Enterocolitis in newborns is an infectious disease that manifests itself as inflammation of the small intestine (enteritis) and large intestine (colitis). Most doctors are inclined to believe that factors of intrauterine pathologies and lack of proper hygiene during pregnancy have a huge impact. Thus, when making a diagnosis and differentiating it from other intestinal infections, risk factors that occurred during pregnancy and the neonatal period are taken into account. We will talk about the causes, signs and treatment in the article.
Causes
Despite the fact that enterocolitis most often occurs in premature babies, in particular those whose birth weight was less than 2 kg, the disease is infectious in nature and can manifest itself in a baby with normal parameters at birth.
It is not possible to name the exact causes of enterocolitis, but doctors identify several characteristic features :
- the woman was treated with antibiotics during the perinatal period;
- intrauterine or postpartum infection of the baby with parasites;
- violation of the vitamin and mineral composition in the mother’s body due to improperly selected nutrition;
- the composition of breast milk is pathologically harmful;
- intrauterine intestinal development disorder (a common occurrence, especially for those born with insufficient body weight);
- infections of staphylococcus, E. coli;
- trauma received during childbirth;
- postpartum complications (asphyxia, hypoxia and severe blood loss);
- incorrect or untimely attachment to the breast.
One of the subtypes is allergic enterocolitis, the main symptoms of which are:
- nausea;
- gagging;
- diarrhea (up to 10 times a day);
- in rare cases, severe pain is observed in the area of the small intestine.
Allergic enterocolitis can occur against the background of a reaction to certain types of pathogens - chicken egg white, which contains lysozyme, certain varieties of berries, and seafood.
Additionally, in patients with suspected allergic enterocolitis, the following was observed:
- iodine-containing medications,
- antibiotics,
- some types of sulfonamides.
The cause may also be poisoning with heavy metal salts, mushrooms, or medications. A pattern was revealed that most cases of the disease in newborns were associated with:
- the onset of labor before the due date;
- living conditions in a family with poor sanitary conditions;
- ignoring doctor's instructions and the presence of bad habits in the mother.
In addition to the main reasons , infants who have :
- an intestinal infection entered the body through the mouth (in such cases, salmonellosis, cholera, dysentery, shigellosis develop);
- infection with enterobiasis (pinworms) or ascariasis (roundworms) has occurred. This is typical for infants;
- the functioning of the pancreas, stomach or gallbladder is impaired;
- food allergies were identified, mainly to gluten and lactose.
On the mother's side, the reasons may be:
- unreasonable use of antibiotics, the intake of which, even in small doses, passes into breast milk;
- unsanitary conditions in the newborn's room, violation of hygiene rules for caring for the baby;
- infection by the staphylococcus virus during gestation;
- consumption of prohibited foods during breastfeeding;
- incorrect introduction of complementary foods.
Intestinal inflammation in infants: symptoms and treatment
A child’s stool is one of the important indicators of his health, proper nutrition and well-being. That is why mothers study the contents of diapers or the potty with trepidation. How to recognize dangerous symptoms from the digestive system in an infant?
Causes of intestinal inflammation in newborns
Enterocolitis - an inflammatory process of the large and small intestines - is a fairly broad concept, since inflammation of the intestinal mucosa can be caused by a variety of causes.
Viruses with selective damage to the intestines - a group of rotaviruses and enteroviruses.
Allergy. Most often, infants experience episodes of allergy to cow's milk proteins from infant formula or when the mother consumes large amounts of whole cow's milk.
Toxic enterocolitis associated with the intake of toxic substances in infants is rare, which cannot be said about older children (about a year), who, while learning about the world, actively reach out to various household chemicals, vinegar essence and other household poisons. Toxic enterocolitis in infants can be caused by an overdose of drugs, for example, antibiotics or antipyretics.
Necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns, or NEC, is a separate group of intestinal lesions. This type of inflammation occurs in premature babies or newborns who have suffered intrauterine or birth hypoxia or oxygen starvation.
The reason for the destruction of the intestinal mucosa here is ischemic, that is, against the background of oxygen starvation, sections of the intestinal mucosa die off - necrosis occurs. And the addition of pathogenic flora occurs secondary. Necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns is a very dangerous situation that requires intensive care, since the mortality rate among premature babies reaches 80%.
