irritating.
Clinical picture
The manifestation of symptoms is episodic, symptoms intensify in the evening and at night, in a lying position.
Typical complaints:
- dry, prolonged, hacking cough without sputum, which can regurgitate the contents of the stomach;
- gastrointestinal disorders, expressed through belching with an unpleasant odor, a feeling of heaviness and pressure in the epigastric region, gas formation, colic in the stomach and intestines, heartburn;
- chronic fatigue, muscle weakness;
- apathy, memory impairment;
- a feeling of suffocation that occurs against the background of a decrease in the body’s defenses, respiratory syndrome and allergies;
- coughing attacks immediately after eating - they provoke the release of contents into the esophagus, vomiting;
- painful dry “barking” an hour after eating, severe pain behind the sternum if a person has gastritis, reflux or an ulcer.
Stomach cough: symptoms in children
Digestive tract disorders in gastrointestinal diseases in children, especially primary school and preschool age, are difficult to diagnose symptomatically. This is due to the fact that it is more difficult for the baby to describe his feelings. Therefore, parents need to pay attention to the following signs:
- wheezing and irregular breathing, especially during sleep
- bluishness of the face due to difficulty breathing
- increased cough reflex at night
- bloating, flatulence, accompanied by abdominal pain
If the urge to cough cannot be treated with expectorants and is accompanied by symptoms of pathology of the digestive organs, parents should immediately contact a medical facility for a detailed diagnosis of the cause of the child’s cough.
Diagnostic methods
As a rule, when the first symptoms appear, the patient begins self-medication aimed at suppressing discomfort, thinning sputum, complaining of having caught an ARVI or a cold. If the cough does not go away within 3-5 days, you should not continue self-medication, which will not give a positive result, but you should consult a doctor.
In addition, it must be borne in mind that self-medication for stomach cough can even be dangerous, since some antitussive drugs can worsen the underlying disease that caused the cough. For example, sugar contained in cough syrups will only contribute to the proliferation of infection, if any, in the gastrointestinal tract. When visiting a doctor, the primary task is to identify the nature of the disease.
For this, various diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- fibrogastroscopy or fibrogastroduodenoscopy, which allows you to see a complete picture of the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus and make a diagnosis;
- a general blood and urine test, which will give an idea of the general condition of the body, the presence of inflammatory processes and other indicators necessary for diagnosis;
- x-ray of the lungs to exclude the possibility of pulmonary pathology, and x-ray of the mediastinal organs;
- stool analysis for the presence of parasites and clarification of the composition of the intestinal bacterial flora;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Additionally, consultations with various doctors are prescribed: an infectious disease specialist if the body is suspected of being damaged by pathogenic microbes, or a gastroenterologist if a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract is detected. After undergoing the examination and receiving diagnostic results, a medical report is made, a final diagnosis is established, and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Diagnostic measures
The doctor’s main task is to confirm the presence of gastritis, excluding other pathologies. Stomach cough occurs in many gastrointestinal diseases. The patient may need to undergo complex treatment to eliminate symptoms and possible complications.
To identify the causes of cough, you may need to undergo fluorography
The sick person is given a referral to:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and blood test for hormones;
- culture from the larynx and endoscopy of the nasopharynx to exclude the possible presence of an inflammatory process;
- fluorography of the lungs with examination of the heart;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- MRI;
- UAC;
- FGDS.
The patient must provide blood, urine and feces for testing. This is necessary to exclude infectious diseases. Thanks to such tests, it is possible to confirm or refute the presence of Helicobacter, since this is one of the main causes of gastritis.
A cough can be a consequence of problems with the thyroid gland, so an ultrasound is performed during diagnosis
The doctor must determine the level of acidity in the body. With inflammation it is usually increased or decreased.
The patient may be recommended additional diagnostic methods. This directly depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and the root cause of stomach cough. You cannot ignore doctor's orders.
How to treat stomach cough
If the cough occurs due to problems with the digestive organs, complex therapy is carried out. To cure the disease and eliminate accompanying manifestations, the patient is prescribed:
- taking medications;
- therapeutic diet;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical intervention.
Surgeries are used for advanced stomach diseases and complications requiring surgical intervention.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, conservative treatment is sufficient, which is aimed at eliminating inflammation and normalizing the motor function of the esophagus.
Treatment of stomach cough is a complex process aimed at combating the underlying disease. Most often it is necessary to treat chronic gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers and gastritis reflux. Below we will look at various drugs that are used in the treatment of these diseases.
