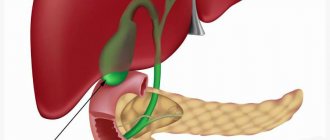
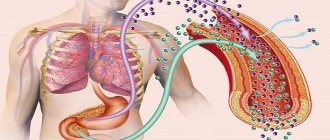
The pancreas plays one of the main roles in the digestion process. The organ produces enzymes that enter the intestines through ducts and, when activated, participate in the breakdown of fats, carbohydrates and proteins. When the release of enzymes is difficult for a number of reasons, they accumulate in the gland itself and destroy it from the inside. Inflammation of the pancreas occurs - pancreatitis, which has two types - acute and chronic. Curing the disease is not easy. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in time to avoid serious complications.
Which doctor treats pancreatitis? This question can be answered by understanding the symptoms of the disease and treatment methods.
Modern classification
ICD 10 presents acute (K85), chronic (K86) pancreatitis, as well as damage to the pancreas due to viral diseases (cytomegalovirus infection (B25.+), mumps - “mumps” (B26.3+)).
Chronic pancreatitis of alcoholic etiology (K86.0) is separately identified as the most common.
Section K86.1 presents other types of chronic disease:
- infectious;
- recurrent;
- repetitive.
Cysts that form as a result of exacerbation and are complications are classified in section K86.2.
What is the difference between acute and chronic process
Acute and exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis by their nature, as well as manifestations, are identical conditions associated with the advanced process of self-digestion and destruction of pancreatic cells. They are an acute surgical pathology, diagnoses must be confirmed by surgeons, treatment must be carried out in the surgical department of the hospital. If the patient’s condition is serious, complications develop - in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit.
The chronic process leads to a sluggish, gradual replacement of previously inflamed tissue with fibrous tissue, which loses the ability to produce enzymes and hormones. It is treated under the supervision of general practitioners or gastroenterologists. The basis of therapy is maintaining the viability of the preserved tissue, taking replacement drugs (enzymes, insulin), and preventing exacerbations.
Acute pancreatitis
In the acute form of pancreatitis, rapid destruction of pancreatic cells occurs. Without assistance, this leads to serious complications, even death.
Symptoms
An attack of acute pancreatitis is accompanied by obvious symptoms that need to be paid attention to in order to prevent worsening:
- Severe cutting pain in the upper abdomen, often of a girdling nature, radiating to the lower back. The pain is almost not relieved by antispasmodic drugs. Painful shock may occur.
- Constant nausea and persistent vomiting, even with blood in severe forms.
- Abdominal bloating, usually on the left, intestinal upset, flatulence.
- Weakness, dizziness, even loss of consciousness.
- Increased body temperature, increased heart rate.
- Yellowness of the skin and sclera of the eyes.
What do we have to do
If these symptoms are detected, measures must be taken immediately. Which doctor should I contact? The most reasonable thing to do in this situation would be to call an ambulance. The doctor will conduct a first examination of the patient, take the necessary measures to alleviate the condition and decide on hospitalization.
If the patient’s condition is serious, but does not cause concern, the person is admitted to the surgical department and treatment is carried out by a surgeon. Symptoms of acute inflammation of the pancreas are often similar to those of appendicitis, cholecystitis or duodenal ulcers. Therefore, the surgeon will be able to make the correct diagnosis. If the patient’s condition causes him to fear for his life, hospitalization is carried out in the intensive care unit.
To clarify the initial diagnosis, a comprehensive examination is carried out, including:
- Blood tests (general and biochemistry).
- General urine analysis.
- X-ray of the abdominal organs.
- Ultrasound examination of the pancreas.
Ultrasound of the pancreas
Based on diagnostic measures, as well as indications obtained during examination and questioning of the patient, treatment is prescribed to the patient. As a rule, taking painkillers and drugs that restore the functionality of enzymes in the pancreas can relieve acute inflammation. In the first days, the patient is prescribed complete fasting. You are allowed to take only medicinal table mineral water without gas in small quantities. In the future, a strict diet is prescribed, excluding the consumption of foods that cause an exacerbation of the disease.
In some cases, in particular, with obstruction of the pancreatic ducts or with severe purulent inflammation, surgical intervention is required.
When the patient's condition with acute pancreatitis has stabilized, the patient is transferred to the gastroenterology department. Here the person remains until complete recovery. The attending gastroenterologist will make detailed prescriptions for taking medications, maintaining a balanced diet and permitted physical activity. After discharge, the patient goes to the clinic at his place of residence, where he is registered under the supervision of a general practitioner.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you suspect acute pancreatitis (usually a sharp girdle pain, vomiting that does not bring relief, increased body temperature), you should consult a surgeon or call an ambulance. An emergency doctor, suspecting inflammation of the pancreas, will provide transportation to the surgical department for urgent diagnosis and selection of treatment.