Fortunately, premature or hypoxic babies are in the intensive care unit under the watchful supervision of neonatologists.
Newborn babies who are breastfed rarely suffer from intestinal infections, that is, enterocolitis caused by bacterial flora or viruses. Mother's milk is in most cases sterile, always at the right temperature and consistency, and is also rich in various immune defense factors. This fact may become another argument in support of natural feeding.
Formula-fed children are more likely to become infected with intestinal infections due to insufficient treatment of bottles, nipples and other attributes for preparing formula.
The main share of infectious enterocolitis occurs in the period from 6 months to a year. This is due to three main factors.
Firstly, during this period various complementary foods are actively introduced, which, if improperly stored or prepared, can become infected with microbes.
Secondly, by this age, most women complete or significantly reduce breastfeeding, and immune defense factors disappear in breast milk. Thirdly, a child of this age very actively explores the world and puts various objects into his mouth.
Symptoms of enterocolitis in infants
Regardless of the causes of intestinal inflammation, enterocolitis in infants will be accompanied by a number of common symptoms:
We list the most significant threatening symptoms that should concern the mother:
Treatment of enterocolitis in children
Only a doctor should treat enterocolitis in an infant! Under no circumstances should you engage in any self-medication such as enemas, giving your baby herbal decoctions, rice water and other folk methods. Without proper professional treatment, infants very quickly become severely dehydrated and intoxicated, which can cause kidney and liver failure, seizures and coma.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor must understand the cause of enterocolitis. Most often, of course, in the case of an acute process, the problem is infection. Therefore, it is important to take a bacteriological analysis of stool to identify the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Allergies or enzyme deficiencies rarely give an active clinical picture, but characteristics in a particular child are always possible. If there is any suspicion of such causes, allergy testing, stool analysis for acidity, enzymes and other indicators are carried out.
What should you do before seeing a doctor?
The only thing that parents can and should do on their own before the doctor arrives or hospitalization is to endlessly water the child. To replenish fluid losses, you can use ordinary boiled warm water. The ideal option would be to use special pharmaceutical products for oral rehydration such as Regidron, Orolite, Gastrolit and others.
Of course, it is very difficult to imagine how you can force an infant to drink. In most cases, inevitable violence must be used. A good way to force-drink a small child is to use a regular syringe without a needle, which is inserted into the baby's cheek.
Intestinal inflammation is an inflammatory process of its mucous membranes. In other words, this disease is characterized by immune inflammation of the intestinal wall. The inflammation can be chronic. It is in one of the first places among childhood pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
The most serious diseases are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. The latter occurs in 6 out of 100,000 people. Children are more susceptible to this disease. The causes of this disease in children have not been identified.
The occurrence of intestinal inflammation is most often associated with poor diet and the presence of viral infections in the body.
UC: symptoms and diagnosis
The first symptoms of this disease can appear in babies aged 3-5 months.
The main symptoms of ulcerative colitis are the appearance of blood in the child's stool followed by diarrhea. In older children, diarrhea occurs immediately. Chronic UC is manifested by frequent loose stools with painful spasms.
Source: https://kishechnik-zhivot.ru/simptomy/vospalenie-kishechnika-u-grudnichka-simptomy-i-lechenie
Symptoms
In children under one year of age, enterocolitis tends to manifest itself in sudden attacks with acute pain, but it happens that the disease proceeds hidden, imperceptibly increasing pain in children.
The disease has the following manifestations:
- frequent and profuse regurgitation;
- frequent loose stools (diarrhea);
- bloody clots in the stool of newborns;
- bloating;
- increased flatulence;
- deterioration of the baby’s general condition (motor activity decreases);
- frequent bowel movements;
- muscle pain and cramps (due to dehydration and loss of chlorides);
- high fever that does not go away within 2 weeks.
The most dangerous is infectious enterocolitis, which is manifested by a sharp increase in body temperature. Most often, this means that an infection has entered the intestines or there has been a case of secondary infection of an already damaged area of the intestine.