Amoxicillin
This drug is prescribed in cases where stomach cough has a bacterial etiology (origin).
Amoxicillin is a drug from the penicillin group that has a fairly wide spectrum of antibacterial action.
Available for sale in tablet form.
It is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, reaches the lesion and destroys pathogenic microorganisms. It has the following contraindications for use:
- Hypersensitivity to penicillin;
- Cross-allergy during treatment with beta-lactam antibiotics;
- Asthma and allergic diathesis;
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia and infectious mononucleosis;
- Severe kidney and liver disorders.
The drug should be taken with caution when treating newborns and premature infants, pregnant and lactating women.
Analogues: Amoxiclav, Clarithromycin, Omeprazole, Omez.
Phosphalugel
The drug is an antacid that normalizes stomach acidity. The product has an enveloping effect, neutralizes toxic substances, and forms a protective layer on the gastric mucosa.
Prescribed for heartburn and stomach cough caused by gastritis, peptic ulcer, functional diarrhea and reflux-esophagitis.
It is not recommended to use for treatment in case of hypersensitivity to the components and severe liver and kidney disorders.
Analogs: Rutacid, Almagel Neo, Gastracid, Maalox.
Maalox
Maalox is an antacid drug designed to neutralize excess hydrochloric acid. Reduces the peptic activity of gastric juice, eliminates waste and toxic substances, envelops the mucous membrane and protects it from aggressive external influences. Available in the form of tablets and suspension for oral administration.
Has the following contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to active and auxiliary substances;
- Lack of phosphate in the body;
- Severe renal failure;
- Fructose intolerance;
- Age up to 15 years.
When used uncontrolled or for too long, Maalox can cause disorders of the nervous and immune systems, in rare cases it provokes diarrhea and nausea, metabolic disorders and loss of appetite are possible.
Motilak
Motilak is an effective drug that is prescribed in cases where gastrointestinal motility is impaired. It affects the motility of the stomach and duodenum, causing them to contract and push food entering the body in the right direction.
Contraindicated for:
- Individual intolerance to components;
- Gastrointestinal bleeding;
- Perforation and mechanical obstruction;
- Prolactinoma.
Pregnant and lactating women can take the drug only after consulting with their doctor. If the permissible dose is exceeded, the components of the medicine can be transferred to the child and cause developmental disorders.
The drug rarely causes any side effects. Undesirable consequences in the form of urticaria and other allergic reactions are observed in patients with intolerance to the components.
Analogues: Motilium Express, Motonium, Domperidone, Passazhiks.
Domperidone
It is an effective antiemetic drug. It is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and has an almost immediate effect. Prescribed for nausea, frequent vomiting, hiccups, postoperative hypotension.
It is not recommended to take for:
- Internal bleeding from the stomach and intestines;
- Mechanical intestinal obstruction;
- Prolactinoma;
- Carrying and feeding a child;
- Hypersensitivity to domperidone.
Possible side effects in the form of intestinal disorders, nervous system disorders and allergic reactions.
Surgery
Sometimes the only way to get rid of a stomach cough is through surgery. The decision to perform an operation is made by doctors of different specializations - pulmonologists, gastroenterologists, surgeons, hepatologists, etc. In severe cases of reflux esophagitis, fundoplication is performed. It is performed laparoscopically, that is, through small holes in the abdominal cavity.
The operation involves wrapping the fundus of the stomach around the esophagus. Due to this, a cuff is formed that prevents the penetration of gastric contents into the ENT organs. After surgery, cough due to stomach pain completely disappears. Thanks to the restoration of the pharyngeal mucosa, associated respiratory complications - pharyngitis, laryngitis - are eliminated.
Nutrition
Getting rid of cough caused by gastritis is impossible without following nutritional recommendations. The diet is selected individually. The patient must also completely eliminate bad habits. You should eat food 5 to 7 times a day. Portions should be small.
Getting rid of cough caused by gastritis is impossible without following nutritional recommendations. The diet is selected individually
With a reduced level of acidity during an exacerbation, preference is given to meat and fish broths. If your condition improves, you should include in your diet:
- porridge;
- pureed soups;
- steamed cutlets;
- boiled chicken;
- cottage cheese.
You should forever forget about everything fatty and fried in oil. Milk is also not recommended. Soda and coffee are excluded from the diet.
With an increased level of acidity, nutrition should be gentle. All food is pre-boiled and ground. It is recommended to drink milk. Do not consume sauces, soda, strong tea or coffee. It is forbidden to eat meat, fish and mushroom broths. They must be vegetable.