Chronic pancreatitis (beyond severe exacerbations) develops gradually, does not require acute care, but requires constant medical supervision.
It is necessary to consult a therapist, general practitioner (family medicine) or gastroenterologist if the following complaints occur:
- abdominal pain spreading all around, worsening after drinking alcohol or fatty, fried, smoked foods;
- bowel dysfunction (weakness or alternation of diarrhea and constipation);
- nausea, vomiting;
- dry mouth, thirst.
The described complaints may be caused by inflammation of the pancreatic tissue.
Which doctor treats pancreatitis?
Pancreatitis or inflammation of the pancreas is treated by a pancreatologist.
He diagnoses the form of the disease, refers for the necessary tests, monitors the patient’s condition and prescribes appropriate treatment. But not every clinic can find a specialist with such a narrow profile. Depending on the patient’s condition, treatment is carried out by other doctors. In addition, against the background of inflammation, other diseases often develop that require consultation with specialized doctors. Every patient should know which doctor treats pancreatitis and which specialists to contact during an exacerbation.
Treatment of acute inflammation
This form of pancreatitis is characterized by sharp, stabbing, and sometimes burning pain in the abdominal area, which can put a person into a state of shock. When acute inflammation develops, the patient experiences severe pain and needs urgent medical attention.
The only correct solution for such symptoms is to call an ambulance. An ambulance specialist will conduct an examination and provide first aid outside the hospital. The patient is then hospitalized to diagnose the disease.
In the acute form of pancreatitis, the patient is examined in the intensive care unit by a resuscitator or surgeon. Also, a specialist from the ambulance team, assessing the nature of complaints, symptoms, and the patient’s condition, can decide to admit the patient to the department of therapy, gastroenterology or surgery.
In a hospital setting, acute forms of inflammation of the pancreas are diagnosed, differential diagnosis with other diseases whose symptoms may overlap with signs of pancreatitis. Correct diagnosis requires collecting all the necessary tests:
- Blood test (biochemical, clinical);
- Urinalysis (general and amylase);
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
- ECG, MRI, CT;
- Retrograde cholecystopancreatography;
- Angiography of the pancreas.
The diagnostic procedure is determined individually, based on an analysis of the patient’s complaints, examination and palpation results. Next, the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed or refuted and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
After first aid is provided, a surgeon or pancreatologist will determine treatment methods. When acute symptoms pass and the patient's condition stabilizes, he is transferred to another department, where he is further treated by a gastroenterologist or surgeon (pancreatologist). The department specialist monitors the patient’s condition and provides appropriate treatment.
With proper treatment, the exacerbation of pancreatitis goes away or the disease is cured completely. In both cases, the specialist prescribes special medications and a diet. Afterwards, the patient’s condition is monitored by a general practitioner, who will also refer the patient to a highly specialized doctor who treats concomitant diseases.
Treatment of chronic inflammation
Exacerbation of the chronic form of inflammation is similar to the manifestation of acute pancreatitis. The patient experiences an attack of severe pain and needs quick medical help. The first thing to do is call an ambulance. Next, the patient is transferred to a hospital and examined by the same doctors as in the acute form.
When the exacerbation passes, chronic inflammation of the pancreas is characterized by symptoms such as dyspeptic disorders and mild pain in the abdominal area.
If such signs bother you, the patient can contact his local general practitioner, who will analyze the patient’s complaints and refer him to a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, oncologist or surgeon.
When should you contact an endocrinologist?
The pancreas produces enzymes necessary for digesting food, as well as insulin, which is involved in regulating blood glucose levels. After a prolonged course of the disease, especially without proper treatment, insulin levels drop significantly. Thus, diabetes mellitus develops, most often this happens with chronic pancreatitis.
Quite often, the local physician recommends checking the state of sugars in the body, taking tests every 6 months. At the first indication of a lack of insulin and an increase in blood sugar levels, you should visit an endocrinologist. The doctor will select the required dose of insulin, prescribe the necessary hormonal medications, register the patient, and monitor his condition.
With the development of diabetes mellitus against the background of pancreatitis, the patient may be hospitalized and treated in a hospital.
When to see an oncologist
One of the causes of inflammation of the pancreas can be tumors of various types. Their presence will be shown by ultrasound examination, MRI, CT scan, which are performed at the first visit with complaints of exacerbation of chronic or acute pancreatitis.
The cause of the tumor can be a prolonged course of pancreatitis without proper treatment. The local doctor regularly refers the patient to all necessary diagnostic procedures. In some cases, the general practitioner may not prescribe the necessary tests in time; in this case, the patient must undergo them independently for clear control over the condition of the body.
Malignant neoplasms and cyst formation are possible. When the ultrasound shows their presence, the oncologist decides to prescribe medications or refer the patient to the surgical department.