In addition to the described symptoms, the following is observed:
- lethargic behavior of the newborn;
- constant drowsiness;
- decreased appetite;
- causeless whims.
In cases of the disease in newborns, the disease is most often necrotic in nature . The risk group of children who may develop necrotizing enterocolitis includes:
- newborns born prematurely;
- full-term infants with abnormalities of intrauterine development;
- babies with birth injuries (cerebral hypoxia, ischemia and heart disease).
If you suspect enterocolitis in a newborn, you need to know in what cases you need to seek emergency medical help :
- the baby is under 1 year old;
- in 12 hours, the child experienced diarrhea up to 10 times;
- temperature rise above 38 degrees;
- feces mixed with blood streaks;
- loss of skin elasticity due to the general weakness of the baby.
The main thing to remember is that after calling an ambulance, you must constantly replenish the baby’s fluid loss with the help of oral hydrants . Otherwise, dehydration, especially in small children, can lead to death. Giving medications is not recommended, since medications can “lubricate” existing symptoms.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of intestinal pathologies are similar, which makes differential diagnosis difficult. But there are distinctive signs that are specific to UC and Crohn's disease. Based on a detailed assessment of symptoms, the doctor can suggest a diagnosis and order confirmatory tests. It is important to promptly contact a specialist for treatment, since prolongation of inflammation is fraught with serious complications.
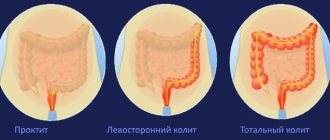
For colitis
The main sign of the development of a progressive nonspecific form of ulcerative inflammation of the intestine is the presence of blood impurities in the stool. After which debilitating diarrhea develops. This picture is typical for infants and children under 3 years of age. In adulthood, diarrhea immediately appears. With a prolonged inflammatory process, the tendency to chronicity increases. As a result, the rectal ampoule loses its elasticity, stool increases in frequency and becomes liquid. The urge occurs every 15 minutes, with this time decreasing after eating. Defecation is accompanied by painful spasms. It is possible to affect only the rectal section or the entire colonic section. The rectum with the descending colon and sigma are most often affected. If the first parts of the intestine are affected, symptoms may appear in the first 3 years of the baby’s life, but more often the signs are visible in a newborn at 3-4 months.
If a child’s diarrhea appears at night, then a particularly severe form of the pathology needs to be treated.
For Crohn's syndrome
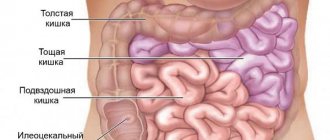
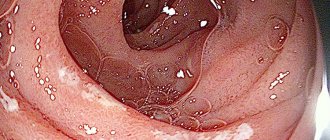
The disease provokes an increased urge to defecate in the child - up to 10 times a day (day and/or night). At the same time, the volume of feces increases significantly. With each meal, severe abdominal pain occurs due to narrowing of the intestinal lumen. The terminal stage is characterized by the appearance of blood in the stool. The disease most likely affects the last portion of the ileum. Fewer cases are recorded with damage to the ileocecal (separating the small and large intestinal sections) structure. Characteristic visual (endoscopic) symptoms of Crohn's disease are:
THIS IS REALLY IMPORTANT! The gastrointestinal tract cannot be neglected - this risks cancer. Cheap product No. 1 against stomach pain. FIND OUT >>
- granulomatous inflammation of any part of the gastrointestinal tract;
- ulceration of the intestinal mucosa;
- narrowing of the lumen;
- formation of fistulas.
Return to contents
Extraintestinal manifestations
Against the background of the development of an inflammatory disorder in the children's intestines, the following external symptoms appear:
- stomatitis with the formation of deep aphthae on the mucous membranes;
- inflammation of two or more joints, usually large ones (oligoarthritis);
- inflammation of the connective tissue structure of the eye sclera (episcleritis);
- conjunctivitis;
- damage to the ocular vessels (uevitis);
- formation of oxalate stones in the kidneys (more often with Crohn's syndrome);
- chronic inflammation of the bile ducts inside and outside the liver (sclerosing cholangitis);
- damage to the joints of the spine (Bechterew's syndrome).