If the acidity level is elevated, you should avoid confectionery and fresh baked goods. Herbal decoctions and tinctures are recommended. Coughing caused by gastritis cannot be ignored. The patient must undergo diagnostics and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
Folk remedies
Before taking folk remedies, you should consult a doctor in order to level out exacerbations.
- For the treatment of chronic gastritis with any acidity, flax seed is good. It contains mucus that envelops and heals damaged cells in the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus. Boil a tablespoon of seeds over low heat for several minutes in 300 ml of water in an enamel bowl. Leave for at least an hour, drink 100 ml 20 minutes before meals for five days. The decoction will help calm stomach coughs, heal ulcers, and cure atrophic gastritis.
- Shilajit has a healing effect in the treatment of respiratory syndrome due to gastrointestinal diseases. 200 mg of the substance is diluted in a spoonful of milk and drunk twice a day 25 minutes before meals.
- A potion made from 100 g of honey and 250 ml of olive oil has a calming effect. Take 1 teaspoon before meals. You can add a tablespoon of lemon juice to the recipe. The product is stored in the refrigerator.
- It is recommended to drink half a glass of fresh raw potato or cabbage juice on an empty stomach. Used for high acidity.
- Traditionally, for any type of cough, especially stomach, teas are brewed and drunk from chamomile, licorice, plantain, calendula, and sage (the raw materials from the latter herb need to be boiled for 5 minutes). Decoctions have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and wound-healing effects.
Of course, coughing is an unpleasant symptom, but it becomes a signal that the body needs help. And if you ignore the sign, a transition to unpleasant chronic respiratory disorders and serious pathologies of the digestive system is likely.
Symptoms of cough with gastritis
Cough with gastritis is not associated with inflammation of the respiratory tract. It occurs due to pathology of the stomach or esophagus. Stomach and antitussive drugs are used in therapy.
The respiratory tract and digestive tract are anatomically located close to each other. Therefore, coughing with stomach diseases is a common occurrence. You cannot suppress one symptom without addressing its cause. Treatment of stomach cough and gastritis is carried out simultaneously.
Why does stomach cough occur?
The causes of such a cough are irritation of the trachea and larynx with acidic digestive juice, impaired peristalsis of the esophagus, stimulation of the vagus nerve. Most often, coughing occurs against the background of reflux gastritis. This is an inflammation in which the contents of the gastrointestinal tract are thrown into the esophagus.
Reflux is a pathological condition, because normally food should go from the stomach to the intestine, and not back. From the esophagus, the acidic contents enter the pharynx, which causes coughing.
With chronic gastritis and peptic ulcers, the innervation (connection with nerve endings) of the esophagus and respiratory tract is disrupted. A person feels constant discomfort in the pharynx, larynx or trachea. This makes you want to cough.
Cough with stomach diseases is observed in 70% of patients. It has varying degrees of severity, which is associated with the severity of the underlying disease.
Features
A cough due to gastrointestinal diseases can be easily distinguished from a common cold, bronchitis or pneumonia. These ailments are preceded by catarrhal phenomena - inflammation of the throat mucosa, runny nose. There is almost always an increase in temperature.
Stomach cough occurs without previous symptoms and is very rarely accompanied by fever.
Even with prolonged bronchitis or pneumonia, the cough lasts no more than 2-3 months. If a person has gastritis or an ulcer, coughing has bothered him for years.
In pulmonary diseases, attacks occur without connection with meals or changes in body position. With reflux gastritis, a sore throat appears after eating and during sleep.
Stomach cough does not occur with sputum, because there is no inflammation of the bronchial mucosa. Its mechanism is a reflex, so it is always dry and irritating.
General symptoms
It is easy to trace the connection between cough and gastritis. Inflammation of the digestive tract develops earlier and by the time a sore throat appears, it already has severe symptoms. The main signs of gastritis and ulcers:
- pain in the stomach - on an empty stomach, immediately after eating or after a few hours;
- heartburn;
- nausea;
- flatulence;
- bowel disorder.
Due to disruption of food processing, the process of absorption of nutrients changes, which affects the condition of the skin. It becomes dry and rashes appear. Hair becomes dull and falls out. Characterized by bad breath and dental caries.
The appearance of cracks and white coating on the tongue are signs of stomach problems.
Features of cough in gastrointestinal diseases
Stomach cough with ulcers and gastritis manifests itself in different ways.