When to see a surgeon
A referral to a surgeon or pancreatologist can be written by a general practitioner, oncologist or pancreatologist. Surgery is necessary to remove stones, cysts, or other tumors, and also, if necessary, to remove the entire pancreas or tissue affected by enzymes.
If the patient knows about the need to visit this specialist, but there is no referral (this can happen for various reasons), then he should seek advice on his own.
Inflammation of the pancreas is a complex disease that contributes to the development of concomitant diseases such as malignant tumors or diabetes mellitus. The main task of the patient is to pay attention to the body and its changes, regular ultrasound examinations and tests for sugar content.
Timely detection of potential complications and knowledge of which doctor to contact will allow you to quickly and correctly adjust treatment and avoid negative consequences.
Source: https://GormonOff.com/zabolevanija/pankreatit/kakoj-vrach-lechit-pankreatit
Where does the specialist meet?
General practitioners and therapists work in all outpatient and inpatient departments of medical institutions. If you suspect pancreatitis, you should contact these specialists. Depending on the diagnostic capabilities of the medical organization, these doctors either prescribe examinations themselves or refer you to a gastroenterologist.
There are gastroenterologist’s offices in clinics, private clinics, as well as in specialized multidisciplinary diagnostic and gastroenterological centers.
Do I need to be examined and what tests should I do before visiting a doctor?
If you suspect pancreatitis (as with any disease), it is better to first consult a doctor. If blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity (ultrasound of the abdomen), or stool analysis (coprogram) have previously been performed, then the results must be shown to the doctor.
Delaying time and wasting it on independent examinations can not only contribute to the aggravation and spread of the process. Expensive studies may not be informative in a particular situation and may need to be repeated after special preparation or using additional methods (for example, contrast in CT or MRI). Therefore, you first need to see a doctor and then undergo examinations.
Oncologist and pancreatitis
Many patients, as soon as they see the name of the doctor in the direction, begin to panic. An initial consultation with an oncologist is scheduled in order to detect problems in time.
After all, pancreatitis, especially if medical care is not provided in a timely manner, can lead to tumor diseases.
Recommendations from Elena Malysheva in the special issue “Live Healthy!” on how to overcome pacreatitis using the healing effects of natural remedies.
In order to identify problems, the oncologist prescribes instrumental diagnostics, in particular: computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging or ultrasound examination.
Now you know which doctors treat acute and chronic pancreatitis. Remember, as soon as the first signs of the disease appear, you must immediately consult a doctor, this will help to quickly identify the causes of the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Also read on our website: Reactive pancreatitis in children: symptoms and treatment
How does a doctor's appointment work?
If the consultation is primary, then after meeting the doctor conducts a survey of complaints, asks about the duration and dynamics of existing manifestations, the development of the disease, examinations performed, previous treatment (independent or as prescribed by specialists), allergic reactions, possible diseases of other organs. Next, the doctor conducts a direct examination of the abdomen (examination, palpation, tapping the abdomen and listening to bowel sounds) and issues directions for the necessary studies.
The appointment can take place in a medical facility, or maybe at home. In order for the doctor to understand the clinical picture and also to suspect inflammation of the pancreas, a medical examination at the patient’s home is sufficient.
List of mandatory examinations:
- general blood test, urine test;
- blood test for amylase, urine test for diastase;
- coprogram;
- stool test for elastase-1;
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal organs.
To clarify the cause and nature of the damage to the pancreas, retrograde cholecystopancreatography may be performed. This method determines the localization of stones in the bile ducts that obstruct the outflow of bile and pancreatic secretions, which causes inflammatory changes in the pancreatic tissue. Cysts and areas of necrosis in acute or exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis are detected using computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (CT) with or without the introduction of contrast, depending on the specific clinical situation.
The doctor also determines the place of treatment (hospital or home conditions under supervision), selects medication treatment, individual dosages, and duration of treatment. Writes prescriptions for medications if necessary (dispensed at the pharmacy only by prescription).
Chronic pancreatitis: we act according to the situation
The development of chronic pancreatitis can develop according to two scenarios:
- Invisible development of the disease without an acute form.
- Acute pancreatitis, developing into chronic.
Even with a sluggish course of the disease and unexpressed pain syndrome, a sharp regression can still occur. In this case, the patient will feel symptoms characteristic of acute pancreatitis. In this case, you need to act as described above - call an ambulance. Doctors will collect anamnesis and decide whether the patient needs emergency hospitalization, or can visit a gastroenterologist at the clinic the next day.
In fact, the methodology for diagnosing and treating chronic and acute pancreatitis is the same, the only difference is in the efficiency of these measures, which is important for preserving the life and health of the patient. Therefore, a gastroenterologist, to whom a person turns with symptoms of chronic pancreatitis, will prescribe the same tests, but in a smaller volume and in a less urgent manner:
- General blood test and biochemistry.