Return to contents
Diagnostics
After a thorough physical examination and study of the medical history, the doctor prescribes a series of diagnostic procedures to clarify the diagnosis and exclude fungal or bacterial sepsis.
If neutropenic enterocolitis is suspected, the child is prescribed x-rays to obtain a visual picture of the disease. The results of the x-ray can show the doctor the presence or absence of enlargement in the inflamed parts of the intestine.
The most effective methods in making a diagnosis of enterocolitis are coprogram and bacteriological culture . When carrying out a coprogram, the physical and chemical composition of feces is examined in detail, according to the results of which hidden bleeding or the presence of helminth eggs can be detected.
On a note! Bacteriological culture will determine the causative agent of the infection and provide information about which antibiotics the parasite is not resistant to.
Despite clearly established diagnostic rules, most often doctors have to start antibiotic treatment before receiving test results . If this is not done, then rapidly progressing enterocolitis can lead to irreversible processes in the intestines or death in a matter of days.
Chronic enterocolitis is much more difficult to diagnose, since this requires a series of studies aimed at determining the degree of intestinal depletion. For these purposes, an X-ray examination is prescribed, which will show whether there are changes in the structure of the tissues and the presence of ulcers.
Necrotizing enterocolitis is determined using ultrasound diagnostics, which shows the presence of free fluid in the abdominal region and the accumulation of gases. An ultrasound will also show whether there is necrosis of intestinal tissue.
Types of illness
The inflammatory process in the large intestine can be small and large-scale. If only a few segments are affected, then the colitis is considered isolated; if the lesion covers the entire colon, then they speak of widespread colitis.
Depending on which segments of the intestine are affected, the isolated type of childhood colitis is as follows:
- typhlitis - an inflammatory process in the cecum;
- typhlocolitis is an inflammatory and degenerative process of both the cecum and ascending colon;
- transversitis - an inflammatory process in the transverse colon;
- angulitis - a process of inflammation in the isthmus between the transverse colon and descending colon;
- sigmoiditis – inflammatory changes in the sigmoid colon;
- proctosigmoiditis is a synchronous inflammatory process in the sigmoid and rectum;
- proctitis - an inflammatory process in the rectum;
- pancolitis is a generalized form.
After identifying the pathogen that caused the inflammatory changes, additional characteristics of the disease are given - it can be infectious (bacterial), nutritional, allergic, toxic, caused by parasites, pharmacological, neurotic (psychosomatic, psychogenic).
Treatment
Therapeutic measures are based on restoring the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract . Treatment prevents the development of exacerbation and also prevents its transition to a chronic form.
Newborns and babies up to one year old are required to be put on a strict diet , and also undergo a course of drug treatment, which includes:
- antimicrobials;
- antiviral;
- vitamin complexes;
- enzymes;
- anti-inflammatory agents.
In cases where the cause of the disease is ascariasis or helminthiasis parasites, first of all, therapy is carried out using antiparasitic drugs. Young patients are shown bed rest and diet No. 4 (after improvement - No. 4B).
Therapy for breastfed children
Therapy for enterocolitis in infants has its own characteristics . First of all, children are prescribed a strict diet. In an infant, symptoms and treatment are directly related: the more acutely a particular symptom of the disease manifests itself, the more targeted the treatment.
In cases where the development of acute enterocolitis is observed in infants, first of all, gastric lavage is performed. Only after this is a diet based on tea and/or water prescribed. Such children are sent to an infectious diseases hospital.
After the end of the diet, the baby can be returned to the previous diet . At first, he needs to be fed frequently and preferably with breast milk. If a woman cannot continue breastfeeding, doctors may prescribe a medicinal formula for artificial feeding.
Important! Infants with a chronic form of the disease are prescribed treatment with probiotics and pribiotics, as well as lactobacilli and sorbents in moderation. In cases of chronic obstruction of feces, the baby is prescribed laxatives.
Treatment of chronic enterocolitis is carried out over a long period of time and in stages. In most cases, treatment lasts from 6 to 10 months, but improvements are obvious as early as 3-4 weeks.
It is worth remembering that even after a significant improvement in the patient’s condition, it is not recommended to suspend the course of treatment , as this may provoke a relapse of the disease.