Differences in symptoms are associated with the mechanism of development of the disease.
Gastritis with low acidity
The disease occurs due to insufficient production of hydrochloric acid. Gastric juice does not completely break down food; it undergoes fermentation. The gas rises, irritating the pharyngeal mucosa.
The cough is mild, the person is more worried about a sore throat and belching with an unpleasant odor.
Atrophic gastritis can be suspected by severe nausea and heaviness in the upper abdomen. The discomfort lasts for several hours after eating.
With high acidity
High acidity of gastric juice is provoked by increased production of hydrochloric acid. This type of gastritis is also called erosive, because areas of damage form on the surface of the mucosa.
If a person also has reflux, that is, the backflow of stomach contents, the esophagus is constantly inflamed. This causes heartburn and paroxysmal cough. It appears a few minutes after eating, during prolonged fasting.
Hyperacid gastritis is assumed if a person is bothered by sharp pain in the upper abdomen that occurs during or immediately after eating.
Stomach ulcer
Cough with a stomach ulcer is most often associated with an effect on the vagus nerve, which has connections with all organs of the chest and upper abdomen.
When an ulcer occurs, a defect forms in the wall of the stomach. It can affect part of the vagus nerve and a reflex cough occurs with suffocation. The attack occurs in the evening and at night - when nerve activity is highest.
However, this is not always observed, only with a certain location of the ulcer - on the front wall of the organ, closer to the entrance to the esophagus.
Duodenal ulcer (DU)
In this case, the defect forms on the intestinal bulb. Coughing occurs rarely and is also associated with activation of the vagus nerve.
The difference is that food reaches the duodenum 3-4 hours after it is consumed. Accordingly, the cough also does not appear immediately.
Manifestation of cough in children
Gastritis and ulcers also occur in childhood. Due to physiological characteristics, these diseases occur differently in children than in adults. Their stomach is smaller, and the esophagus with intestines is shorter, so the time for coughing is reduced.
A small child cannot fully explain what exactly is bothering him. He is not aware of the connection between abdominal pain and the subsequent occurrence of cough.
If a child has been coughing for more than a month, his gastrointestinal tract needs to be examined.
Necessary examination
Diagnosis of chronic cough includes not only examination of the bronchi and lungs. If a person has symptoms indicating inflammation of the stomach, you need to undergo the appropriate examinations:
- Blood test. Detects signs of inflammation, anemia, and lack of vitamins.
- Fibrogastroscopy (FGS). Using this method, you can see the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach, and detect erosions or ulcers on it.
- The acidity of digestive juice can be determined using ph-metry. Based on this analysis, the type of gastritis is determined - hyperacid or hypoacid.
- Breath test. Determines the presence of Helicobacter pylori, a microorganism that causes peptic ulcers.
- X-ray of the lungs. Necessary to exclude the bronchial origin of cough.
- Examination of sputum - if it is released from a person. Allows you to determine the cause of bronchial inflammation.
Based on the results obtained, differential diagnosis is carried out - gastric cough is distinguished from pulmonary cough.
A blood test alone is not enough to diagnose gastritis or ulcers. It is necessary to conduct FGS.
Methods for getting rid of cough
You will have to treat gastric cough comprehensively. The main goal of therapy is to suppress inflammation in the stomach.
Only by achieving this can you get rid of respiratory tract irritation.
Medications
The inflammatory process can only be effectively suppressed with the help of medications. They help normalize the acidity of gastric juice, heal damaged mucous membranes, and prevent reflux.
The treatment regimen is selected individually, depending on the existing disease.
Antibiotics
You cannot do without them if a peptic ulcer associated with H. pylori is diagnosed. You can influence Helicobacter with the following drugs:
- Amoxicillin;
- Clarithromycin;
- Metronidazole.
Duration of therapy is from 7 to 14 days. The dosage and frequency of administration are prescribed by the doctor.
According to modern recommendations, an antibiotic should also be prescribed for hyperacid gastritis.
Proton pump inhibitors
This group of drugs regulates acidity. For hyperacid gastritis and ulcers, the following is prescribed:
- Omeprazole;
- Rabeprazole;
- Pantoprazole.
The drugs are used in conjunction with an antibiotic. The standard regimen is one tablet 2 times a day before meals.
Proton pump inhibitors should not be taken without interruption. A long course can transform a hyperacid state into a hypoacid state.
Antacids
Means that allow you to quickly normalize high acidity. Used in liquid form and tablets:
- Phosphalugel;
- Almagel;
- Gaviscon;
- Rennie;
- Maalox.