- Coprogram.
- Urine analysis, in particular for amylase.
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal organs.
- MRI or CT.
Help from an endocrinologist
In the case of chronic pancreatitis, the patient may need a consultation and conversation with an endocrinologist. This is due to necrosis of pancreatic cells that produce not only enzymes, but also hormones that regulate the metabolic processes of glucose in the blood. If these hormones are not produced enough, the patient may acquire another diagnosis - diabetes.
It is this specialist who will prescribe the necessary tests, monitor the dynamics of the patient’s condition, and, if necessary, prescribe insulin or hormone replacement pharmaceuticals, selecting the exact dosage and regimen.
Video - Chronic and acute pancreatitis
Help from an oncologist
A person who has been suffering from chronic pancreatitis for a long time and does not know about his diagnosis or ignores the disease is a potential patient in the oncology department. Long-term disease without adequate treatment transforms into tumors inside and on the walls of the pancreas.
Also, the tissues of the inflamed pancreas are susceptible to the formation of cysts and pseudocysts, cysts and formations of a benign and malignant nature. If a gastroenterologist or therapist suspects such a complication in his patient, he must immediately write a referral for a consultation with an oncologist.
Neoplasms can be detected through ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, after which an oncologist prescribes conservative therapy or a course of chemotherapy, and in some cases decides on the need for surgical intervention.
Features of the disease depending on age and gender
There are differences in the clinical picture and causes of the disease depending on gender. In men, pancreatitis more often occurs with regular consumption of alcoholic beverages, in women - as a complication of bile outflow disorders due to stone formation in the gallbladder.
In old age, depending on the state of health, there may also be features of manifestations. If the cardiovascular system is damaged (atherosclerosis), metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus) with damage to nerve endings, pain can be significantly reduced. Such patients do not seek medical help in a timely manner, more often when complications develop associated with the body’s general reaction to local inflammation in the pancreas (a sharp drop in blood pressure, liver and kidney dysfunction, the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane of the digestive tube, hemorrhages or blockage of small vessels ( thrombosis)).
Which related specialist can the doctor refer you to?
When pancreatic cells that secrete hormones that regulate sugar metabolism are destroyed, blood glucose levels increase and fat metabolism suffers. If there is a disturbance in glucose metabolism or the development of diabetes mellitus, consultation with an endocrinologist is necessary, and subsequently treatment under his supervision.
Suspicion of acute or exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis is an indication for urgent consultation with an abdominal surgeon (specializing in surgical interventions on the abdominal organs).
For a patient with a chronic course of the disease, in some cases it is necessary to consult an oncologist.
Symptoms of a long-term disease that cause concern:
- gradual weight loss;
- reduction of pain with a simultaneous increase in general weakness;
- chronic stool disorders with a tendency to diarrhea;
- increased fragility of blood vessels, tissue bleeding;
- pain in the bone area.
The described signs occur not only with pancreatic pathology, but are also likely to occur with malignant neoplasms. In addition, long-term chronic pancreatitis itself can lead to degeneration of pancreatic tissue and the development of tumors.
Who should you contact if you have a chronic illness?
In the chronic course of the disease, the patient has a pronounced clinical picture.
General symptoms:
- the patient experiences pain in the upper abdomen, pain can also radiate to the left hypochondrium;
- nausea is observed, up to severe vomiting;
- the patient has problems with stool;
- belching;
- general weakness due to depression and loss of appetite.
Also read on our website: Acute pancreatitis: symptoms and treatment at home
It should be noted that with chronic pancreatitis, only pain in the left hypochondrium can occur, which is also characteristic of osteochondrosis. Therefore, patients most often miss this sign and do not seek help in a timely manner.
Chronic pancreatitis is a consequence of an acute form that is not treated in a timely manner.
If severe pain occurs in the epigastric area, you should immediately consult a physician. Before making an accurate diagnosis and starting to treat pancreatitis, the doctor conducts a thorough initial examination of the patient.
After the examination, a referral to a specialist, in particular a gastroenterologist, is issued.
To the question: is it possible to cure a stomach or duodenal ulcer at home, a gastroenterologist, head of the gastroenterology department, Mikhail Vasilievich Arkhipov, answers.
What questions to ask your doctor
The main question, in addition to timely treatment, is “how to change lifestyle and nutrition in order to further prevent exacerbations of pancreatitis and its further progression?”
To cope with this task, you should ask your doctor:
- Is it possible to smoke and drink alcohol?
- What to do if pain suddenly appears?
- What foods, in what form, can be consumed after the exacerbation of the disease subsides?
- Should I stick to a diet for the rest of my life?
- How often should control examinations of the pancreas (ultrasound) and laboratory tests be done?