Children at the common table should be limited in their consumption of:
- spicy, salty and sour;
- cow's milk;
- fatty fish and meat;
- honey;
- flour products.
Products that are allowed to be consumed for enterocolitis:
- soups with low-fat broth;
- cottage cheese, kefir;
- eggs (boiled);
- jelly;
- butter;
- lean fish;
- meatballs;
- baked vegetables and fruits.
Mothers of newborns should adhere to the above diet during breastfeeding.
Prevention
Measures to prevent the development of inflammation in the child’s intestines include adequate nutrition in accordance with the age-related needs of the body. Additionally, it is worth monitoring and preventing parasitic infection and the development of intestinal infections. As they appear, it is important to promptly suppress pathogens. In order to prevent exacerbations and prolong remission in chronic forms of inflammation, it is important to carefully follow basic nutritional intake and balance the menu.
Additionally, preventive courses of vitamin and enzyme therapy are prescribed with monitoring of the condition and number of bowel movements. Warm mineral water (Essentuki No. 4) is periodically taken, and courses of exercise therapy and abdominal massage are conducted. Children should not swim in open water. Parents should exclude the possibility of injury to the peritoneum. In case of UC and Crohn's syndrome, vaccination and physical exercise are prohibited. In other cases there are no such restrictions.
Enterocolitis is a dangerous disease that manifests itself in the form of inflammation of the large intestine (colitis) and small intestine (enteritis), which provokes disruption of the main functions of the organ: digestion, excretion, absorption and peristalsis. Many babies suffer from this pathology, the reasons may lie in the immaturity of internal organs, the harmful effects of certain factors during intrauterine development.
Possible consequences
The prognosis of the disease depends on its causes and timely initiation of therapy. Prevention consists of preventing and treating intestinal infections . Correct lifestyle and diet play a big role in further prevention.
Despite the overall favorable prognosis, if not treated in a timely manner, enterocolitis can cause the following complications:
- development of necrotizing enterocolitis;
- pathogens can spread to other organs and cause, for example, meningitis or pneumonia;
- development of pseudomembranous enterocolitis (characterized by the complete absence of bacteria in the intestines).
How to treat colitis in children
The main principles of treatment of colitis in children include:
- elimination of the infectious agent;
- replenishment of lost fluid due to diarrhea;
- normalization of stool;
- restoration of intestinal motility;
- prevention of exacerbation.
The pathogen is combated with antibiotics, sulfonamides, and nitrofuran drugs. The doctor prescribes potent medications, individually determining the dose, frequency of administration and course of treatment.
To restore the water-electrolyte balance, Regidron, Gastrolit, and Oralit are used. The product powder is diluted in a liter of warm boiled water and given to drink throughout the day. You can give your baby water, weak chamomile tea, or compote. A packet of Smecta dissolved in 100 ml of boiled water will help stop diarrhea.
Intestinal dysbiosis can be treated with probiotics and prebiotics. Probiotics are preparations with live dried bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Prebiotics are a nutrient medium for beneficial bacteria - inulin, fiber, starches. Combined products with prebiotics and probiotics are called symbiotics.
What if the complaints disappeared during the diet, but doubts remained?
It is possible to reintroduce the allergen protein: the previous complaints have reappeared - doubts have been resolved.
Important: this should not be done in case of acute and severe allergic conditions; anaphylactic shock is possible!
But proctocolitis is not an acute, not serious condition, so the experiment is possible.
The prognosis for non-IgE conditions is usually good.
Complaints will disappear even if you do nothing at all... but it’s better not to do that!
Often, when discussing complaints from a baby, parents remember that older children also had blood in the stool in the first months of life, but then disappeared on their own. With hindsight we understand that most likely they also had allergic proctocolitis.
In most children with proctocolitis, complaints disappear before the age of one year, with FPE between the ages of 1 and 3 years, with FPIES between the ages of 1 and 5 years.
Very rarely, allergic proctocolitis persists into older age or occurs for the first time in older children or adults.
In these cases, it is very difficult to exclude a certain trigger food product; drug treatment is often required - corticosteroids, aminosalicylates. The range of conditions for a differential diagnosis by a doctor is also different.
2, total, today