Dosage - measuring spoon or tablet 30 minutes before meals.
Children are allowed only Phosphalugel; other medications are taken from the age of 14.
Means for regulating peristalsis
The purpose of prescribing these drugs is to prevent the backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus. This happens by regulating peristaltic contractions. They use tools such as:
- Motilak;
- Domperidone;
- Trimedat.
Medicines are approved for use from the age of three. Prescribe one tablet 2 times a day.
Antitussives
Direct cough medicines for gastritis and ulcers are also used. It makes no sense to prescribe expectorants, since there is no inflammation in the bronchi, and accordingly, sputum is not produced. Medicines that affect the cough center of the brain are used:
- Sinecode;
- Stoptussin;
- Bronholitin.
Under their influence, the irritability of nerve cells decreases. This helps relieve obsessive, severe coughing.
Medicines are allowed even for one-year-old children. The standard dosage is a tablet or measuring spoon of the drug 3 times a day.
If coughing bothers you at night, you can take an antacid and a drug that affects the center in the brain before going to bed.
Traditional medicine recipes
The use of folk remedies is an auxiliary method of treatment. They enhance the effect of medications and prolong their effect. Folk remedies, like medications, should act simultaneously on inflammation of the stomach and irritation of the respiratory tract.
- Flaxseed decoction is an effective remedy for regulating acidity. Thanks to its mucous consistency, it protects the surface of the gastrointestinal tract from irritation by digestive juices. Pour a tablespoon of seeds into a glass of water and bring to a boil. Then cool, filter and drink 50 ml before meals.
- Infusion of coltsfoot has an anti-inflammatory effect. Flowers and leaves of the plant are crushed, 1 tbsp. l. pour 200 ml of boiling water over the raw materials and let it brew for half an hour. Then filter, take 100 ml in the morning and evening.
- Potato juice reduces the acidity of the gastrointestinal tract. To prepare it, grate fresh potatoes and squeeze out the juice. Drink it according to Art. l. before eating.
- Shilajit will help with an irritating sore throat. You need to take a dose of this remedy the size of your fingernail and dissolve it in a glass of warm milk. Drink before bed.
Remember that folk remedies are an auxiliary method. You cannot refuse to use medications in favor of home recipes.
Physiotherapy
- Physiotherapy can be used to soften the pharyngeal mucosa and reduce an irritating cough. It is not necessary to visit the appropriate clinic office for this. Many procedures are easy to do at home, especially since there are now portable devices.
- Steam inhalations effectively suppress cough. They are carried out either using a special apparatus or independently - over a pan of hot water. You can add a few drops of tea tree or mint essential oil.
- Magnetic therapy has an anti-inflammatory effect. It is also carried out using devices - Almag, Mag-30. The devices are equipped with a variety of functions that allow them to be used not only for the treatment of coughs and stomach diseases.
Physiotherapy procedures can only be carried out in short courses with the permission of the attending physician.
Prevention methods
If you follow some recommendations, you can reduce the risk of developing stomach cough. Preventive measures are based on the mechanism of the problem.
If you have reflux and hyperacid gastritis, you need to carefully adhere to your diet. If the acidity of gastric juice is low, you should establish a strict diet and exercise.
Diet
The purpose of dietary nutrition is to ensure the functioning of the stomach, normalize the acidity of digestive juice, and prevent reflux. In case of hyperacid gastritis, you will need to exclude from the diet:
- fatty foods;
- smoked meats;
- canned food;
- spices;
- carbonated drinks;
- mushrooms;
- alcohol.
Create a menu of dietary varieties of meat and fish, cereal dishes, pasta, and dairy products. Vegetables and fruits are only non-acidic varieties; it is best to eat them boiled or baked.
For hypoacid gastritis, remove from your diet foods that linger in the stomach for a long time and contribute to the development of flatulence:
- fresh bakery;
- legumes;
- millet, pearl barley;
- fat meat;
- pickled vegetables.
It is useful to eat dietary meat, day-old bread and crackers, fermented milk products, dishes made from buckwheat and rice. For drinks, it is better to drink herbal teas.
Cough is a common symptom of gastric pathologies. It has an indirect development mechanism, that is, it is not associated with inflammation of the bronchi or lungs, but appears reflexively. To get rid of it, act on the cause - inflammation of the stomach. For this purpose, medications and folk remedies are used in accordance with the type of disease.
Source: https://gastrox.ru/symp/kashel-pri-gastrite.html